UPPSC Monthly Current Affairs: March 2025 | Monthly Current Affairs UPPSC - UPPSC (UP) PDF Download
Startup Ecosystem Report 2025
 Uttar Pradesh Startups
Uttar Pradesh Startups
Why in News?
According to the Startup Ecosystem Report-2025, Uttar Pradesh has achieved 3rd place in the country's startup ecosystem, with 26 startups reaching unicorn status.
Key Points
About:
- Uttar Pradesh has shown impressive growth in its startup ecosystem, leading to the emergence of over 14,000 startups.
- It is the first state in India to have startups operating in 49 districts.
- Previously, startups were concentrated in major cities like Noida, Ghaziabad, Lucknow, and Kanpur, but they are now expanding into smaller cities.
Top 10 Startup Hub Cities of Uttar Pradesh:
- Noida: 3,418 startups
- Lucknow: 1,789 startups
- Ghaziabad: 1,582 startups
- Kanpur: 586 startups
- Varanasi: 406 startups
- Agra: 359 startups
- Meerut: 291 startups
- Prayagraj: 283 startups
- Gorakhpur: 201 startups
- Bareilly: 177 startups
Contribution of Uttar Pradesh to the Country:
- Uttar Pradesh accounts for 9.6% of all recognised startups in India.
- While it is just behind Delhi ( 10%. and Karnataka ( 10.6% ), Uttar Pradesh's growing share may soon place it in second position.
Unicorn
Introduction:
- A unicorn is a privately owned company valued at over USD 1 billion.
- This indicates the rise of new businesses focused on providing innovative solutions and new business models.
Categories:
- Unicorns can be found in various sectors such as FinTech, EdTech, and B2B companies.
Features:
- Innovative. Most unicorns introduce new ideas in their sectors; for instance, 'Uber' has transformed commuting.
- Technology-driven. Their business models rely on the latest technological advancements.
- Consumer-focused. They aim to make tasks easier for consumers and integrate into daily life.
- Private ownership. Most unicorns are privately held, and their value often increases with investment from established companies.
- Software-based. Reports show that 87% of unicorn products are software, 7% are hardware, and 6% consist of other products and services.
Bithoor Mahotsav 2025
 Bithoor Heritage
Bithoor Heritage
Why in News?
The Bithoor Mahotsav, a cultural festival showcasing the rich history and heritage of the region, took place in Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, from March 21st to 23rd, 2025. This annual festival is held in Bithoor, a place known for its historical and mythological significance. In 2025, the festival focused on the shared culture and historical heritage of Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra. It featured captivating displays of imagery, theatre, music, drama, and diverse cultures, highlighting the rich history of the area.
Role of Bithoor in the Revolution of 1857
- Bithoor, located in the Kanpur district of Uttar Pradesh, played a crucial role in the First War of Independence in 1857. The Siege of Kanpur, which was a significant event during this period, started near Bithoor Fort. Nana Saheb, the adopted son of the Maratha Peshwa Baji Rao II, was exiled to Bithoor by the British. His fort in Bithoor became a base for planning the rebellion against British rule.
- Notable freedom fighters such as Nana Saheb, Ramchandra Pandurang, and Tatya Tope began their fight against British rule from Bithoor.
- On July 19, 1857, British General Havelock took control of Bithoor, and the British forces subsequently set fire to Bithoor Fort, the ghats, and numerous temples in the area.
- During this tragic event, Nana Saheb’s 14-year-old daughter, Mainavati, lost her life in the fire. In her memory, a road in Kanpur was named ‘Mainavati Marg’.
- The Bithoor Mahotsav 2025 not only celebrated the cultural heritage of the region but also commemorated the significant historical events and figures associated with Bithoor and the Revolution of 1857.
Nation's First Textile Machine Park

The Uttar Pradesh Minister has announced the establishment of the country's first textile machine park on 875 acres of land near Kanpur.
About the Park:
- The park will be developed in Chaparghata village of the Bhongaon area near Kanpur.
- It aims to use modern technology to reduce reliance on imports and boost local manufacturing.
- The focus is on producing machines for the textile industry that are currently imported from countries like China, Vietnam, South Korea, Taiwan, and Europe.
- More than 200 large and medium units are expected to be established, providing employment to around 1.5 lakh people.
- The park is projected to generate exports worth up to Rs 30,000 crore.
- Previously imported machines such as circular knitting machines, flat knitting machines, dyeing machines, printing machines, sewing machines, patient gown machines, and technical textile machines will now be produced in Uttar Pradesh.
- This initiative aims to reduce machine costs by 40% and train local technical experts for repair and maintenance.
Textile Sector in Uttar Pradesh:
- Banarasi silk
- The Uttar Pradesh government is making significant progress in the textile sector, known for chikankari, handloom, and powerloom industries.
- Under the Textile and Apparel Policy 2022, various initiatives have been launched to strengthen the textile industry and establish the state as a textile hub.
- As part of the PM Mitra scheme, 10 new textile parks are being set up in 10 districts, including areas near Lucknow.
- India’s textile market is projected to reach USD 350 billion by 2030.
Make in India Initiative
- Launched in 2014, this campaign aims to attract investments, promote innovation and skill development, protect intellectual property, and build superior manufacturing infrastructure.
- Led by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, it invites global investors and partners to join in the growth of ‘New India’.
- The initiative has seen significant achievements in 27 sectors, including key manufacturing and service areas.
Objective:
- Attracting foreign investment for new industrialisation and enhancing the existing industrial base in India to surpass China.
- Aiming to increase manufacturing sector growth to 12-14% annually in the medium term.
- Increasing the share of the manufacturing sector in the country’s GDP from 16% to 25% by 2025.
- Creating 100 million additional jobs by 2022.
- Promoting export-led growth.
Dolphin Safari in Varanasi
 Dolphin Conservation
Dolphin Conservation
The government of Uttar Pradesh has announced plans to create a dolphin safari in Varanasi, which is known for having the largest population of dolphins in the Ganga River.
About the Dolphin Safari
- The safari aims to increase the dolphin population in the Ganga River and protect their natural habitat.
- It will also promote eco-tourism and educate people about the importance of dolphin conservation.
- The initiative is in collaboration with Dolphin Mitras and the Forest Department.
Ganges River Dolphin
The Ganges river dolphin ( Platanista gangetica ), also known as 'the Tiger of the Ganges,' was officially identified in 1801. These dolphins are found in the major river systems of India, Nepal, and Bangladesh, including the Ganga and its tributaries.
Features of Ganges River Dolphins
- Ganges river dolphins can only live in freshwater and are essentially blind.
- They use ultrasonic sounds to hunt, creating a mental image of their prey.
- Dolphins are usually seen alone or in small groups, often with a mother and her calf.
- Female dolphins are larger than males and give birth every two to three years.
- As mammals, they need to breathe air and surface every 30 to 120 seconds.
- They are locally known as 'Sons' or Susuk because of the sound they make when breathing.
Importance of Ganges River Dolphins
- Ganges river dolphins are vital indicators of the health of the entire river ecosystem.
