Reflection of Light Chapter Notes | General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board) PDF Download
What Makes Things Visible?
Have you ever wondered how are we able to see the world around us? And why is it difficult to see things at night?
Light is a type of energy that helps us see different things in our surroundings. We see an object when light from that object enters our eyes. Some objects produce their own light, like the sun and a bulb, while others just reflect light. Therefore, we can sort all objects into:
- Luminous objects that create their own light, such as the sun, bulb, and tube light.
- Non-luminous objects that do not emit light on their own but reflect light from other sources, like the moon (which reflects sunlight), trees, tables, and paintings.
Reflection of Light
- The ray of light which falls on the mirror surface is called an incident ray.
- The point at which the incident ray strikes the mirror is called the point of incidence.
- The ray of light which is sent back by the mirror is called the reflected ray.
- The ‘normal’ is a line drawn at right angles to the mirror surface at the point of incidence.
- The angle between the incident ray and normal is called the angle of incidence.
- The angle between the reflected ray and normal is called the angle of reflection.
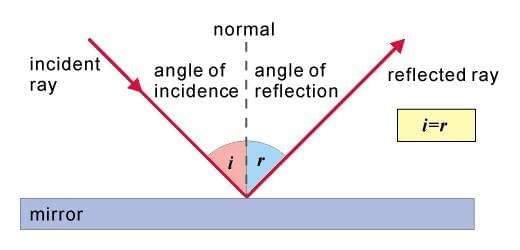 Reflection of Light by a Plane Mirror
Reflection of Light by a Plane Mirror
Laws of Reflection
- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal (at the point of incidence), all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence.
Image Formation in a Plane Mirror
Have you ever wondered how are we able to see images in the mirror? It is when the light on the mirror is reflected to the eyes. Let's learn about this step-by-step:
- Imagine a light source O with rays OA and OB hitting the mirror.
- When we draw normals from points A and B, the light reflects back to our eyes along rays AC and BD.
- If we extend these reflected rays backwards, they seem to meet at a point 'I'.
- This means a virtual image of point O is formed at I. This type of image cannot be captured on a screen.
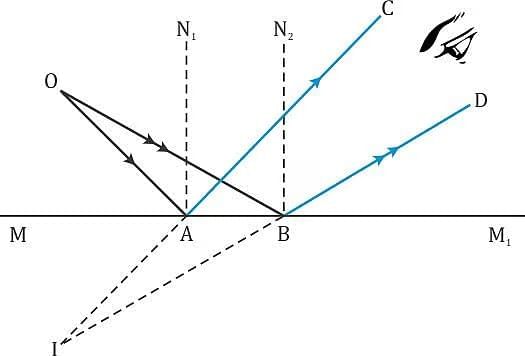 Image Formation in a Plane Mirror
Image Formation in a Plane Mirror
Properties of the image formed:
- The image obtained is virtual.
- The image is laterally inverted. Lateral inversion is when the left and right sides of an image are flipped when you look at it in a mirror.
- The image is erect.
- The size of the image is the same as the size of the object.
- The distance between the image obtained from the mirror is the same as the distance between the object from the mirror.
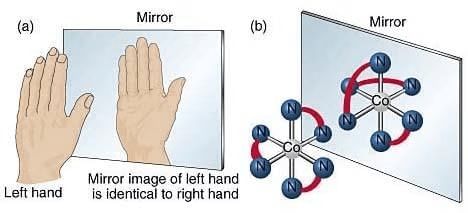 Plane Mirror
Plane Mirror
Regular and Diffused Reflection
Light undergoes either diffuse or regular reflection.
Regular Reflection
- Surface Type: Occurs on smooth, shiny surfaces like mirrors or calm water.
- Reflection Behavior: The reflected rays remain parallel to each other.
- Image Formation: Produces a clear and sharp image, like the reflection you see in a mirror.
- Example: Looking at yourself in a mirror.
