Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Geography Class 11 > Cheat Sheet: Structure and Physiography
Cheat Sheet: Structure and Physiography | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Introduction
The Earth, ~4.6 billion years old, has evolving landforms shaped by endogenic (internal) and exogenic (external) forces. The Indian plate, once south of the equator, moved north, separating from the Australian plate, and continues to influence the Indian subcontinent's environment through ongoing northward movement.
Geological Divisions of India
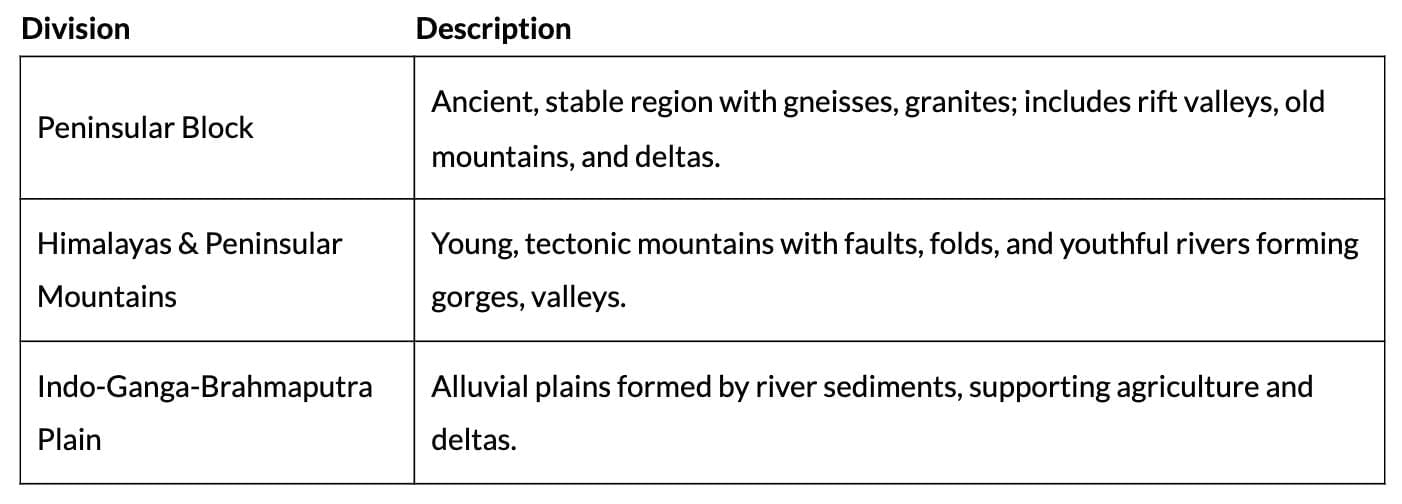
The Peninsular Block
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Boundary | Uneven line from Kachchh, along Aravali Range near Delhi, parallel to Yamuna and Ganga, to Rajmahal Hills and Ganga delta. |
| Extent | Includes Karbi Anglong, Meghalaya Plateau (northeast), Rajasthan (west, desert-covered). |
| Faults | Malda fault separates northeast from Chotanagpur; block faulting forms Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi rift valleys, Satpura block mountains. |
| Composition | Ancient gneisses, granites; stable since Cambrian, with some western coast submerged, tectonic activity. |
| Features | Old mountains (Aravali, Nallamala, Javadi, Veliconda, Palkonda, Mahendragiri); shallow, low-slope river valleys; deltas by east-flowing rivers (Mahanadi, Krishna, Kaveri, Godavari). |
The Himalayas and Other Peninsular Mountains

Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin | Geosynclinal depression formed ~64 million years ago during Himalayan formation's third phase. |
| Formation | Filled with sediments from Himalayan and Peninsular rivers; alluvial deposits 1,000-2,000 m deep. |
| Features | Flat plains with riverine islands, sand bars, meanders, oxbow lakes, deltas (e.g., Sunderbans). |
Physiography
Physiography results from structure, process, and developmental stage, showcasing India's diverse landscape.
