RPSC Monthly Current Affairs: February 2025 | Monthly Current Affairs RPSC - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) PDF Download
12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum

Why in News?
- India is preparing to host the 12th Regional 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific. This event is scheduled to take place at the Rajasthan International Centre in Jaipur from March 3 to 5, 2025.
Key Points
- About the Forum:
- The upcoming forum will emphasize the theme of "Realising Circular Societies Towards Achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Carbon Neutrality in Asia Pacific."
- Objective:
- The primary goal of this conference is to serve as a significant platform for promoting the 3R principles in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It aims to offer policy recommendations to government officials and share successful practices among stakeholders.
- Addressing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) will be a central focus of the forum, along with efforts to support progress toward carbon neutrality.
- India’s Leadership and Vision:
- India’s participation will be highlighted by the ‘India Pavilion,’ showcasing the country’s achievements in the realm of 3R and Circular Economy, reflecting a holistic governmental approach to these issues.
- Notably, India had previously hosted the 11th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Indore, Madhya Pradesh, in 2018.
- Jaipur Declaration:
- The forum is expected to conclude with the adoption of the ‘Jaipur Declaration,’ aimed at promoting the transition towards a resource-efficient, circular economy in Asia-Pacific nations.
- This declaration (2025-34) will build upon the earlier Hanoi Declaration (2013-23) and provide a framework for developing policies related to 3R and circular economy initiatives.
- The Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum
- Established in 2009 by the United Nations Centre for Regional Development (UNCRD), this forum plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable development in Asia-Pacific countries.
- It aims to offer policy strategies for integrating 3R and circularity principles in the region and serves as a valuable platform for sharing best practices related to 3R initiatives.
Embroidery and Surface Ornamentation Exhibition

Why in News?
A few days ago, the first-ever exhibition in India dedicated to embroidery and surface ornamentation was held in Jodhpur.
About the Exhibition:
- The exhibition featured 60 artworks created by over 20 artists from both local and international backgrounds.
- This event not only highlights the talent of the artists but also provides a platform for showcasing their creations.
Handicrafts on Display:
- Chikankari from Lucknow
- Kheta Quilts from Bihar
- Kantha from West Bengal
- Intricate embroidery styles from Kutch, Gujarat
The exhibition emphasizes the richness and diversity of Indian craftsmanship through various forms of embroidery.
Highlighting the Artwork
- The primary goal of the exhibition is to showcase embroidery as a vibrant and expressive art form that goes beyond mere clothing.
- It aims to demonstrate various embroidery techniques and the connection between traditional craftsmanship and modern textiles, thereby empowering artisans.
Jodhpur: An Overview
Location and Significance
- Jodhpur, known as the ‘Blue City’ due to its distinctive indigo-painted buildings, is the second-largest city in Rajasthan, after Jaipur.
- It is also referred to as ‘Sun City’ because of its sunny weather.
Historical Background
- Jodhpur was founded in 1459 by Rao Jodha, the leader of the Rathore dynasty.
- Initially, the settlement was at Mandore, but later it was moved to the present location, which became the centre of the Rathore dynasty.
Geographical Location
- Jodhpur is located at a latitude of 26°-27°37’ North and a longitude of 72°55’-73°52’ East.
Major Attractions
- Mehrangarh Fort. A massive fort situated on a hill, offering panoramic views of the city.
- Jaswant Thada. A beautiful memorial dedicated to Maharaja Jaswant Singh, known for its exquisite architecture.
- Umaid Bhawan Palace. A magnificent palace that also functions as a luxury hotel, showcasing stunning architecture and history.
Culture and Economy
- Jodhpur is rich in culture, featuring traditional Rajasthani architecture, music, dance, and art forms.
- The city’s economy is bolstered by tourism, handicrafts, and textiles, with a growing reputation as a cultural and historical hub.
Rajasthan Economic Review 2024-25

Why in News?
In the Assembly, the Rajasthan government unveiled its economic review for the financial year 2024-25, offering a comprehensive look at the state's economic landscape, growth rate, various schemes, and statistics.
Ten Resolutions for Inclusive Development:
The Revised Budget 2024-25 sets forth objectives for inclusive growth rooted in the principle of "Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas – Inclusive Growth for All." This principle is integral to a five-year action plan titled "Amrit Kaalkhand – Developed Rajasthan @2047," which encompasses 10 resolutions for the state's implementation.
Aiming for a USD 350 Billion Economy:
Rajasthan aspires to develop a USD 350 billion economy by 2029. The strategy to achieve this goal includes:
- Technological innovation in agriculture
- Expansion of industrial production
- Investment in renewable energy
- Promotion of tourism leveraging the state's rich cultural heritage
Overview of the Rajasthan Economy:
- The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) at current prices is projected at Rs 17.04 lakh crore for 2024-25, reflecting a growth rate of 12.02% from Rs 15.22 lakh crore in 2023-24.
- The agriculture sector is expected to contribute 26.92% to the Gross State Value Added (GSVA) for 2024-25 at current prices.
- The industrial sector is projected to contribute 27.16% to GSVA.
- The services sector is anticipated to be the largest contributor, accounting for 45.92% of GSVA.
- Per capita income is expected to increase by 11.04% to Rs 1,85,053 at current prices and by 6.88% to Rs 96,638 at constant (2011-12) prices in 2024-25 compared to the previous year.
Agricultural Development and Farmers Welfare:
- The Gross State Value Added (GSVA) from agriculture is projected to contribute 26.92% to the state's economy in 2024-25.
- GSVA at current prices has increased from Rs 1.19 lakh crore in 2011-12 to Rs 4.23 lakh crore in 2024-25.
- Expected production of food grains (cereals and pulses) is 267.67 lakh metric tonnes, reflecting a 10.67% increase from the previous year.
- Estimated production of oilseeds is 96.17 lakh metric tonnes, marking a 4.99% decline from 101.22 lakh metric tonnes in 2023-24.
- Projected production of sugarcane is 4.40 lakh metric tonnes, representing a 21.21% increase from 3.63 lakh metric tonnes in the previous year.
- Expected production of cotton is 18.45 lakh bales, indicating a 29.61% decrease from 26.21 lakh bales in 2023-24.
Chief Minister Seed Swavalamban Yojana (2024-25):
- Distribution of 19,836 quintals of seeds for Kharif crops.
- Distribution of 42,000 quintals of seeds for Rabi crops.
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY):
- Distribution of Rs 2,777 crore in insurance claims to eligible farmers.
