NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Chemistry Class 11 > Infographic: Thermodynamics
Infographic: Thermodynamics | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
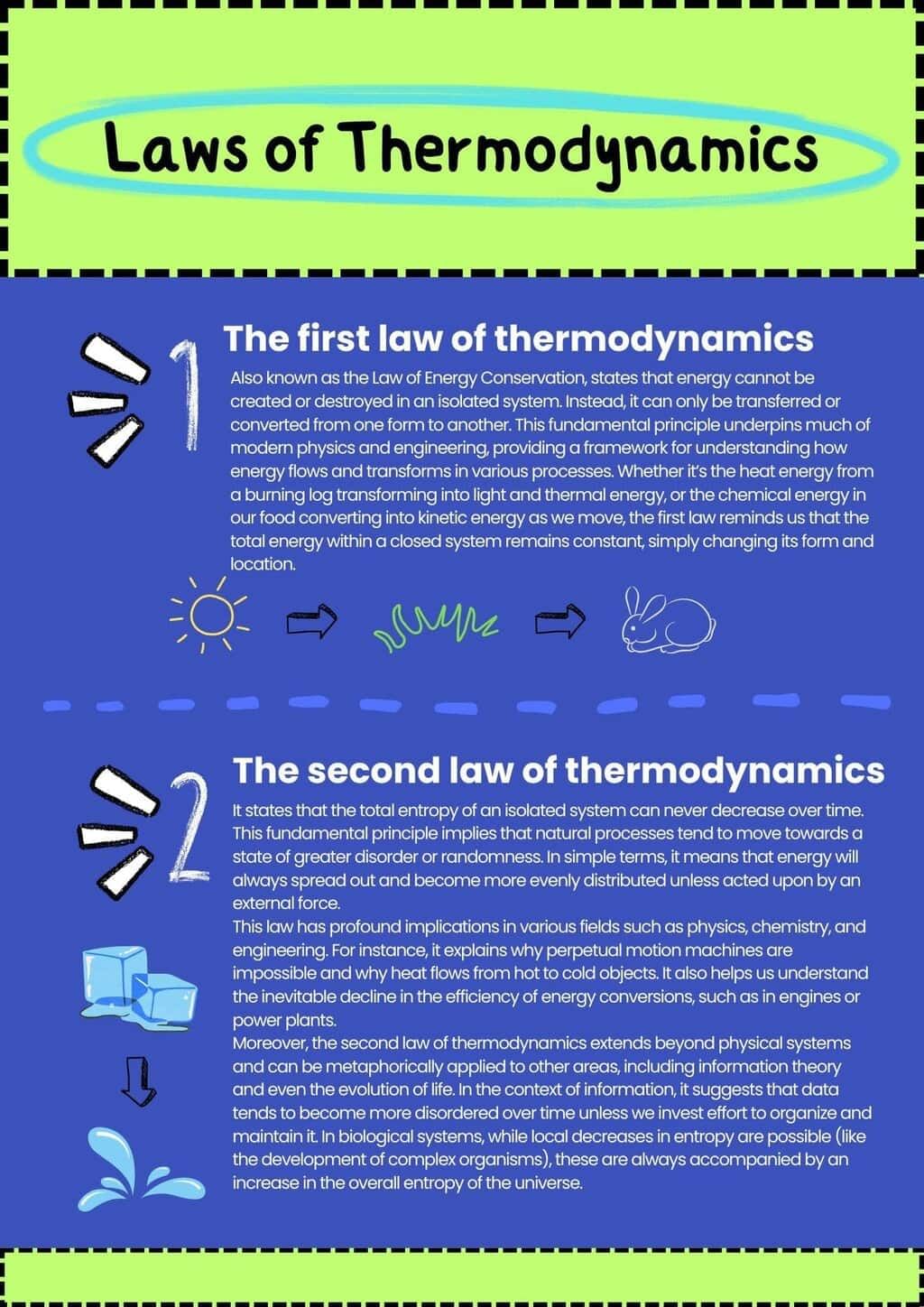

The document Infographic: Thermodynamics | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Chemistry Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Infographic: Thermodynamics - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic laws of thermodynamics? |  |
Ans. The basic laws of thermodynamics include four main principles:
1. The Zeroth Law states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
2. The First Law, also known as the law of energy conservation, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
3. The Second Law states that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time, indicating that natural processes tend to move toward a state of greater disorder.
4. The Third Law states that as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero.
| 2. How is thermodynamic efficiency calculated? |  |
Ans. Thermodynamic efficiency is calculated as the ratio of useful work output to the total energy input. It is expressed as a percentage and can be represented by the formula:
Efficiency = (Useful Work Output / Total Energy Input) × 100%.
Higher efficiency indicates that more of the input energy is being converted into useful work, while lower efficiency suggests more energy is wasted, often in the form of heat.
| 3. What is the significance of entropy in thermodynamics? |  |
Ans. Entropy is a central concept in thermodynamics, representing the degree of disorder or randomness in a system. It is significant because it helps predict the direction of thermodynamic processes. According to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, in any natural process, the total entropy of an isolated system will always increase, indicating that systems evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium and greater disorder over time.
| 4. Can you explain the difference between isothermal and adiabatic processes? |  |
Ans. An isothermal process occurs at a constant temperature, meaning the internal energy of the system remains unchanged as heat is transferred in or out. In contrast, an adiabatic process occurs without any heat transfer between the system and its surroundings. During an adiabatic process, the internal energy of the system changes, which can result in temperature changes as work is done on or by the system.
| 5. What are some real-world applications of thermodynamics? |  |
Ans. Thermodynamics has numerous real-world applications, including:
1. Heat engines, which convert heat energy into mechanical work (e.g., car engines, power plants).
2. Refrigeration and air conditioning systems, which utilize thermodynamic principles to transfer heat from cooler to warmer areas.
3. Chemical reactions, where thermodynamics helps predict the direction and extent of reactions based on energy changes.
4. Biological processes, where thermodynamic principles govern metabolic reactions and energy transfer within living organisms.
Related Searches
