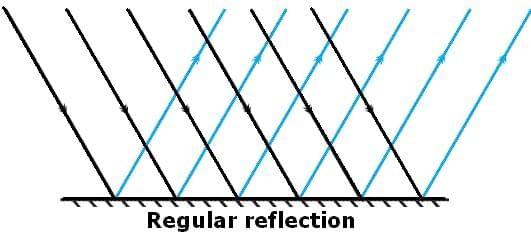
Diffused Reflection
- Surface Type: Occurs on rough, uneven surfaces like paper, wood, or a wall.
- Reflection Behavior: The reflected rays scatter in many different directions.
- Image Formation: Does not produce a clear image; instead, it causes the surface to look uniformly lit.
- Example: Light reflecting off a wall or a piece of paper.
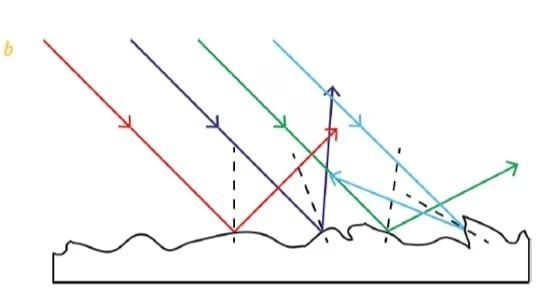 Diffused Reflection
Diffused Reflection
Reflected Light can be Reflected Again
Imagine you are at your hairdresser's. To show you how it looks from the back, the hairdresser uses two mirrors. 
How It Works:
1. First Mirror (Behind You):
- The hairdresser holds up a mirror behind your head. The light from your haircut reflects off this mirror.
- But since this mirror is behind you, you can't see the reflection directly.
2. Second Mirror (In Front of You):
- There is another mirror in front of you. The light that reflected off the mirror behind you now reflects off this mirror as well.
- This second reflection sends the image of your haircut to your eyes.
Result:
- The light bounces (or reflects) twice—first off the mirror behind you, then off the mirror in front of you.
- Because of this double reflection, you can see the back of your head in the front mirror.
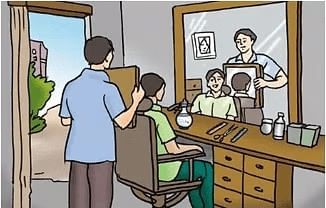 Multiple reflections of light
Multiple reflections of light
Based on the same principle, a cool device called periscope has been innovated.
Periscope
A periscope is a device that uses a long tube and mirrors, and lets you see things that are hidden or out of sight, like over a wall.
How a Periscope Works
- It has two mirrors inside a long tube.
- The top mirror catches light from the object and sends it down to the second mirror.
- The second mirror reflects the light into your eyes, allowing you to see what's on the other side.
- For instance, in a submarine, a periscope lets you view above the water while staying hidden below.
Multiple Images
- When two or more mirrors are placed at an angle to one another, we can see multiple images of an object.
- If two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle q, then the number of images formed in them is given by the formula:
No. of images formed = (360°/q) - 1. - If the given two mirrors are at a right angle to each other, 3 images will be obtained. If the given mirrors are at 60° angle, we shall get 5 images.
- When the two mirrors are kept opposite and parallel to each other, we will get an infinite number of images formed.