Mukhyamantri Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana (2024-25):
- Provision of an additional Rs 2,000 per year to farmers under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana, with a proposed budget allocation of Rs 1,400 crore.
Samman Pension Scheme for Small and Marginal Old Farmers (2024-25):
- Monthly pension of Rs 1,150 for women farmers aged 55 and above and male farmers aged 58 and above. As of December 2024, 2,09,530 beneficiaries have received benefits totaling Rs 246.64 crore.
Rajasthan Krishak Samman Yojana (2024-25):
- Payment of a bonus of Rs 125 per quintal at MSP rates, totaling Rs 150.66 crore.
Micro-Irrigation under PMKSY (2024-25):
- Coverage of 34,469 hectares under drip and mini-sprinkler irrigation.
- Coverage of 56,727 hectares under sprinkler irrigation.
- Expenditure of Rs 123.79 crore on the scheme till December 2024.
Industrial Development and Investment Promotion
- Industrial Growth in Rajasthan (2024-25): The industrial sector is anticipated to grow by 5.77% in Gross State Value Added (GSVA) at constant (2011-12) prices. GSVA from industry is projected to increase from Rs 1.36 lakh crore (2011-12) to Rs 4.26 lakh crore (2024-25), reflecting a 9.17% CAGR at current prices. The industry sector contributed 27.16% to Rajasthan’s GSVA, with manufacturing being the largest contributor.
- Industrial Production & Growth: The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) has improved from 122.34 (2021-22) to 157.31 (Nov 2024), indicating industrial expansion.
Investment & Policy Initiatives:
- Launch of the Rajasthan Investment Promotion Scheme (RIPS) to attract investments.
- Implementation of the Rajasthan Export Policy-2024 to enhance the state’s export potential with targeted support for exporters.
- Promotion of small and medium enterprises through the Rajasthan MSME Policy-2024, fostering a conducive business environment.
- Encouragement of the production and use of manufactured sand (M-Sand) as a sustainable alternative to river sand in construction through the Rajasthan M-Sand Policy-2024.
Rajasthani Rising: Economic Growth and Development Overview
 Rajasthan Road Development
Rajasthan Road Development
Rising Rajasthan Investment Summit The summit resulted in Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs) worth an impressive Rs 35 lakh crore, showcasing the state’s commitment to economic progress and development.
Exports (2023-24)
Rajasthan’s exports for the year reached a total of Rs 83,704.24 crore. The primary contributors, including engineering goods, gems and jewellery, metals, textiles, and handicrafts, accounted for over 65% of the total exports, highlighting the state’s strong export sectors.
Transportation
Road Network in Rajasthan (2024)
- Total road network spans 3,17,121 km.
- Road density stands at 92.66 km per 100 square kilometres.
- A total of 39,408 villages are connected by roads.
- Upgrades are underway for 47 national highways and 23 state highways to facilitate high-speed travel.
Investment & Development
- A budget of Rs 60,000 crore has been allocated for road development over the next five years.
- For the fiscal year 2024-25, Rs 11,986 crore has been set aside.
- By December 2024, Rs 10,705 crore of this budget had already been utilized.
- The Bharatmala Pariyojana is a crucial initiative aimed at enhancing road infrastructure, playing a significant role in the state’s development strategy.
- Under the National Highway Development Programme (NHDP), approximately Rs 15,920 crore has been invested in developing 845.32 km of national highways.
Highway & Road Distribution
- National highways cover a distance of 10,790 km.
- State highways extend for 17,376 km.
- Rural roads span approximately 2,06,318 km.
Water Supply
Surface Water Resources in Rajasthan
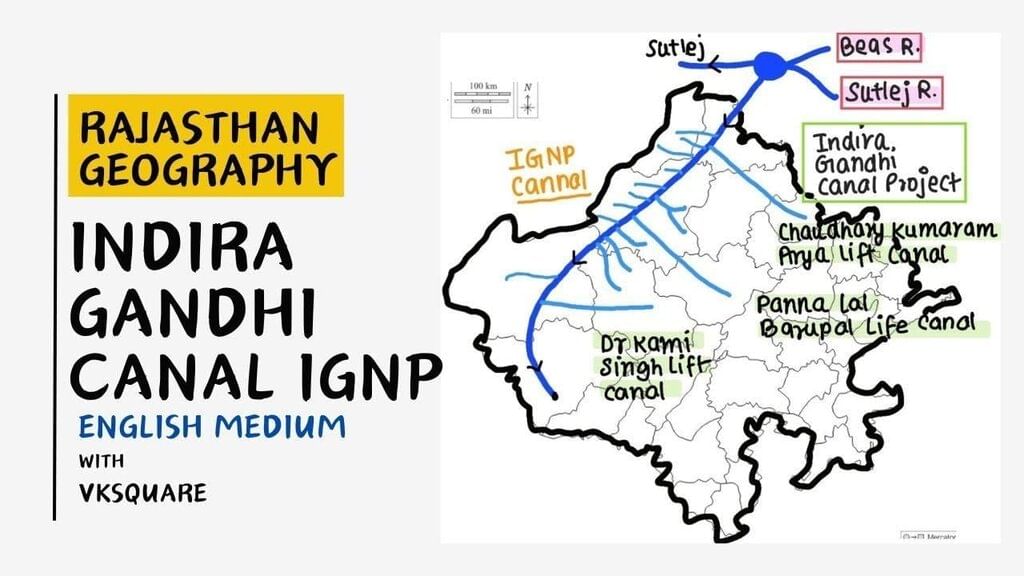 Water Supply Initiative
Water Supply Initiative
- Indira Gandhi Canal Project: This project provides water to 5,719 villages and 39 towns.
- Chambal River: Supplies water to 4,899 villages and 29 towns.
- Narmada River: Serves 902 villages and 3 towns.
- Bisalpur Dam: Provides water to 3,109 villages and 22 towns.
- Jawai Dam: Supplies water to 811 villages and 10 towns.
Urban & Rural Water Supply Initiatives
- AMRUT 2.0: Launched on October 1, 2021, this initiative aims to provide drinking water to all households under the 'Har ghar nal' scheme by the year 2025-26.
- Investment: An amount of Rs 5,123.06 crore has been approved for water supply projects in 183 urban local bodies.
Water Infrastructure Development (2024-25)
 Water Development
Water Development
- Tube wells installed: 1,012 in rural areas.
- Hand pumps installed: 1,268 in rural areas.
