Metals and Nonmetals Chapter Notes | General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board) PDF Download
Everything around us is categorized into either metals or non-metals. Hence, it is important to know what non-metals and metals are and how to distinguish them. We will discuss the various physical and chemical properties of metals and non-metals.
What are Metals?
Metals are minerals or substances that form naturally below the surface of the Earth. Most metals are lustrous or shiny. Metals ate inorganic, which means they are made of substances that were never alive.
- Metals are natural compounds of the earth’s crust, which are generally found in the form of metal ores, associated both with each other and with many other elements.
- They are also naturally present in the rocks washed by surface water and groundwater and in atmospheric dust.
Examples of Metals
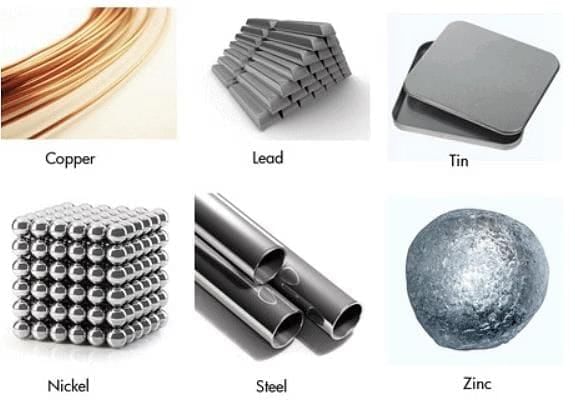

- Metal is very strong and durable and therefore is used to make many things. These are used for making automobiles, satellites, cooking utensils, etc.
- Most metals are hard but some are not. Sodium and potassium are such metals that can be cut by knife whereas mercury is a liquid metal at room temperature. Iron is solid in nature.
Physical Properties of Metals
- Metals are hard to touch.
- Metals are lustrous i.e., freshly Cut surfaces of metals have characteristic shining.
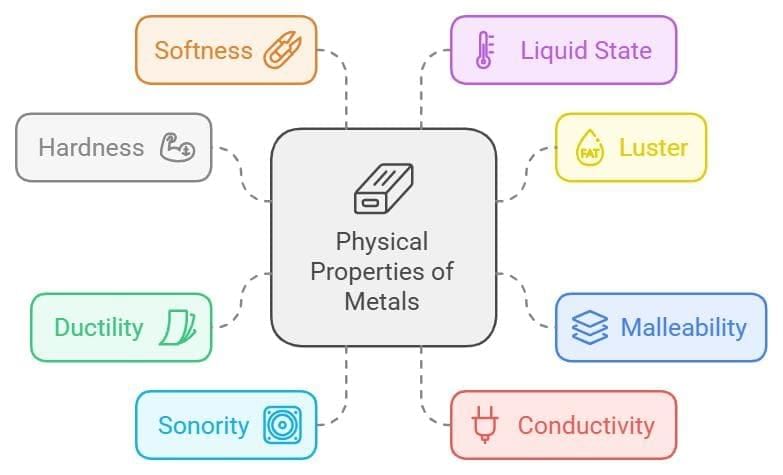
- Metals are malleable; the property of metals by which they can be beaten in thin sheets is called malleability.
- Metals are ductile; the property of metal by which it can be drawn into wires is called ductility.
- Metals are sonorous i.e, metals produce a ringing sound when struck on a hard surface.
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
 Metals
Metals
- Metals like sodium and potassium are soft and can be cut with a knife.
- Mercury is the only metal that is found in the liquid state at room temperature.
What are Non-Metals?
Non-metals are the elements that form negative ions by accepting or gaining electrons. Non-metals usually have 4, 5, 6 or 7 electrons in their outermost shell.
- Non-metals are those which lack all the metallic attributes.
- They are good insulators of heat and electricity. They are mostly gases and sometimes liquid.
- Some of them are even solid at room temperature like Carbon, sulfur and phosphorus.
Physical Properties of Non-Metals
- Non-metals are soft and dull (e.g., coal and sulfur).
- Non-metals are generally brittle, i.e., they break down into a powdery mass on tapping with a hammer.
- They are not sonorous.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
 Non-Metals
Non-Metals
Chemical Properties of Metals & Non-Metals
1. Reaction of Metals with Oxygen
Metals form their oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + oxygen → Metal oxide
Metal oxides are basic in nature.
Example:
- Reaction of Iron metal with oxygen:
When iron reacts with moist air, it forms rust. Rust is iron oxide. Articles made of iron, such as grills, fencing, etc. are getting rusted because of the reaction with moist air.
Iron (Fe) + Water (H₂O) + Oxygen (O₂) → Fe₃O₄·nH₂O Iron(II,III) oxide (Rust) Rust is reddish-brown in colour and is iron oxide. Iron oxide is basic in nature. It turns red litmus blue.
