How to Study Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current for NEET | Physics Class 12 PDF Download
Introduction
Electromagnetic induction and alternating current are two important parts of NEET Physics, together worth around 8–14 marks. In electromagnetic induction, you’ll learn how a changing magnetic field creates an emf. Focus on Faraday’s and Lenz’s laws, simple flux calculations, and figuring out polarity fast. In alternating current, you’ll work with sine-wave voltages and currents, learn RMS and peak values, draw phasor diagrams, and understand how resistors, inductors, and capacitors affect the flow. Practice these topics with clear examples and handy shortcuts to build confidence and speed on exam day.
Understanding NEET Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Syllabus
To build a solid foundation, begin by understanding which key topics are covered under this unit in NEET Physics.
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Lenz's Law
Self-Induction and Inductance
Mutual Induction
Alternating Current (AC) Circuits
Power in AC Circuits
Transformers
Eddy Currents
AC Generator
Impedance and Reactance
Focus on Core Concepts
As we have segregated the topics that are in the NEET Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current syllabus, let us focus on the most frequently asked topics for targeted and high-yield preparation
The chart at the beginning illustrates the frequency of subtopics asked from the Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current chapter in NEET exams from 2016 to 2025.
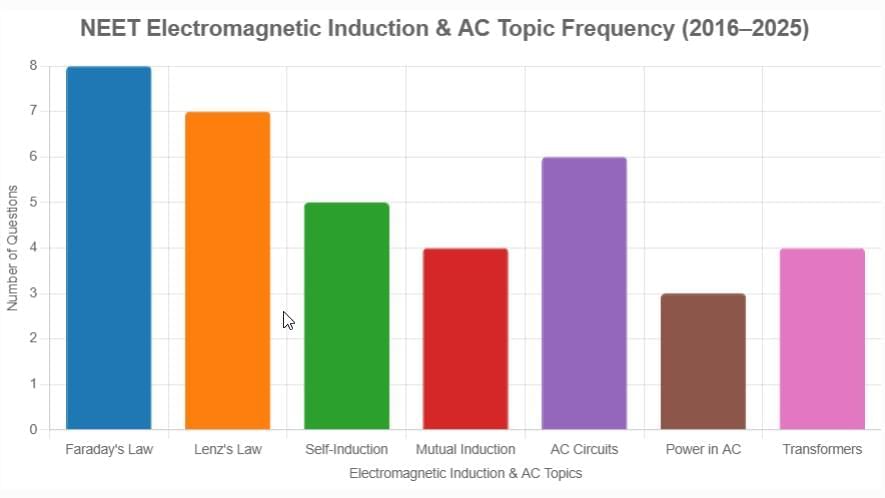
Faraday's Law (8 questions): Induced EMF and magnetic flux changes.
Lenz's Law (7 questions): Direction of induced current and opposition to change.
AC Circuits (6 questions): Resonance, phasors, and circuit analysis.
Self-Induction (5 questions): Inductance in coils and back EMF.
Mutual Induction (4 questions): EMF induced in nearby coils.
Transformers (4 questions): Efficiency and voltage transformation.
Power in AC (3 questions): Power factor and average power.
Eddy Currents (2 questions): Energy loss and applications.
AC Generator (2 questions): Working and output.
How to Study Important Topics
Here’s a breakdown of how to tackle each high-priority topic, with a focus on strategy, problem-solving, and understanding.
Faraday's Law
Focus: Master induced EMF (ε = -dΦ/dt) and its dependence on magnetic flux; understand Faraday's Law of Induction, often tested with coil and magnet problems.
Method: Solve 10–15 problems daily on flux changes, derive the formula, and analyze scenarios like moving magnets.
Lenz's Law
Focus: Grasp the principle that induced current opposes flux change; commonly tested with Lenz's Law applications in loops and coils.
Method: Practice 5–10 problems daily on current direction, using right-hand rule, and visualize magnetic field interactions.
AC Circuits
Focus: Understand resonance, phasors, and impedance (Z = √(R² + (X_L - X_C)²); frequently tested with RLC circuit analysis.
Method: Solve 5–10 problems daily on series and parallel circuits, plot phasor diagrams, and calculate impedance.