- Hand pumps repaired: 164,684 until September 2024.
- Drinking water provided to 15,417 villages and settlements.
Electricity Infrastructure in Rajasthan
- Total Installed Capacity. 26,325.19 MW (as of December 2024).
- Renewable Energy Leadership.
- Solar Power. 5,482.66 MW.
- Wind Power. 4,414.12 MW.
Power Transmission & Electrification
- Extra High Voltage (EHV) Transmission Network: 44,638 circuit km (as of December 2024).
- Rural Electrification.
- Villages electrified. 43,965.
- Dhanis electrified. 1.14 lakh.
- Rural households electrified. 108.09 lakh.
Consumer Growth & Agricultural Support
 Metro Development
Metro Development
- The total number of consumers increased from 190.61 lakh in March 2024 to 196.22 lakh in December 2024, marking a growth of 2.94%.
- Agricultural connections provided reached 72,373 by December 2024.
- A tariff subsidy of Rs 22,755.22 crore was allocated for farmers in 2024-25.
Quality of Life: Civic Amenities
Metro Expansion & Development Authority Expenditure
- Jaipur Metro Expansion is underway in phases with an investment exceeding Rs 18,000 crore.
- Capital expenditurefor 2024-25 (up to December 2024):
- Jaipur Development Authority: Rs 913.34 crore.
- Kota Development Authority: Rs 420.11 crore.
Urban Infrastructure & Smart Cities
- UIDSSMT Projects: 12 projects sanctioned, comprising 11 sewerage projects and 1 water supply project, with a total investment of Rs 646.24 crore.
- Smart Cities Initiative:
- Selected cities: Jaipur, Udaipur, Kota, Ajmer.
- Funds utilised:Rs 3,740.30 crore (out of Rs 3,820 crore received, as of December 2024). The remaining amount is still available for use.
Housing & Land Allotment
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban):
- Total houses sanctioned: 2,88,550.
- Completed: 1,96,700.
- Under construction: 73,603.
- Land Allotment for Marginalised Communities:
- Vimukta, Nomadic & Semi-Nomadic plot/patta allotment drive initiated on October 2, 2024.
- Total plots/leases allocated: 17,156 for homeless families.
Disaster Management and Mitigation Measures
 Disaster Relief Funding
Disaster Relief Funding
- State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF). Rs 4,408.38 crore (as of December 2024).
Utilization Areas:
- Agricultural subsidies.
- Flood-affected area repairs.
- Disaster mitigation
Rajasthan Budget 2025-26 Overview

Why in News?
On February 19, 2025, the State Finance Minister of Rajasthan presented the Rajasthan Budget for the year 2025-26 in the Assembly. This budget is noteworthy as it is the first one centered around green initiatives, aiming to promote rural development, infrastructure, and renewable energy. It includes various schemes tailored to address the needs of women, farmers, and youth.
Key Announcements
Drinking Water
- Allocation of Rs 425 crore for providing drinking water in rural areas, targeting 20 lakh households for connections in the upcoming year.
- Launch of the Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) with a provision of Rs 5830 crore.
Energy
- Plans to generate over 6400 MW of electricity in the coming year.
- Provision for 50,000 new agricultural connections and five lakh domestic connections.
- Construction of various substations, including one 765 KV, five 400 KV, thirteen 220 KV, twenty-eight 132 KV, and one hundred thirty-three 33/11 KV substations.
- Generation of 10 GW of power through private sector initiatives.
- Implementation of the Chief Minister Free Electricity Scheme, providing 150 units of free electricity per month.
Transport Development
- Initiatives worth over Rs 5000 crore for road improvement.
- Construction of nine Greenfield Expressways.
- Allocation of Rs 60,000 crore for non-pavable road works at Rs 10 crore each in every assembly.
- Development of the 'Atal Pragati Path' in 250 villages at a cost of Rs 500 crore.
- Provision of 500 new roadways buses on the GCC model and 500 buses for urban areas.
- Extension of Jaipur Metro from Sitapura Industrial Area to Ambawadi and Vidyadhar Nagar at a cost of Rs 12,000 crores.
- Allocation of Rs 550 crore under the ‘Panchgaurav Yojana’.
- Implementation of the Swamitva Scheme to provide leases to 2 lakh families under MNREGA, creating 3400 lakh man days.
- Improvement of traffic systems in Jaipur with a budget of Rs 250 crore and removal of the BRTS corridor.
- Provision of Rs 100 crore each for Dang, Mewat, and Bridge regional development schemes.
- Creation of 'Zero Accident Zones' on key highways.
- Allocation of Rs 50 crore for strengthening 20 Trauma Centres under PPP mode.
- Provision of 25 Advanced Life Support Ambulances.
Urban Development
- Allocation of Rs 780 crore for expansion and development of parking, renovation, residential flats, and bus stands.
- Funding of Rs 12050 crore over 7 years for the Pandit Deendayal Upadhyaya Urban Development Scheme.
- Installation of 50,000 street lights in all cities.
- Provision of Rs 175 crore for the construction of 500 pink toilets.
- Establishment of Mechanised Transfer Stations in 30 municipal councils.
Industrial Development
- Streamlining online permissions through the ‘Single Window – One Stop Shop’ to 149 to encourage industrial growth.
- Implementation of a Competitive Index for departmental performance.
- Establishment of a Project Management Unit (PMU) to ensure effective MoUs under the Rising Rajasthan initiative.
- Introduction of the Flatted Factory system to promote industrial activities.
- Development of industrial areas under a Plug and Play Model.
- Promotion of the Global Capability Centre (GCC) Policy to attract service sector investments.
- Establishment of various parks, including Toy Park in Kota, Stone Park in Nimbahera-Chittorgarh and Bundi, Ceramic Park in Soniana-Chittorgarh, Pharma Park under DMIC, Textile Park expansion in Bhilwara, and Block Printing Zone in Sanganer-Jaipur.
- Allocation of Rs 150 crore for infrastructure development in 18 new industrial areas.
- Assistance for setting up Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETP) in private industrial parks.
- Construction of two logistics parks connected to the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC).
Tourism, Arts, and Culture
- Allocation of Rs 975 crore for tourism development initiatives.
- Hosting of the IIFA Awards in Jaipur to promote the city.
- Development of 10 iconic tourist destinations under the Heritage Tourism initiative.
- Allocation of Rs 100 crore to promote night tourism activities.
