State PCS CA Consolidation (Rajasthan) January 2025 | Monthly Current Affairs RPSC - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) PDF Download
New Solar Project in Rajasthan

Why in News?
Jakson Green (India) and Blueleaf Energy (Singapore) are collaborating to develop 1 GW of solar capacity in Rajasthan with an investment of USD 400 million (Rs 3,400 crore ).
Key Points
Project Scope & Timeline:
- The 1 GW portfolio comprises three solar projects funded through debt and equity.
- The projects will utilize both Intra State (InSTS) and Inter State (ISTS) Transmission Systems.
- Specific project names will be announced later.
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
- PPAs have been established with Rajasthan Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Ltd (RUVNL), Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited (SECI), and National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) Limited.
- These agreements, secured through bidding, last for 25 years.
- The three solar projects are expected to be commissioned progressively between 2025-2026.
Renewable Energy Expansion Goals:
- The collaboration aims to add over 5 GW of renewable energy to the Indian grid by 2030.
- The Rajasthan projects are projected to generate 1,800 GWh of green energy annually, enough to power 1.5 million households.
Environmental Impact:
- The project is expected to reduce 22 million tons of CO₂ emissions over 25 years, equivalent to removing 5 million cars from the roads.
Job Creation & Economic Benefits:
- The initiative is expected to create jobs during both the construction and operational phases.
Financial & Banking Support:
- Ernst & Young (EY) was appointed as the investment banker for this transaction.
- Jakson Green secured credit facilities of:
- Rs 2.96 billion from First Abu Dhabi Bank (Mumbai).
- Rs 600 million from HSBC (Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation).
EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction)
- The funds will support both domestic and international operations under the EPC model.
- PPAs typically last for 25 years and involve electricity generators and buyers, usually public utilities.
- Generators agree to supply power at fixed rates, ensuring substantial generating capacity.
- These agreements are rigid and do not adapt to changing market conditions.
Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) Model
- In the EPC model, the government covers all costs, including engineering, procurement, and construction.
- Private companies are invited to bid for engineering expertise, with limited participation.
- A challenge of this model is the significant financial burden it places on the government.
Rajasthan High Court's Directive on Web Portal for Live-in Relationship Registration

Why in News?
The Rajasthan High Court has directed the state government to create a web portal for the registration of live-in relationships. This initiative aims to provide legal protection and recognition to couples in such arrangements.
Background and Legal Justification
- The court's decision is rooted in the need to protect live-in couples who often face threats from their families and society. Many of these couples seek protection under Article 226 of the Indian Constitution.
- Article 226 empowers High Courts to issue orders and writs to enforce fundamental rights and can be invoked against government actions that violate citizens' rights.
- The Rajasthan High Court has the authority to issue orders to any individual or authority under this article.
Supreme Court Precedents
The Rajasthan High Court referenced several Supreme Court cases to support its decision:
- Khushboo vs Kannaiammal (2010)
- Lata Singh vs State of UP (2006)
- Indira Sarma vs V.K. Sarma (2013)
These cases established that live-in relationships, while not explicitly mentioned in Indian law, are not criminal and fall under the right to life and personal liberty as per Article 21 of the Constitution.
Need for Regulation
- The court emphasized the necessity to regulate live-in relationships due to their social stigma, which can lead to legal complications, especially for women and children.
- Until formal legislation is enacted, the court ordered the establishment of a competent authority in each district to register live-in relationships and address related grievances.
- The state government is required to submit a compliance report by March 1, 2025, outlining the steps taken in this regard.
- The court also raised the issue of whether married individuals entering live-in relationships without divorce can seek legal protection, referring this matter to a larger bench for clarification.
New Legal Framework for Live-in Couples
The court's order includes the creation of a formal registration process for couples entering into live-in relationships. This process will require couples to agree to specific terms before commencing their relationship. Key aspects of the registration format include:
- Education. Provisions related to the education of children, if any.
- Healthcare. Agreement on healthcare responsibilities for partners and children.
- Child Support. Couples must outline a "child plan" detailing their responsibilities for any children resulting from the relationship.
- Maintenance. The male partner will be obligated to financially support the non-earning female partner and any children, ensuring their economic security.
Landmark Judgments on Constitutional Morality
- Lata Singh vs State of UP (2006). This case emphasized the need for protection of inter-caste and inter-religious couples from harassment and violence.
- S. Khushboo vs Kannaiammal & Anr. (2010). The court ruled that sexual relations between consenting adults outside marriage are legal and fall within the right to privacy.
- Naz Foundation vs Government of NCT of Delhi (2009). This judgment decriminalized consensual homosexual acts between adults, stating that Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code violates fundamental rights.
- Joseph Shine vs Union of India (2018). The Supreme Court decriminalized adultery, declaring it a violation of rights to equality, dignity, privacy, and autonomy.
- Navtej Singh Johar vs Union of India (2018). This case affirmed the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals to express their sexual orientation and identity with dignity.
- Shafin Jahan vs Asokan K.M. (2018). The court upheld the right to marry a person of one’s choice regardless of religion or caste, nullifying the annulment of a Hindu-Muslim marriage.
- Shakti Vahini vs Union of India (2018). This judgment condemned honour killings and violence against inter-caste and inter-religious couples, issuing guidelines for their prevention and protection.
Rajasthan Government to Introduce Suicide Prevention Bill for Coaching Students

Why in News?
The Rajasthan government has notified the Rajasthan High Court about its intention to introduce a bill aimed at preventing suicides among students in coaching institutes. This initiative comes in response to the alarming increase in suicides, particularly in Kota, which is known as India's coaching hub.
