Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Accountancy Class 12 > Short Notes: Accounting for Share Capital
Short Notes: Accounting for Share Capital | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Features of a Company |

|
| Types of Companies |

|
| Share Capital of a Company |

|
| Types of Shares |

|
| Issue of Shares |

|
| Forfeiture and Reissue of Shares |

|
Introduction
- A company is an artificial entity registered under the Companies Act, 2013, with a separate legal identity, distinct from its shareholders, and uses a common seal as its signature.
- Managed by a Board of Directors, as direct management by all members is impractical.
- Capital raised through share capital (ownership via shares) and debentures (debt with fixed interest).
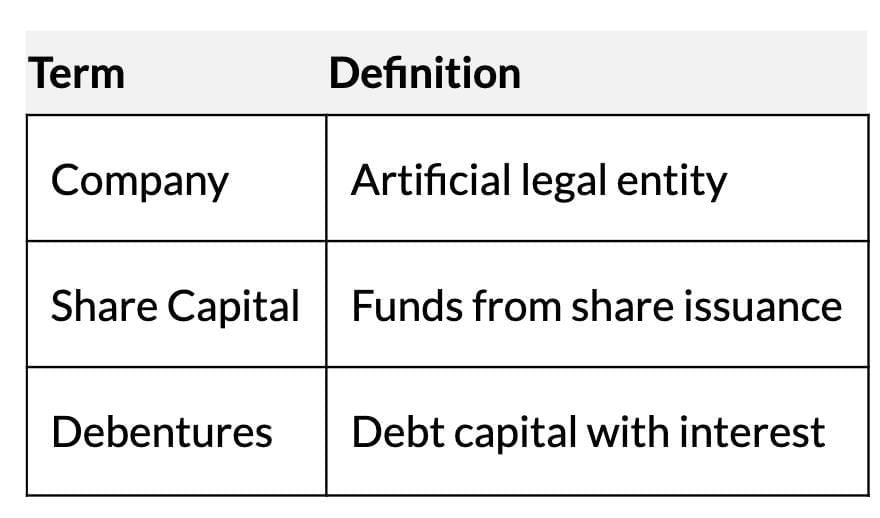
Features of a Company
- Body Corporate: Formed under Companies Act (except banks/insurance).
- Separate Legal Entity: Can own property, enter contracts, maintain bank accounts.
- Limited Liability: Members liable only for unpaid share amounts or guaranteed amounts (for guarantee companies).
- Perpetual Succession: Continues despite member changes; dissolved only legally.
- Common Seal: Acts as company’s signature for legal documents.
- Transferability of Shares: Public company shares freely transferable.
- May Sue or Be Sued: Can enforce or face lawsuits independently.
Types of Companies
Based on Liability:- Limited by Shares: Liability limited to unpaid share value.
- Limited by Guarantee: Liability limited to guaranteed amount during winding up.
- Unlimited: No limit on member liability; rare in India.
- Public Company: Not private, no member limit.
- Private Company: Restricts share transfers, 2–200 members.
- One Person Company (OPC): Single member, Indian citizen, ≤ ₹50L paid-up capital, ≤ ₹2Cr turnover.
Question for Short Notes: Accounting for Share CapitalTry yourself: What is a characteristic of a Public Company?View Solution
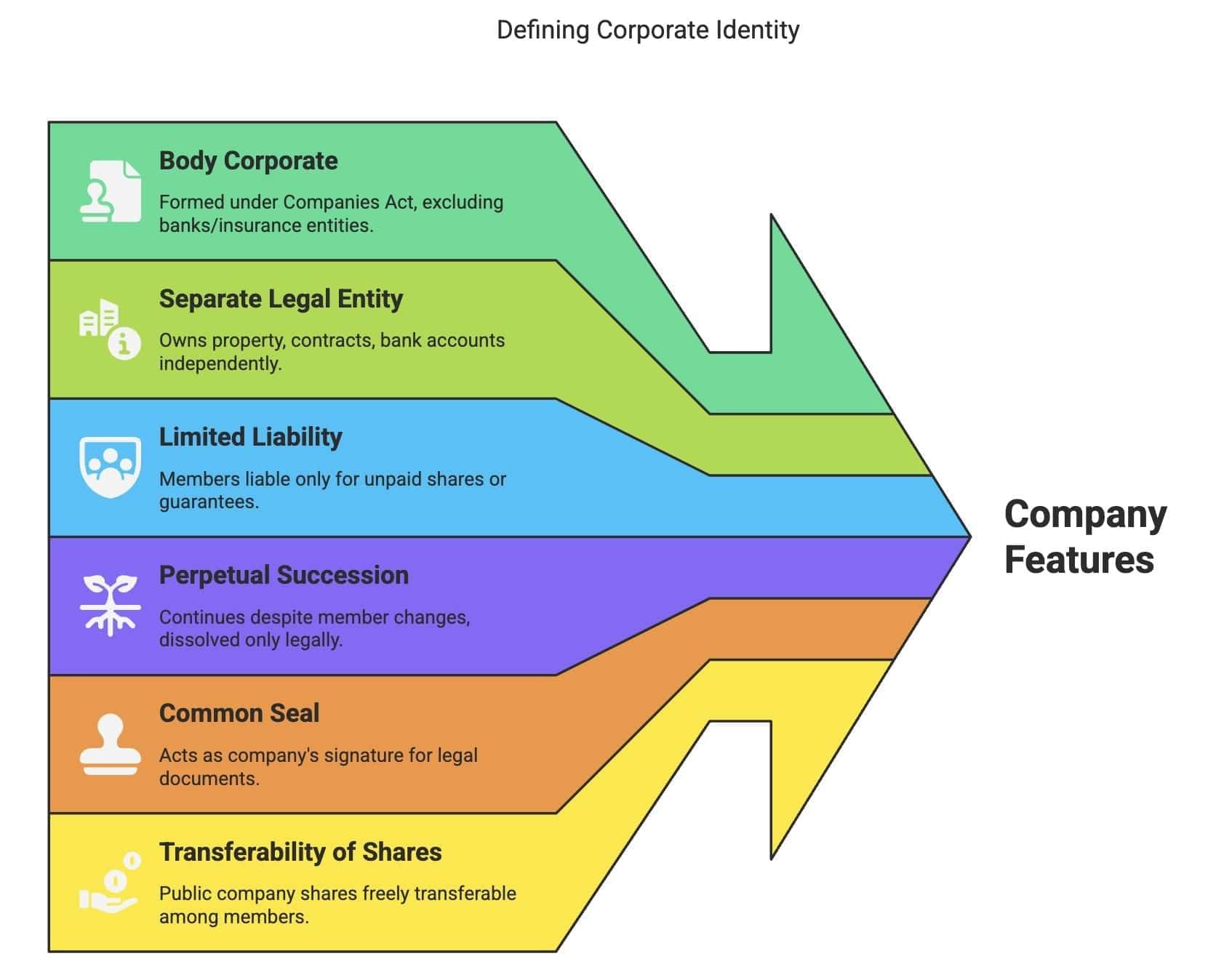
Share Capital of a Company
Share Capital: Funds raised through shares, pooled in Share Capital Account.
Categories:- Authorised: Maximum share capital per Memorandum.
- Issued: Offered to public for subscription.
- Subscribed: Portion of issued capital subscribed by public.
- Called-up: Amount requested from shareholders.
- Paid-up: Amount received from called-up capital.
- Uncalled: Subscribed capital not yet called.
- Reserve: Uncalled capital for winding up only.
Example: Sunrise Company Ltd. with ₹40,00,000 authorised capital, issued 2,00,000 shares (₹10 each), received ₹2 on application, ₹3 on allotment, ₹3 on first call; unpaid on 2,000 shares.
Types of Shares
Preference Shares:- Preferential dividend and capital repayment rights.
- Types: Participating/Non-Participating, Cumulative/Non-Cumulative, Redeemable/Irredeemable.