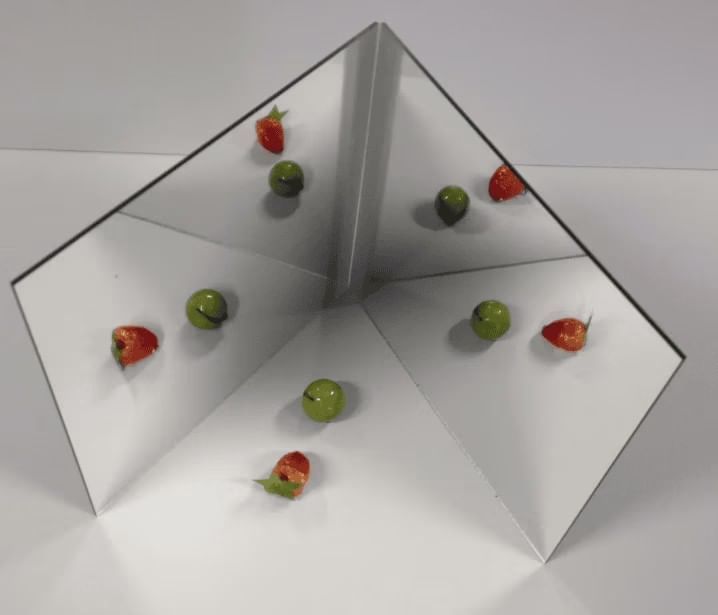 Multiple images formed by mirrors
Multiple images formed by mirrors
Kaleidoscope
The kaleidoscope is an instrument which produces multiple reflections of coloured glass pieces (or coloured plastic pieces) and creates beautiful patterns.
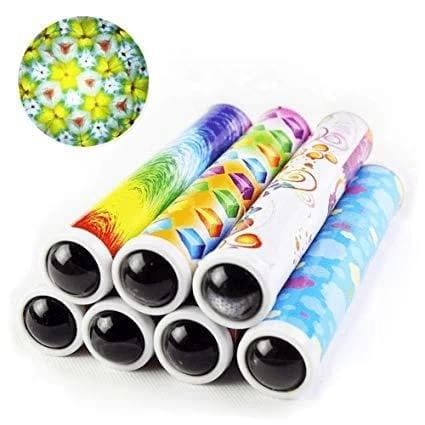 Kaleidoscope changing pattern of colourful images
Kaleidoscope changing pattern of colourful images
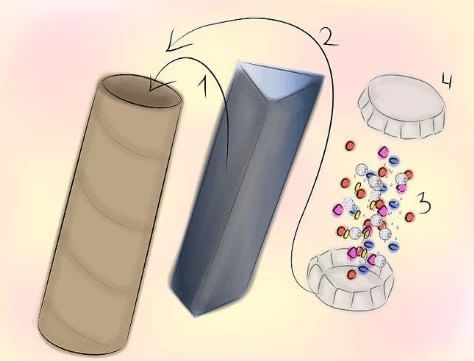
How to Make a Kaleidoscope
- Get three rectangular mirrors, about 15 cm long and 4 cm wide.
- Join them to form a prism and place this in a circular cardboard tube that is slightly longer than the mirrors.
- Seal one end with a cardboard disc that has a hole for viewing.
- For durability, attach a piece of transparent plastic under the disc.
- At the other end, attach a circular glass plate and add small pieces of coloured glass, like broken bangles.
- Close this end with a ground glass plate, allowing space for the pieces to move.
- Your kaleidoscope is now ready; looking through the hole will reveal various patterns.
 Patterns formed by Kaleidoscope
Patterns formed by Kaleidoscope
Sunlight - White or Coloured?
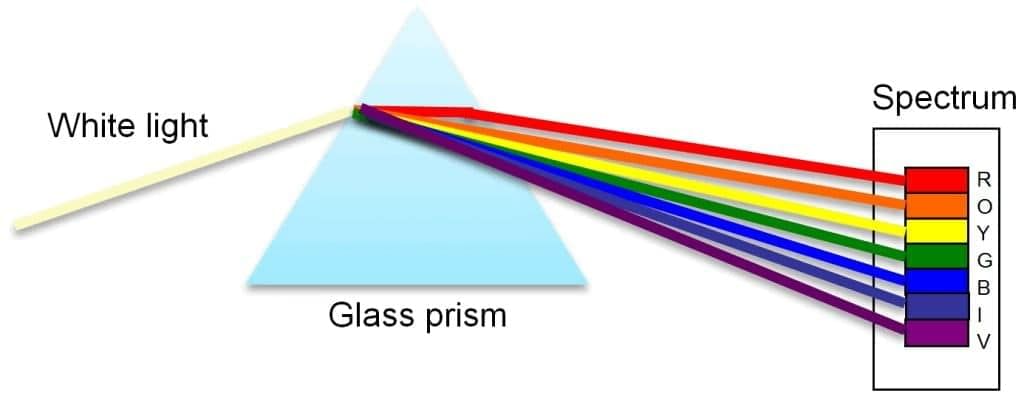
The splitting up of white light into seven colors on passing through a transparent medium like a glass prism is called dispersion of light. The seven colours of the spectrum of white light are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red.