Alarming Rise in Suicides in Kota
- Since the start of 2023, there have been six reported cases of coaching students taking their own lives, contributing to a longstanding crisis.
- Over the past decade, a total of 127 suicides have been recorded, with 26 occurring in 2023 and 17 in 2024 alone.
Deteriorating Reputation of Kota
- The escalating suicide crisis has tarnished Kota's reputation as a premier coaching destination, resulting in a decline in student enrolments.
Urgent Need for Enhanced Mental Health Support
- The rising incidence of student suicides underscores the inadequacy of current mental health support and stress management strategies, highlighting the urgent need for improvement.
Understanding Suo Moto Cognizance
- Suo Moto cognizance refers to the action taken by a government body, court, or authority based on its own awareness of a situation.
- A court exercises Suo Moto cognizance when it becomes aware of rights violations or breaches of duty through media reports or notifications from other sources.
Role of Public Interest Litigation (PIL)
- Articles 32 and 226 of the Indian Constitution provide the framework for filing PILs in the Supreme Court and High Courts, empowering courts to take legal action based on their own recognition of a matter.
Judicial Activism and Suo Moto Actions
- Actions taken by Indian courts under Suo Moto cognizance are considered examples of judicial activism, reflecting the proactive role of the judiciary in addressing issues.
Other Suicide Prevention Initiatives in India
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP): The District Mental Health Programme (DMHP) functions in 738 districts, offering outpatient services, counselling, ongoing care, and a 10-bed inpatient facility at the district level.
- National Tele Mental Health Programme: Launched in 2022 to improve access to quality mental health counselling and care services across the country.
- As of December 2023, 34 States and Union Territories have established 46 Tele MANAS Cells, handling over 500,000 calls on the helpline.
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has introduced a 24/7 toll-free helpline called “KIRAN” to provide mental health support.
Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary
 Wildlife Sanctuary Update
Wildlife Sanctuary Update
Why in News?
The Forest Department has begun the process of updating the boundaries of the Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary to address ongoing legal issues. This initiative was kickstarted during a meeting in Jaipur, chaired by Rajasthan's Principal Chief Conservator of Forests and Chief Wildlife Warden.
Discussion in the meeting:
- The meeting's objective was to resolve discrepancies between:
- The sanctuary's original notification dated September 22, 1980.
- The eco-sensitive zone (ESZ) notification issued on March 8, 2019.
- The Deputy Conservator of Forests (Wildlife) from Jaipur Zoo presented the original boundary information.
- The 1980 notification specified the sanctuary's boundaries using only 11 GPS coordinates.
- In contrast, the 2019 ESZ map incorporated 100 reference points, leading to significant boundary variations.
- These discrepancies have resulted in numerous legal disputes and court challenges.
Decision on Revising Sanctuary Map:
- Authorities reached a decision to formulate a revised sanctuary map based on the 1980 notification.
- The responsibility of drafting the new map was assigned to the Deputy Conservator of Forests (Wildlife) at Jaipur Zoo.
- Once drafted, the map will undergo review by a committee before being submitted to the state government for approval.
Opposition from Environmental Activists:
- Environmental activists raised concerns regarding the discrepancies between the sanctuary and ESZ maps.
- A complaint was filed with the Lokayukta, which recognized the issue.
Response from Forest Authorities:
- In response to the Lokayukta, the Office of the Chief Conservator of Forests (HoFF) in Rajasthan stated:
- Questioning the maps after a seven-year period was deemed inappropriate.
- The sanctuary and ESZ maps were approved and considered accurate.
About:
- The Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Aravalli hills, approximately 20 kilometers from Jaipur, Rajasthan.
- The sanctuary is named after the Nahargarh Fort, an 18th-century fort constructed by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II, the founder of Jaipur.
- Spanning an area of 720 hectares, the sanctuary includes the Nahargarh Biological Park, renowned for its safaris.
- The landscape features dry deciduous forests and grasslands.
Flora:
- The flora of Nahargarh Wildlife Sanctuary primarily consists of scrublands, characterized by hardy shrubs and bushes adapted to the region's climate.
Fauna:
- Mammals:The sanctuary is home to various mammals, including:
- Leopards
- Deer
- Tigers
- Sloth bears
- Common species such as wild boars, lions, and smaller mammals.
- Birds:Birdwatchers will find a diverse range of bird species, including:
- Peacocks
- Owls
- Eagles
- Various other bird species, making it a birdwatching paradise.
- Reptiles and Amphibians:The sanctuary also hosts several reptiles and amphibians, such as:
- Indian rock pythons
- Monitor lizards
- Frogs
- Toads and other amphibians.
Rajasthan High Court Addresses Transgender OBC Reservation Issue

Why in News?
The Rajasthan High Court has responded to a petition regarding the classification of transgender individuals within the Other Backward Classes (OBC) for reservation purposes in public education and employment.
The petitioner, Ganga Kumari, who made history as the first transwoman to join the Rajasthan police force as a constable, is challenging the state government's categorization of transgender people under OBC.
Background of the Issue
- In January 2023, the Rajasthan government issued a circular that classified transgender individuals within the OBC category for reservation benefits.
- Ganga Kumari argues that this classification could potentially exclude transgender people from both OBC and specific transgender-related benefits.
Legal Arguments
- Ganga Kumari contends that the Rajasthan government's classification violates a Supreme Court judgment.
- The Supreme Court ruling emphasizes that transgender individuals should be recognized as a distinct group eligible for reservations, independent of the OBC category.