- In 2009, the Government of India declared the Ganges river dolphin the National Aquatic Animal.
- It is also the state aquatic animal of Assam.
Protection Status
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972. Schedule I
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES). Appendix I
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS). Appendix I
Related Government Initiatives
- Project Dolphin
- Vikramshila Ganga Dolphin Sanctuary in Bihar
- National Ganges River Dolphin Day on October 5
Neja Fair

The Uttar Pradesh administration has recently prohibited the Neja fair that takes place in Sambhal.
About the Fair:
- The Neja fair is conducted in honor of Syed Salar Masood Ghazi, a commander associated with a foreign invader.
- Mahmud Ghaznavi was a foreign invader who attacked India several times between 1000 and 1027 AD. During his invasions, he destroyed numerous Hindu religious sites, including the famous Somnath temple.
- The tomb of Abdul Salar Ghazi is located in the Bahraich district of Uttar Pradesh. It was constructed by Prithviraj Chauhan, a historical figure known for his battles against foreign invaders.
- Many soldiers from Ghaznavi's army died during conflicts in India, and their burial sites were established in Sambhal. Over time, this area became a place of faith for devotees, leading to the organization of Neja fairs in these locations.
- Ajmer was the capital city of Prithviraj Chauhan, where he ruled and managed his kingdom.
Reason for the Ban:
- The fair has been banned due to its historical association with foreign invasions, which could potentially incite communal tensions.
- Organizing a fair in memory of a figure linked to violence and conflict is considered controversial and sensitive.
- Ghaznavi's campaigns, particularly his attacks on the Somnath temple, have had a lasting impact on cultural perceptions and sensitivities in the region.
Government Digitech Awards 2025

Uttar Pradesh was honored with five awards in various categories of digital governance at the ET Government Digitech Awards held in New Delhi on March 18, 2025.
Awards Received by Uttar Pradesh
- Best Use of AI/ML, Data Analytics, and Emerging Technologies in Public Services
- Recipients: Prayagraj Smart City Limited and UP Police
- Project: AI-based surveillance and crowd management system for Maha Kumbh 2025
- Excellence in Smart Mobility and Transportation Technologies
- Recipient: Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (UPSRTC)
- Project: Vehicle Location Tracking Device (VLTD) with Panic Button for safety
- Innovative Digital Health Services and Public Health Data Analytics
- Recipient: Hamirpur District Administration
- Initiative: TB Free Hamirpur under Project Jagriti
- Innovative Use of Digital Technology in Public Service Delivery
- Recipient: UP Development Systems Corporation Limited (UPDESCO)
- Initiative: Swami Vivekananda Yuva Sashaktikaran Yojana
- Innovations in Digital Governance
- Recipient: Government of Uttar Pradesh
- Reason: Improving administrative functions through digital initiatives and technological upgrades
About Government Digitech Awards
- The ET Government Digitech Awards are endorsed by the Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- These awards honor individuals and organizations leading the digital transformation in public services.
- A total of 30 winners from across India were recognized at the event, with several states including Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, Telangana, Odisha, Kerala, Tripura, West Bengal, and Haryana receiving awards in various categories.
- Digital governance involves managing an organization’s digital presence, including websites, mobile sites, social media channels, and other internet-based services.
- It ensures clear decision-making processes and coordinates various aspects such as design, technical infrastructure, security, and financing.
- A robust governance framework enhances public trust by improving services, organizational performance, and customer experience.
Zaid Crops Under Kisan Credit Card (KCC)

On 19th March 2025, the Uttar Pradesh government decided to include 9 Zaid crops under the Kisan Credit Card scheme.
About Zaid Crops:
- Zaid crops are grown in the period between seasons.
- These crops can tolerate intense heat and dry winds.
- Major Zaid crops include:
- cucumber
- bitter gourd
- watermelon
- In North India, Zaid crops are typically sown in March and April.
Benefits of KCC and PMFBY for Zaid Crops
Farmers will now be able to access the benefits of the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) for various Zaid crops such as:
- Groundnut
- Maize
- Green Gram
- Urad
- Papaya
- Litchi
- Watermelon
- Melon
- Amla
This inclusion will provide farmers with easy loans for agricultural activities and compensation for crop losses due to natural disasters.
Kisan Credit Card (KCC)
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) provides loans to farmers at low interest rates based on their requirements.
- Farmers who repay their loans on time can receive an interest discount of up to 3%.
- The scheme was initiated in 1998 to provide timely credit facilities to farmers for agricultural expenses and related activities.
- In 2004, the scheme was expanded to cover investment credit for allied and non-agricultural activities such as fisheries and livestock.
- In the Budget for 2018-19, the government announced the expansion of KCC to assist farmers in meeting their working capital needs.
Implementing Agencies
- Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Small Finance Banks
- Co-operative Societies
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- PMFBY was launched in 2016 to provide insurance coverage to farmers for crop failure due to natural disasters, pests, and diseases.
- It is overseen by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare and aims to stabilise farmers' income and ensure continuity in farming.
- The scheme encourages farmers to adopt modern agricultural methods and ensures the flow of credit to the agricultural sector.
Eligibility for PMFBY
- All farmers, including tenant and holding farmers, growing notified crops in the designated areas are eligible for coverage.
- The scheme aims to provide comprehensive insurance cover in case of crop failure due to natural disasters, pests, and diseases.
- This helps to stabilise farmers' income and ensures continuity in farming.
- It encourages farmers to adopt modern agricultural methods and ensures the flow of credit to the agricultural sector.
Solar Cities Initiative in Uttar Pradesh
 Solar City Initiative
Solar City Initiative
Overview
- The government of Uttar Pradesh has announced plans to develop all 17 municipal corporations in the state as solar cities.
Goals and Focus
- The initiative aims to promote renewable energy and enhance environmental protection.
Key Aspects of the Initiative
- The focus is on solar energy to achieve energy self-sufficiency.
- Various projects will be implemented, including solar power plants, solar street lights, and solar water-heating systems.
- The initiative aims to reduce energy costs and encourage the use of renewable energy sources.
- It aligns with the national goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2070, as set by Prime Minister Modi.
List of Municipal Corporations in Uttar Pradesh
- Kanpur
- Lucknow
- Ghaziabad
- Agra
- Varanasi
- Prayagraj
- Meerut
- Bareilly
- Aligarh
- Moradabad
- Saharanpur
- Gorakhpur
- Firozabad
- Mathura
- Ayodhya
- Jhansi
- Shahjahanpur
Concept of a Solar City
- A Solar City primarily relies on solar energy to meet its energy needs.
- This includes using solar power for electricity generation, transportation, water supply, and other essential services.
- The main objective is to maximize the use of renewable energy sources and significantly reduce carbon emissions.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- The NCAP is a systematic approach to combat air pollution in India by involving various stakeholders.
- It has identified 131 cities across the country for implementing specific action plans to improve air quality.
- This initiative marks the first effort in India to establish a national framework for air quality management.
