Current Electricity and Magnetism Chapter Notes | General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Electric Components & Their Symbols |

|
| Electrical Circuit & Diagram |

|
| Heating Effect of Electric Current |

|
| The Magnetic Effect of Electric Current |

|
| Electric Bell: Construction and Working |

|
Imagine life without electricity—no lights, no gadgets, no communication. Ever wondered how flipping a switch lights up a room? In this chapter, we’ll explore how electric current works and powers our everyday lives. Let’s uncover the secrets behind this invisible force!
Electric Components & Their Symbols
Electric Components are the parts of an electric circuit that help it function like batteries, switches and bulbs or motors. Each component has a specific role in making the circuit work properly.
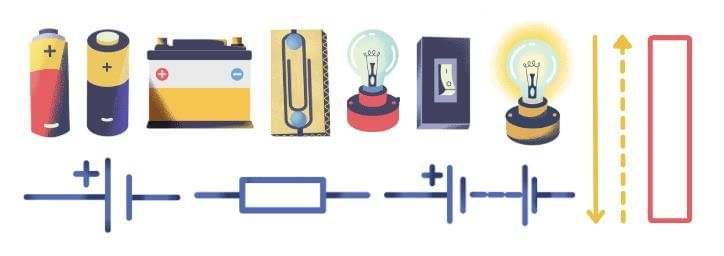
Common Symbols of Electric Components
Electric circuits can be complicated to draw using real components. Therefore, standard symbols are used to represent different electrical components in circuit diagrams.
- Electric Cell: Represented by a longer line (positive terminal) and a shorter, thicker line (negative terminal).
- Battery: A combination of multiple cells, represented by repeating the cell symbol.
- Switch (ON and OFF positions): Represented by different symbols indicating the circuit's status.
- Bulb, Wire: Symbols for these components are also standardized for easy representation.
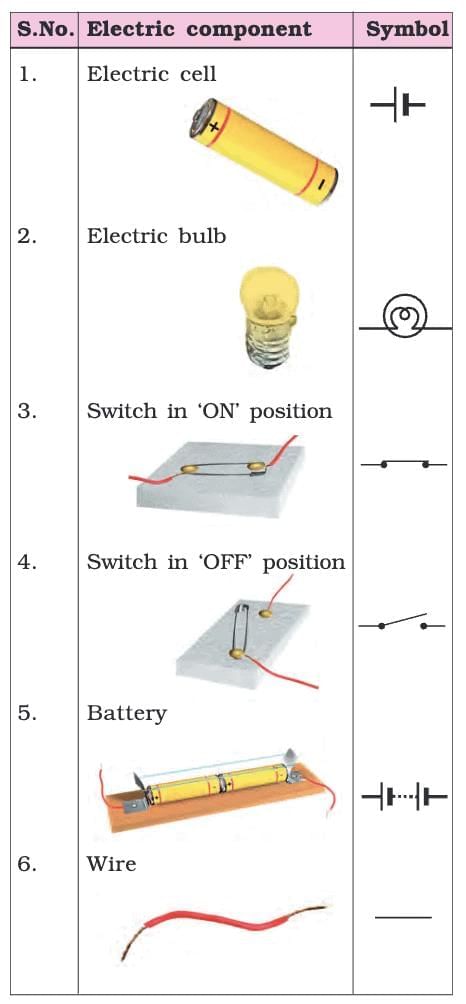
Symbols of various Electric Components
Electrical Circuit & Diagram
An electrical circuit is a closed path formed by the interconnection of electrical components through which electric current flows.