NALSA Judgment Context
- The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) judgment in 2014 directed governments to provide reservations for transgender individuals, acknowledging them as "socially and educationally backward."
- However, it remains unclear whether this judgment intended to include transgender individuals within existing socio-economic categories like OBCs.
Variations in State Interpretations
- Different states have interpreted the NALSA judgment in varying ways.
- For instance, Madhya Pradesh has included transgender individuals within the OBC category, while states like Karnataka, Madras, and Calcutta have supported the idea of horizontal reservation for transgender people.
Understanding Transgender Individuals
- A transgender person is defined as someone whose gender identity differs from the sex assigned to them at birth.
- This definition encompasses individuals with intersex variations and includes both transgender men and women, regardless of whether they have undergone surgical or hormonal interventions.
Overview of the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019
- Non-discrimination: The Act prohibits discrimination against transgender individuals in various areas, including education, employment, healthcare, and access to public facilities. It affirms their rights to movement, property, and office.
- Certificate of Identity: Transgender individuals have the right to self-perceived gender identity, and district magistrates are mandated to issue certificates of identity without requiring medical examinations.
- Medical Care: The Act ensures access to medical care, including sex reassignment surgeries and therapy, with insurance coverage for these services.
- National Council for Transgender Persons:. National Council for Transgender Persons has been established to advise the government on issues related to transgender individuals and to address grievances.
- Offences and Penalties: The Act prescribes penalties for offences such as forced labour, abuse, and denial of rights, with imprisonment ranging from six months to two years and fines.
UGC Suspends PhD Admissions at Three Rajasthan Universities

University Grants Commission (UGC)
The University Grants Commission (UGC) has taken action against three universities in Rajasthan by halting their Ph.D. admissions due to the discovery of fake and backdated degrees being issued by these institutions.
Affected Universities
- The universities that have been restricted from admitting new Ph.D. students are OPJS University in Churu, Sunrise University in Alwar, and Singhania University in Jhunjhunu.
Allegations Against the Universities
- A committee formed by the UGC found that these universities were not complying with the UGC PhD Regulations and were failing to meet the necessary academic standards for awarding PhD degrees.
UGC’s Recommendations
- The committee has recommended that the UGC should impose a five-year ban on these universities from enrolling new Ph.D. students.
Implications of the UGC’s Decision
- This decision raises significant concerns about the quality and credibility of higher education institutions in Rajasthan.
- It underscores the necessity for strict oversight and enforcement of academic standards to protect students’ interests and ensure the integrity of doctoral programs.
- The UGC was founded on December 28, 1953, and became a legal entity under the University Grants Commission Act of 1956. Its primary purpose is to coordinate and uphold standards in teaching, examination, and research within university education.
- Operating under the Ministry of Education, the UGC is governed by a Chairman, a Vice-Chairman, and ten members appointed by the Central Government. The Chairman is chosen from individuals not affiliated with the Central or State Governments.
- Besides granting funds to qualifying universities and colleges, the UGC also advises the Central and State Governments on crucial measures for enhancing higher education.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, the UGC has regional offices in Bangalore, Bhopal, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Kolkata, and Pune. It also oversees the recognition of fake universities, autonomous colleges, deemed universities, and distance education institutions.
Mount Abu Records Lowest Temperature at 2.4°C

Why in News?
Mount Abu, the sole hill station in Rajasthan, has experienced a record low temperature of 2.4 degrees Celsius, marking the coldest temperature in the state.
Aravalli Range
- Guru Shikhar is the highest point in Mount Abu.
- The highest peak in the region is [peak name], located on [location].
Other Regions
- In the plains, Sangaria in Hanumangarh recorded a minimum of 5.8°C.
- Lunkaransar followed with 6.8°C.
- Sirohi and Fatehpur both recorded 7.3°C.
Indian Meteorological Department (IMD)
- According to the IMD, Pilani recorded 7.6°C.
- Churu had 7.8°C.
- Sikar and Sriganganagar each noted 8.2°C.
- Nagaur recorded 8.8°C.
Weather Conditions
The cold weather has impacted many areas in Rajasthan, with temperatures significantly lower than the usual levels for this time of year.
Impact
This unexpected cold snap has sparked discussions about its potential effects on daily life and agriculture in the region.
India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- The IMD, founded in 1875, serves as India’s National Meteorological Service.
- It is the primary government body for meteorological and related activities.
- The department functions under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India.
- Its headquarters is situated in New Delhi.
World Meteorological Organization
- IMD is recognized as one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres by the World Meteorological Organization.
Roles and Responsibilities
- To conduct meteorological observations and provide current and forecast weather information for weather-sensitive activities such as agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, and offshore oil exploration.
- To issue warnings for severe weather events, including tropical cyclones, dust storms, heat waves, heavy rain and snow, and cold weather, which pose threats to life and property.
- To supply essential weather statistics for agriculture, water resource management, industries, oil exploration, and other critical national activities.
- To foster research in meteorology and related disciplines.
Centre Extends Deadline for Soybean Procurement

Why in News?
The Union Agriculture Ministry has chosen to prolong the deadline for soybean procurement in the states of Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Telangana.
Extension of Soybean Procurement Deadline:
- So far, a total of 13.68 lakh tonnes of soybean have been procured across all states, falling short of the target of 33.60 lakh tonnes.
- The decline in procurement has been attributed to challenges faced by state governments responsible for coordinating these efforts.
Review Meeting on Agricultural Issues:
- The Agriculture Minister conducted a review meeting with senior officials to address critical weather conditions affecting agriculture.
- Discussion topics included management of farm produce, marketing of agricultural products, and import-export dynamics.