Self-Induction
Focus: Learn inductance (L = Φ/I) and back EMF; often tested with self-inductance in solenoids.
Method: Practice 5–10 problems daily on coil inductance, derive L, and analyze energy storage.
Resources for Important Topics
Core Materials: NCERT Physics Class 12 (Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction, Chapter 7: Alternating Current), HC Verma's Concepts of Physics (Electromagnetic Induction), DC Pandey's Objective Physics for NEET.
Supplementary Resource: EduRev app (EduRev) for video lectures, practice questions, and mock tests tailored to NEET preparation.
Memorize and Understand Formulas
A quick reference to key formulas will strengthen both your understanding and application during the exam.

Learning Approach
Develop a formula sheet and derive equations (e.g., Faraday's Law) to deepen understanding.
Use flashcards for quick recall.
Apply formulas in numerical problems to reinforce concepts and avoid rote learning.
Numerical Practice
Consistent numerical practice reinforces theoretical concepts and boosts calculation speed and accuracy.
- Consistent Objective: Keep solving numerical problems alongside each topic you study. Solve 20–30 numerical problems of each high-frequency topic: Faraday's Law, Lenz's Law, AC Circuits, and Self-Induction.
- Problem Sources: DC Pandey's Objective Physics, past NEET question papers, and the EduRev app question banks.
- Strategy Time: Practice sessions to 1–2 minutes per question and maintain an error log to address recurring mistakes.
Analysis of Previous Years Papers
A close review of past NEET questions helps identify trends and refine your approach accordingly.
- Purpose: Identify patterns and difficulty levels in Electromagnetic Induction and AC questions.
- Scope: Review NEET Physics papers from 2016–2025, focusing on Faraday's Law (e.g., coil experiments), AC Circuits (e.g., RLC resonance), and Lenz's Law (e.g., opposing flux).
- Expectation: Anticipate 3–5 questions, with a strong likelihood of Faraday's Law and AC Circuits problems.
- Resource: Utilize EduRev app (EduRev) for past papers.
Mock Test Practice
- Objective: Simulate exam conditions to improve time management and accuracy.
- Goal: Aim for 1–2 minutes per question during timed mock tests.
- Resource: Use EduRev app (EduRev) for mock tests and analyze performance on high-priority topics.
Exam Day Tips
Quick Formula Review: Before the exam, glance at your formula sheet for Faraday's Law, Lenz's Law, and AC Circuits to reinforce key equations.
Prioritize High-Weightage Questions: Start with Faraday's Law and AC Circuits questions, as they are more likely to appear and often solvable with clear formulas.
Time Allocation: Spend 1–2 minutes per question; skip complex numericals initially and return if time permits.
Check Units and Calculations: Ensure units are consistent (e.g., volts for EMF) and double-check multi-step calculations, especially for AC Circuits.
Stay Calm: If stuck on a transformer or impedance problem, take a deep breath and break it into smaller steps (e.g., draw circuit diagrams).
Additional Preparation Strategies
Consistency: Maintain a daily commitment of 2 hours to Electromagnetic Induction and AC for steady progress.
Precision: Verify calculations in multi-step numericals (e.g., AC Circuits, Self-Induction) to minimize errors.
Time Management: Allocate 1–2 minutes per question initially, revisiting complex problems as needed.
Well-being: Prioritize 6–8 hours of sleep, incorporate 5-minute breaks hourly, and maintain a balanced diet to support focus and stamina.
Motivation: Set achievable short-term goals (e.g., mastering Faraday's Law) and acknowledge progress to sustain momentum.
This structured guide, grounded in NEET trends and enriched with targeted strategies, is your ultimate roadmap to conquer Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current. Focus on Faraday's Law, Lenz's Law, AC Circuits, and Self-Induction to maximize your Physics score. Best wishes for your NEET preparation!
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on How to Study Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current for NEET - Physics Class 12
| 1. What are the core concepts of Electromagnetic Induction that students should focus on for NEET? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively memorize and understand formulas related to Alternating Current? |  |
| 3. What strategies can be employed for numerical practice in Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current? |  |
| 4. Why is analyzing previous years' papers important for NEET preparation in Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current? |  |
| 5. What are some effective tips for exam day when tackling questions on Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current? |  |





