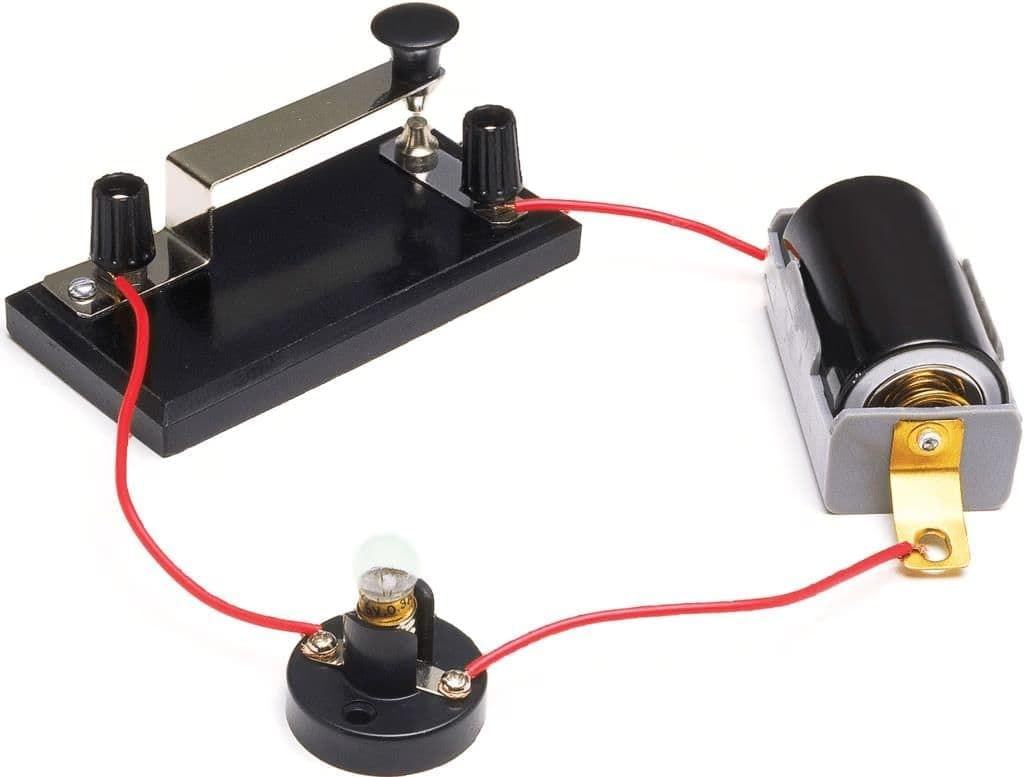

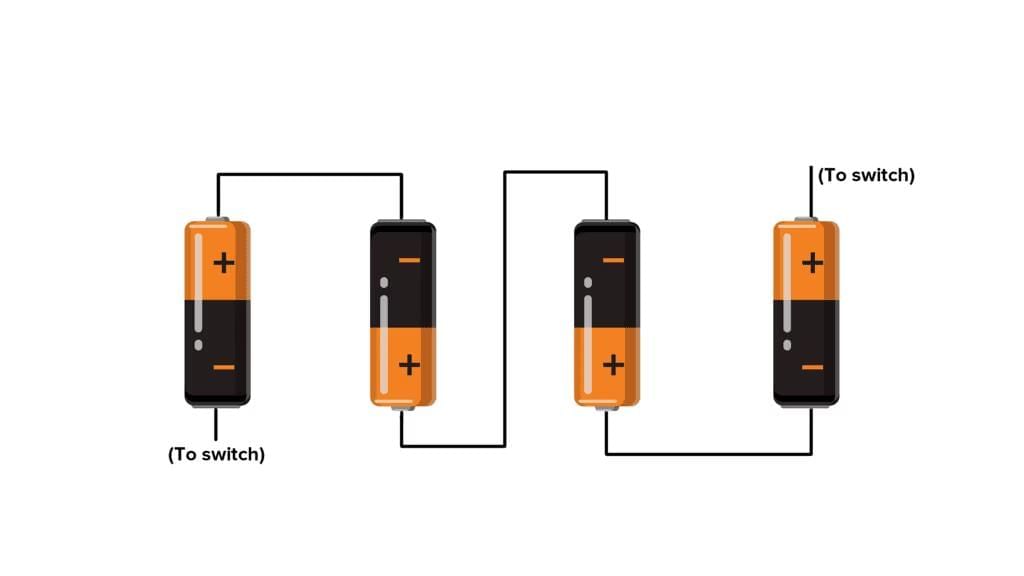
- Power Requirements in a Circuit: When a device like a bulb requires more power than a single cell can provide, it needs to be connected to a battery instead. A battery, which is formed by combining two or more cells, supplies the necessary power for such devices. Therefore, if a circuit demands more power, a battery should be used.
- Battery: A combination of two or more cells connected together is called a battery. It is formed by connecting the positive terminal of one cell to the negative terminal of another and so on. To identify the positive and negative terminals, they are denoted as + and -, respectively. These batteries are used in many devices, such as torch lights, mobile phones, calculators and even automobiles.
- Electric Circuit Diagrams: An electric circuit can be represented on paper using standardized symbols for each component. This representation is known as an Electric Circuit Diagram. The diagram includes a key or switch that controls the flow of electricity and can be placed anywhere within the circuit.
