NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Chemistry Class 12 > Infographic: Chemical Kinetics
Infographic: Chemical Kinetics | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
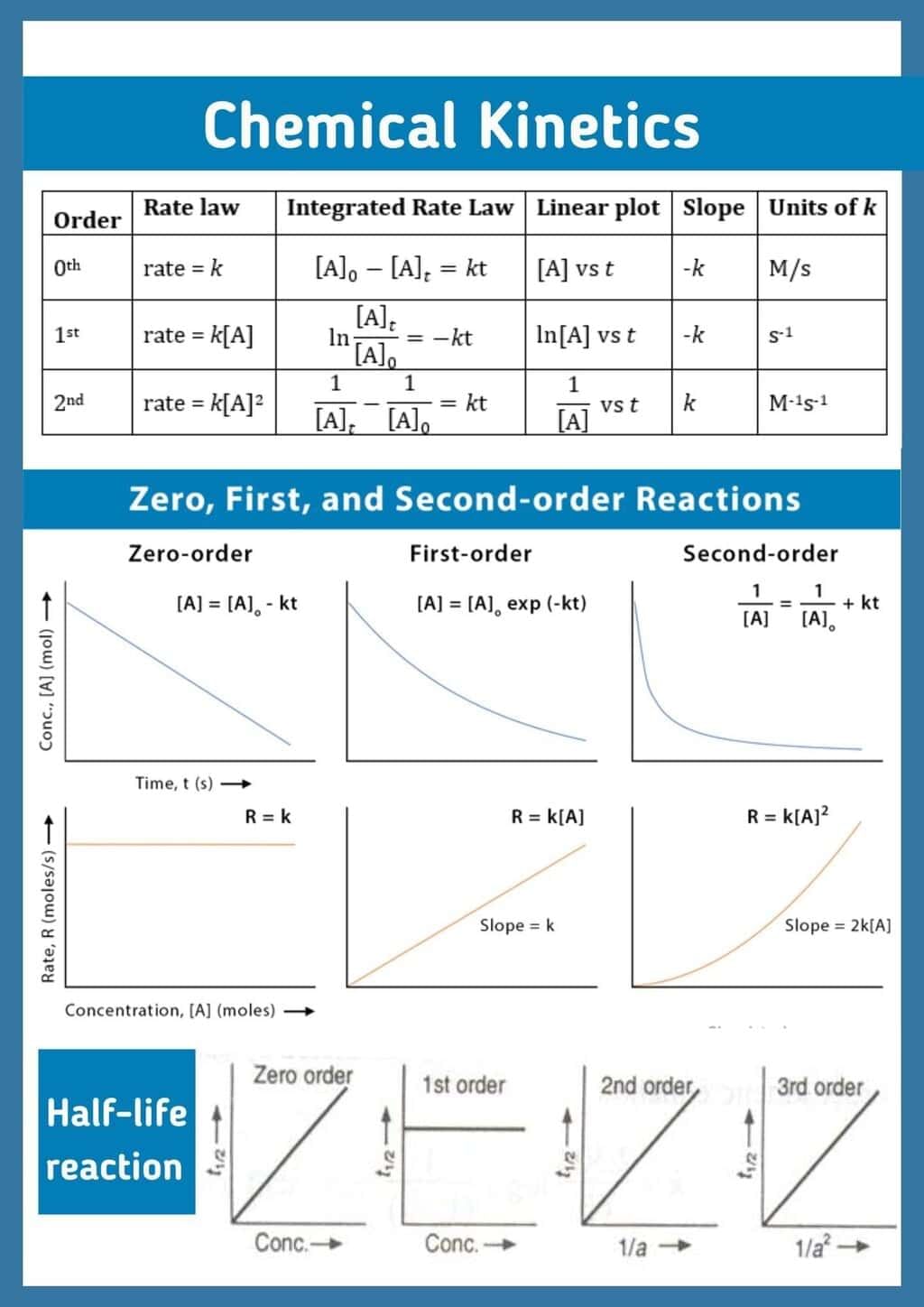
The document Infographic: Chemical Kinetics | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Chemistry Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Infographic: Chemical Kinetics - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is chemical kinetics and why is it important in chemistry? |  |
Ans.Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry that studies the rates of chemical reactions and the factors affecting these rates. It is important because it helps us understand how quickly reactions occur, which is essential in fields like pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and industrial processes. By knowing the kinetics of reactions, chemists can optimize conditions to improve yields and efficiency.
| 2. What factors affect the rate of a chemical reaction? |  |
Ans.The rate of a chemical reaction can be affected by several factors, including temperature, concentration of reactants, surface area, and the presence of catalysts. Higher temperatures usually increase reaction rates by providing more energy to the molecules, while increased concentration can lead to more frequent collisions between reactants. Catalysts speed up reactions without being consumed, and larger surface areas allow more reactant molecules to interact.
| 3. How do catalysts work in chemical reactions? |  |
Ans.Catalysts work by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy compared to the uncatalyzed reaction. This means that more reactant molecules can achieve the energy necessary to react at a given temperature, thus increasing the reaction rate. Catalysts do not alter the overall energy change of the reaction and can be reused multiple times.
| 4. What is the difference between zero-order, first-order, and second-order reactions? |  |
Ans.Zero-order reactions have a constant rate that does not depend on the concentration of the reactants, meaning that the rate remains the same until the reactants are depleted. First-order reactions have a rate that is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant, meaning if the concentration doubles, the reaction rate doubles. Second-order reactions depend either on the concentration of one reactant squared or the product of the concentrations of two different reactants, leading to a more complex relationship between concentration and rate.
| 5. What is the role of the Arrhenius equation in chemical kinetics? |  |
Ans.The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant of a reaction to the temperature and activation energy. It is expressed as k = Ae^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the frequency factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation helps predict how changes in temperature will affect reaction rates and is crucial for understanding reaction mechanisms in chemical kinetics.
Related Searches





















