NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Infographics: Dicot Leaf
Infographics: Dicot Leaf | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
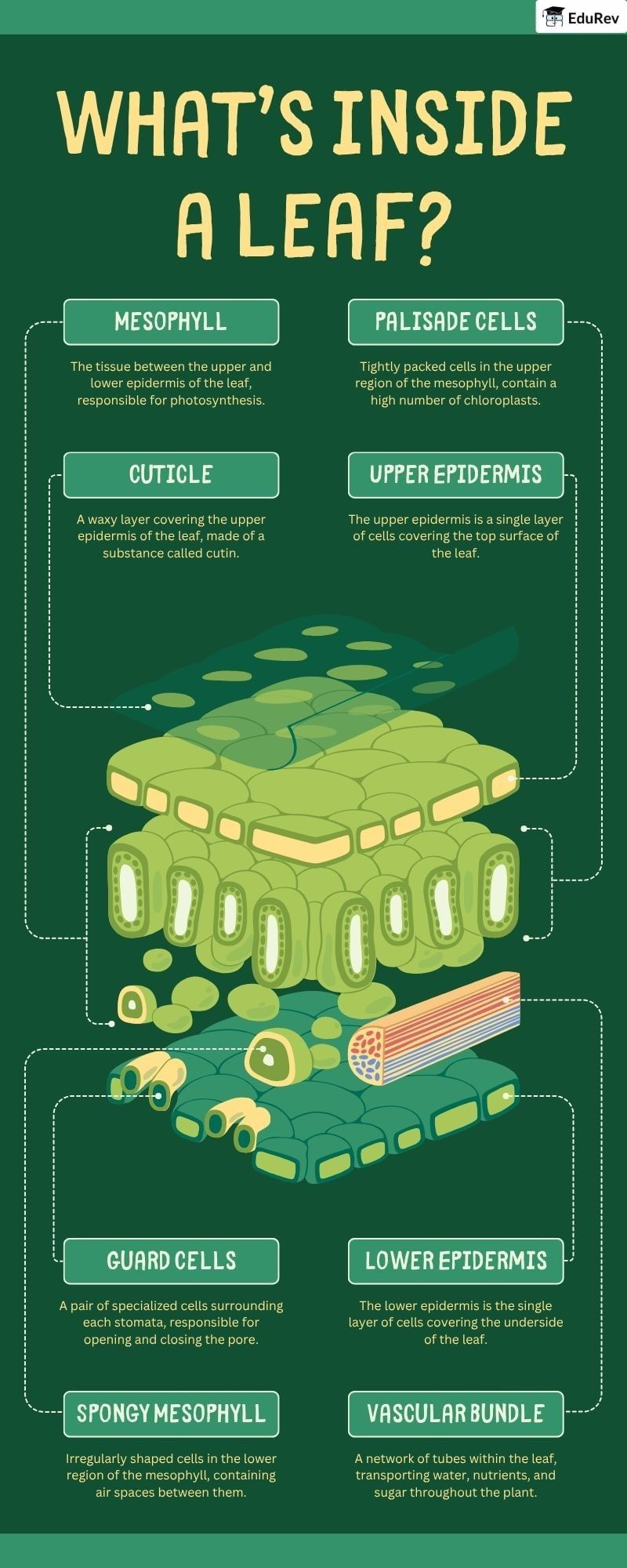
The document Infographics: Dicot Leaf | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Dicot Leaf - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main characteristics of dicot leaves? |  |
Ans. Dicot leaves typically exhibit a broad, flat blade with a network of veins, known as reticulate venation. They usually have a petiole that connects the leaf to the stem and can vary in shape, size, and margin. The presence of two seed leaves, or cotyledons, is a defining feature of dicots, and their leaves often display a variety of colors and textures.
| 2. How do dicot leaves differ from monocot leaves? |  |
Ans. Dicot leaves differ from monocot leaves in several ways. Dicot leaves generally have a broad, flat shape with reticulate venation, while monocot leaves are typically long and narrow with parallel venation. Additionally, dicots usually possess a petiole, whereas monocots often have leaves that directly attach to the stem without a petiole. Furthermore, dicot leaves can have a greater diversity in form and structure compared to monocots.
| 3. What is the significance of stomata in dicot leaves? |  |
Ans. Stomata are tiny openings found on the surface of dicot leaves that play a crucial role in gas exchange. They allow for the intake of carbon dioxide, which is essential for photosynthesis, and facilitate the release of oxygen as a byproduct. Stomata also help regulate water loss through transpiration, thereby maintaining the plant's water balance. The distribution and density of stomata can vary among different dicot species based on their environmental adaptations.
| 4. What adaptations do dicot leaves have for different environments? |  |
Ans. Dicot leaves have developed various adaptations to thrive in different environments. For example, in arid regions, some dicots may have thick, waxy cuticles and reduced leaf size to minimize water loss. In contrast, dicots in tropical environments may have large, broad leaves to maximize sunlight capture. Additionally, some dicots exhibit leaf modifications, such as spines or tendrils, to deter herbivores or support climbing.
| 5. How does the structure of dicot leaves facilitate photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. The structure of dicot leaves is optimized for photosynthesis through several features. The broad, flat shape increases surface area for light absorption, while the arrangement of chloroplasts within the mesophyll cells ensures efficient light capture. The presence of palisade mesophyll cells, which are densely packed with chloroplasts, enhances photosynthetic efficiency. Furthermore, the vascular system within dicot leaves supports the transport of water and nutrients, essential for the photosynthetic process.
Related Searches















