Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science and Technology Class 10 (Maharashtra SSC Board) > Chapter Notes: Periodic Classification of Element
Periodic Classification of Element Chapter Notes | Science and Technology Class 10 (Maharashtra SSC Board) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Dobereiner’s Traids |

|
| Newland’s Law of Octaves |

|
| Mendeleev’s Periodic Table |

|
| Modern Periodic Table |

|
Introduction
- Matter exists in various forms, including elements, compounds, and mixtures.
- Elements are the most basic units of matter, consisting of only one type of atom. Examples include sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), and gold (Au). There are currently 118 known elements, each with its own distinct properties.
- To make studying these elements easier, scientists group them based on similarities in their properties.
Dobereiner’s Traids
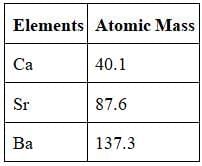
- When elements were arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses, groups of three elements (known as traids), having similar chemical properties are obtained.
- The atomic mass of the middle element of the triad was roughly the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements.
Limitations of Dobereiner’s Traids
- Limited Scope: Dobereiner's Triads only applied to a small number of elements (around 20) and couldn't explain the properties of many other elements.
- Inconsistent Pattern: The triad pattern of elements with similar chemical properties did not always hold, especially for heavier elements, leading to exceptions and inconsistencies.
- No Atomic Structure Explanation: Dobereiner's triads did not consider atomic structure or the role of atomic number in determining element properties, which later led to the development of the periodic table based on atomic number.
Newland’s Law of Octaves
- Newland arranged the known elements by increasing atomic mass and observed that the properties of every 8th element were similar to those of the 1st element.
- This pattern was likened to musical octaves, hence it was named the 'Law of Octaves.'
- For example, the properties of lithium (Li) and sodium (Na) were found to be similar.
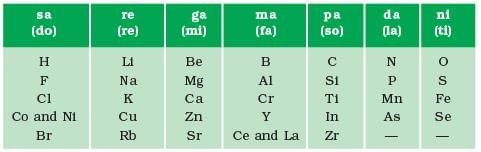 Limitations of Newland’s Law of Octaves
Limitations of Newland’s Law of Octaves
- It was applicable upto calcium (for lighter elements only).
- Properties of new discovered elements did not fit into the law of octave.
- To fit elements into his table, Newlands put even two elements together in one slot and that too in the column of unlike elements having very different properties.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- When elements are arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses, the element with similar properties occur at regular intervals.
- The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.
- Mendleev’s periodic table is based on the chemical properties of elements. It contains 7 periods (horizontal rows) and 8 groups (vertical columns).
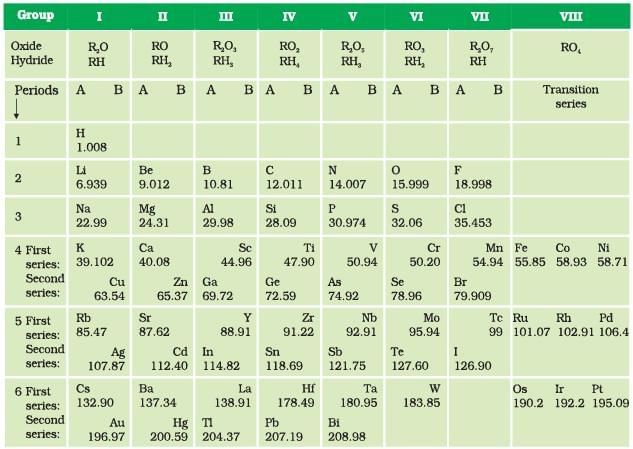
Merits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Some gaps were left for the undiscovered elements like gallium (Ga), Scandium (Sc) and Germanium (Ge).
- Predict properties of elements on the basis of their positions in the periodic table.
- Accommodate noble gases when they were discovered without disturbing the original arrangement.