 Dispersion of Light
Dispersion of Light
What is Inside our Eyes?
We are able to see when light enters our eye. Are you curious to know how does your eye sees everything? The eye is one of our most vital sense organs, so understanding its structure and function is essential.
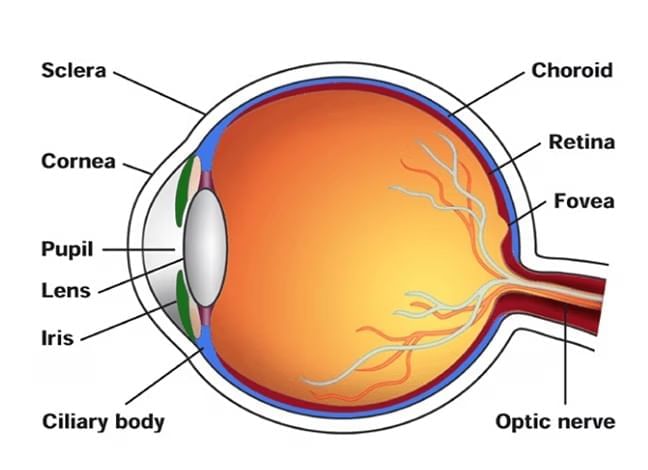
Let us start by understanding the main parts of the human eye. These are:
- Cornea
- Iris
- Pupil
- Ciliary muscles
- Eye lens (which is a flexible convex lens)
- Retina
- Optic nerve
 Human Eye
Human Eye
Working of the eye
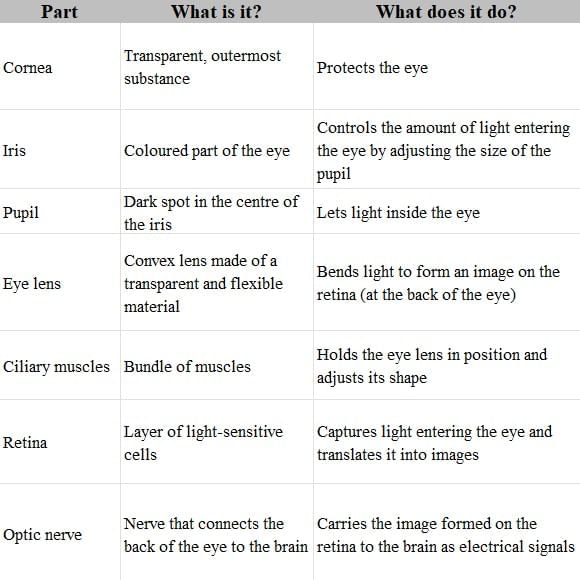
- Cornea is made of a transparent substance
- The light coming from an object enters into the eye through cornea. Function of cornea is to protect the eye.
- Iris is the colored part of the eye. The iris has a hole at its centre which is called pupil.
- Pupil appears like a dark spot in the centre of iris because no light is reflected from it. Iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of pupil.
- The eye-lens is a convex lens made of a transparent and flexible material.
- The eye-lens is held in position by ciliary muscles. The function of ciliary muscle is to hold the lens & changes its size according to the need.
- The retina is a screen on which the image is formed in the eye.
- The optic nerve carries the image formed on retina to the brain in the form of electrical signals.
 Parts of the Eye and their Functions
Parts of the Eye and their Functions
Rods and Cones
- Rods are the rod-shaped cells present in the retina of an eye which are sensitive to dim light.