- Conservation of historical havelis under the Shekhawati Haveli Conservation Scheme to preserve cultural heritage.
- Provision of Rs 25 crore for the upgradation of the Jaipur Albert Hall Museum to enhance visitor experience.
- Development of a Tribal Tourist Circuit with an investment of Rs 100 crore to promote tribal tourism.
- Establishment of a Flying Training Organisation (FTO) in Pratapgarh, Jhalawara, and Jhunjhunu to promote aviation training.
- Launch of a hop-on-hop-off bus service in Jaipur, Jodhpur, and Udaipur to facilitate tourist movement.
Objective
 Vedic Tourism Development
Vedic Tourism Development
- Rs 101 crore allocated for upgrading temples.
- Monthly amount offered in temples increased to Rs 3,000.
- Priests' honorarium raised to Rs 7,500 per month.
Youth Development and Welfare
- Introduction of the Rajasthan Employment Policy-2025.
- Creation of the ‘Vivekananda Employment Assistance Fund’ with Rs 500 crore.
- Recruitment for 1.25 lakh posts in the upcoming year.
- Employment of 1.50 lakh youth in the private sector.
- Launch of the ‘Vishwakarma Yuva Udham Protsahan Yojana’ offering 8% interest subsidy on loans up to Rs 2 crore.
- Assistance to 5 lakh youth with margin money support.
- Establishment of Advanced Skills and Career Counselling Centres in each division.
- Development of Vedic Gurukul and Vedic tourism centres in Jaipur, Jodhpur, and Udaipur.
- Land allotment for Dronacharya Award-winning coaches.
- Construction of special sports complexes for parasports in Udaipur, Kota, Bikaner, Bharatpur, and Ajmer divisions.
Medical and Health
- Constitution of the ‘MAA Fund’ with Rs 3,500 crores for free testing and medicines.
- Implementation of interstate portability in the MAA scheme.
- Provision of free medicine at home for senior citizens over 70 years of age.
- Establishment of diabetic clinics in all district hospitals.
- Availability of Digital X-ray, TRU-NAAT, and CB-NAAT machines at CHCs for TB control.
- Cervical cancer screenings for women with HIV and those at risk.
- Launch of the MAA Eye Voucher Scheme for free eye check-ups and surgeries.
- Establishment of 148 Urban Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (UAAM).
- Upgrading of the Vitreo Retina Surgery Unit in Bikaner Hospital.
- Augmentation of Spinal Injury Centre capacity to 120 beds at Jaipur, Bikaner, Jodhpur, Udaipur, and Kota.
- Allocation of Rs 195 crore for a cancer unit and cottage ward in Kota Medical College.
- Establishment of Ultra Advanced Burn Care Centres at each divisional headquarters.
- Allocation of Rs 500 crore for upgrading the Rajasthan Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS), Jaipur; creation of 750 doctor and 1,500 paramedical posts.
- Provision of Rs 50 crore for the ‘Fit Rajasthan’ campaign; focus on reducing oil intake by 10%.
- Introduction of a new AYUSH Policy.
- Incentive of Rs 11 lakh for declaring villages as Ayushman Arogya Gram.
- Establishment of food laboratories in 7 districts. Hanumangarh, Sawai Madhopur, Jaisalmer, Pali, Sirohi, Chittorgarh, and Dungarpur.
Social Security
- Increase in social security pension to Rs 1,250 per month.
- Provision for a Gig and Unorganised Workers Fund.
- Allocation of Rs 350 crore for unorganised workers.
- Distribution of 35 thousand scooters to girls.
- Establishment of the ‘Rani Lakshmibai Centre’ in higher secondary schools or colleges in every block.
- Lakhpati Didi initiative to uplift 20 lakh women.
- Launch of the ‘Dadudyal Nomadic Empowerment Scheme’ to support nomadic communities.
- Implementation of the One Time Settlement Scheme (OTSS) for SC, OBC, and Minority Corporation loans.
- Establishment of ‘Annapurna Bhandar’ at 5 thousand fair price shops.
- Implementation of the Chief Minister’s Nutrition Nutri-Kit Scheme for additional nutrition to pregnant women.
Law and Order and Good Governance
- Strengthening of the surveillance and security system under the ‘Rajasthan Civil Security Act’.
- In 2 years. Creation of 1,000 vehicles and 3,500 new posts for the police.
- Provision of Rs 350 crore for establishing the Sardar Patel Centre for Cyber Control and War-Room.
- Establishment of 400 Video Conference (VC) Nodes for undertrial prisoners.
- Installation of T-HCBS system to block illegal mobile signals in 7 Central Prisons.
- Provision of minimum wages for convicted prisoners.
- Upgrading of the Ajmer Jail Training Institute.
- Establishment of Additional Superintendent of Police Offices in Shahpura (Jaipur) and Ringas (Sikar).
- Establishment of Deputy Superintendent of Police Offices in Raipur–Biawar and Khatushyamji (Sikar).
- Provision for establishing 8 new cyber police stations.
- In the coming year, establishment of ‘Atal Gyan Kendras’ in Panchayat headquarters with a population over 3 thousand.
- Establishment of the Ambedkar Constitution Studies and Research Institute.
- Provision of Rs 250 crore for tablets for officers and employees for digitisation.
- Implementation of modern RajNET 2.0 system at a cost of Rs 400 crore to double connectivity capacity.
- Establishment of a Disaster Recovery Data Centre in Jodhpur.
- Provision of Rs 300 crore for the Brahmagupta Frontier Technologies Centre.
Organic Farming
- 1 Lakh Farmers: Over one lakh farmers will benefit from the use of bio-pesticides in their farming practices.
- Incentives for Traditional Farming: Small and marginal farmers will receive an incentive of Rs 30,000 for farming with bulls. Additionally, there will be a subsidy for biogas plants to support sustainable farming practices.
Water Self-Reliance Campaign
- Chief Minister's Initiative: The Chief Minister's Water Self-Reliance Campaign 2.0 aims to enhance water harvesting capabilities.
- Financial Allocation:. significant fund of Rs 2,700 crore is allocated for the construction of water harvesting structures.
- Targeted Areas: These structures will be built in over 4,700 villages, promoting water conservation and self-reliance in water resources.
Developed Rajasthan @2047
- GIS-based Green Land Use Perspective Plan: Introduction of a Geographic Information System (GIS)-based plan for sustainable green land use, guiding development and conservation efforts.