Rust is reddish-brown in colour and is iron oxide. Iron oxide is basic in nature. It turns red litmus blue. - The reaction of Magnesium metal with oxygen:
When magnesium is burnt in the air, it forms magnesium oxide. Burning in the air means reacting with oxygen.
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) → MgO (Magnesium oxide)
Magnesium oxide forms magnesium hydroxide with water. The solution of Magnesium oxide turns red litmus paper blue. This means magnesium oxide is basic in nature.
MgO(s) + H₂O(l) → Mg(OH)₂(aq)
2. Reaction of Non-Metals with Oxygen
Non-metals form their oxides when reacting with oxygen.Non- metal + Oxygen → Non- metal oxide
Thus, Non-metal forms their oxide when reacts with oxygen.
Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature.
- Reaction of sulphur with oxygen:
When sulphur is burnt in the air, it forms sulphur dioxide.
S(s) + O₂(g) → SO₂(g)
The solution of sulphur dioxide turns blue litmus paper red. Sulphur dioxide forms sulphurous acid when dissolved in water. Thus, sulphur dioxide is basic in nature.
SO₂(g) + H₂O(l) → H₂SO₃(aq) - Reaction of carbon with oxygen:
When carbon is burnt in the air, it forms carbon dioxide. You can observe that when coal (carbon) is burnt it forms smoke, which contains carbon dioxide.
C(s) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g)
Carbon dioxide is acidic in nature. The solution of carbon dioxide in water turns blue litmus paper red.
CO₂(g) + H₂O(l) → H₂CO₃(aq)
3. Reaction with Water
Generally, metals form respective hydroxides when they react with water. Some metals react vigorously with water like in the case of sodium. It is stored in kerosene. While some metals react very slowly with water like in the case of iron.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide
- Reaction of sodium metal with water:
Sodium metal vigorously reacts with water and forms sodium hydroxide along with a lot of heat.
2Na(s) + 2H₂O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H₂(g)
 Reaction of Sodium with Water
Reaction of Sodium with Water
- Reaction of potassium with water:
Potassium metal vigorously reacts with water and forms potassium hydroxide along with a lot of heat.
2K(s) + 2H₂O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H₂(g) + Heat
For Non-metals:
Non-metals generally do not react with water. Rather some non-metals that react with air vigorously are stored in water.
4. Reaction with Acid
Metals give hydrogen gas when they react with dilute acid.Metal + Acid → Hydrogen gas
- Reaction of zinc with dilute acid:
Zinc gives hydrogen gas along with zinc chloride when it reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl₂(aq) + H₂(g)
Similarly, zinc gives hydrogen gas along with zinc sulphate when it reacts with sulphuric acid.
Zn(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → ZnSO₄(aq) + H₂(g)
This method is used to produce hydrogen gas in the laboratory. - Reaction of sodium metal with dilute acid:
Sodium gives hydrogen gas and sodium chloride when reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl).
2Na(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H₂(g) - The reaction of Aluminium with dilute acid:
Aluminium gives hydrogen gas along with aluminium chloride when it reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl₃(aq) + 3H₂(g)
Copper does not react with dilute sulphuric acid even on heating, but it reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid. Copper, silver and gold are considered noble metals as do not react with dilute acid.
For Non-Metals: Generally, non-metals do not react with dilute acid.
5. Reaction with Base
Metals give hydrogen gas when they react with a base.
Metal + Base → Hydrogen gas
- Reaction of aluminium metal with sodium hydroxide:
Aluminium metal forms hydrogen gas and sodium aluminate when it reacts with sodium hydroxide.
2Al(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 6H₂O(l) → 2NaAl(OH)₄ + 3H₂(g)
Similarly, zinc gives sodium zincate and hydrogen gas when it reacts with sodium hydroxide.
What is Displacement Reaction?
During reaction, if a metal replaces another metal from its compound then such reactions are called displacement reaction.
Metals can actually be arranged as per their reactivity order, thus, a more reactive metal will always displace a less reactive metal from its compound but a less reactive one cannot replace a more reactive metal.
Metal A + Salt Solution of Metal B → Salt Solution of Metal A + Metal B
In the above equation, metal A is more reactive than metal B.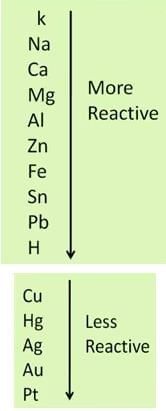
Example:
- When aluminium metal is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate, it forms aluminium sulphate and copper.
2Al(s) + 3CuSO₄(aq) → Al₂(SO₄)₃(aq) + 3Cu(s) - When iron reacts with a solution of copper sulphate, it gives iron sulphate and copper.
