Grade 6 Exam > Grade 6 Notes > Science for Grade 6 > Chapter Notes: Types of Reproduction
Types of Reproduction Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 6 PDF Download
Introduction
Reproduction is how living things, like animals and plants, make new living things. This chapter explains two main types of reproduction: asexual and sexual. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and creates offspring that are exactly like the parent. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and creates offspring that are different from both parents. We will learn how sea stars, plants, and other organisms reproduce, and the advantages and disadvantages of each type. This helps us understand how life continues and grows in nature.
How can one organism make more organisms?
- Regeneration is when a new organism grows from a piece of the parent. For example, Sea stars increased in number even after being cut up. This happens through a process called regeneration.
- Some plants can also reproduce without seeds, using parts like leaves or stems. This is called vegetative reproduction, a type of asexual reproduction.
- Asexual reproduction means one parent or part of it makes a new organism. The new organism is exactly the same as the parent in its genes.
How do other organisms reproduce asexually?
- Many plants, animals, and other organisms can reproduce asexually. Not all organisms use the same way to reproduce asexually.
- Hydra, a small water animal, reproduces by budding. Budding is when a new organism grows on the parent’s body.
Why do some organisms have two parents?
- In asexual reproduction, offspring are exactly like the parent.
- In sexual reproduction, offspring are not exactly like their parents.
- Offspring from two parents have different traits, like eye or hair color.
- Sexual reproduction combines genetic material from two parents.
- Each parent gives half of the genes to the offspring.
- Offspring have two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent.
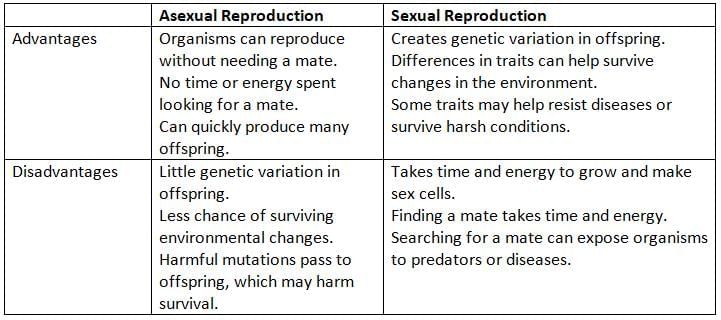
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction?
A Closer Look: Cloning and the Future
- Cloning is a type of asexual reproduction done in a lab.
- It creates identical copies from a cell or group of cells.
- The clone has the same genes as its parent.
- Farmers and scientists use cloning to copy organisms with good traits, like plants with big flowers.
- Scientists have cloned animals like sheep, pigs, deer, and horses.
- The first cloned mammal was a sheep named Dolly, born in 1996.
- Dolly was cloned at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh.
- Cloning helped learn more about making copies of animals.
- In 2001, a gaur, a type of wild cattle, was the first endangered species cloned.
- Cloning does not add genetic variety to a species.
- Some worry about the high cost and ethical issues, like cloning humans.
The document Types of Reproduction Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 6 is a part of the Grade 6 Course Science for Grade 6.
All you need of Grade 6 at this link: Grade 6
|
252 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Reproduction Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 6
| 1. How does a sea star reproduce? |  |
Ans. Sea stars can reproduce both sexually and asexually. In sexual reproduction, male and female sea stars release sperm and eggs into the water, where fertilization occurs. Asexually, some species can regenerate lost arms or even split in half to form new individuals.
| 2. How can one organism make more organisms? |  |
Ans. An organism can reproduce by using methods such as sexual reproduction, where genetic material from two parents combines to create offspring, or asexual reproduction, where a single organism can produce offspring without the need for a partner, often through processes like budding or fragmentation.
| 3. How do other organisms reproduce asexually? |  |
Ans. Many organisms reproduce asexually through methods such as binary fission, budding, and fragmentation. For example, bacteria reproduce by binary fission, where a single cell divides into two identical cells. Yeast can reproduce by budding, where a new organism grows off the parent organism.
| 4. Why do some organisms have two parents? |  |
Ans. Some organisms have two parents because sexual reproduction allows for genetic diversity. By combining genetic material from both parents, the offspring can inherit a mix of traits, which can lead to greater adaptability and survival in changing environments.
| 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Sexual reproduction provides genetic diversity, which can help populations adapt to new challenges. However, it requires more time and energy to find a mate. Asexual reproduction is faster and allows for rapid population growth, but it produces genetically identical offspring, which may be less adaptable to environmental changes.
Related Searches