Solar Initiatives
- Solar Didi Program: Launch of a new honorarium program called "Solar Didi" to promote the use of solar equipment. Under this initiative, 25,000 women will be trained to increase the adoption of solar technology.
- Solar Energy for PHED Pumping Stations: The pumping stations operated by the Public Health Engineering Department (PHED) will be powered by solar energy. This will be implemented through the Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM), facilitating the integration of solar energy into public water supply systems.
Circular Economy Initiatives
- Rajasthan Circular Economy Incentive Scheme-2025: Introduction of a scheme to promote the circular economy widely across the state, encouraging sustainable practices and resource efficiency.
- R&D Grant for Recycling and Reuse: Provision of a grant of Rs 2 crore for research and development projects focused on recycling and reuse, fostering innovation in waste management.
- Financial Support for MSMEs and Startups: Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and startups working in the circular economy sector will receive an additional discount of 0.5% on loans, supporting their financial sustainability and growth.
Rajasthan Vehicle Scrap Policy
- Implementation: The Rajasthan Vehicle Scrap Policy has been successfully implemented in the state to promote the scrapping of old and unfit vehicles.
- Waste to Wealth Parks: Plans are in place to establish Waste to Wealth Parks in all district headquarters. These parks will focus on converting waste into valuable resources, contributing to a circular economy.
- Utensil Banks: Utensil banks will be set up in gram panchayats (village councils) to provide reusable utensils for various community needs, further supporting the waste reduction and resource efficiency goals of the policy.
Clean Technology Development
- Establishment of Clean and Green Technology Development Centre:. dedicated centre will be established with a budget of Rs 250 crore to focus on the development of clean and green technologies. This initiative aims to promote sustainable technological advancements in the state.
- Development of Ecological City: Plans are in place to develop a clean and green ecological city with an investment of Rs 900 crore over the next three years. This project aims to create a model city that embodies sustainable living and environmental conservation.
Sustainable Development Goals
- Sustainable Development Goals Coordination and Acceleration Centre (SDGCAC): Establishment of a centre to coordinate and accelerate efforts towards achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the state.
- Rajasthan Green Credit Mechanism: Development of a green credit mechanism similar to carbon credits, allowing for tradable credits that incentivize environmental conservation efforts.
- Rajasthan Green Challenge Fund: Introduction of a Green Challenge Fund with a budget of Rs 100 crore to support innovative projects aimed at environmental sustainability.
- Green Aravali Development Project: Initiation of the Green Aravali Development Project with an investment of Rs 250 crore to enhance green cover and promote ecological balance in the Aravali region.
- Budget Estimates for the year 2025-26.
Financial Overview
- Revenue Receipts: Rs 2,94,536.49 crore.
- Revenue Expenditure: Rs 3,25,545.90 crore.
- Revenue Deficit: Rs 31,009.41 crore.
- Fiscal Deficit: Rs 84,643.63 crore (4.25% of GSDP).
- Projected GSDP: Over Rs 19,89,000 crore for the year 2025-26.
- Target for 2030: Building a USD 350 billion economy.
Celebrating Soil Health Card Day

Why in News?
On 19 February 2025, India marked the 10th Soil Health Card Day, a significant occasion to promote soil health and fertility.
Overview of the Soil Health Card Scheme
- The Soil Health Card Scheme was inaugurated by the Prime Minister on 19 February 2015 in Suratgarh, Rajasthan.
- The scheme's theme is "Healthy Earth, Green Fields", emphasizing the importance of soil health for sustainable agriculture.
- Under this program, farmers receive soil health cards every two years, providing essential information and guidance to improve soil health and fertility.
Key Features of the Soil Health Card
- The soil health card offers detailed insights into the nutrient status of the soil, including macro nutrients. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium ), secondary nutrients. Sulfur ), micronutrients. Zinc, Iron, Copper, Manganese, Boron ), and physical parameters. pH, Electrical Conductivity, Organic Carbon ).
- Based on this information, the card provides fertilizer recommendations and necessary soil amendments to optimize crop production.
- The scheme also aims to strengthen Soil Testing Laboratories. STL ) to ensure accurate and timely soil testing.
Objectives and Goals
- The primary goal of the Soil Health Card Scheme is to address the issue of soil fertility across various states in India.
- By providing corrective measures and guidance, the program aims to enhance soil health, leading to better agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- The Soil Health Card Portal facilitates the generation of soil health cards in a standardized format, available in all major languages and five dialects, ensuring accessibility for farmers.
Soil Testing and Monitoring
Soil samples are typically collected twice a year in India, after the harvest of Rabi and Kharif crops, or when there is no standing crop in the field. This regular testing helps monitor soil health and make necessary adjustments to soil management practices.
Review of Major Infrastructure Initiatives
 Infrastructure Review
Infrastructure Review
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has conducted an examination of the primary challenges impacting significant infrastructure projects in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
The purpose of this review is to expedite the resolution of these issues through enhanced coordination between various ministries and state authorities, with the assistance of the Project Monitoring Group (PMG).
Main Areas of Focus in the Review
- DPIIT investigated 21 specific issues related to 14 critical infrastructure projects.
- This includes the Khavda Renewable Energy Park, which is anticipated to generate 81 billion units of electricity annually.
- Another project under review is Reliance Jio’s 5G/4G expansion, aimed at delivering benefits such as faster internet speeds, reduced latency, and broader coverage.
Overview of DPIIT
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) was established in 1995.
- In 2000, the Department of Industrial Development was merged into DPIIT.
- On 27 January 2019, the department was renamed from the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion to its current title.
- DPIIT is responsible for formulating and implementing policies to promote and develop the industrial sector, aligning with national objectives and social needs.
- The department also manages foreign direct investment (FDI) and aims to enhance investment inflows into India.
- DPIIT operates under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India.
Second All India State Water Ministers Conference
 Water Security Initiative
Water Security Initiative
The Second All India State Water Ministers Conference was held in Udaipur, Rajasthan on February 18-19, 2025. Organized by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, the conference aimed to address the critical issue of water security and promote effective water management across the country.
Objectives and Theme
- The theme of the conference, “India@2047 – Water Secure Nation,” aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision for a developed and water-secure India by 2047.
- The conference aimed to enhance collaboration among states and various ministries for sustainable and integrated water resource management.
Key Focus Areas
- Strengthening water governance to ensure effective management and distribution of water resources.
- Improving water storage infrastructure and supply systems to meet the growing demand for water.
- Providing reliable water distribution services for both drinking water and irrigation purposes.