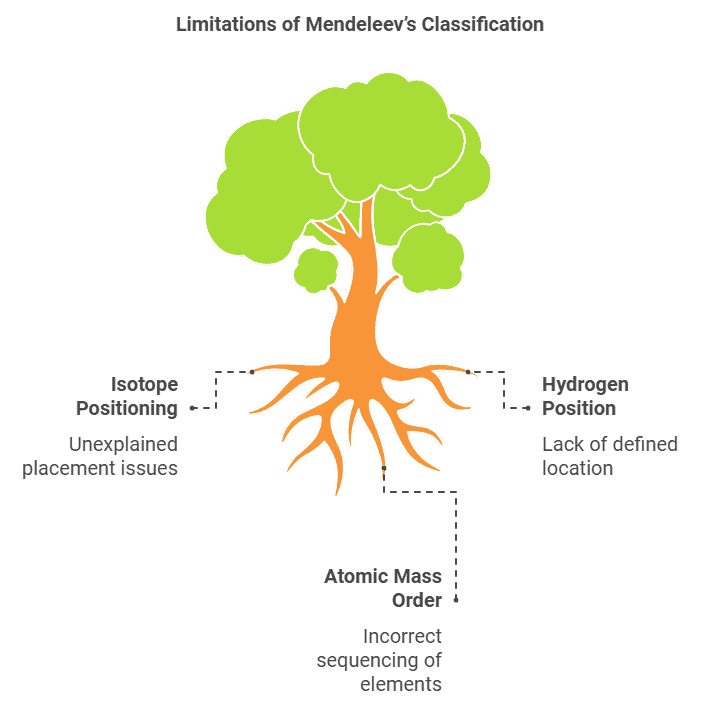
Modern Periodic Table
- Atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
- According to the Modern Periodic law: The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
- All the anomalies of Mendeleev’s classification disappear.
Explanation of the Anomalies by Modern Periodic Table
- Explanation for the position of isotopes (Same atomic number put at one place in the same group).
- Cobalt with atomic number 27 came first and nickel (28) should come later.
- Unlike atomic masses, atomic number is always a whole number, so there is no element between hydrogen and helium.
- Atomic Number: It is denoted by Z and equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Modern Periodic table has 18 vertical columns known as ‘groups’ and 7 horizontal rows known as ‘periods’.
- Elements with same number of valence electrons are placed in the same group.
Example:
Li : 2, 1
Na : 2, 8, 1
K : 2, 8, 8, 1 - Outermost or valence shell in all the three contains 1 electron. These elements have been placed in the same group.
- Number of shells increases as we go down the group.
- Elements with same number of occupied shells are placed in same period.
- For example, Li (2, 1); Be (2, 2); B (2, 3), C (2, 4), N(2, 5). These elements have same number of shells (two).
- Each period marks a new electronic shell getting filled.
- Number of elements placed in a particular period depends upon the fact that how electrons are filled into various shell.
- Maximum number of electrons that can be filled in a shell is given by 2n2 where n is shell number.
Example:
K shell n = 1 or 2n2 = 2(1)2 = 2 (First period has 2 elements.)
L shell n = 2 or 2n2 = 2(2)2 = 8 (Second period has 8 elements.) - Position of an element in the periodic table tells us its chemical reactivity.
- Valence electron determine the kind and number of bonds formed by the element.
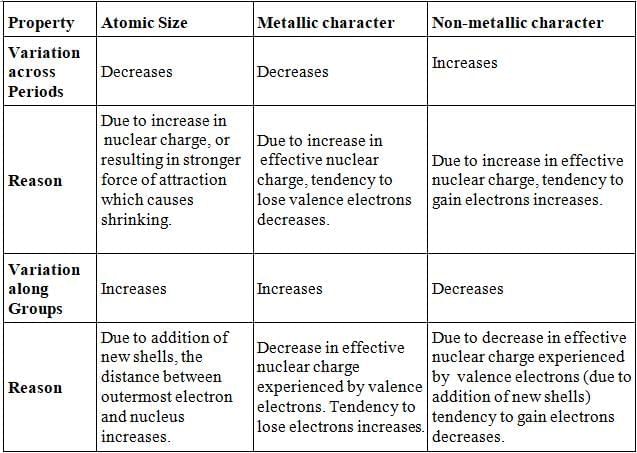
Trends in the Modern Periodic Table
- Valency: No. of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of its atom. On moving from left to right in each period, the valency of elements increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to 0.
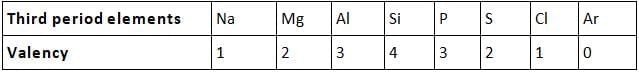 Valency remains the same down in a group.
Valency remains the same down in a group.