- The primary goal of the NCAP is to reduce the levels of PM10 and PM2.5 particulate matter by at least 20% over a period of five years, using 2017 as the baseline year.
Monitoring and Implementation
- The PRANA portal, launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) , is a key tool for monitoring the NCAP.
- This portal tracks the action plans and their implementation status in the identified cities.
- Additionally, the PRANA portal facilitates the sharing of best practices adopted by various cities, enabling others to learn and replicate successful strategies.
National Conference on NCAP

NCAP (National Clean Air Programme) Conference was held in Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh.
Overview of the Conference:
- The conference was a collaborative effort between the Gorakhpur Municipal Corporation and WRI India.
- The Chief Minister emphasized the significance of environmental protection and the need to reduce carbon emissions.
- He stressed that reaching the Net Zero target by 2070 requires a blend of technology and public awareness.
- Since 2017, Gorakhpur has replaced 17 lakh halogen street lights with LED street lights, resulting in savings of Rs 1000 crore and reduced energy consumption.
- The Chief Minister also announced the establishment of a plant in Lakhimpur for producing biodegradable items from banana fibre, which decomposes in three months and enriches the soil.
- Discussions during the conference focused on strategies to eliminate open burning of waste in Gorakhpur by 2027.
- The goal is to reduce emissions and energy consumption by at least 20% over the next five years, using 2017 as the baseline year.
About World Resources Institute India
- WRI India is an independent research organization focused on environmental and development issues.
- It is inspired by the World Resources Institute founded in Washington, DC, in 1982.
- WRI India promotes environmentally sustainable and socially just development.
- The organization develops solutions to protect the environment, improve livelihoods, and enhance well-being through research and policy recommendations.
- WRI India is involved in sustainable development projects across various states in India.
Headquarters of WRI India
- WRI India is headquartered in New Delhi.
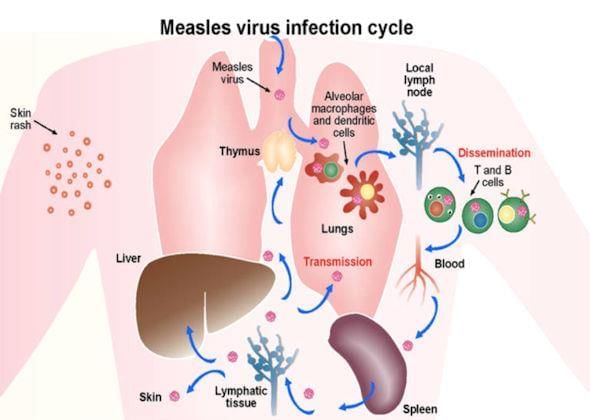
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)
 SSPE Risk
SSPE Risk
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a severe health concern, especially in regions with low vaccination rates like Uttar Pradesh.
Understanding SSPE
SSPE and Measles Infection
- SSPE is a progressive and deadly brain disorder that is associated with a past measles infection.
- It can manifest many years after the initial measles infection, even if the individual appeared to have fully recovered.
- This condition primarily affects children and adolescents, with a higher incidence in males compared to females.
- While SSPE has been documented globally, it is considered rare in the general population. However, its occurrence may be more frequent in areas with low vaccination coverage.
- Typically, the measles virus does not affect the brain. SSPE may occur due to an atypical immune response or specific variants of the virus.
- In SSPE, there is prolonged inflammation in the brain, which can persist for many years.
- The abnormal immune reaction to the measles virus can result in severe complications and is potentially fatal.
Symptoms of SSPE
- Initial symptoms of SSPE may include:
- Decline in academic performance
- Memory problems
- Increased irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disturbances
- Experiencing hallucinations
- As the disease progresses, patients might experience:
- Sudden jerks in hand, head, or body muscles
- Seizures and involuntary muscle movements
- Muscle stiffness
- Difficulty swallowing and vision problems
- In the advanced stages, elevated body temperature, irregular blood pressure, and pulse may occur
Treatment Options for SSPE
- Currently, there is no specific treatment for SSPE, and the disease is associated with a high mortality rate.
- Management may involve antiviral medications and drugs aimed at boosting the immune system to alleviate symptoms.
Measles Virus Overview
- The measles virus is part of the Morbillivirus genus and is highly contagious, capable of infecting over 90% of unprotected close contacts.
- The virus initially infects the respiratory tract before spreading throughout the body.
- Measles is a disease exclusive to humans and does not affect animals.
- It is completely preventable through a two-dose vaccination schedule and has been eradicated in several countries with advanced healthcare systems.
- Presently, there is no specific antiviral treatment available for measles.
Model Village Campaign in Ayodhya District

The Uttar Pradesh government has initiated a Model Village Campaign aimed at transforming 1,147 villages in the Ayodhya district into model villages.
Overview of the Campaign
- The campaign commenced in Mahanamau village, situated in the Tarun block of Ayodhya district.
- The primary objectives include improving transportation by connecting villages to main roads, eradicating open defecation, and establishing efficient waste disposal and recycling systems.
Objectives of the Model Village Campaign
- To elevate the standard of living in the targeted villages.
- To promote economic and social mobility among residents.
- To enhance cleanliness and environmental protection measures.
Criteria for Model Villages
A model village is defined by its commitment to cleanliness, safety, and active community participation. Key features include:
- Complete eradication of open defecation practices.
- Provision of toilets in every household.
- Access to safe and clean drinking water sources.
- Establishment of compost pits for cow dung.
- Implementation of separate collection systems for wet and dry waste.
- Development of connecting roads to enhance accessibility.
About Ayodhya District
Ayodhya is a city of significant religious and historical importance, located along the banks of the river Saryu. It is renowned as the birthplace of Lord Rama and was historically the capital of the Kosala Kingdom. The nearby city of Faizabad, established in 1730 by Saadat Ali Khan, the first Nawab of Awadh, adds to the historical richness of the area. The total area of Ayodhya district is 2522.0 sq. km.
