NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Chemistry Class 12 > Infographic: D and F - Block Elements
Infographic: D and F - Block Elements | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
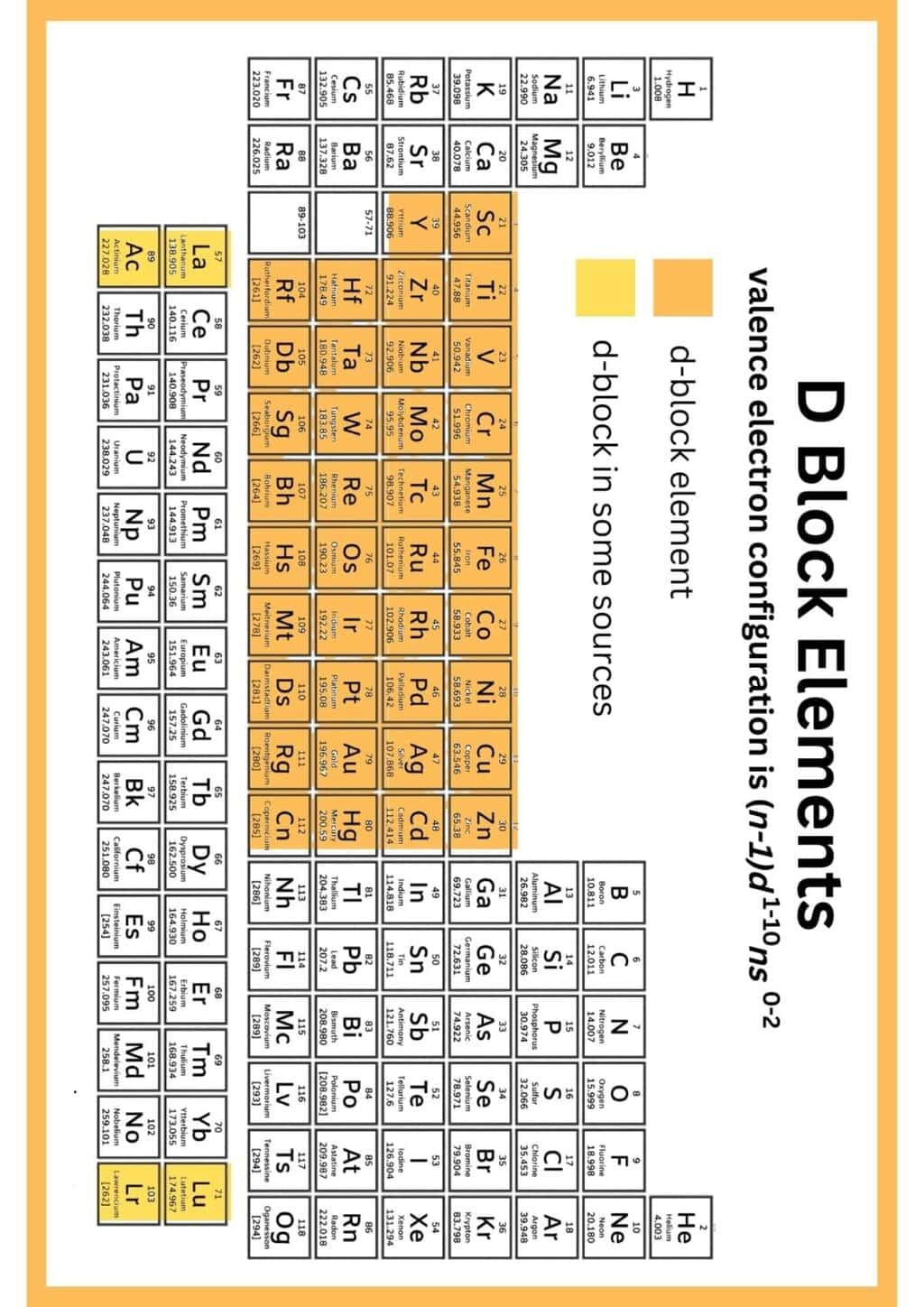
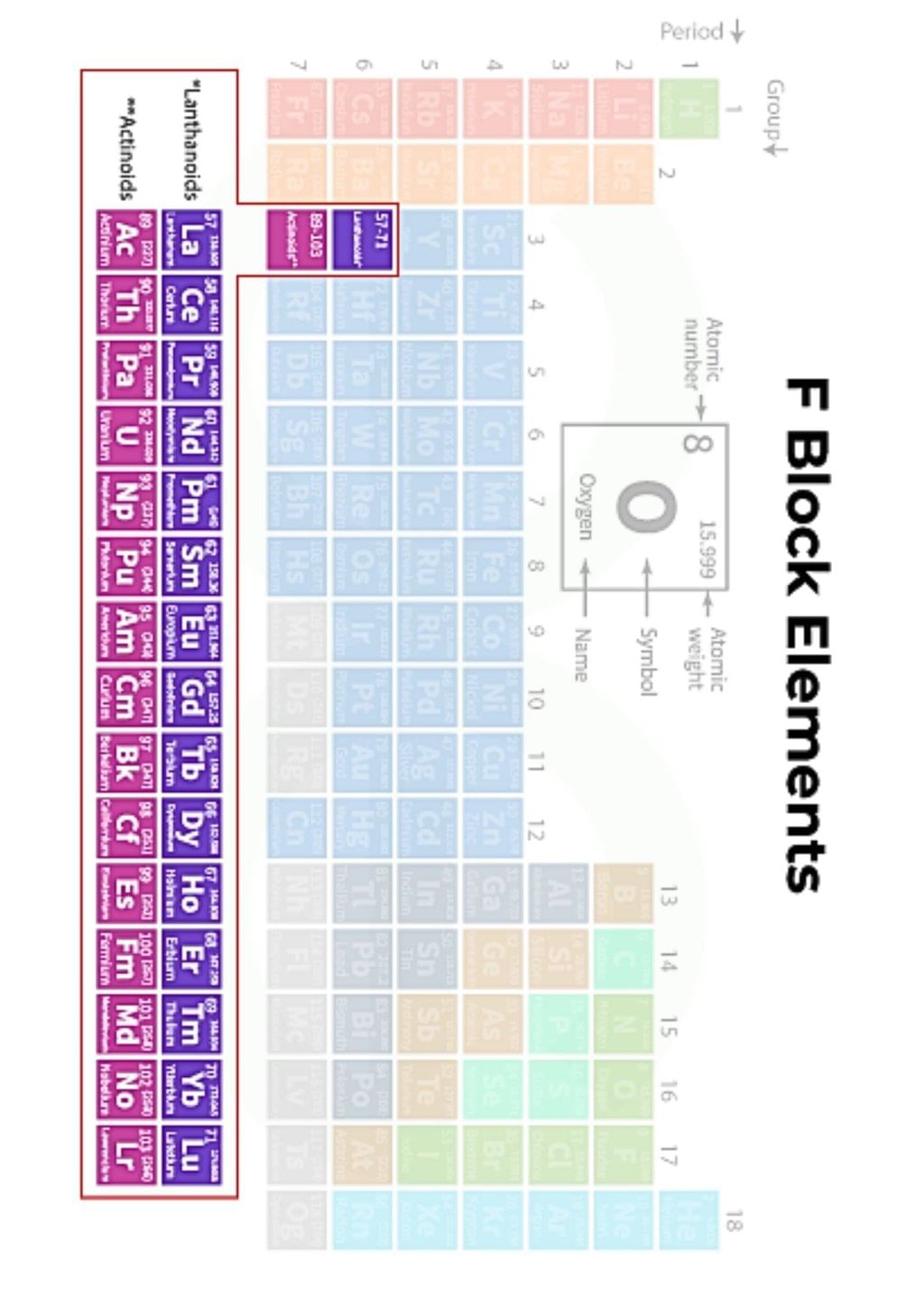
The document Infographic: D and F - Block Elements | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Chemistry Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Infographic: D and F - Block Elements - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are D and F block elements in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. D and F block elements are transition metals and inner transition metals, respectively. D block elements are found in groups 3 to 12 of the periodic table and are characterized by the filling of d orbitals. F block elements, which include lanthanides and actinides, are located at the bottom of the periodic table and involve the filling of f orbitals.
| 2. How do the properties of D block elements differ from those of F block elements? |  |
Ans. D block elements typically exhibit variable oxidation states, good conductivity, and form colored compounds. They are often used as catalysts. In contrast, F block elements tend to have more complex electron configurations, exhibit a wider range of oxidation states, and are often radioactive. They also have important applications in nuclear chemistry and materials science.
| 3. What is the significance of D and F block elements in biological systems? |  |
Ans. D and F block elements play crucial roles in various biological processes. For example, iron (a D block element) is essential for oxygen transport in hemoglobin, while cobalt (another D block element) is vital for vitamin B₁₂. Some F block elements, like cerium, are being studied for their potential in environmental applications, such as catalytic converters.
| 4. What are some common compounds formed by D and F block elements? |  |
Ans. D block elements form a variety of compounds including transition metal complexes, oxides, and halides. For example, Fe₂O₃ (iron(III) oxide) and CuSO₄ (copper(II) sulfate) are well-known compounds. F block elements, such as those from the lanthanide series, often form complex ions and phosphors used in lighting and display technologies.
| 5. How does the atomic size of D and F block elements compare to that of S and P block elements? |  |
Ans. Generally, the atomic size of D block elements is smaller than that of S block elements due to increased nuclear charge, which pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus. F block elements are usually larger than D block elements due to the additional electron shielding effect from the f orbitals. However, trends may vary based on specific elements and their positions in the periodic table.
Related Searches
