- No preferential rights; dividends vary based on profits.
- Types: With Voting Rights, With Differential Rights.
Issue of Shares
- Process:
- Prospectus: Invites public investment.
- Applications: Received with application money (min. 5% face value).
- Allotment: Shares allotted if minimum subscription (90% of issued) met within 120 days, else refunded within 130 days.
- Payment Stages: Application, allotment, calls (first, second, final).
- Issue Types: At par (issue price = nominal value), at premium (issue price > nominal value).
- Accounting: Application money to Share Application Account, transferred to Share Capital on allotment; excess refunded or adjusted.
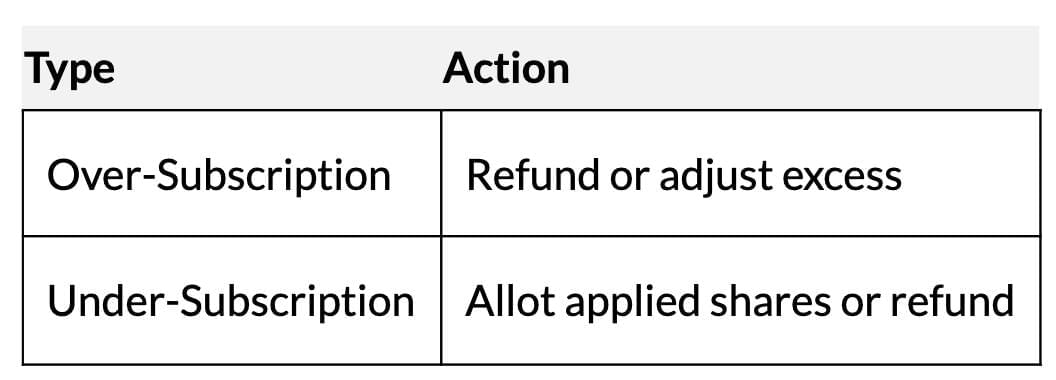
Over/Under Subscription
- Over-Subscription: More applications than shares offered.
- Options: Reject some, pro-rata allotment, or both.
- Excess money refunded or adjusted to allotment/calls.
- Under-Subscription: Fewer applications than offered; allot applied shares if minimum subscription met, else refund.
Shares at Premium/Discount
- Premium: Issue price > nominal value; credited to Securities Premium Account (used for bonus shares, expenses, etc.).
- Discount: Issue price < nominal value; rare, allowed for forfeited shares/sweat equity.
- Non-Cash Consideration: Shares issued for assets (e.g., building); number based on issue price and payable amount.
Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP)
- Allows employees to buy shares at below-market price in future.
- Terms:
- Grant: Option to subscribe.
- Vesting: Right to apply after conditions met.
- Exercise: Applying for shares at exercise price.
- Requires special resolution, SEBI compliance for listed shares.
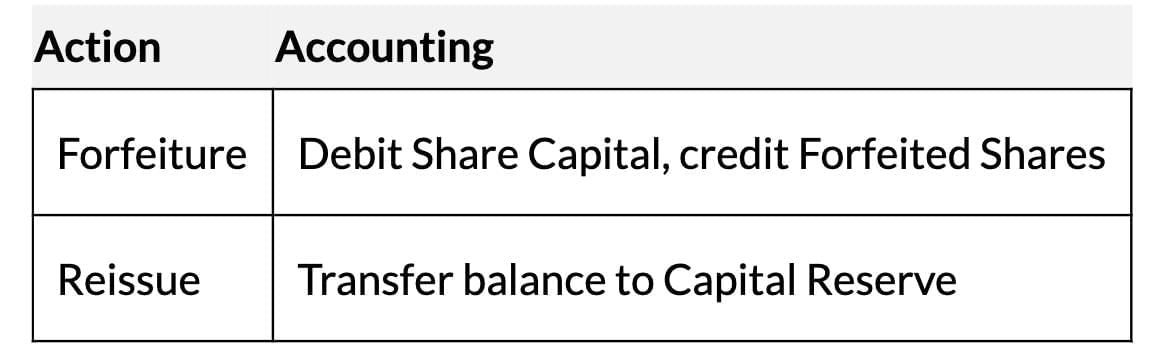
Forfeiture and Reissue of Shares
- Forfeiture: Shares cancelled for non-payment of calls; Share Capital debited, unpaid calls/Forfeited Shares credited.
- Reissue: Forfeited shares reissued at par/premium/discount (discount ≤ forfeited amount); balance to Capital Reserve.
- Premium Handling: If premium received, not debited; if unpaid, Securities Premium Reserve debited.
The document Short Notes: Accounting for Share Capital | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Accountancy Class 12.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
42 videos|199 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Short Notes: Accounting for Share Capital - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main features of a company? |  |
Ans. The main features of a company include legal personality, limited liability, perpetual succession, and the capacity to own property. A company is a separate legal entity from its owners, meaning it can enter into contracts, sue or be sued, and hold assets in its name. Limited liability protects shareholders by limiting their financial responsibility to the amount they invested. Perpetual succession ensures that the company continues to exist even if ownership changes. Furthermore, a company can raise capital through the issuance of shares.