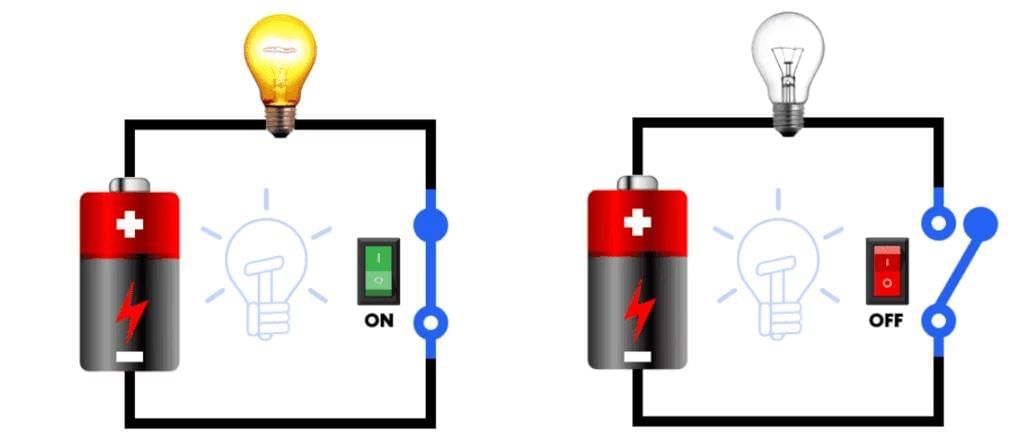 Basic Electric Circuit Diagram
Basic Electric Circuit Diagram - Types of Circuits
Open Circuit: When the key is switched off or in the open position, the circuit is incomplete, and electricity cannot flow, making it an open circuit.
Closed Circuit: When the key is switched on or in the closed position, the circuit is complete, allowing electricity to flow, making it a closed circuit. - The Light Bulb and Its Filament: The electric circuit in the diagram includes a light bulb. Inside the bulb, there is a thin wire called a filament. When electricity flows through the filament, it heats up and produces light. If the filament breaks, the circuit becomes incomplete, causing the bulb to stop glowing as it no longer receives electricity.
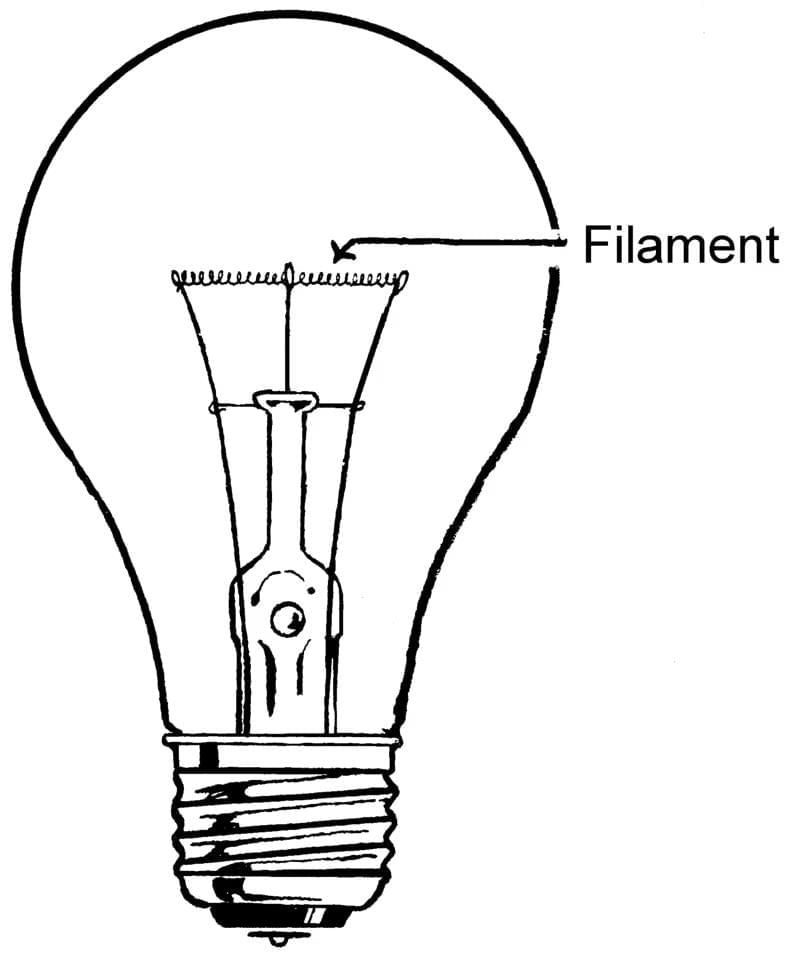
Heating Effect of Electric Current
In the 19th century, James Joule studied a property, which says that "when an electric current flows through the filament of a bulb, it generates heat, and so the bulb becomes hot". This property is named the heating effect of electric current.
