Case-Based Questions: Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Case 1: Karigar Furniture Ltd.
Karigar Furniture Ltd., a company manufacturing and trading furniture, was started by Saransh with five of his friends under Start Up India Program. It provides a diverse collection of wooden, plastic, cane, bamboo, and steel furniture at reasonable rates to the customers. They import raw-material from China for the same abiding by the government policy and procedures for imports. The company is earning good profits and donating 5% of profits earned for plantation of trees on highway roadside. The company organises training and skill development programme for its workers. The efficient planning and marketing strategy of the company has offered the owners of the company reasonable appreciation of capital employed.
Q1: Providing furniture at the reasonable rates is an example of social responsibility towards which of the following?
(a) Consumers
(b) Community
(c) Creditors
(d) Owners
Correct Answer: Option (a)
Providing furniture at the reasonable rates is an example of social responsibility towards consumers. "Exercise your purchasing power as a consumer, volunteer and bring joy to those in need, and share your experiences, tell your stories, and inspire others along the way."
Q2: “The company organises training and skill development programme for its workers.” Which of the following is not an example of the category of business responsibility stated?
(a) Providing safe working conditions
(b) Fair deals from management
(c) Earn fair returns on capital employed
(d) Develop sense of belongingness
Correct Answer: Option (c)
Earning fair returns on capital employed is not an example of the category of business responsibility stated.
Q3: “…donating 5% of profits earned for plantation of trees…” Identify the kind of social responsibility undertaken by the company.
(a) Legal
(b) Personal
(c) Discretionary
(d) None of these
Correct Answer: Option (c)
Discretionary is the kind of social responsibility undertaken by the company. Companies have a moral duty to improve the society by donating a small share of revenues to good causes, and this is a discretionary responsibility.
Q4: “…import raw-material from China for the same abiding by the government policy and procedures for imports.” Identify the kind of responsibility fulfilled here.
(a) Discretionary
(b) Legal
(c) Economic
(d) Ethical
Correct Answer: Option (b)
Legal responsibility is fulfilled here. Legal responsibility: All companies are subject to legal responsibilities and are required to follow the law, which impact organizations planning process. In order to operate soundly, a company must familiarize itself with external factors that govern the industry that the company operates within.
Case 2: Shuddh Masala Udyog
Shuddh Masala Udyog is a Partnership firm, which deals in trading of all varieties of spices. The partners focus on maximising the profits on the basis of customer satisfaction. Due to increasing competition in the market, the level of profits is falling. One of the partners advised to use substandard raw-material, to do little adulteration in products, and to maintain their profit margin. But the other partners opposed it by saying that the consumers can take legal action against the firm. Suggestion came from other partners to cut down the wages of workers and to withdraw the brunch facility given to them, but it was discarded on the ground that it will create discord and unsatisfactory environment. Finally it was decided that to maintain their profits the firm has to boost its sale and public image by fulfilling the social responsibility.
Q5: “…public image by fulfilling the social responsibility…” Social responsibility improves public image because of the following reasons?
(a) Mandatory for the business
(b) Legal obligation for business
(c) Satisfied workers and consumers contribute in the success of the business
(d) Avoidance of government interference
Correct Answer: Option (c)
Satisfied workers and consumers contribute in the success of the business.
Q6: “…cut down the wages of workers.” What is the reality of social responsibility that business firms don’t do this?
(a) Threat of government interference
(b) Development of business education
(c) Pressure of labour movements
(d) Burden on consumers
Correct Answer: Option (c)
Pressure of labour movements is the reality of social responsibility that business firms don’t do this.
Q7: “…will create discord and unsatisfactory environment.” Identify the argument in favour of social responsibility in this regard.
(a) Better community to conduct business
(b) Business creates social problems
(c) Justification for growth of business
(d) For maintenance of society
Correct Answer: Option (a)
Better community to conduct business. Community involvement is an easy and effective way to increase brand awareness, establish a positive reputation, and grow your business. Plus, it allows you to establish meaningful connections and give back to those in need.
Q8: If the business resorts to substandard raw-material, and does little adulteration in products, which of interest group will be affected?
(a) Workers
(b) Government
(c) Supplier
(d) Consumer
Correct Answer: Option (d)
Consumer organizations are advocacy groups that seek to protect people from corporate abuse like unsafe products, predatory lending, false advertising, astroturfing and pollution. Consumer Organizations may operate via protests, litigation, campaigning, or lobbying.
Case 3: Matching Stakeholders and Responsibilities
Q9: Match the following stakeholders given in Column I with expected social responsibility of enterprise given in Column II.