- Managing water demand and enhancing water use efficiency to conserve this precious resource.
- Integrated management of rivers and coastal areas to protect and preserve these vital ecosystems.
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)
The Jal Jeevan Mission, launched in 2019, aims to provide 55 litres of water per person per day to every rural household through functional household tap connections (FHTC) by 2024.
- The mission focuses on ensuring the functionality of existing water supply systems, monitoring water quality, and promoting sustainable agriculture.
- It supports the combined use of conserved water and aims to enhance drinking water sources, supply systems, greywater treatment, and reuse.
Integrated Water Management
- The Jal Jeevan Mission emphasizes the integrated management of water demand and supply at the local level.
- It aims to create local infrastructure for sustainable water sources, including rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and managing domestic wastewater for reuse.
- The mission adopts a community-based approach to water management, prioritizing information, education, and communication to raise awareness and promote sustainable practices.
Regional Official Language Conference
 Devanagari Script
Devanagari Script
Official Language
- A recent joint regional conference was conducted in Jaipur, organized by the Official Language Department of the Home Ministry.
- Approximately 3,000 participants from Central Government offices and Town Official Language Implementation Committees attended the event.
- Institutions excelling in promoting Hindi within government work were recognised and honoured for their efforts.
- The primary objective of the conference was to foster and encourage the use of Hindi in various government departments.
Hindi Language
Introduction:
- Hindi is an Indo-Aryan language mainly spoken in the Indian subcontinent.
- It is the official language of India as per the Constitution and is crucial for Indian society, culture, and literature.
- Globally, Hindi is the third most spoken language and one of the ten official languages of the United Nations.
History:
- Hindi has its roots in Sanskrit and has been spoken in the Indian subcontinent for many centuries.
- Over time, Hindi has absorbed words from Persian, Arabic, and English, especially during the Mughal Empire and British rule.
Script:
- Hindi is written in the Devanagari script, which is derived from the Sanskrit script.
- Devanagari comprises 11 vowels and 33 consonants.
- This script is also used for several other Indian languages.
Linguistic Diversity:
- Hindi encompasses various dialects, including Awadhi, Bhojpuri, Braj, Haryanvi, and Marwari.
Expansion:
- Hindi is spoken not only in India but also in countries like Nepal, Pakistan, Malaysia, Thailand, Fiji, and others.
Place in the Constitution:
- Article 343 of the Indian Constitution recognises Hindi as the official language of the Union, included in the Eighth Schedule.
- Hindi is also acknowledged as one of the 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution.
Ammonia Gas Leak in Kota
 Ammonia Leak Incident
Ammonia Leak Incident
Ammonia gas leaked from a Chambal Fertilisers and Chemicals Limited (CFCL) plant near Gadepan village in Kota district, Rajasthan. This leak caused nausea and fainting among children after they inhaled the gas’s sharp, suffocating smell.
Impact of the Gas Leak:
- The leak affected students who went to the school grounds to fetch water.
- Some students complained of breathlessness and abdominal pain.
- The close proximity of the school to the CFCL factory likely increased students' exposure.
- School staff promptly took the students to the hospital as their condition worsened.
Precautionary Measures:
- The school was closed as a precaution, and children were sent home after the incident.
- This raised concerns among local residents.
- Lok Sabha Speaker and local officials visited the hospital to check on the affected students.
Ammonia gas (NH3) is a compound made of nitrogen and hydrogen. It is a colourless gas with a strong, penetrating odour. Ammonia is very reactive and dissolves easily in water, and it is better described as a weak base.
Mode of Production:
- Natural:
- Produced in soil through bacterial processes.
- Generated during the breakdown of organic matter, including plants, animals, and animal waste.
- Bacteria in the intestines also produce ammonia, and a small amount is created by lightning strikes.
- Commercial:
- Produced through steam reforming of natural gas and coal gasification.
Uses:
- Used to produce nitrogen compounds like urea, which is the most commonly used source of nitrogen in fertilisers.
- Applied directly to soil for crops, lawns, and plants.
- Utilised in various cleaning products.
- Forms compounds like ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, and various ammonium phosphates.
- Used in the manufacture of explosives.
- Used in refrigeration and cooling systems.
Impact:
- Plants:
- Causes direct toxic damage to leaves.
- Alters plant susceptibility to frost, drought, and pathogens, including insect pests and invasive species.
- Health Risks:
- Long-term exposure to low levels or short-term exposure to high levels can lead to health issues from inhalation.
- Symptoms may include burning sensations in the nose, throat, and irritation of the respiratory tract.
Joint Special Forces Exercise: Cyclone-III between India and Egypt
 Joint Military Exercise
Joint Military Exercise
Cyclone-III is an annual joint military exercise between India and Egypt, aimed at enhancing military relations and cooperation between the two nations. The exercise alternates between the two countries, with the last edition held in Aswan, Egypt, in January 2024.
The Indian team participating in Cyclone-III consists of 25 soldiers from two special forces battalions, while the Egyptian team also includes 25 soldiers from Egypt's Special Forces Group and Task Force.
The objectives of the exercise include improving physical fitness, joint planning, tactical exercises, and counter-terrorism operations in desert and semi-desert areas. It involves rehearsing and validating tactical exercises in various scenarios. Additionally, the exercise will feature a demonstration of indigenous military equipment by Egypt and an inspection of the defense manufacturing industry.
About Egypt
Egypt is located in northeastern Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula extending into Asia. The capital city is Cairo.
Boundaries. Egypt is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gulf of Suez and the Red Sea to the east, Libya to the west, and Sudan to the south.
Maritime Borders. In the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt shares maritime borders with Cyprus, Turkey, and Greece. In the Red Sea, maritime borders are shared with Jordan and Saudi Arabia.
History. Egypt gained modern independence in 1922. The official language is Modern Standard Arabic, while the widely spoken dialect is Egyptian Arabic (Masri). The predominant religion is Islam, with 85-90% of the population being Sunni Muslim.
Major River. The River Nile is the only river in Egypt that flows year-round, and about 98% of the population resides in the Nile River Valley.