Ayodhya's Significance in Jainism
Ayodhya holds a special place in Jainism as the birthplace of five out of the twenty-four Tirthankaras:
- Rishabhanatha. the first Tirthankara
- Ajitnath Ji. the second Tirthankara
- Abhinandan Nath Ji. the fourth Tirthankara
- Sumatinath. the fifth Tirthankara
- Anantnath Ji. the fourteenth Tirthankara
Major Attractions in Ayodhya
Visitors to Ayodhya can explore several significant sites, including:
- Ramjanmabhoomi
- Kanak Bhawan
- Hanumangarhi
- Dashrath Mahal
Low-Level Transportable Radar
 Transportable Radar
Transportable Radar
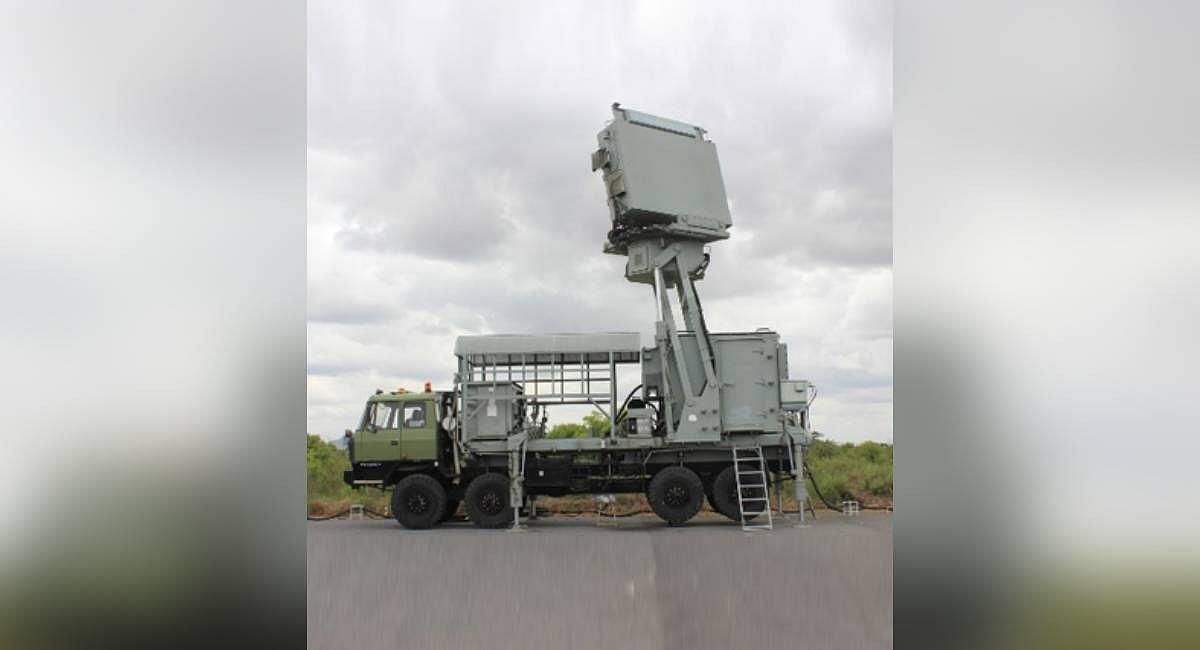
The Ministry of Defence has entered into a contract worth ₹ 2,906 crore with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in Bengaluru to procure the ‘Ashwini’ transportable radar for the Indian Air Force.
Overview of Low-Level Transportable Radar
- The Low-Level Transportable Radar (LLTR) ‘Ashwini’ is a cutting-edge radar system that employs an active electronically scanned phased array technology.
- It is specifically engineered to monitor slow-moving targets such as high-speed fighter aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and helicopters.
- This radar system is built on solid-state technology, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
About Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
- BEL has indigenously designed and developed the ‘Ashwini’ radar through its Electronics and Radar Development Establishment (LRDE).
- The company is a Navaratna Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) under the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- Established in 1954, BEL's mission is to fulfill the defence needs of the nation.
- BEL is engaged in various areas of defence electronics and professional electronics, providing advanced technical support to the Indian Defence Forces.
Production Units
- BEL has several manufacturing units across India, including:
- Bengaluru (Head Office)
- Ghaziabad (Uttar Pradesh)
- Panchkula (Haryana)
- Kotdwar (Uttarakhand)
- Hyderabad and Machilipatnam (Andhra Pradesh)
- Navi Mumbai and Pune (Maharashtra)
- Chennai (Tamil Nadu)
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is another crucial player in India's defence technology sector. It functions as the research and development wing of the Ministry of Defence, aiming to bolster India's capabilities in advanced defence technologies.
- DRDO is involved in several key projects, including the Agni and Prithvi missile series, the Tejas light combat aircraft, and the Pinaka and Akash defence systems.
- A significant focus of DRDO is on achieving self-reliance through the indigenous development of strategic systems, which encompasses various radars and electronic warfare systems.
Establishment and Structure of DRDO
- DRDO was founded in 1958 by integrating the Technical Development Establishments (TDEs) and the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP) of the Indian Army with the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- The organisation comprises a network of over 50 laboratoriesdedicated to advancing defence technologies across several domains, including:
- Aeronautics
- Armament
- Electronics
- Combat vehicles
- Engineering systems
Loudspeakers at Religious Places
 Loudspeaker Regulations
Loudspeaker Regulations
The Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh emphasized the need for long-term noise pollution control measures regarding loudspeakers at religious sites.
Important Instructions:
- The Chief Minister directed officials to ensure that noise levels during religious and public events adhere to established standards.
- He also called for a permanent solution concerning the use of loudspeakers in religious venues.
High Court Decision:
- The Allahabad High Court had previously issued a significant ruling regarding the use of loudspeakers at religious locations.
- The court determined that the use of loudspeakers for prayers is not a legal right, as it can cause inconvenience to others.
- Therefore, the use of loudspeakers does not constitute a legal right.
Noise Pollution:
- Noise pollution is defined as any sound that is uncomfortable or excessively loud.
- The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB), with a decibel scale used to evaluate sound levels.
- For example, a sound level of up to 20 dB is similar to a whisper.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that sound levels below 70 dB are generally safe for most individuals, although sensitivity to sound can vary from person to person.
- Prolonged exposure to noise levels exceeding 85 dB for more than 8 hours can be detrimental to health.
- Common sources of noise pollution include:
- Loud music
- Transportation
- Construction activities
- These sources have a negative impact on human well-being.
- The adverse effects of noise pollution may include:
- Elevated blood pressure
- Hearing loss
- Sleep disturbances
- Cardiovascular diseases
Pilibhit Tiger Reserve
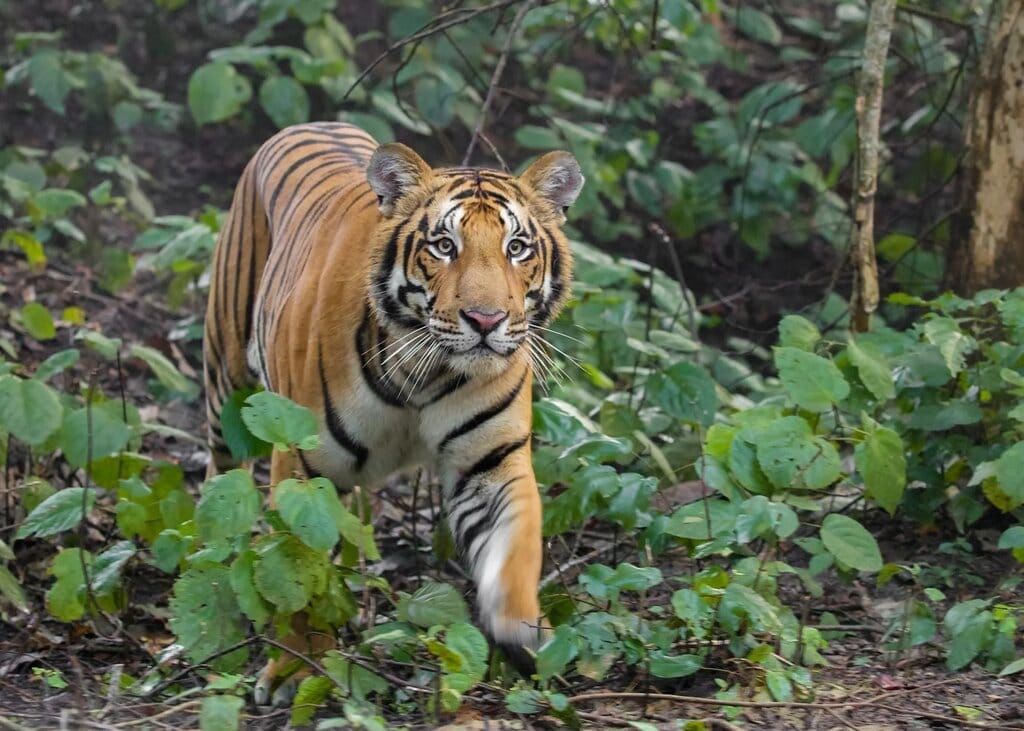 Rhino Habitat
Rhino Habitat
- Pilibhit Tiger Reserve (PTR) is being developed as a new refuge for rhinoceroses from Nepal, where efforts are ongoing to establish a permanent habitat for these animals.