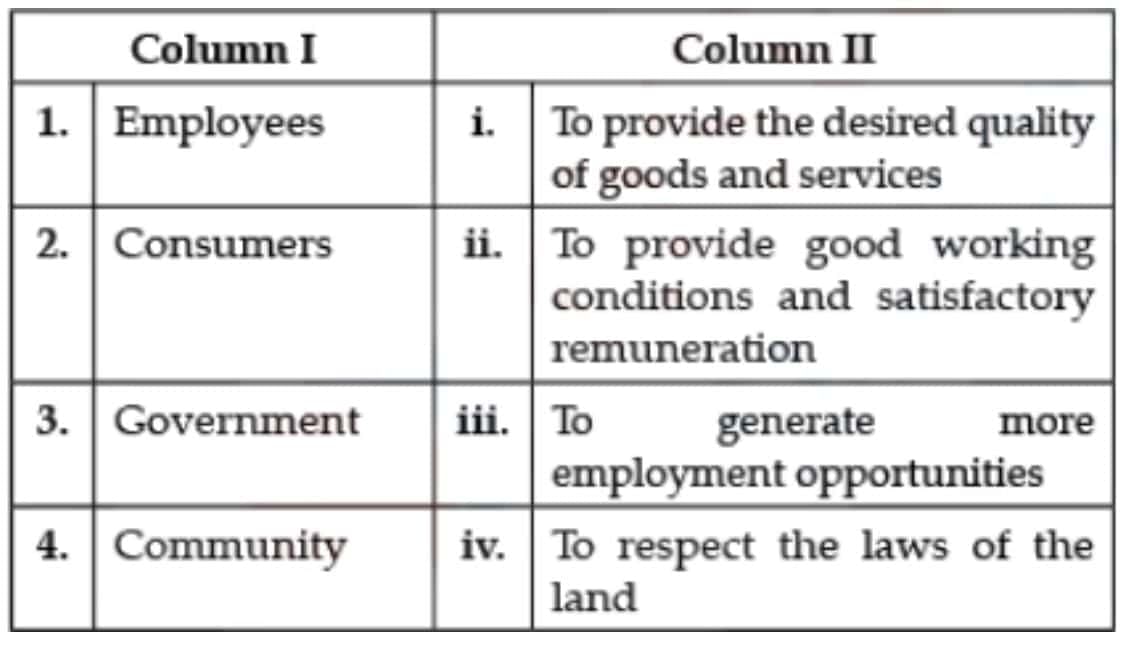
Select the correct matching:
(a) 1. (ii), 2. (iii), 3. (iv), 4. (i)
(b) 1. (iv), 2. (iii), 3. (ii), 4. (i)
(c) 1. (iii), 2. (i), 3. (iv), 4. (ii)
(d) 1. (ii), 2. (i), 3. (iv), 4. (iii)
Correct Answer: Option (a)
In option a the categories are matched accurately.
Case 4: Matching Business Ethics Elements
Q10: Match the statement given in Column I with the elements of business ethics given in Column II.
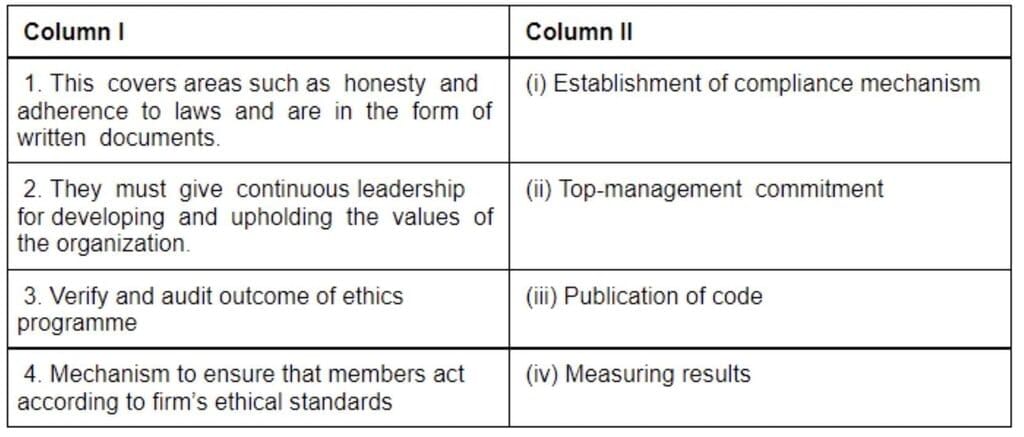
Select the correct matching:
(a) 1. (iv), 2. (ii), 3. (iii), 4. (i)
(b) 1. (iii), 2. (i), 3. (iv), 4. (ii)
(c) 1. (iv), 2. (iii), 3. (i), 4. (ii)
(d) 1. (ii), 2. (iii), 3. (i), 4. (iv)
Correct Answer: Option (d)
In option d the categories are correctly matched.
Publication of a ‘Code’: Enterprises with effective ethics programmes do define the principles of conduct for the whole organisation in the form of written documents which is referred to as the “code”. This generally covers areas such as fundamental honesty and adherence to laws; product safety and quality; health and safety in the workplace; conflicts of interest; employment practices; fairness in selling/marketing practices; and financial reporting.
Establishment of compliance mechanisms: In order to ensure that actual decisions and actions comply with the firm’s ethical standards, suitable mechanisms should be established. Some examples of such mechanisms are: paying attention to values and ethics in recruiting and hiring; emphasising corporate ethics in training; auditing performance regularly to analyse the degree of compliance; and instituting communication systems to help employees report incidents of unethical behaviour.
Measuring results: Although it is difficult to accurately measure the end results of ethics programmes, the firms can certainly audit to monitor compliance with ethical standards. The top management team and other employees should then discuss the results for further course of action.
|
38 videos|180 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Case-Based Questions: Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key principles of business ethics? |  |
| 2. How can businesses fulfill their social responsibilities? |  |
| 3. Why is ethical behavior important in business? |  |
| 4. What role does corporate governance play in business ethics? |  |
| 5. How do cultural differences impact business ethics? |  |





