Subsidy on Electric Vehicles
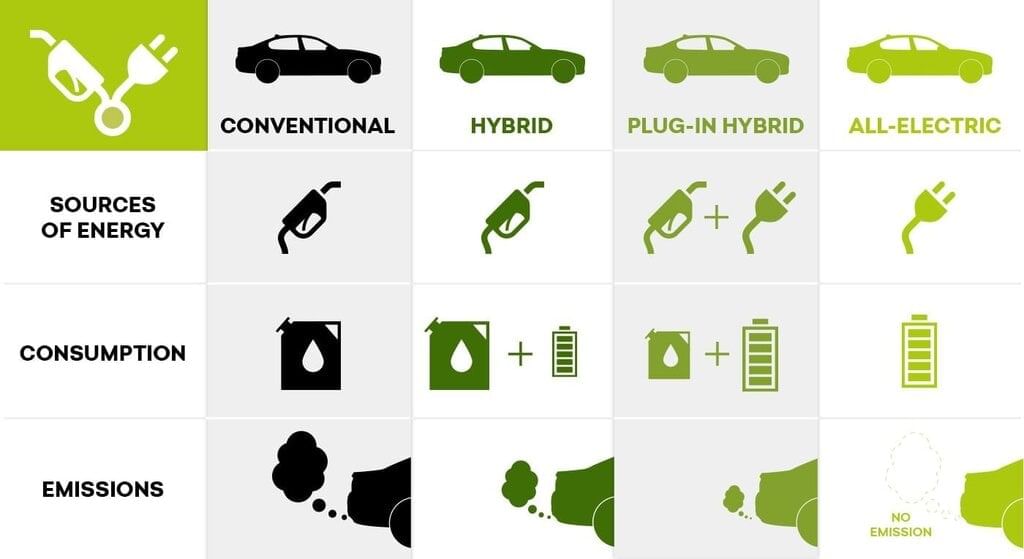 Electric Vehicle Types
Electric Vehicle Types
To promote electric vehicles, the Rajasthan government has established an e-vehicle promotion fund amounting to Rs 200 crore under the Electric Vehicle Policy.
About the Fund:
- GST
- The State Government’s “Electric Vehicle Policy-2022” includes a plan to reimburse the state for expenses and provide a one-time grant from the E-Vehicle Promotion Fund to buyers of electric vehicles with modern batteries, in line with FAME-2 (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles).
- The reimbursement and one-time grant will apply to vehicles bought from 1st January 2022 and registered in the state.
The Process:
- Vehicle manufacturers must register on the departmental portal to access the subsidy.
- After verification, the department will allow the vehicle buyer to apply for the grant.
- The policy covers all types of electric vehicles, including two-wheelers and heavy vehicles.
- The government aims to promote electric vehicles over diesel and petrol options to reduce pollution and maintain environmental balance.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles:
- Zero Tailpipe Emissions: Electric vehicles (EVs) produce no harmful emissions from their tailpipes, which significantly improves air quality and benefits public health.
- Lower Fuel Costs: Charging an EV with electricity is often cheaper than refuelling a petrol or diesel vehicle, leading to reduced fuel costs per kilometre.
- Quieter Operation: Electric motors operate much more quietly than traditional petrol or diesel engines, contributing to reduced noise pollution.
- Higher Energy Efficiency: Electric motors convert a higher percentage of the energy from their power source into usable power for movement, making them more efficient than internal combustion engines (ICE).
- Alternative Power Source: EVs use electric motors for propulsion, as opposed to ICE vehicles that rely on burning fossil fuels like petrol or diesel.
Types of Electric Vehicles:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV): These vehicles run entirely on battery power, producing zero tailpipe emissions.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV): PHEVs combine an electric motor with a petrol engine. They can be charged from an external power source and primarily run on electric power for short distances, switching to the petrol engine for longer trips.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV): HEVs use both an electric motor and a petrol engine, but the battery is charged through regenerative braking and the petrol engine, not by plugging it in.
Beneshwar Fair 2025
 Beneshwar Fair
Beneshwar Fair
Beneshwar Dham
The Beneshwar Fair took place from February 8 to 12, 2025, in the Dungarpur district of Rajasthan.
About the Fair:
- The Beneshwar Fair is an annual celebration held in January or February to honour Baneshwar Mahadev, another name for Lord Shiva.
- This fair attracts visitors from Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh, who come to bathe at the confluence of the Mahi and Som rivers.
- The event showcases the rich tribal culture of the Bhils and is often referred to as the “Kumbh Mela of Tribals.”
Cultural Programs and Sports:
- The district administration, tourism department, and tribal development department organise various cultural and sports activities during the fair.
- Activities include volleyball, tug of war, women’s matka race, bhajan groups, and turban-tying competitions.
Bhil Community
The Bhils are one of India’s largest tribal communities, living in states such as Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Their name comes from ‘billu,’ meaning bow, reflecting their reputation for excellent archery skills and knowledge of local geography.
Historically, the Bhils were known for their expertise in guerrilla warfare. Today, many are farmers, agricultural workers, and skilled sculptors.
Traditionally, Bhil women wear saris, while men dress in long frocks and pyjamas. Women also wear heavy jewellery made of silver and brass, along with beaded rosaries and earrings.
Saddle Dam
 Saddle Dam Overview
Saddle Dam Overview
Rana Pratap Sagar Dam
- The Chief Minister visited the saddle dam located upstream at Rawatbhata.
- During the visit, the Chief Minister assessed the progress of the planned works and provided necessary directions to the officials from the Department of Water Resources, Government of Rajasthan.
- The officials briefed the Chief Minister about the Rana Pratap Sagar-Brahmani flood protection management and water diversion project at Bisalpur Dam in detail.
Brahmani River
- Surplus water from the saddle dam will be channelled to Bisalpur Dam through a connecting channel.
- This initiative aims to optimize the use of surplus water, preventing any wastage.
- The project plans to construct a barrage on the Brahmani River at Shripura village.
- Additionally, it involves the construction of tunnels and the filling of Garada, Abhaypura, and Gudha dams in Bundi district.
Rana Pratap Sagar Dam:
- Located near Rawatbhata in the Chittaurgarh district of Rajasthan.
- Part of the Chambal Valley Project, which includes Gandhi Sagar and Jawahar Sagar Dams.
- Serves purposes such as irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and flood control.
- The reservoir created by the dam is called Rana Pratap Sagar Lake.
- The Brahmani River is a tributary of the Chambal River, originating in Madhya Pradesh and flowing into Rajasthan.
- It is important to distinguish this river from another Brahmani River, which originates in the Dumka district of Jharkhand and flows eastward into Odisha.
- The Odisha Brahmani River is formed by the confluence of the Shankh and South Koel rivers near Rourkela.