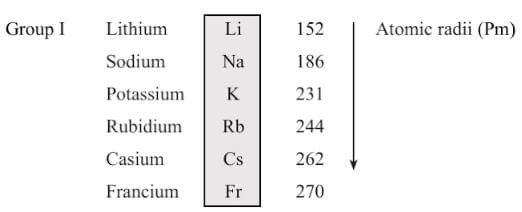
- Atomic size: Atomic size refers to the radius of an atom. It may be visualized as the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell.
- Atomic size or radius of an atom decreases as we move from left to right in a period because due to large +ve charge on the nucleus, the electrons are pulled in more close to the nucleus and size decreases.
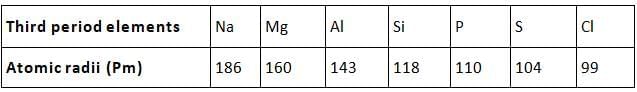
- Atomic size increases as we move down the group because new shells are being added and this increases the distance between nucleus and outermost electron.
Metallic Character
- Metallic character means the tendency of an atom to lose electron.
- Metals occupy the left hand side of the periodic table.
- On moving left to right in a period, the metallic character of an element decreases because the effective nuclear charge increases. It means tendency to lose electron decreases.
- Metals are electropositive as they tend to lose electrons while forming bonds.
- Metallic character increases as we go down a group as the effective nuclear charge is decreasing.
Non-metallic Character
- Non-metals are electronegative as they tend to form bonds by gaining electrons.
- Non-metals occupies the right side of the periodic table.
- Non-metallic character increases across a period because due to increase in effective nuclear charge that means tendency to gain electron increase.
- Non-metallic character decreases as we move down a group due to decrease in effective nuclear charge experienced by the valence electron thus the tendency to gain electron decreases.In
- the middle of periodic table we have semi-metals or metalloid because they exhibit some properties of metals and non-metals.
- Oxides of metals are basic in nature while oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature.
Atomic size, Metallic character and non-metallic according to Periodic table
The document Periodic Classification of Element Chapter Notes | Science and Technology Class 10 (Maharashtra SSC Board) is a part of the Class 10 Course Science and Technology Class 10 (Maharashtra SSC Board).
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
26 videos|131 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Periodic Classification of Element Chapter Notes - Science and Technology Class 10 (Maharashtra SSC Board)
| 1. What are Dobereiner's Triads and how do they relate to the periodic classification of elements? |  |
Ans. Dobereiner's Triads are a grouping of three elements discovered by Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner in the early 19th century. He observed that when elements were arranged in groups of three, the atomic mass of the middle element was approximately the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements. This concept was significant as it was one of the first attempts to classify elements based on their properties, laying the groundwork for the development of the periodic table.
| 2. Can you explain Newland’s Law of Octaves and its significance in the periodic classification? |  |
Ans. Newland’s Law of Octaves, proposed by John Newlands in 1865, states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, every eighth element shares similar properties, much like musical octaves. This law highlighted the periodicity of element properties, although it had limitations, such as not accommodating all known elements at the time. Nonetheless, it was an important step toward the eventual formulation of a more comprehensive periodic table.
| 3. How did Mendeleev's periodic table differ from the modern periodic table? |  |
Ans. Mendeleev's periodic table, created by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 19th century, was organized based on increasing atomic mass and grouped elements with similar properties together. He also left gaps for undiscovered elements, predicting their properties. In contrast, the modern periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number, which resolves some inconsistencies found in Mendeleev’s arrangement, and incorporates knowledge of electronic configuration, leading to a clearer understanding of element behavior.
| 4. What is the significance of the modern periodic table in chemistry? |  |
Ans. The modern periodic table is crucial in chemistry as it organizes all known elements based on their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. This organization allows scientists to predict the characteristics and behaviors of elements, understand chemical reactions, and recognize trends such as electronegativity and atomic radii. It serves as a fundamental tool for chemists in both education and research.
| 5. How do the concepts established by early scientists like Dobereiner and Newlands contribute to our current understanding of the periodic table? |  |
Ans. The ideas proposed by early scientists like Dobereiner and Newlands were foundational in the development of the periodic table. Their observations about the relationships between element properties and atomic masses spurred further research and led to more systematic approaches in classifying elements. Their work paved the way for Mendeleev and eventually the modern periodic table, illustrating the evolution of scientific thought and the importance of systematic classification in understanding the natural world.
Related Searches