| 2. What are the different types of companies? |  |
Ans. Companies can be classified into various types based on different criteria. The primary classifications include private companies, which restricts the transfer of shares and has a limited number of shareholders, and public companies, which can offer shares to the general public. Additionally, there are limited companies, which have limited liability, and unlimited companies, where owners have personal liability for debts. Other classifications may include non-profit organizations, which operate for charitable purposes, and multinational corporations, which operate in multiple countries.
| 3. What is share capital and how is it important for a company? |  |
Ans. Share capital refers to the funds raised by a company through the issuance of shares. It represents ownership in the company and can be classified into equity share capital and preference share capital. Share capital is crucial as it provides the necessary funds for a company to conduct its operations, invest in projects, and grow. It also reflects the company's financial health and ability to attract investors. Companies may issue shares to raise additional capital and support their business objectives.
| 4. What are the differences between shares issued at a premium and shares issued at a discount? |  |
Ans. Shares issued at a premium are sold at a price higher than their nominal or par value, while shares issued at a discount are sold below their nominal value. When shares are issued at a premium, the additional amount received above the par value is credited to a separate account called the Securities Premium Account, which can be used for specific purposes such as issuing bonus shares or writing off expenses. In contrast, issuing shares at a discount is generally restricted by law and may require approval, as it can affect the company's capital structure and financial stability.
| 5. What is an Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP) and its significance? |  |
Ans. An Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP) is a program that provides employees with the opportunity to purchase shares of the company at a predetermined price, typically lower than the market rate. ESOPs serve as a motivation tool, aligning the interests of employees with those of shareholders, as employees gain from the company's success. They can enhance employee retention and attract talent by providing a sense of ownership. Additionally, ESOPs can be a means for companies to raise capital while incentivizing employee performance and commitment.
Related Searches