32nd National Convention of Dhakad Samaj
 Dhakad Community Convention
Dhakad Community Convention
In Kota, the Chief Minister of Rajasthan addressed the 32nd National Convention of the Dhakad Samaj.
- Contribution to National Development: The Chief Minister praised the Dhakad community for their significant contributions to the overall development of the country, highlighting their history, hard work, and spirit of service.
- Focus on Upliftment: He emphasized the importance of uplifting farmers, youth, and women during his address at the convention.
- Farmers' Prosperity: Om Birla, who attended the convention, stressed the crucial role of farmers' prosperity in national progress.
The Dhakad Society
- Community Overview: The Dhakad community is a Hindu peasant group primarily engaged in agriculture, predominantly found in the states of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
- Geographic Distribution: In Rajasthan, they are located in districts such as Tonk, Bundi, Kota, Jhalawar, Sawai Madhopur, Chittaurgarh, and Ajmer.
- Meaning of 'Dhakad': The term 'Dhakad' refers to individuals who are fearless and face challenges with courage.
- Ancestral Belief: The community believes they are descendants of Balramji, the elder brother of Lord Krishna.
- Language: Members of the Dhakad community primarily speak Hindi and Devanagari.
Celebration of Lord Devnarayan's Birth Anniversary
 Devnarayan Celebration
Devnarayan Celebration
Lord Devnarayan
- The 1113th birth anniversary of Lord Devnarayan, an incarnation of Lord Vishnu and a revered figure in the Gurjar community, was celebrated in the state.
Folk Deity in Rajasthan
- Lord Devnarayan, also known as Uday Singh Dev, is considered a folk deity in Rajasthan.
- He was born in Malaseri, Rajasthan, and is believed to have belonged to the Bagrawat dynasty.
Significance of Birth
- His birth is commemorated on the sixth day of the Shukla Paksha in the Magh month.
- During this time, he is worshipped by the Gurjar community, particularly on Makar Sankranti and Dev Ekadashi.
- Devnarayan is also believed to have lived in various regions of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, in addition to Rajasthan.
Appointment of New Director of Minority Affairs
 Minority Affairs Leadership
Minority Affairs Leadership
On February 5, 2025, Matadeen Meena, an officer, took over as the Director of Minority Affairs in Rajasthan.
After assuming his role, he visited the Madrasa Board to assess the functioning of its various sections. During this visit, he collected feedback from the officers and employees of the Directorate and urged them to work with honesty, dedication, discipline, and a spirit of service.
The Government of Rajasthan established a new Minority Department in 2009 aimed at the overall development and socio-economic and educational upliftment of minority communities, including Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Jains, Buddhists, and Parsis in the state.
This department is responsible for reviewing and coordinating policies, schemes, and development programs for the benefit of minority communities. It is headed by the Minister of Minority Affairs.
Anti-Conversion Bill
 Anti-Conversion Legislation
Anti-Conversion Legislation
The Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Bill, 2025
Religious conversions
- The Rajasthan government proposed the Bill to prevent conversions that occur through force, fraud, or inducement.
- The Bill includes penalties of up to 10 years in prison and fines of up to Rs 50,000 for various offenses.
Approval and Purpose:
- In November 2024, the State Cabinet approved the draft of the Bill to address the rise of ‘love jihad’ in certain areas of the State.
- This term refers to Muslim men marrying Hindu women to convert them to Islam.
Bill Provisions:
- The offenses are cognizable and non-bailable.
- The State Medical and Health Minister introduced the Bill, which makes offenses subject to trial in court.
- The Bill makes conversions through misrepresentation, force, coercion, allurement, fraud, or marriage illegal.
- Individuals wishing to convert their religion must submit a declaration to the District Magistrate at least 60 days in advance.
Rationale Behind the Bill:
- The Bill aims to uphold the right to religious freedom while preventing coercive conversions.
- According to the Bill’s statement, other states have laws on this issue, but Rajasthan did not.
- The Bill seeks to balance the individual right to religious freedom with the need to prevent proselytism, which could threaten secularism.
Religious Conversion
- Religious conversion involves adopting the beliefs of a specific religious group while rejecting those of others, signifying a shift from one religion to another.
- This process may include changes within the same faith, such as from Christian Baptist to Methodist or Catholic, or from Muslim Shi’a to Sunni.
- In some instances, conversion marks a significant change in religious identity and is celebrated with special rituals.
Global List of Wetland Accredited Cities
 Wetland City Accreditation
Wetland City Accreditation
The Ramsar Convention
Indore and Udaipur have made history as the first Indian cities to receive accreditation as wetland cities under the Ramsar Convention.
International Recognition for Wetland Conservation:
- The Wetland City Accreditation programme honours cities dedicated to preserving both natural and human-made wetlands.
- Recently, the Advisory Committee on Wetland City Accreditation approved 31 new cities for this recognition, including Indore and Udaipur, bringing the total number of accredited cities worldwide to 74.
Bhopal Misses Out on Accreditation:
- Bhopal, which was nominated along with Indore and Udaipur, did not receive accreditation due to concerns regarding its wetland ecosystem.
- Local citizen groups raised alarms about a proposed road project that could potentially harm the wetland’s catchment area, jeopardising local water bodies and wildlife.
Criteria for Wetland City Accreditation:
- To be eligible for accreditation, cities must fulfil six international criteria, which include:
- Protecting wetlands and the ecosystem services they provide.
- Ensuring sustainable socio-economic benefits for local communities.
- Presently, China tops the list with 22 accredited cities, followed by France with 9 cities.
- The accreditation initiative encourages the sustainable management of urban and peri-urban wetlands.
Wetland City Accreditation (WCA):
- The WCA is a voluntary recognition system established by the Ramsar Convention during the Conference of the Contracting Parties (COP) 12 in 2015.
- It acknowledges cities that have made substantial efforts to safeguard their urban wetlands.
- The WCA is valid for a period of 6 years.
- The initiative aims to foster the conservation and prudent use of urban and peri-urban wetlands, along with ensuring sustainable socio-economic advantages for local populations.
FAQs on RPSC Monthly Current Affairs: February 2025 - Monthly Current Affairs RPSC - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
| 1. What are the key objectives of the Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Soil Health Card Day? |  |
| 3. What are the major themes discussed at the All India State Water Ministers Conference? |  |
| 4. How does the Ammonia Gas Leak in Kota impact public safety and the environment? |  |
| 5. What are the expected outcomes of the Review of Mega Infrastructure Projects? |  |




