- The Minister emphasized the importance of regular meetings with State Agriculture Ministers to effectively address agricultural challenges.
Soybean Crop
- Kharif crop
- Soybean ( Glycine max. is a crucial crop in India and is the world’s most important seed legume. It accounts for approximately 25% of the global edible oil supply and about two-thirds of the world’s protein concentrate for livestock feed.
- Soybean is also a valuable ingredient in formulated feeds for poultry and fish.
- In India, soybean is primarily grown as a rainfed crop in Vertisols and similar soils, requiring an average rainfall of around 900 mm during the crop season.
- Major producing states in India include Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Western Disturbance in Rajasthan

Why in News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has predicted the activation of a western disturbance over Rajasthan on January 21, 2025. This weather phenomenon is anticipated to bring light rainfall to the northwestern and northeastern regions of the state. In response to this forecast, the IMD has issued a warning for these areas.
Western Disturbances
- Western disturbances are meteorological events originating in the Caspian or Mediterranean Sea, delivering non-monsoonal rainfall to northwest India.
- These disturbances are classified as extra-tropical storms.
- The storms generate areas of low pressure, leading to abrupt showers, snowfall, and fog in northwest India.
- The term 'Western Disturbance' signifies the storm's movement from the west to the east.
Westerly Jet Streams
- Westerly jet streams consist of rapidly moving winds that traverse eastward at elevated altitudes.
- Within this context, disturbance pertains to a region of diminished air pressure.
- This phenomenon establishes a natural equilibrium, prompting the air in the affected area to strive for pressure normalization.
Utricularia Found in Keoladeo National Park

Role in Biodiversity:
- A rare and unique carnivorous plant, Utricularia, has been discovered in the wetlands of Rajasthan.
- Commonly known as bladderworts, this plant is typically found in regions like Meghalaya and Darjeeling.
- Experts believe that the presence of bladderworts in Keoladeo National Park enhances biodiversity and contributes positively to the park's ecosystem.
- Utricularia plays a crucial role in maintaining environmental balance by trapping small insects.
- This plant was last recorded in India in 2021 in Chamoli, Uttarakhand, after a lengthy gap of 36 years.
Feeding Mechanism:
- Utricularia captures tiny organisms such as protozoa, insects, and tadpoles using its specialized bladder-like traps.
- Once an organism is trapped, it dies inside the bladder.
- Terrestrial varieties of Utricularia thrive in waterlogged soil, where they capture small swimming creatures.
Ideal Growth Conditions:
- The growth of Utricularia is facilitated by the ample water supply from the Panchana Dam, creating optimal conditions for the plant.
- Keoladeo National Park boasts a diverse wetland ecosystem that supports a wide range of plants and animals.
- The park is not only a bird sanctuary but also a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Bharatpur, Rajasthan.
- In 1981, Chilika Lake (Odisha) and Keoladeo National Park were designated as the first Ramsar Sites in India.
- Keoladeo National Park and the Siberian crane are included in the Montreux Record, highlighting their significance.
- The park is renowned for its rich bird diversity, with over 365 species recorded, including rare and threatened species like the nilgai.
- Various animals such as jackals, sambar deer, wild cats, and wild boars inhabit the area.
Flora:
- The predominant vegetation consists of tropical dry deciduous forests, primarily Acacia nilotica, interspersed with dry grassland.