- Cones are the cone-shaped cells present in the retina of an eye which are sensitive to bright light. Cones also cause the sensation of color of objects in our eyes.
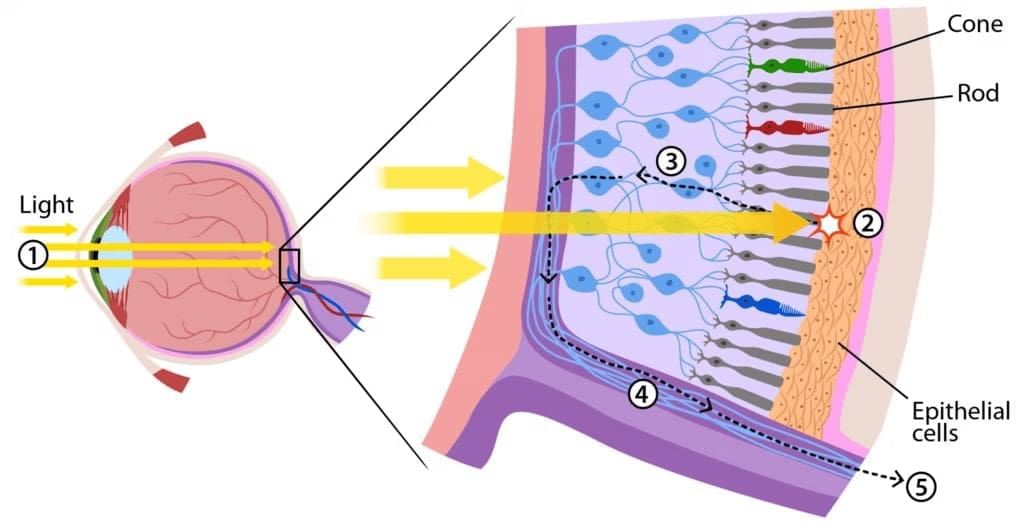
Blind Spot
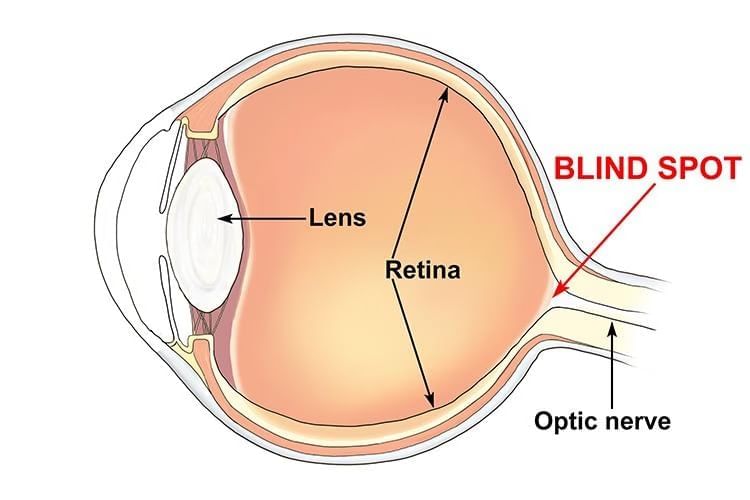 Blind Spot
Blind SpotPersistence of Vision
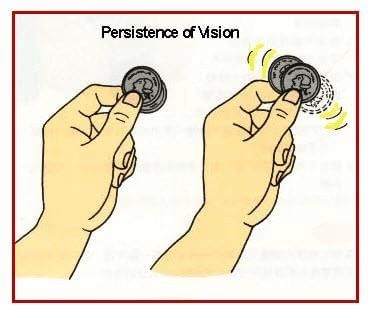 Persistence of Vision
Persistence of VisionDefects of the Eye
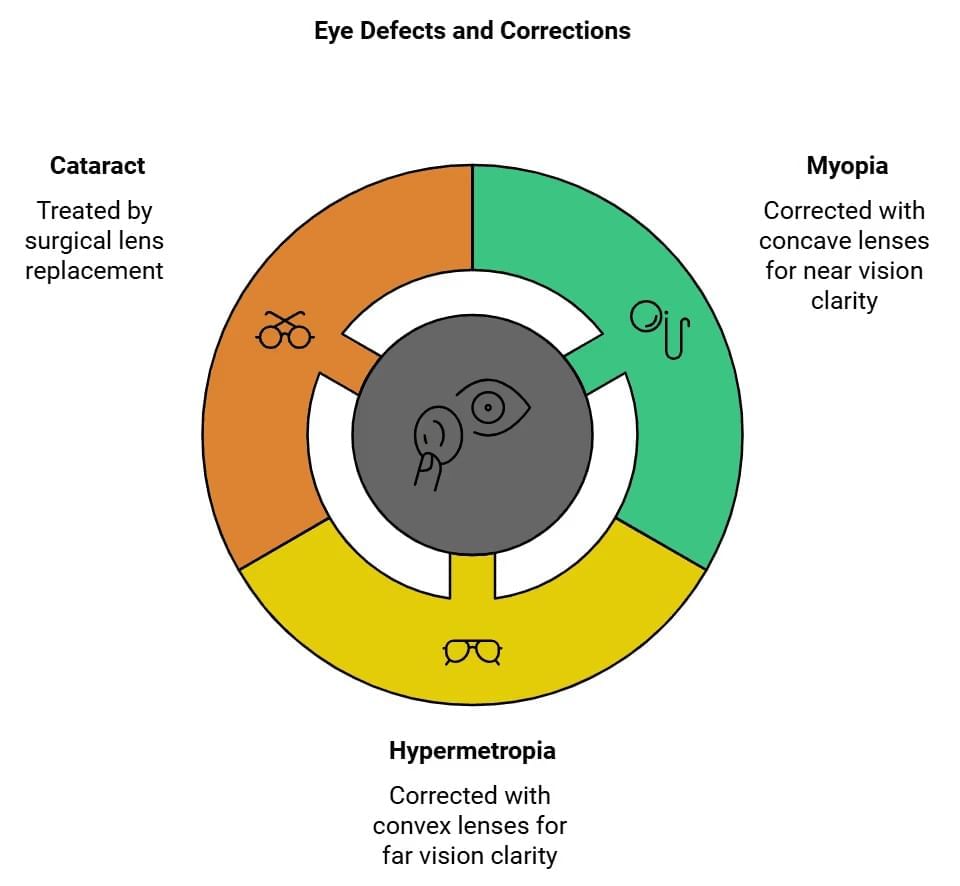
- Myopia (short-sightedness) : In this defect the person is able to see the near by objects but not able to see the far-off objects.
This defect can be corrected by using spectacles containing Concave lens. - Hypermetropia (Far-sightedness) : In this defect the person is able to see the far-off objects but not able to see the near by objects.
This defect can be corrected by using spectacles containing Convex lens. Myopia and Hypermetropia
Myopia and Hypermetropia - Cataract: Cataract develops when the eye lens of person becomes cloudy (or even opaque) due to the formation of membrane over it. Cataract decreases the vision of the eye gradually. It can even lead to total loss of vision of the eye. The opaque lens is removed from the eye of the person by surgical operation & a new artificial lens is inserted in its place.
Care of the Eyes
- It is necessary that we take proper care of our eyes. If there is any problem we should go to an eye specialist.
- Too little or too much light is bad for eyes. Insufficient light causes eyestrain and headaches. Too much light, like that of the sun, a powerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina.
- Never rub eyes. If particles of dust go into eyes, wash eyes with clean water. If there is no improvement go to a doctor. Wash eyes frequently with clean water.
- Always read at the normal distance for vision. Do not read by bringing book too close to eyes or keeping it too far.