Fe(s) + CuSO₄(aq) → FeSO₄(aq) + Cu(s)
In the above two reactions, aluminium and iron are more reactive than copper, that’s why they replace copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
When copper metal is dipped in the solution of aluminium nitrate, no reaction takes place. Because copper is less reactive than aluminium.
Al(NO₃)₃ + Cu → No reaction
Uses of Metals & Non-Metals
Uses of Metals
- Metals are hard, and tough and are used in manufacturing automobiles, machinery, trains, satellites, aeroplanes, and industrial gadgets.

- Due to its characteristic of being a good conductor of electricity and ductility, it is used in making wires, electrical appliances, circuits and many more.

- Being a good conductor of heat it is used in making utensils, and water boilers.

- Gold is used in making ornaments.
- Silver is used in making ornaments.
Uses of Non-Metals
 Uses of Non-Metals
Uses of Non-Metals
- The number of non-metals is very less in comparison to metals and non-metals are more useful for us. So far only 22 non-metals have been discovered.
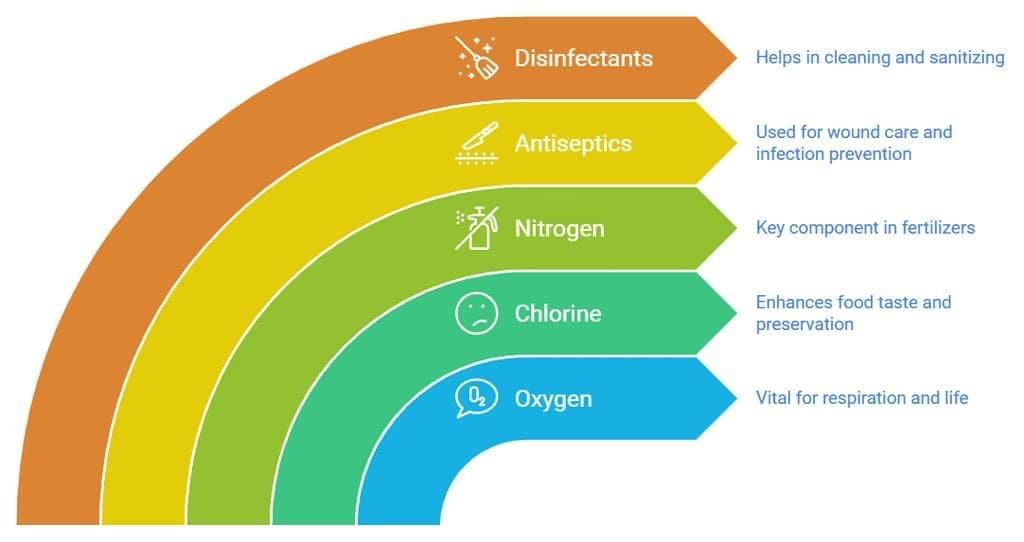
- We breathe oxygen which is non-metal. Without oxygen, no one can live.
- Sodium chloride (common salt) cannot be formed without chlorine (a non-metal) which we use to enhance the taste of food. Without using common salt, food is tasteless.
- Nitrogen is used in making fertilizers.
- It is used as an antiseptic and applied to wounds.
- It is used as a disinfectant.
- It is used in crackers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What is a metal? Mention the physical properties of metals.
Ans: Substances having characteristic properties like malleability, ductility, sonority, conductivity, lustre, – and solidness are called metals. For example, aluminium, copper, zinc, iron, etc
The physical properties of metals are:
- Malleable
- Lustre
- Sonorous
- Ductile
- Solid
- Good conductor of heat and electricity
Q.2. What are non-metals? What are the physical properties of non-metals?
Ans: Substances that are soft and dull, i.e., non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-ductile, non-malleable, and poor conductors of heat and electricity are called non-metals. For example, oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, etc.
The physical properties of non-metals are:
- Non-malleable
- Non-sonorous
- Non-lustrous, i.e., dull in appearance
- Non-ductile
- Poor conductor of heat and electricity
Q.3. How do metals and non-metals react with water?
Ans: Metals produce their hydroxides or oxides and hydrogen when they react with water. Sodium and potassium react with cold water producing a large amount of heat. Magnesium reacts with boiling water and iron with steam. Gold, silver, and platinum do not react with water. Non-metals do not react with water.
|
52 videos|175 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Metals and Nonmetals Chapter Notes - General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board)
| 1. What are the primary differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of common metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 4. What is a displacement reaction and how does it occur with metals and non-metals? |  |
| 5. What are some common uses of metals and non-metals? |  |





