River:
- The National Park is traversed by two rivers, Banganga and Gambhir.
Great Indian Bustards in Rajasthan
 Great Indian Bustard
Great Indian Bustard
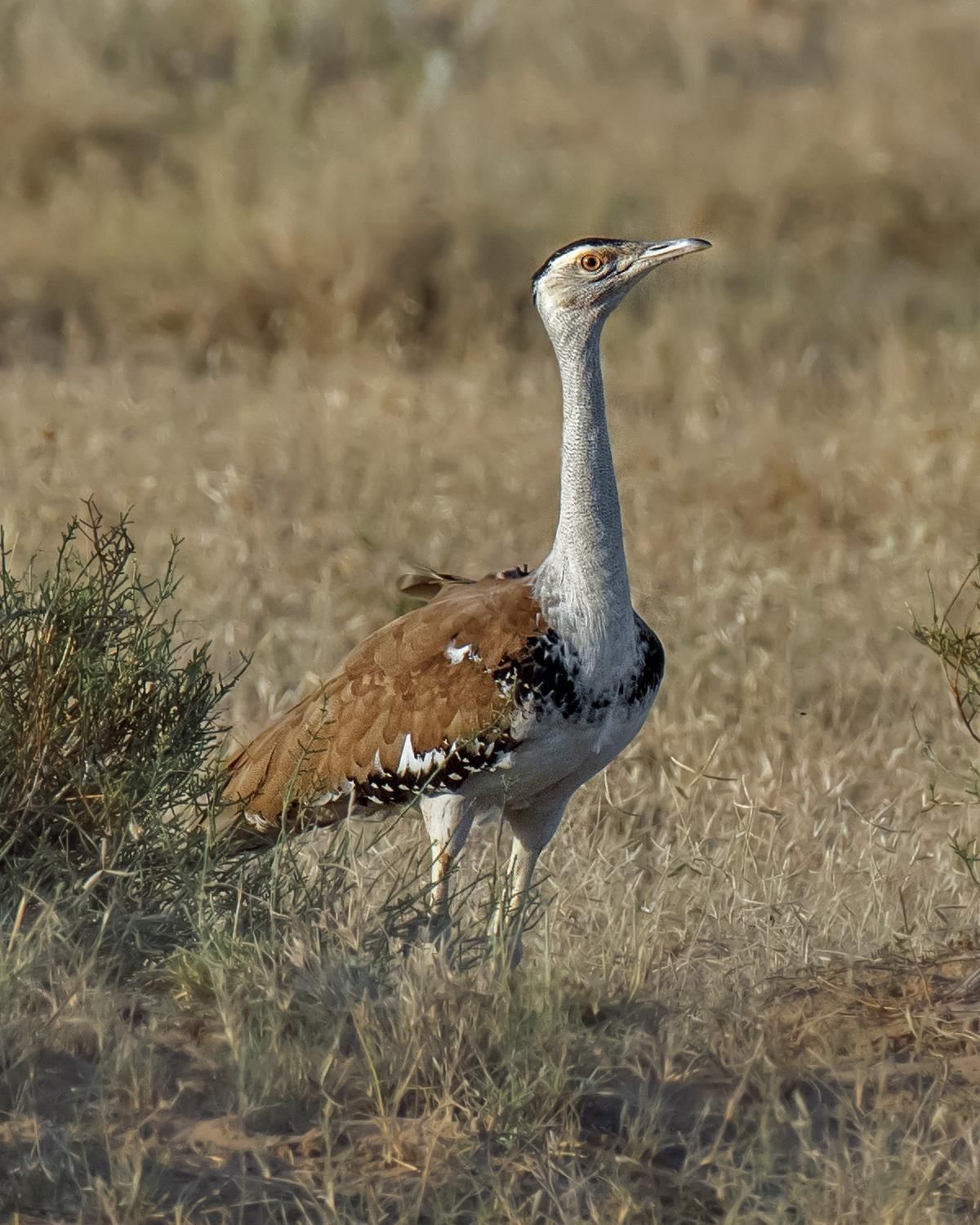
Great Indian Bustards (GIBs) spotted in Rajasthan's Desert National Park (DNP)
GIB Population Status:
- Critically endangered species with only 173 birds remaining.
- 128 birds are in the wild, while the rest are in captivity.
- Found in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Conservation Efforts:
- Listed as “critically endangered. by the IUCN in 2011 due to hunting, habitat loss, and fragmentation.
- Rajasthan launched a Rs 12.90 crore project in 2013 for habitat protection and breeding conditions.
- Project has bred 45 chicks in confirmed breeding areas Sam and Ramdevra.
Habitat Protection and Breeding:
- Spotted birds were mainly young females and a few young males.
- Threats from predators such as desert foxes and mongooses.
- Habitat protection efforts include enhancing grasslands and fencing to keep predators away.
Milestone in Conservation:
- In 2018, a breeding centre was established in Jaisalmer for GIBs.
- In October 2024, a GIB chick was hatched through artificial insemination.
- GIB is the state bird of Rajasthan and a symbol of grassland ecosystem health.
Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- CMS: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Located in Jaisalmer and Barmer Districts of Rajasthan.
- Natural species include Chinkara, Khejri, and Rohida.
- Home to Great Indian Bustards, state animal, tree, and flower.
UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980 and 1992.
Rajasthan Chief Minister Approves Land for Petrozone
 Petrochemical Hub
Petrochemical Hub
In a significant step to enhance Rajasthan's industrial sector, Chief Minister Bhajan Lal Sharma has given the green light for land allocation to establish a dedicated petrochemical zone. This initiative aims to attract substantial investments and foster economic growth in the region.
Approval for Land Allotment:
- The Rajasthan State Industrial Development and Investment Corporation (RIICO) has approved land allotments for the Rajasthan Petrozone and new industrial areas.
- Land has been allocated to the Rajasthan Solar Park Development Company for a solar energy project.
- Additionally, land is earmarked for a large-scale drinking water scheme.
The proposed Petrozone is expected to host various petrochemical industries, creating a hub for manufacturing and processing activities.
Conducive Environment and Manufacturing:
- This initiative is in line with the state's vision to enhance industrial infrastructure and foster a supportive business environment.
- The development of the Petrozone is expected to generate numerous employment opportunities, contributing to the socio-economic upliftment of the local population.
- It will also promote technological advancements and innovation in the petrochemical sector.
- This move is likely to attract both domestic and international investors, further boosting the state's economic prospects.
Hydrocarbon Sector in Rajasthan:
- Rajasthan is endowed with significant hydrocarbon resources located within four petroliferous basins: Jaisalmer Basin, Barmer – Sanchore Basin, Bikaner – Nagaur Basin, and Vindhyan Basin.
- These basins stretch across 14 districts: Barmer, Jaisalmer, Bikaner, Ganganagar, Hanumangarh, Jalore, Jodhpur, Kota, Jhalawar, Baran, Bundi, Bhilwara, Churu, and Chittorgarh, covering a vast area of 150,000 sq km.
- One of the notable discoveries in this sector is the Mangla Oil discovery in the Barmer-Sanchore Basin, recognized as one of the largest on-land oil discoveries in India in the past three decades.