- The Lagga-Bhagga region within Pilibhit Tiger Reserve is adjacent to the Shukla Phanta Sanctuary in Nepal. This proximity is a key reason why rhinoceroses from Nepal frequently visit this area.
- This region, with its abundant grasslands, ample water resources, and continuous wildlife corridors, provides an ideal setting for a stable population of rhinoceroses.
- As part of the 'Project Rhino' initiative, rhinoceroses will be relocated from Assam and Nepal to this area.
Importance and Benefits
- The project aims to conserve the dwindling rhino population and enhance the overall wildlife ecosystem.
- It is expected to boost tourism, thereby improving the economic conditions of local communities.
- Establishing protected areas will mitigate the issue of rhinos straying into agricultural lands, reducing conflicts between farmers and wildlife.
Pilibhit Tiger Reserve:
- Established as a Tiger Reserve in 2014.
- Located in the Pilibhit and Shahjahanpur districts of Uttar Pradesh.
- Recognized as part of the international TX2 award.
- In 2020, acknowledged for doubling the tiger population in just four years.
- Part of the Terai Arc landscape in the Upper Gangetic Plain.
- Several rivers, including Sharda, Chuka, and Mala Khannot, flow through the reserve.
- Habitat to various wild animals, including endangered species like the tiger, swamp deer, Bengal florican, hog deer, and leopard.
- Project Rhino is an important conservation initiative in India focused on protecting the dwindling population of one-horned rhinoceroses.
- It started in the 1980s when the threat of extinction for rhinos was seriously recognised.
The project has evolved into a comprehensive effort involving:
- Protecting rhino habitats
- Engaging local communities
- Enforcing laws to prevent poaching
- Conducting scientific research to support conservation efforts
Memorial for Freedom Fighter Chittu Pandey

The government of Uttar Pradesh has announced plans to create a memorial in Ballia district in honour of freedom fighter Chittu Pandey.
About Chittu Pandey:
- Chittu Pandey was a prominent freedom fighter and revolutionary known as the “Lion of Ballia. for his bravery and leadership during the Quit India Movement of 1942.
Birth:
- Chittu Pandey was born on 10 May 1895 in Rattuchak village, Ballia district, Uttar Pradesh.
Establishment of Independent Government:
- On August 19, 1942, Chittu Pandey led a group of revolutionaries in Ballia to oust British officials and declare the independence of Ballia, setting up a temporary national government.
- Chittu Pandey became the interim administrator of this short-lived government, which managed to transfer power to the Collector and release arrested Congress leaders.
- However, the British army recaptured Ballia after a few days, arresting Chittu Pandey and other revolutionaries.
Demise:
- Chittu Pandey passed away on 6 December 1946.
Quit India Movement
- The Quit India Movement was initiated by Mahatma Gandhi on 8 August 1942, calling for an end to British rule in India.
- Gandhi urged the people to “Do or Die. during his speech at the All-India Congress Committee session in Mumbai.
- Leaders like Aruna Asaf Ali played a crucial role by hoisting the Indian flag at Gowalia Tank grounds in Mumbai during this period.
Reasons for Movement:
- The movement was triggered by the failure of the Cripps Mission and the British demand for unconditional support from India during World War II, which was rejected by the Indian National Congress.
- Widespread anti-British sentiments and demands for complete independence fueled the movement among the Indian public.
Success of the Movement:
- Emergence of Future Leaders: Leaders such as Ram Manohar Lohia, JP Narayan, and others like Aruna Asaf Ali, Biju Patnaik, and Sucheta Kripalani engaged in underground activities during the movement and later became prominent leaders in India.
- Participation of Women: Women played an active role in the movement, with leaders like Usha Mehta establishing underground radio stations to spread awareness and rally support.
- Rise of Nationalism: The Quit India Movement fostered a strong sense of unity and brotherhood across India, leading many students to leave educational institutions and individuals to resign from their jobs in support of the cause.
Maharishi Dadhichi Kund
 Maharishi Dadhichi Pond
Maharishi Dadhichi Pond
On March 10, 2025, the Uttar Pradesh government announced plans to develop Maharishi Dadhichi Kund as a state tourist center.
About Dadhichi Kund:
- Dadhichi Kund is situated in the Mishrikh region, roughly 12 kilometers from Naimisharanya.
- The pond is believed to combine waters from all pilgrimage sites worldwide, giving rise to the name Mishrikh.
- This site is associated with Maharishi Dadhichi, who sacrificed his bones to the gods for a thunderbolt to defeat Vritrasura.
- Dadhichi Kund spans approximately 2 acres of land.
- Adjacent to the pond is a magnificent temple dedicated to Maharishi Dadhichi, showcasing statues of him in various postures.
- The temple's architectural design and the surrounding environment foster a serene and spiritual ambiance.
- Maharishi Dadhichi was a prominent ascetic, a knowledgeable scholar of the Vedas, and a benevolent sage.
- He is believed to be the son of sage Atharva and mother Shanti.
- His life was devoted to Shiva and the welfare of humanity.
- When the gods needed his bones and thunderbolts to vanquish the demon Vritrasura, he willingly gave up his body through the power of yoga.
Naimisharanya:
- Naimisharanya is an ancient pilgrimage destination located in the Sitapur district of Uttar Pradesh.
- This site is nestled along the banks of the Gomti River.
- Naimisharanya is renowned as a place of penance for sages.
- According to religious beliefs, eighty-eight thousand sages performed penance here, elevating its status as a sacred site in Hinduism.
Swavalambini
 Women Empowerment
Women Empowerment
Recently, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) launched the Swavalambini programme at Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut, in collaboration with NITI Aayog.
About Swavalambini
- Swavalambini is an initiative aimed at empowering women by fostering an entrepreneurial mindset and providing necessary resources for business success.
Programme Structure
- The programme follows a phase-wise approach, including:
- Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP)
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP)
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP)
- Financing
- Successful enterprises will be recognized and rewarded to inspire others.