- Lack of vitamin A in foodstuff is responsible for many eye troubles. Most common amongst them is night blindness. One should, therefore, include in the diet components which have vitamin A. Raw carrots, broccoli and green vegetables (such as spinach) and cod liver oil are rich in vitamin A.
Visually Challenged Persons can Read and Write
Some individuals, including children, may have visual impairments. They may have very limited vision or be completely blind from birth or due to illness or injury. These individuals often:
- Identify objects by touching and listening closely.
- Enhance their other senses.
- Benefit from additional resources to further develop their skills.
What is the Braille System?
- Louis Braille, who was visually impaired himself, created a system for the blind and introduced it in 1821.
- The Braille (Reading system for blind people ) system consists of 63 dot patterns or characters, with each character representing a letter, a group of letters, a common word, or a punctuation mark.
- Dots are organised in cells containing two vertical rows of three dots each.
- A Braille code exists for various languages, mathematics, and scientific notation, and many Indian languages can also be read using this system.
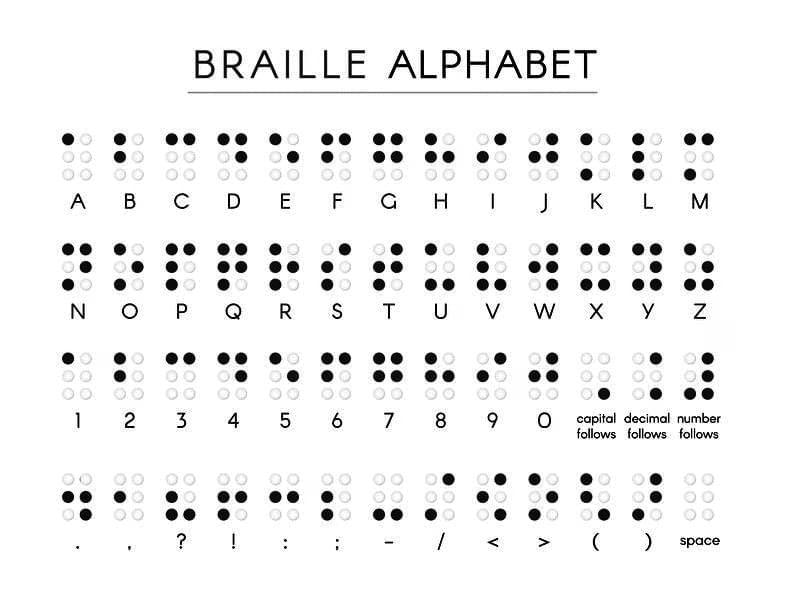
These dot patterns, when raised on Braille sheets, enable visually impaired individuals to recognise words through touch. The dots are slightly elevated to facilitate this.
People with visual impairments learn the Braille system starting with letters, followed by special characters and combinations. The learning process relies on touch recognition, requiring memorisation of each character. Braille texts can be created manually or using machines, including typewriter-like devices and printing machines.
Some visually impaired individuals in India have achieved remarkable success. Diwakar, a child prodigy, has delivered incredible singing performances. Ravindra Jain, who was completely blind from birth, earned his Sangeet Prabhakar degree from Allahabad and excelled as a lyricist, singer, and music composer. Lal Advani, also visually impaired, founded the Helen A. Keller Association for the special education and rehabilitation of disabled individuals in India and represented the country on Braille issues at UNESCO.
Helen A. Keller, a renowned American author and lecturer, is perhaps the most famous inspiring figure among the visually impaired. She lost her sight at just 18 months old but, through determination, graduated from university and authored several books, including "The Story of My Life" (1903).
|
52 videos|175 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Reflection of Light Chapter Notes - General Science Class 8 (Maharashtra Board)
| 1. What are the laws of reflection and how do they apply to everyday life? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between regular and diffused reflection? |  |
| 3. How does a periscope work? |  |
| 4. Why is sunlight referred to as white light, and can it be separated into colors? |  |
| 5. What are common defects of the eye, and how can they be corrected? |  |