Rajasthan's River-Link Project
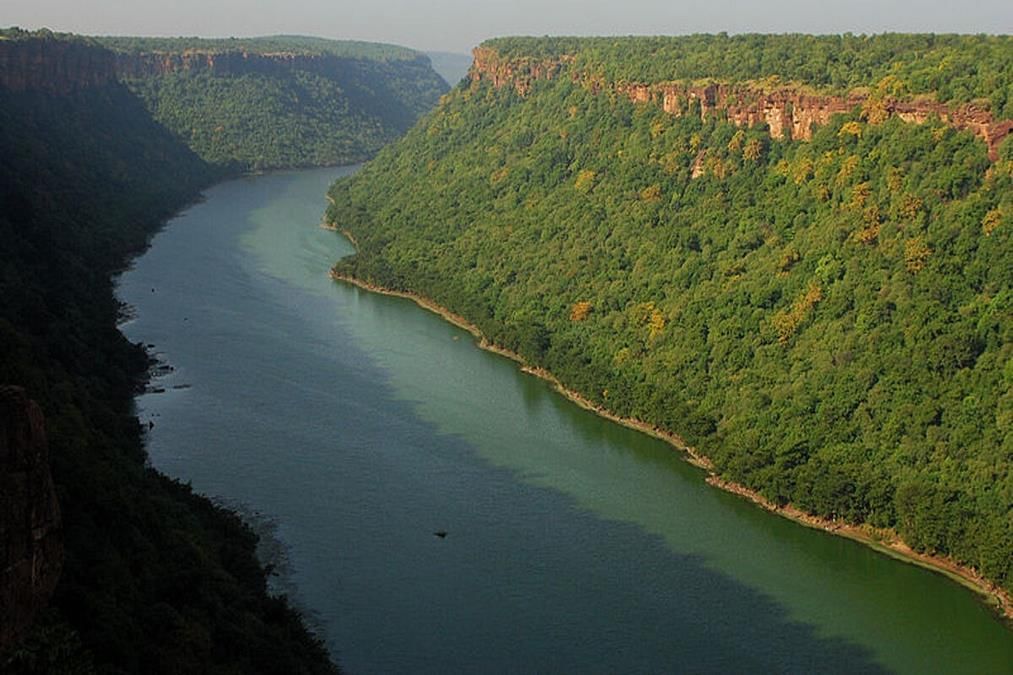

Why in News?
The proposed river-linking project in Rajasthan aims to address the growing issue of water scarcity in the state. However, this initiative has sparked significant discussions regarding its potential environmental impacts.
Chambal River
- The canal project intends to redirect surplus water from the Chambal River basin to provide drinking and industrial water across 23 districts in Rajasthan. This initiative is expected to benefit approximately 3.45 crore people.
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
- The river linking initiative raises concerns about the potential flooding of around 37 square kilometres within the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP)
- The submergence in the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve will result from the largest dam proposed under the PKC-ERCP, which is part of the broader project.
- The PKC-ERCP project is expected to cause a total submergence area of 408.86 square kilometres, with 227 square kilometres submerged under the proposed dam on the Banas River, a tributary of the Chambal.
- The dam is planned to be 39 meters high and 1.6 kilometers long, located near Doongri village, approximately 30 kilometers from Sawai Madhopur.
Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary
- The project will impact 37.03 square kilometres of Ranthambore National Park, which spans 392 square kilometres and is part of the larger 1,113 square kilometre Ranthambore Tiger Reserve, currently home to 57 tigers.
- Ranthambore is the third tiger reserve facing land loss due to the creation of new reservoirs.
- Conservationists are concerned about the environmental cost of the project, warning that flooding parts of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve could jeopardize the biodiversity of this crucial wildlife area, including its stable population of tigers.
Other Projects
- Other projects facing land loss due to similar initiatives include the North Koel Reservoir Project, which will flood 10.07 square kilometres in Jharkhand and 41.41 square kilometres in Madhya Pradesh.
Geographical Overview
- The Chambal River originates at Singar Chouri peak in the northern slopes of the Aravalli Range in Indore, Madhya Pradesh. It flows 346 kilometres northward in Madhya Pradesh before moving 225 kilometres north-east through Rajasthan.
- The river enters Uttar Pradesh and flows for about 32 kilometres before joining the Ganges River in Etawah District.
- The Chambal River is rainfed and is bordered by the Vindhyan mountain ranges. Its basin drains the Malwa region of northwestern Madhya Pradesh.
- The Hadauti plateau in Rajasthan is situated in the upper catchment area of the Chambal River, southeast of the Mewar Plains.
Tributaries and Power Projects
- Significant tributaries of the Chambal River include the Banas and Kali Sindh rivers.
- Major power projects and dams on the river include the Jawahar Sagar Dam and Kota Barrage, along with the Gandhi Sagar Dam and Rana Pratap Sagar Dam.
National Chambal Sanctuary
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is located along the Chambal River at the tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
- This sanctuary is home to critically endangered species such as the Gharial, red-crowned roof turtle, and the endangered Ganges river dolphin.
Chintan Shivir for Women and Child Development

Why in News?
The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) is set to organise a Chintan Shivir from January 10 to 12, 2025 in Udaipur, Rajasthan. This three-day event aims to address the challenges hindering the development and welfare of women and children across the country and to formulate effective solutions.
Focused Sessions
- Mission Vatsalya: This session will focus on enhancing child welfare through improvements in childcare institutions, foster care, adoption, and aftercare services.
- Mission Shakti: This session aims to tackle issues related to women’s safety, prevention of child marriage, and empowering women through technology, including initiatives like the SHe-Box portal.
- Mission Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0: This session will emphasize strengthening Anganwadi Centres as crucial hubs for providing nutrition, education, health, and awareness services.
Open Discussions and Collaborative Problem-Solving
The Chintan Shivir will also facilitate open discussions with representatives from State and Union Territories (UTs) to:
- Identify and address challenges faced in the implementation of various missions.
- Share innovative solutions and best practices from different states.
The discussions will particularly focus on:
- Improving and intensifying child welfare programs at Anganwadi Centres.
- Leveraging technology for women’s empowerment and safety.