- A clear framework to promote women-led enterprises in India.
- The initiative aims to foster a culture of entrepreneurship in higher education, making business a viable career option for women and positioning women-led enterprises as a crucial driver of India’s economic transformation.
Alignment with National Policies
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 advocates for skill integration, industry collaboration, and entrepreneurship-focused education.
- Swavalambini aligns with NEP 2020 by offering financial and consultancy support to women entrepreneurs.
Connection with Other Initiatives
- Stand-up India and PM Mudra Yojana reinforce similar objectives of supporting women entrepreneurs.
- Union Budget initiatives, such as a Rs 10,000 crore startup fund and tax exemptions on startup dividends, provide crucial financial backing for emerging women-led enterprises.
Current Scenario of Women Entrepreneurship in India
- Total MSMEs: Over 63 million, with 20% (12.39 million) being women-owned.
- Women-led MSMEs employ between 22-27 million people.
- India’s Ranking in Women Entrepreneurship:
- 57th out of 65 countries in the Mastercard Index on Women Entrepreneurship (MIWE) 2021.
- 70th among 77 nations in the Global Female Entrepreneurship Index (FEI) by the Global Entrepreneurship and Development Institute.
- Top States for Women-led MSMEs:West Bengal: 23.42% Tamil Nadu: 10.37% Telangana: 7.85% Karnataka: 7.56% Andhra Pradesh: 6.76%
Multi-Modal Logistics Park in Varanasi

A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between NHLML and IWAI to create a modern Multi-Modal Logistics Park (MMLP) in Varanasi.
About MMLP:
- The park aims to enhance the supply chain by enabling smooth freight movement via road, rail, and water routes.
- This will lower costs and improve business efficiency.
Significance and Impact:
- Spread over 150 acres, the park will connect directly to NH7 and the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor, simplifying and lowering freight transportation costs.
- Linking with National Waterway-1 (NW-1) will allow easier cargo transport via water, further reducing costs.
- The logistics park is expected to attract significant investments, boosting the economy of Uttar Pradesh.
- Local and national traders, industries, and MSMEs will gain, leading to increased production and exports.
- This project will create both direct and indirect job opportunities locally.
- Modernising the logistics sector will encourage similar projects in other cities.
Prime Minister’s Gati Shakti scheme
- The park will serve as a model under the Prime Minister’s Gati Shakti scheme and multi-modal connectivity, inspiring similar projects in other states.
- IWAI is a statutory body under the Ministry of Shipping, responsible for developing and maintaining inland water transport infrastructure on national waterways.
- It receives funding from the Ministry of Shipping and has offices in Noida, Patna, Kolkata, Guwahati, and Kochi, with sub-offices in Prayagraj, Varanasi, Bhagalpur, Rakka, and Kollam.
Objective:
- To ensure integrated planning and execution of essential infrastructure projects over the next four years, focusing on accelerating progress, cutting costs, and generating jobs.
- The Gati Shakti plan incorporates the ₹110 lakh crore National Infrastructure Pipeline initiated in 2019.
- Besides lowering logistics expenses, the scheme aims to enhance cargo handling capacity and reduce turnaround times at ports to facilitate trade.
- It also plans to establish 11 industrial corridors and two new defence corridors in Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- Furthermore, there are plans to expand 4G connectivity to all villages and add 17,000 km of capacity to the gas pipeline network.
- This integrated approach involves coordinating 16 ministries focused on infrastructure.
- The Gati Shakti Digital Platform will create an umbrella system for effective planning and implementation of infrastructure projects through real-time collaboration among various ministries and departments.
RISE App for Immunization in Uttar Pradesh
 Vaccination Support
Vaccination Support
The Uttar Pradesh government has launched the RISE app, which stands for Rapid Immunization Skill Enhancement, to promote regular immunization for children.
About the RISE App
- The RISE app, which stands for Responsive Immunisation Support for Everyone, is a digital platform aimed at improving immunisation programmes through training and monitoring.
- The app provides real-time updates to assist health workers in various aspects of immunisation, including tracking vaccination schedules, ensuring safety protocols, managing the cold chain, and monitoring adverse effects post-immunisation.
The RISE App plays a vital role in bolstering the efforts of the Government of India in enhancing routine immunisation for children.
- Target Users: The app is specifically designed for staff nurses and auxiliary nurse midwives (ANMs) to help them monitor and manage immunisation effectively.
- Goal: The primary aim is to increase vaccination coverage, identify families hesitant to vaccinate, and ensure proper immunisation practices.
- Digital Transformation: By replacing traditional training methods with a digital learning system, the app enhances the safety and effectiveness of vaccinations.
Training and Implementation of the RISE App
- Training of health workers on the RISE App is being conducted in three phases to ensure effective implementation.
- District-level officers have been successfully trained across all 75 districts in Uttar Pradesh.
- Training for block-level officers is currently ongoing to facilitate ground-level implementation.
- Target: Once fully implemented, approximately 52,175 vaccination personnel will be equipped with digital devices, enhancing their efficiency and data management capabilities.
Mission Indradhanush
- Launch Date: Mission Indradhanush was launched on December 25, 2014, by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- Purpose: The mission aims to boost vaccination coverage in 201 districts with low immunisation rates.
- Vaccines: Initially, the mission targeted seven vaccines against seven diseases included in the Universal Immunisation Programme: Tuberculosis, Poliomyelitis, Hepatitis B, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, and Measles.
- Expansion: The number of vaccines has increased to 12, now including Measles, Rubella, Rotavirus, Haemophilus Influenzae Type-B, and Polio.
Intensified Mission Indradhanush
- To further improve immunisation coverage, India has launched the Intensified Mission Indradhanush plan, targeting selected states and districts for enhanced vaccination efforts.
- Additional vaccines provided in selected states and districts include Japanese Encephalitis and Pneumococcus.