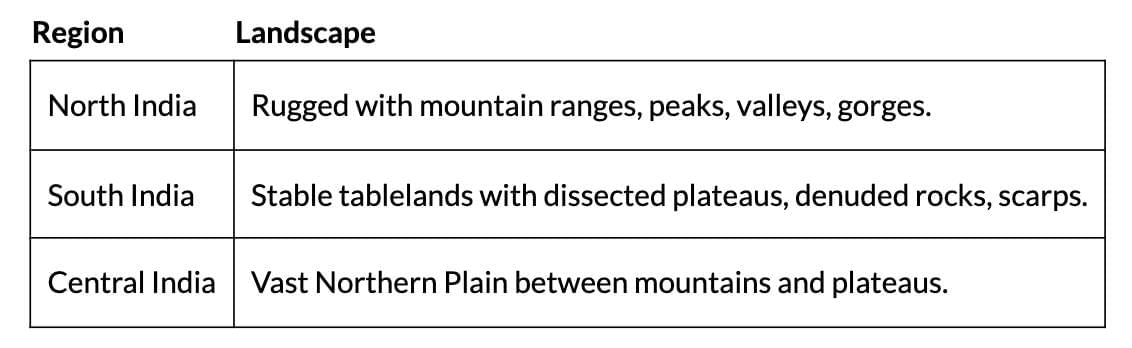
Physiographic Divisions
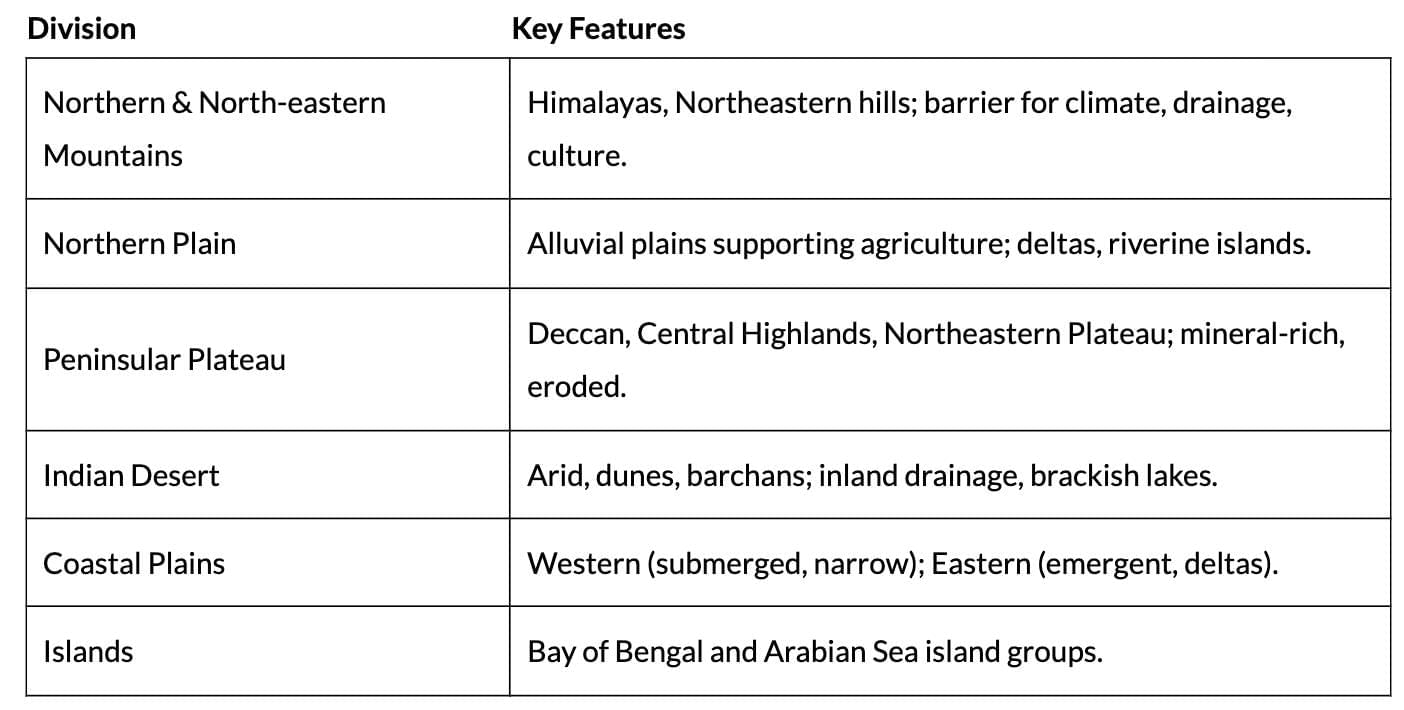
The Northern and North-eastern Mountains
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | Himalayas and Northeastern hills. |
| Ranges | Greater Himalayas (~2,500 km long, 160-400 km wide), Shiwalik Range. |
| Orientation | Northwest-southeast (northwest India); east-west (Darjeeling, Sikkim); southwest-northwest (Arunachal Pradesh); north-south (Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram). |
| Role | Physical, climatic, drainage, cultural barrier separating India from Central/East Asia. |
The Northern Plains
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Formation | Alluvial deposits from Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra; ~3,200 km long, 150-300 km wide, 1,000-2,000 m deep. |
| Zoning |
|
| Features | Sand bars, meanders, oxbow lakes, braided channels; Brahmaputra riverine islands; Sunderbans delta. |
| Elevation | 50-150 m above sea level. |
| Water Divide | Haryana/Delhi separates Indus and Ganga systems. |
| Agriculture | Fertile soil supports wheat, rice, sugarcane, jute. |
The Peninsular Plateau
| Region | Details |
|---|---|
| Deccan Plateau | Bounded by Satpura Range (north), Western/Eastern Ghats; relict mountains with erosion. |
| Central Highlands | 700-1,000 m elevation, slopes north/northeast; Aravali (west), Vindhyan/Kaimur Ranges; Banas River (Chambal tributary). |
| Northeastern Plateau | Meghalaya, Karbi Anglong Plateaus; Garo, Khasi, Jaintia Hills; fault-separated; rich in coal, iron, limestone, uranium; eroded by heavy rainfall (e.g., Cherrapunji). |
| Features | Metamorphic rocks (marble, slate, gneiss); Rajmahal Hills, Chotanagpur Plateau mineral-rich. |
The Indian Desert
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Northwest of Aravali Hills, called Marusthali. |
| Characteristics | Undulating terrain, longitudinal dunes, barchans; arid, <150 mm rainfall, minimal vegetation. |
| Geology | Underwater in Mesozoic era (Aakal Fossil Park, ~180 million-year-old marine deposits); Peninsular Plateau extension shaped by weathering, wind. |
| Features | Mushroom rocks, shifting dunes, oases (south); slopes to Sindh (north), Rann of Kachchh (south). |
| Hydrology | Ephemeral rivers; Luni River significant; inland drainage into brackish lakes/playas for salt. |
The Coastal Plains
Western Coastal Plains
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Submerged coast (e.g., Dwaraka submerged). |
| Characteristics | Narrow, ideal for ports; wider north/south, narrower middle. |
| Ports | Kandla, Mazagaon, JLN Port Navha Sheva, Marmagao, Mangalore, Cochin. |
| Divisions | Kachchh/Kathiawar (Gujarat), Konkan (Maharashtra), Goan (Goa), Malabar (Karnataka/Kerala). |
| Features | No deltas; 'Kayals' (backwaters) for fishing, navigation, tourism (e.g., Nehru Trophy Vallamkali, Punnamada Kayal). |