The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013
In 2023, the Ministry of Women and Child Development launched a portal to enhance the implementation of the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act. Here are the key features of the portal:
- Confidentiality: The portal masks the details of the complainant to ensure confidentiality. Only the Local Committee (LC) has access to this information.
- Complaint Filing: Aggrieved women or their representatives can file complaints by providing basic details such as work status, name, phone number, and email.
- Automatic Forwarding: Complaints are automatically forwarded for action if the workplace’s Internal Committee (IC) or LC is registered on the portal.
- Monitoring Dashboard: The portal includes a dashboard for nodal officers to track the number of complaints filed, resolved, and pending.
- Inquiry Timeframe: The prescribed time for inquiry under the Act is 90 days.
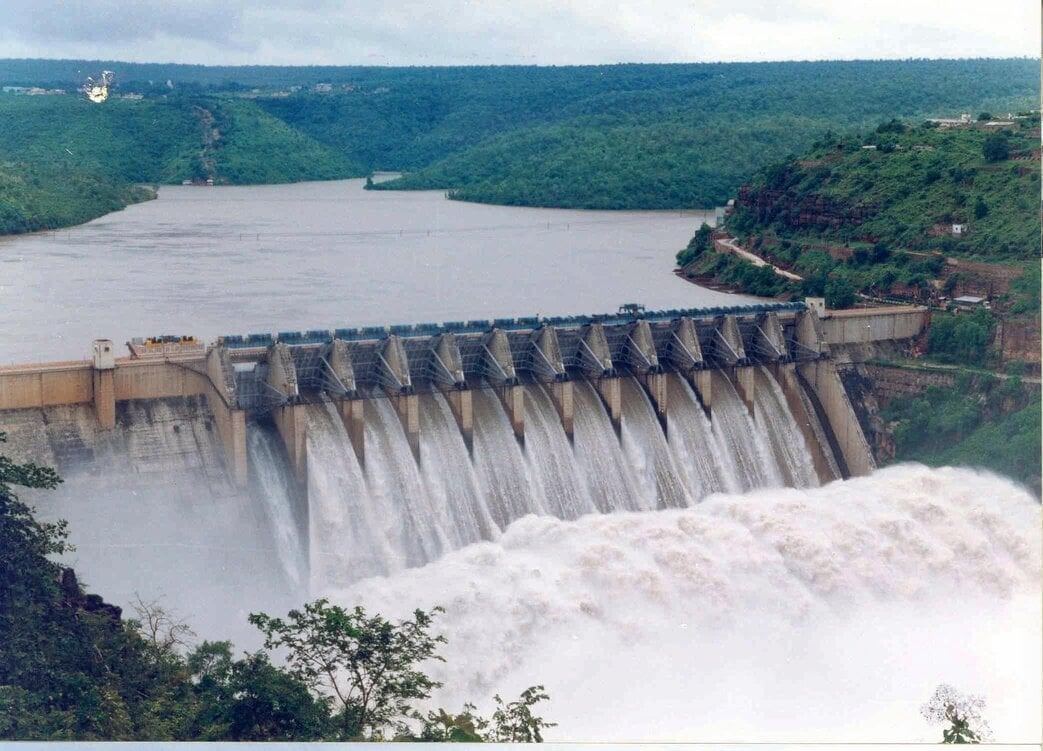
Water Storage Advisory Issued by the Bhakra Beas Management Board
 Water Storage Alert
Water Storage Alert
Why in News?
The Bhakra Beas Management Board (BBMB) has issued a warning to its member states regarding the need to carefully assess their water requirements. This caution comes in light of low water storage levels and predictions of below-normal rainfall in the region.
According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), North India is expected to experience a significant 86% reduction in rainfall compared to the long-term average from January to March 2025.
Current Water Levels in Bhakra and Pong Dams
- The Sutlej Bhakra Dam is currently at 43% of its total capacity.
- The Beas Dam is at 30% of its total capacity.
- Both dams’ levels are reported to be below the 10-year average, as per the Central Water Commission (CWC).
Advisory Issued to Member States
- The BBMB has alerted Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan about the low water availability.
- Member states are advised to adjust their water demands in accordance with the current situation.
Details about the Bhakra Nangal Dam
- Bhakra Dam is a concrete gravity dam situated on the Sutlej River, near the border of Punjab and Himachal Pradesh in northern India.
- It ranks as the second tallest dam in India, standing at 225.55 meters, following the 261-meter Tehri Dam.
- The dam’s reservoir, known as “Gobind Sagar,” has a storage capacity of 9.34 billion cubic meters of water.
- Nangal Dam is located downstream of Bhakra Dam. Despite being separate structures, both dams are collectively referred to as the Bhakra-Nangal Dam.
Information about Pong Dam
- The Pong Dam, also known as the Pong Reservoir or Maharana Pratap Sagar, was constructed in 1975 on the Beas River.
- In 1983, the Himachal Pradesh government declared the entire reservoir a Wildlife Sanctuary.
- In 1994, the Government of India recognized it as a “Wetland of National Importance”.
- The Pong Dam Lake was designated a Ramsar Site in November 2002.