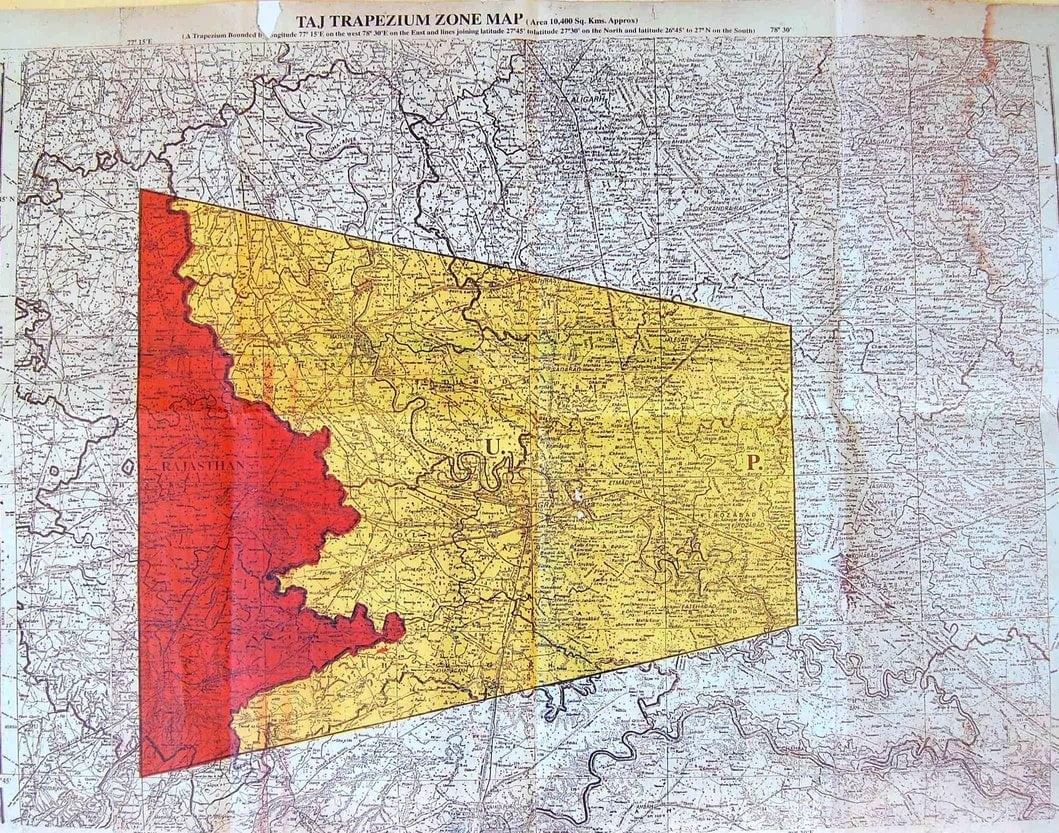
Taj Trapezium Zone
 Taj Mahal Protection
Taj Mahal Protection
- Supreme Court: The Supreme Court of India
- Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ) Authority: Responsible for managing the Taj Trapezium Zone
- Forest Research Institute (FRI):. premier research institution in forestry and environmental studies
Supreme Court Decision:
- The Supreme Court emphasized the importance of conducting a tree census in the Taj Trapezium Zone to prevent illegal tree cutting.
- The court issued fresh directions, stating that the Uttar Pradesh Tree Protection Act, 1976 aims to count and protect trees.
- It highlighted that without a tree census, the regulations of the Act cannot be effectively implemented.
Agroforestry:
- The Supreme Court reaffirmed the need to obtain permission before cutting down trees for specific purposes, such as agroforestry.
- In a previous ruling in 2015, the court had confirmed that the rules of the 1976 Act regarding agroforestry still apply, meaning necessary permissions must be secured before tree cutting.
About Taj Trapezium Zone
- The Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ) is a protected area covering 10,400 square kilometres around the Taj Mahal to prevent pollution and environmental degradation.
- The zone is named for its trapezoidal shape and its location around the Taj Mahal, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- It includes three World Heritage Sites. Agra Fort, Fatehpur Sikri, and the Taj Mahal itself.
- The TTZ spans several districts in Uttar Pradesh, including Agra, Firozabad, Mathura, Hathras, and Etah, as well as Bharatpur district in Rajasthan.
- The area is divided into four zones based on the type of industry allowed: red, green, orange, and white.
- Only eco-friendly, non-polluting small, tiny, and micro-scale industries are permitted to operate within this zone, ensuring the protection of the Taj Mahal and its surroundings from industrial pollution.
Forest Research Institute (FRI)
- The Forest Research Institute (FRI) is located in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, and was established in 1878 as a Forest School.
- In 1906, it was reconstituted as the Imperial Forest Research Institute during the British colonial period and later became known as the Forest Research Institute and College.
- FRI has several research and training centres across India that focus on forestry research and the training of forest officers and rangers.
- After the Indian forestry research system was restructured and the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) was established in 1988, these centres became independent entities.
- FRI currently operates under ICFRE, which was granted Deemed University status in December 1991.
COAIEMA Conference

The 8th International COAIEMA (Council of Asian Industry and Emerging Market Alliances) conference took place in Lucknow on 8th March 2025. This event was hosted at the Ambalika Institute of Management and Technology, Lucknow. The focus was on enhancing cooperation among industries and promoting sustainable development initiatives. Participants included representatives from various countries, policymakers, and industry experts. The primary aim was to empower the industrial and innovation sectors of Asian nations.
Topics of discussion:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Challenges and Opportunities in Engineering and Management Applications
- Latest technological advancements
- Green Energy
- Digital Transformation
About COAIEMA:
COAIEMA is a prominent regional organisation aimed at boosting cooperation among industries and emerging markets within Asian countries.
Main objectives:
- Promoting innovation.
- Accelerating the adoption of green technology.
- Taking quick steps towards the digitalisation of industries.
- Strengthening trade relations among Asian nations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are designed to think and learn. The term "artificial intelligence" was first coined by American computer scientist John McCarthy, who is recognised as the father of AI. It encompasses techniques such as machine learning, deep learning, big data, neural networks, computer vision, and large language models. The ideal feature of artificial intelligence is its ability to perform and reason actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal.
Women’s Taekwondo Championship
 Women's Taekwondo Championship
Women's Taekwondo Championship
On March 8, 2025, the Women’s Taekwondo Championship was held in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
About the Championship:
- The championship was organized by the Union Ministry of Sports and Youth Welfare, Khelo India, and the Uttar Pradesh Taekwondo Association.
- Competitions took place in various weight categories at the senior level.
Chief Medalist:
- Lucknow:. gold, 4 silver, 6 bronze
- Agra:. gold, 1 silver
- Mathura and Farrukhabad:. gold each and additional medals
About Taekwondo:
- Taekwondo is a Korean martial art that emphasizes punching and kicking techniques.
- It is known for high head kicks, spinning jump kicks, and fast kicking techniques.
- Taekwondo not only develops physical skills but also mental strength.
History:
- The origins of Taekwondo can be traced back to Korea’s Three-Kingdoms era (around 50 BC).
- It was influenced by a martial art called Taekkyon, which was practiced by the Hwarang warriors of the Silla Dynasty.
- By the early 20th century, Taekwondo had become the predominant martial art in Korea.
- The World Taekwondo Federation (WTF) was founded in 1973.
Integrated Solar Manufacturing Unit
 Solar Manufacturing Initiative
Solar Manufacturing Initiative
On March 8, 2025, the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh inaugurated the foundation stone for Avaada Group's 5 gigawatt (GW) integrated solar manufacturing unit in Gautam Buddha Nagar (Noida) and also opened a 1.5 GW solar module manufacturing facility. Avaada Group, a well-known Indian company based in Mumbai, is dedicated to generating energy through various renewable sources including solar, wind, pumped hydro, and green fuels.
- The Chief Minister highlighted that this initiative not only boosts the state's contribution to renewable energy but also creates job opportunities and aligns with the vision of a USD 1 trillion economy.
- This project supports Uttar Pradesh's goal of achieving 22,000 MW of solar power generation by the year 2026-2027.
- The initiative aims to significantly reduce carbon emissions by 2070.