Eastern Coastal Plains
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Emergent coast, broader than western plains. |
| Features | Well-developed deltas (Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri); continental shelf up to 500 km, limiting ports. |
| Ports | Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Kolkata, Paradip. |
The Islands

The document Cheat Sheet: Structure and Physiography | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Geography Class 11.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
70 videos|289 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Structure and Physiography - Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the main geological divisions of India? |  |
Ans. The main geological divisions of India include the Peninsular Block, the Himalayas and other Peninsular Mountains, and the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain. Each of these divisions has distinct topographical features and geological characteristics that contribute to the overall physiography of the country.
| 2. What is the significance of the Peninsular Block in India's geology? |  |
Ans. The Peninsular Block is one of the oldest landmasses in India, primarily composed of crystalline rocks and is characterized by a stable geological structure. It forms the base of the Deccan Plateau and plays a crucial role in the drainage systems of peninsular rivers, significantly influencing the climate and biodiversity of the region.
| 3. How do the Himalayas affect the climate and ecology of India? |  |
Ans. The Himalayas act as a barrier to the cold winds from Central Asia, helping to moderate the climate of the Indian subcontinent. They also contribute to the monsoon system, as they trap moisture-laden winds, resulting in heavy rainfall in the northern plains. This unique geography supports diverse ecosystems, ranging from alpine to subtropical flora and fauna.
| 4. What are the key characteristics of the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain? |  |
Ans. The Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain is characterized by its flat, fertile land formed by the alluvial deposits of the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers. This region is crucial for agriculture due to its rich soil and abundant water supply, and it supports a large population, making it one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
| 5. What distinguishes the Indian Desert from other geographical divisions in India? |  |
Ans. The Indian Desert, primarily the Thar Desert, is distinguished by its arid climate, sandy terrain, and minimal vegetation. Unlike the lush plains or mountainous regions, the desert region experiences extreme temperatures and has adapted flora and fauna. Its unique landscape and climatic conditions shape the lifestyle and culture of the communities living there.
Related Searches
