Here are some practical applications of Heating Effect of Electric Current:
1. Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL's): Unlike traditional bulbs, which waste energy due to the heating effect, CFLs produce light without relying on heat. They use two electrodes and a fluorescent coating to generate bright light, making them more energy-efficient than ordinary bulbs.
2. Everyday Appliances: Many household appliances operate on the principle of the heating effect of electric current. These include electric room heaters, irons, toasters, hairdryers, roti makers, stoves, immersion heaters, food warmers, coffee makers, rice cookers, and geysers.
3. Heating Elements: These appliances contain coils of wire, known as heating elements, that produce heat when electric current flows through them. The coils often glow bright orange-red due to the intense heat. The type and design of the heating element vary depending on the appliance’s purpose, with some requiring more heat than others.
The Importance of ISI Mark
ISI stands for Indian Standards Institute.
- The ISI mark ensures that products meet specific safety standards.
- Using products with the ISI mark helps guarantee safety and reliability.
- Choosing energy-efficient electrical appliances is advisable to prevent electricity wastage.
- The Bureau of Indian Standards in New Delhi assigns the ISI mark to compliant products.

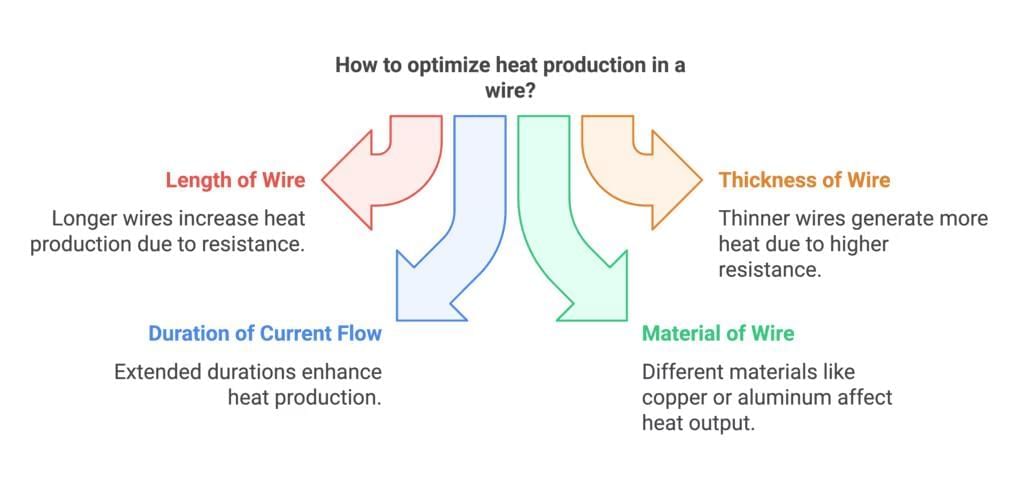
Factors Affecting Heat Production in a Wire
- Length of the Wire: Longer wires produce more heat.
- Thickness of the Wire: Thinner wires generate more heat.
- Duration of Current Flow: Longer durations lead to greater heat production.
- Material of the Wire: Different materials affect the amount of heat produced (e.g., copper vs. aluminum).
Electric Fuse
An electric fuse is a safety device to prevent damage to an electrical circuit when excessive current flows through it. The electric fuse works on the principle of the heating effect of electric current.