- The Chief Minister emphasized that this endeavour is a crucial step towards realizing the vision of a sustainable energy future.
Renewable Energy
- Hydropower
- Biomass
- Geothermal
- Tidal
Renewable energy is derived from natural sources that are replenishable, such as solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal sources. These energy types are sustainable and environmentally friendly, contributing to a reduction in the reliance on fossil fuels.
Types of Renewable Energy:
- Solar Energy: Captured from the sun's radiation using solar panels or solar thermal systems.
- Wind Energy: Generated by converting the kinetic energy of wind into electricity using wind turbines.
- Hydroelectricity: Produced by harnessing the energy from flowing water, such as rivers, dams, and waterfalls.
- Biomass Energy: Created from organic materials like plant residues and animal waste, used for heating, electricity, and biofuels.
- Geothermal Energy: Obtained from the Earth's internal heat, using hot water or steam for power generation and direct heating.
- Tidal and Wave Energy: Generated by utilizing the movement of seawater, either through gravitational pull or surface waves, to produce electricity.
Coastal areas such as the Gulf of Kutch and the Sundarbans offer potential sites for tidal energy generation.
Introduction of India’s First Lithium-Grade Refinery
 Lithium Refinery
Lithium Refinery
Lohum Company has inaugurated India's inaugural lithium-grade refinery in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh.
This facility is set to produce 1,000 metric tonnes of battery-grade lithium annually, with plans to scale up to 20,000 tonnes by 2029.
E-Waste Recycling for Lithium Extraction
The refinery will recycle black mass from e-waste to extract lithium, contributing to sustainable resource management.
Advancements in Cathode Active Material (CAM) Production
- Lohum is also ramping up its production of Cathode Active Material (CAM), essential for large-scale lithium-ion batteries.
- The company currently refines over 90% of lithium in India, with technical efficiency comparable to China and cost-effectiveness superior to facilities in the US and Europe.
Importance of Lithium Refining
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices.
- Growing Demand: The demand for electric vehicles and battery storage is projected to increase significantly in India, driving the need for lithium.
- Dependency on Imports:. large portion of India's lithium supply currently comes from China, posing strategic and economic challenges. Lohum's expansion is crucial for reducing this dependency.
Understanding Lithium
- Lithium, represented by the symbol Li in the periodic table, is a soft, silver-white metal and the lightest metal and solid element under standard conditions.
- It is highly reactive and flammable, necessitating storage in mineral oil. Lithium is classified as both an alkaline and rare metal.
- Alkali Metals: Lithium, along with sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium, forms group-1 in the s-block of the periodic table. Hydrogen is also included in this group.
Rare Metals (RM) include niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta), lithium (Li), beryllium (Be), and cesium (Cs). Rare Earths (RE) consist of scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), and lanthanum (La) to lutetium (Lu).
- These metals are strategically important and are used in nuclear and high-tech industries such as electronics, telecommunications, information technology, space, and defence.
Recognition by UNESCO for Cultural Cities
 Cultural Heritage Recognition
Cultural Heritage Recognition
The Uttar Pradesh government is set to apply for UNESCO recognition for five cities as intangible cultural heritage and creative cities. This initiative aims to preserve the state’s rich cultural heritage and gain global acknowledgment.
Selected Cultural Cities and Their Elements:
- Kannauj: Known for its exquisite perfume industry.
- Braj: Famous for its vibrant Holi celebrations, particularly the unique Lathmar Holi.
- Varanasi: Renowned for the Ganga Aarti, a significant spiritual ritual.
- Firozabad: Celebrated for its traditional glass art.
- Azamgarh (Nizamabad): Recognized for its black pottery craftsmanship.
Additional Efforts:
- The state government aims to include the folk art and folk literature of Bundelkhand in UNESCO’s intangible cultural heritage list.
- Research will delve into the Deg-Bhapka method and its impact on Kannauj perfume, along with the Ganga Aarti’s significance in Varanasi and the folk traditions of Bundelkhand.
Historical Background and UNESCO Recognition:
- In 2017, UNESCO recognized certain cultural practices in Uttar Pradesh as intangible cultural heritage of humanity, thanks to the efforts of the central and state governments.
Impact and Potential Advantages:
- Global recognition by UNESCO will enhance the international profile of these cultural heritages.
- This recognition is expected to boost tourism and, consequently, the local economy.
- It will also provide protection to local artisans, artists, and traditional industries, improving their livelihoods.
- Furthermore, it will encourage the preservation of culture and heritage, ensuring these traditions are safeguarded for future generations.
UNESCO Overview:
- UNESCO, a specialized agency of the United Nations, promotes peace through international cooperation in education, science, and culture.
- Its programs contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals outlined in Agenda 2030.
- UNESCO has 193 member countries and 11 associate members, with India being a member since 1946.
- The organization’s headquarters is in Paris, France.
Taj Festival
 Taj Mahotsav
Taj Mahotsav
The Taj Mahotsav took place at Shilp Gram in Agra from February 18 to March 2, 2025.
Crafts and Dance
The Taj Mahotsav showcased a captivating blend of crafts, dance, and food. Throughout the festival, there were various cultural programs, craft exhibitions, and food fairs. This marked the 33rd edition of the Taj Mahotsav, organized by the Taj Mahotsav Committee. The festival's theme, ‘Dharohar,’ highlighted India’s rich cultural heritage.
Major Events
- Flower show at Atal Garden
- Garment Show
- Our Heritage, Our Identity
- Bird watching at Sur Sarovar Bird Sanctuary
Held every year at Shilp Gram in Agra, this vibrant 10-day festival celebrates the rich traditions of the region. It draws inspiration from the Nawabi culture that thrived in Uttar Pradesh during the 18th and 19th centuries. The Taj Mahotsav was initiated in 1992 to support local artisans and promote the cultural heritage of Agra.
Agra District
Agra is situated on the banks of the Yamuna River in the western part of Uttar Pradesh. Its geographical coordinates are 27.11° N latitude and 78.0° to 78.2° E longitude. The district shares its borders with the states of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. Modern Agra was established by Sikandar Lodi in 1504 AD when he relocated his capital from Delhi to Agra.
Major Places of Interest
- The Taj Mahal
- Fatehpur Sikri
- Tomb of Itmad-ud-Daulah
- Akbar’s Tomb
- Lofty Gate
- Moti Masjid
- Keetham Lake (Suri Sarovar Bird Sanctuary)
FAQs on UPPSC Monthly Current Affairs: March 2025 - Monthly Current Affairs UPPSC - UPPSC (UP)
| 1. What is the significance of the State PCS CA Consolidation in Uttar Pradesh? |  |
| 2. How does the State PCS CA Consolidation impact civil service examinations in Uttar Pradesh? |  |
| 3. What are the expected outcomes of the State PCS CA Consolidation for the public? |  |
| 4. What challenges might arise during the implementation of the State PCS CA Consolidation? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare for changes resulting from the State PCS CA Consolidation? |  |
















