Grade 6 Exam > Grade 6 Notes > Science for Grade 6 > Chapter Notes: Reproduction and Growth of Animals
Reproduction and Growth of Animals Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How do animals find mates? |

|
| How are young animals protected? |

|
| What factors affect how baby animals grow? |

|
Introduction
Animals have special ways to find mates, reproduce, and protect their young ones so they can grow strong and healthy. This chapter explores how animals, like birds of paradise, attract mates using dances, sounds, or gifts. It also explains how young animals are kept safe by their parents or through special behaviors. Additionally, we learn about the factors, such as genes from parents and the environment, that affect how baby animals grow into adults. By understanding these processes, we see how animals ensure the survival of their species.
How do animals find mates?
- Animals are choosy about their mates to pass on good traits to their babies.
- They use different strategies to attract and select a mate.
- Some animals, like terns, offer gifts like fish to impress their mates.
Courtship Behaviors
- Animals show behaviors to attract mates, like dancing or singing.
- These behaviors are a way to communicate with potential mates.
- Animals use sounds, lights, chemicals, or body movements to attract mates.
- Some animals compete with others of their species to win a mate.
- Examples include sandhill cranes doing a courtship dance.
- Some animals bring gifts, like food, to get attention from a mate.
Examples of Courtship Behaviors: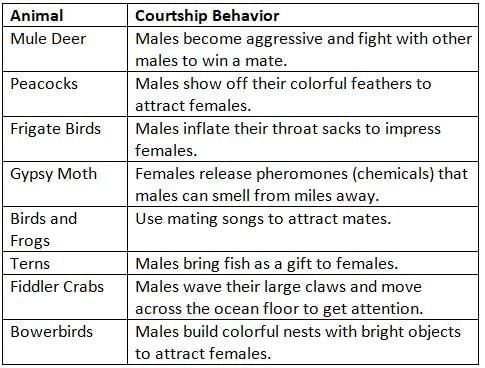
Did You Know?
Norman Platnick: The Spider Mating Dance
- Norman Platnick is an arachnologist who studies spiders.
- He discovered over 1,800 spider species worldwide.
- Spiders have pedipalps, which look like legs but act like antennae and mouthparts.
- Male spiders use pedipalps to help with reproduction.
- When ready to mate, a male spider puts sperm on a silk sheet and uses pedipalps to pick it up.
- Males find females by touch or by sensing chemicals released by females.
- Some male spiders court females with a special dance or offer gifts like a fly wrapped in silk.
- During mating, males use pedipalps to transfer sperm to the female.
- After mating, some male spiders are eaten by the female, while others find new mates.
- Spiders reproduce sexually, so each baby spider has a unique mix of genes from its parents.
- This mix of genes creates the great variety of spider species we see today.
How are young animals protected?
- Animals have behaviors to protect their young and help them survive.
- Some behaviors are innate (born with), and some are learned over time.
Innate Behaviors Vs. Learned Behaviors
- Innate Behaviors:
- Innate behaviors are instincts animals are born with.
- Spiders know how to build webs to catch food without being taught.
- Tadpoles can swim as soon as they hatch to avoid danger.
- Learned Behaviors:
- Learned behaviors develop through practice or experience.
- Birds learn to fly by trying and getting help from their parents.
- Sea turtles return to the beach where they were born to lay eggs, a behavior called imprinting.
Protecting Offspring
- Many animals build nests or dens to protect their young from predators and weather.
- Birds, mammals, amphibians, fish, reptiles, and insects make nests or dens using different materials.
- Herding is when animals stay close to their young to keep them safe.
- Elephants take turns watching each other’s babies so mothers can rest.
- Musk oxen form a circle around their young with horns facing out to protect them.
- Bison form two circles: females around the young, and males around the females.
- Wild horses protect their young by staying close and defending them.
What factors affect how baby animals grow?
- Baby animals grow differently based on genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic factors are traits passed down from parents through genes.
- Environmental factors are things like food, water, and the place where the animal lives.
- Some traits are affected by both genes and the environment.
Factors Influencing the Growth of Animals
- Genetic factors come from parents and determine traits like fur type in dogs (straight, curly, or wiry).
- Environmental factors, like diet, affect traits such as an animal’s weight.
- Some traits, like a dog’s obedience, are shaped by the environment.
- Weight is influenced by both genes and diet.
- Scientists are still learning if some traits come from genes, the environment, or both.
- Because many factors affect growth, it’s hard to predict an animal’s traits.
The document Reproduction and Growth of Animals Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 6 is a part of the Grade 6 Course Science for Grade 6.
All you need of Grade 6 at this link: Grade 6
|
124 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Reproduction and Growth of Animals Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 6
| 1. How do animals find mates in the wild? |  |
Ans. Animals use various strategies to find mates, including visual displays, vocal sounds, and chemical signals called pheromones. For example, male birds may sing or display bright feathers to attract females, while some insects release scents to signal their readiness to mate.
| 2. What are some common methods animals use to protect their young? |  |
Ans. Animals employ different strategies to protect their young, such as building nests, providing care, or using camouflage. For instance, birds often build nests in safe locations to shield their eggs, while mammals, such as elephants, stay close to their young to defend them from predators.
| 3. How do environmental factors influence the growth of baby animals? |  |
Ans. Environmental factors such as temperature, food availability, and habitat conditions significantly affect the growth of baby animals. For example, warmer temperatures can accelerate growth in some species, while a lack of food can stunt development. Additionally, the presence of predators can impact how much young animals eat and grow.
| 4. Why is parental care important for the survival of young animals? |  |
Ans. Parental care is crucial as it helps ensure the survival of young animals by providing them with food, protection, and learning opportunities. For many species, the time spent with parents allows the young to acquire essential skills and knowledge needed for survival in their environment.
| 5. What role do social behaviors play in animal reproduction? |  |
Ans. Social behaviors, such as mating rituals and group dynamics, play a vital role in animal reproduction. Many species engage in complex courtship behaviors to attract mates, and social structures can influence mating opportunities. For example, in some species, dominant males may have access to more females, thereby increasing their reproductive success.
Related Searches