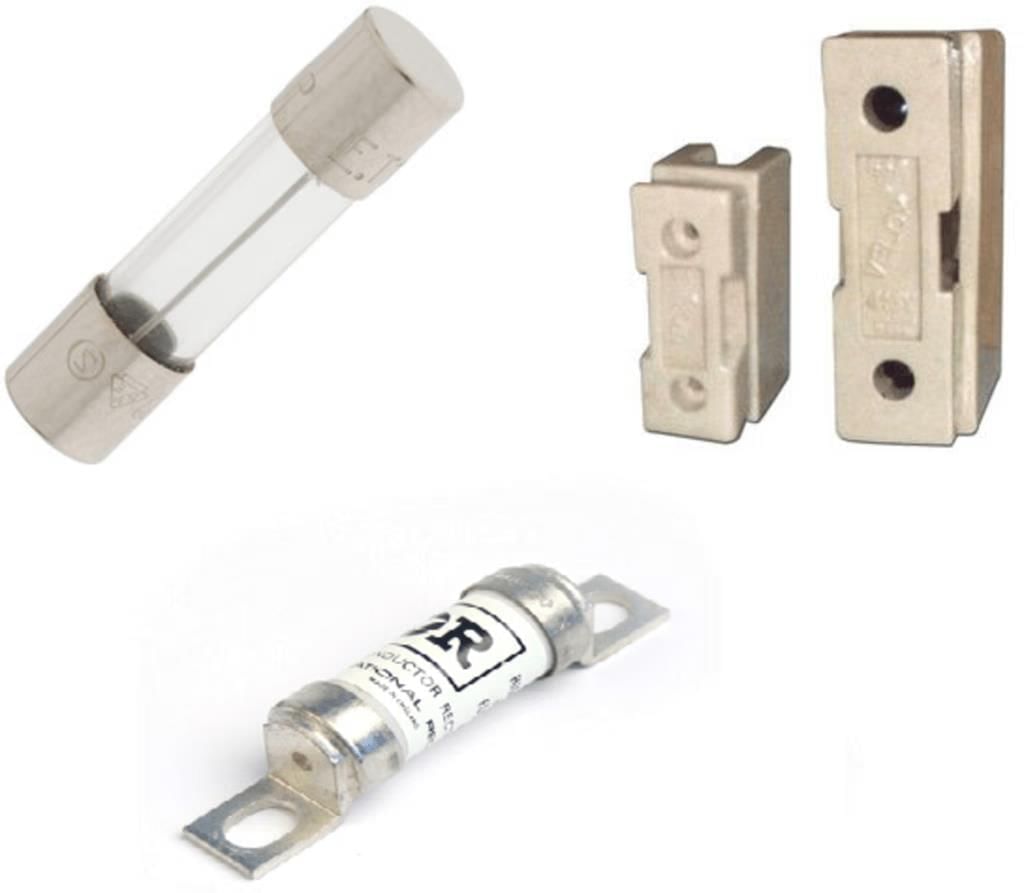

Operation:
- Made of a material that melts when current exceeds a safe limit.
- Melting breaks the circuit, stopping current flow and preventing fires.
Types:
- Some fuses are designed for building circuits.
- Others are made for specific appliances.
Reasons for Excessive Current:
- Overloading: This occurs when too many devices are plugged into one socket, increasing the load.
- Short Circuit: This happens when the insulation on wires is damaged, causing them to touch directly, which can lead to sparks and fires.
Safety Guidelines:
- Always use proper fuses that are specified for particular applications and carry the ISI mark.
- Never replace a fuse with just any wire or piece of metal.
- Consider using Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) as an alternative to fuses; these automatically turn off when the current exceeds a safe limit.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to investigate an electric fuse connected to mains circuits on your own. It is best to seek help from an electric repair shop.
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB)
These days, Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are becoming more popular than fuses. They are automatic switches that turn off when the current in a circuit goes over a safe limit. You can easily turn them back on to restore the circuit. Remember to check for the ISI mark on MCBs.
The Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
When electric current flows through a wire wound around an iron bar, the bar behaves like a magnet.
Electromagnet
When electric current flows through a wire wound around an iron bar, the bar behaves like a magnet. This magnet is called an electromagnet.
- An electromagnet is formed due to the magnetic effect of electric current. This magnetic effect of electric current was discovered by Hans Christian Oersted.
- Once, while preparing for a lecture, he noticed that there was a deflection in the needle of a magnetic compass kept near a wire that was connected to a battery.
- This deflection occurred every time the battery was switched on and off. He realized that a magnetic field is created around a current-carrying wire in a circuit.
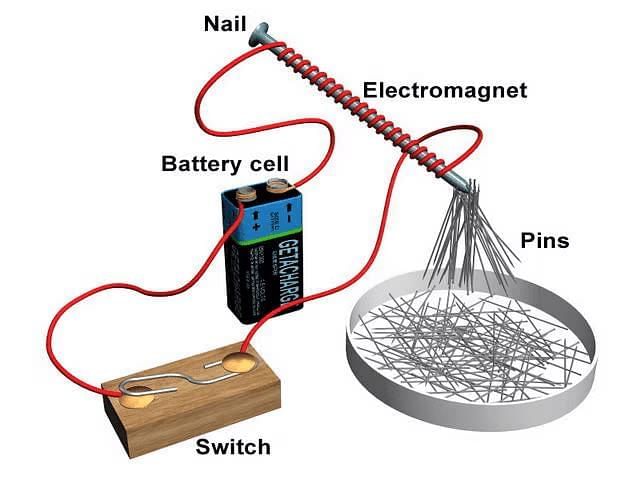
- The components required to create an electromagnet are two pieces of insulated copper wire, a nail, a battery containing two cells, a bulb with a holder, and some paper clips made of iron.
