Grade 7 Exam > Grade 7 Notes > Science for Grade 7 > Mind Map: Ecosystems
Mind Map: Ecosystems | Science for Grade 7 PDF Download
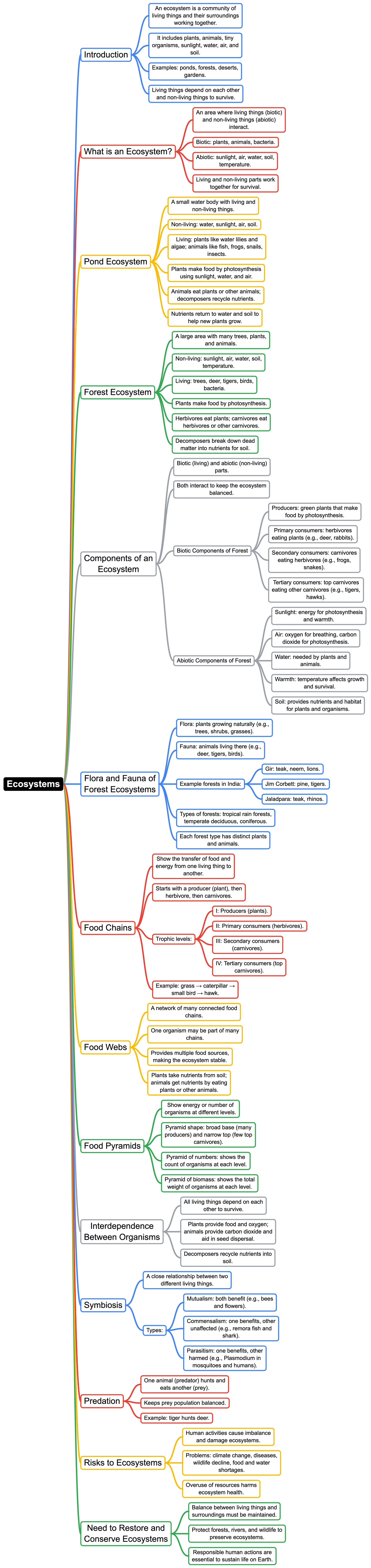
The document Mind Map: Ecosystems | Science for Grade 7 is a part of the Grade 7 Course Science for Grade 7.
All you need of Grade 7 at this link: Grade 7
|
75 videos|160 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Ecosystems - Science for Grade 7
| 1. What is an ecosystem and what are its main components? |  |
Ans. An ecosystem is a community of living organisms (plants, animals, and microorganisms) interacting with their physical environment (air, water, soil). The main components of an ecosystem include biotic factors (living things) and abiotic factors (non-living things). Biotic factors include producers (plants), consumers (herbivores, carnivores), and decomposers (fungi, bacteria). Abiotic factors include sunlight, temperature, water, soil, and nutrients.
| 2. How do energy and nutrients flow in an ecosystem? |  |
Ans. Energy flow in an ecosystem follows a one-way path, starting from the sun, which is captured by producers during photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to consumers when they eat the producers and subsequently to higher-level consumers. Nutrients, however, cycle within the ecosystem. Decomposers break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil, where they can be reused by plants, thus completing the nutrient cycle.
| 3. What roles do producers, consumers, and decomposers play in an ecosystem? |  |
Ans. Producers, mainly plants, are the foundation of an ecosystem as they convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Consumers, including herbivores and carnivores, rely on producers and other consumers for energy. Decomposers, like fungi and bacteria, play a crucial role in breaking down dead matter and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, ensuring its sustainability.
| 4. What is the significance of biodiversity in ecosystems? |  |
Ans. Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms within an ecosystem and is crucial for maintaining ecological balance. High biodiversity enhances ecosystem resilience, allowing it to recover from disturbances. It also ensures a greater variety of resources, such as food and medicine, and supports essential processes like pollination, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation.
| 5. How do human activities impact ecosystems? |  |
Ans. Human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, pollution, and climate change significantly impact ecosystems. These actions can lead to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and disruption of natural processes. Overexploitation of resources can deplete populations of species, while pollution can harm both land and aquatic ecosystems, threatening the health of organisms and the services ecosystems provide to humanity.
Related Searches
