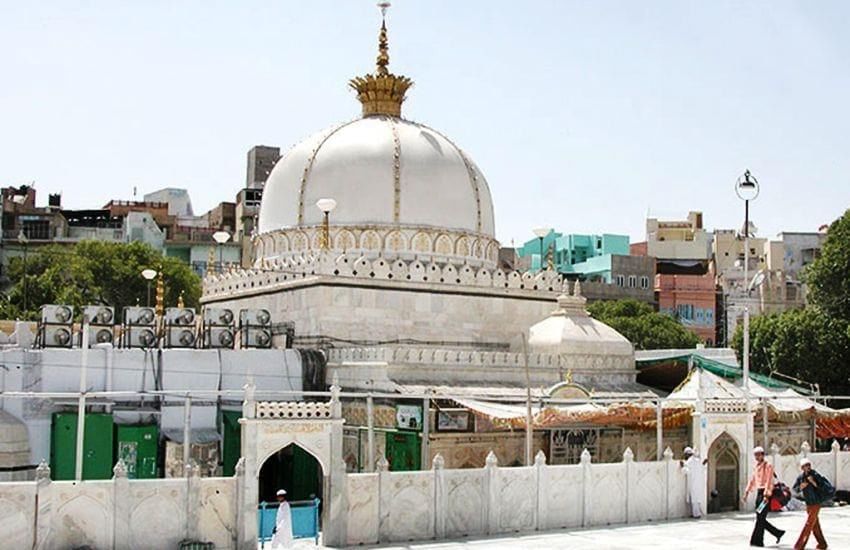
Prime Minister's Offering to Ajmer Sharif Dargah
 Ajmer Sharif Offering
Ajmer Sharif Offering
Why in News?
Recently, during the 'Urs' festival, the Prime Minister presented a 'chadar' to Kiren Rijiju, the Minister of Minorities Affairs, to be offered at the Ajmer Sharif Dargah. The Urs festival commemorates the death anniversary of Sufi saint Moinuddin Chishti and takes place annually in Ajmer, Rajasthan.
Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti
- Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti, also known as Moinuddin Hasan Chishti, was born around 1141-42 CE in the Sistan region, which is now part of Iran.
- After the Second Battle of Tarain in 1192, where Muizuddin Muhammad bin Sam of Ghor defeated Prithviraj Chauhan and gained control over Delhi, Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti moved to Ajmer, India, to live and teach.
- His spiritual teachings attracted a diverse following, including nobles, peasants, and those in need.
- Over time, his shrine in Ajmer became a significant place of pilgrimage, visited by many, including Mughal Emperor Jahangir.
Chishti Order (Chishtiya)
- The Chishti Order, founded in India by Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti, promotes the concept of unity with God (wahdat al-wujūd ).
- It advocates for peace and spiritual simplicity, encouraging members to avoid material possessions, which are seen as distractions from God.
- The Order emphasises the recitation of God's names, both aloud (dhikr jahrī. and in silence (dhikr khafī ).
- Prominent disciples, such as Khwaja Qutbuddin Bakhtiyar Kaki, Fareeduddin Ganj-e-Shakar, Nizamuddin Auliya, and Naseeruddin Charagh, continued and spread Chishti teachings.
Sufism is a mystical branch of Islam that emphasises the spiritual quest for God and rejects materialism. It focuses on ascetic practices and deep devotion to God. Self-discipline is key for gaining knowledge of God through personal experience. Sufis prioritise inner purity over external behaviour, unlike some orthodox Muslims. They believe that helping others is the same as serving God.
Rajasthan's Initiative for Indigenous Trees
 Indigenous Tree Initiative
Indigenous Tree Initiative
Why in News?
Agricultural centers of excellence in Rajasthan are set to adopt Tamil Nadu's nursery model to promote indigenous tree species suitable for the state's climate. These centers play a crucial role in training farmers on modern farming practices and advanced horticulture techniques.
Tamil Nadu's Nursery Model
- Part of the Green Tamil Nadu Mission, this model focuses on planting native trees and saplings.
- Facilitates the purchase of high-quality seedlings from local nurseries through an online platform.
- Aims to enhance environmental sustainability and boost afforestation efforts.
Visit by Agriculture & Horticulture Secretary
- The Secretary visited various centers in Rajasthan, including the State Seed Corporation's field center, pomegranate center, and olive cultivation center.
- Emphasized the high capacity and income-boosting impact of these centers on farmers.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Suggested the implementation of rainwater harvesting for crop irrigation.
- Reviewed the training module for farmers, highlighting water conservation techniques such as micro-irrigation and mulching.
Modern Infrastructure at Dhindhol Center
- Features advanced vegetative propagation structures including greenhouses, shade houses, nursery blocks, and automation units.
- Engages in intensive gardening, grading, packing, and technology transfer to assist horticulturists with fertigation and technical upgrades.
The Green Tamil Nadu Mission
- Aims to increase the state's forest and tree cover through various initiatives.
Tree Planting
- The mission has raised and distributed 73 lakh seedlings to the Department of Agriculture and plans to plant over 47 lakh saplings across Tamil Nadu.
Nurseries
- Established 260 nurseries in 43 forest divisions statewide.
- Launched a mobile app for daily updates on nursery activities.
Green Committees
- Formed State and District Green Committees for the protection and management of trees.
E-Nursery Portal
- Introduced an e-nursery portal in Chennai for free native tree saplings, with plans for expansion to other cities.
These initiatives collectively aim to enhance environmental sustainability in the region.
FAQs on State PCS CA Consolidation (Rajasthan) January 2025 - Monthly Current Affairs RPSC - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
| 1. What is the significance of the State PCS CA Consolidation in Rajasthan? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the State PCS CA Consolidation initiative? |  |
| 3. How does the State PCS CA Consolidation impact aspirants preparing for civil services in Rajasthan? |  |
| 4. What are the expected outcomes of the State PCS CA Consolidation for governance in Rajasthan? |  |
| 5. How can candidates stay updated about the changes introduced by the State PCS CA Consolidation? |  |





