- The bulb is also used for making an electromagnet since it serves as a resistance to the current in the circuit and it prevents the battery from quick discharge.
Construction of an Electromagnet
- Take a nail and wind a copper wire around it without any overlap, as shown in the figure.
- Remove the insulation on the wire at the two ends
- Connect one end of the wire to the battery and the other to one terminal of the bulb holder.
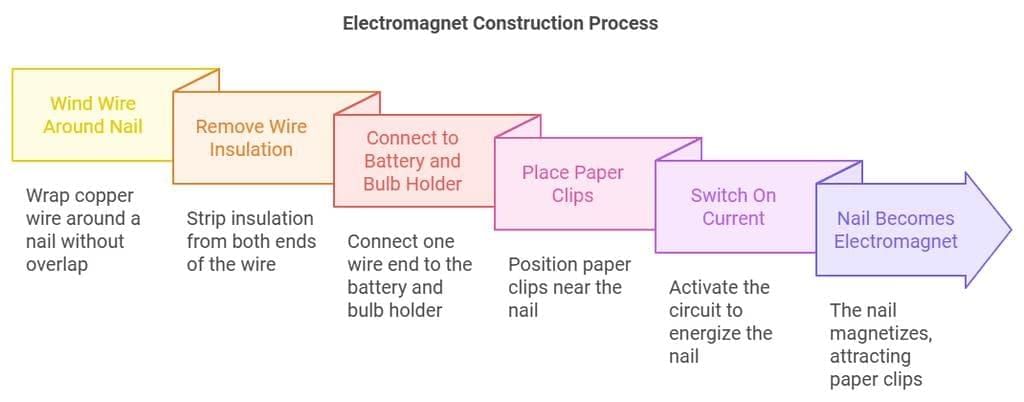
- Connect one end of the second wire to the remaining terminal of the bulb holder and the other end to the battery.
- Place the paper clips near the nail.
- When you switch on the current, the paper clips will cling to the nail. This is because the nail becomes an electromagnet.
- When the battery is disconnected, the nail is no more an electromagnet. The paper clips will not cling to the nail.
Application of Electromagnet
Electromagnets are used in medicines, toys, iron industries, and most commonly in the electric bell. Cranes are used for lifting material, separating iron from scrap in industries, and to lift cars. These work on the principle of the electromagnet. Electromagnets are also used in electromagnetic trains called Maglev's.
Electric Bell: Construction and Working
An electric bell is a device that uses electricity to produce sound, typically used in schools, homes, and offices as a signaling device.Construction
- Electromagnet: A coil of wire wound around an iron core.
- Armature: A piece of iron that moves back and forth.
- Hammer: Attached to the armature, strikes the gong (bell) to produce sound.
- Spring: Returns the armature to its original position after each strike.
- Gong: The metal bell that produces sound when struck by the hammer.
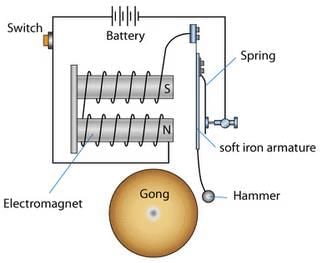
Working
- When the bell switch is pressed, electric current flows through the coil, turning it into an electromagnet.
- The electromagnet attracts the armature, causing the hammer to strike the gong, producing sound.
- As the armature moves, it breaks the circuit, causing the electromagnet to lose its magnetism.
- The spring pulls the armature back to its original position, reconnecting the circuit.
- The cycle repeats as long as the bell switch is pressed, producing a continuous ringing sound.
|
52 videos|175 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Current Electricity and Magnetism Chapter Notes - General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board)
| 1. What are the main electric components and their symbols used in electrical circuits? |  |
| 2. How does the heating effect of electric current work? |  |
| 3. What is the magnetic effect of electric current? |  |
| 4. How does an electric bell work in terms of construction and operation? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of understanding current electricity and magnetism in everyday applications? |  |














