Grade 8 Exam > Grade 8 Notes > Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8 > Chapter Notes: Independent and dependent variables
Independent and dependent variables Chapter Notes | Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8 PDF Download
Introduction
In math, equations can show how things in the real world are related. When an equation has two variables, one is the independent variable, which you choose or control, and the other is the dependent variable, which changes based on the independent one. Think of the independent variable as the input that affects the output, or dependent variable. This guide uses simple examples to explain how these variables work in real-life situations.
Independent and dependent variables
- Equations often model real-world situations. When an equation with two variables models a real-world situation, one variable is independent and the other is dependent.
- For Examples
- Example 1: Each sandwich at Sam's Subs costs $5. The equation c = 5s tells you the total cost, c, for s sandwiches.
The total cost depends on the number of sandwiches. So, c is the dependent variable, and s is the independent variable. - Example 2: Marie can read 30 pages in one hour. The equation p = 30h tells you the total number of pages, p, Marie can read if she reads for h hours.
The number of pages Marie reads depends on the number of hours she spends reading. So, p is the dependent variable, and h is the independent variable.
- Example 1: Each sandwich at Sam's Subs costs $5. The equation c = 5s tells you the total cost, c, for s sandwiches.
Tip: You can often think of the independent variable as the input. The dependent variable is the output. You input the independent variable to determine the output, or dependent variable.
Expressions and equations
- An expression is a mathematical phrase that contains numbers, variables, or both. Expressions never have an equal sign. Here are some examples of expressions.
14 ÷ 7
2x
5(12 + 2)
g + 25 – 7 - An equation is a mathematical sentence that says two expressions are equal. Equations always have an equal sign. Here are some examples of equations.
14 ÷ 7 = 2
2x = 12
5(12 + 2) = 90 – 20
g + 25 – 7 = 7g
Parts of expressions and equations
- Expressions and equations are made up of different parts.
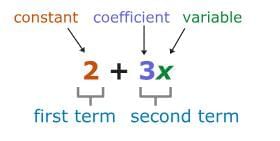
- A variable is a letter that represents an unknown amount. For example, in the equation 2b + 7 = 15, b is the variable.
- A coefficient is a number multiplied by a variable. A coefficient is written immediately in front of the variable. For example, in the expression 9n – 1/2, 9 is a coefficient.
- A constant is a term that contains only a number and no variables. For example, in the equation 7 – 0.6t, 7 is the constant.
- A term is a part of an expression or equation that is added or subtracted. For example, in the expression 3x – 9 + 2/y, 3x, 9, and 2/y are all terms.
- Look at the example below to see how these parts come together to form an expression:
Real-world expressions and equations
- You can use expressions and equations to model real-world problems.
- For Example: Shannon drives 8 miles each time she visits her grandmother. Shannon visits her grandmother v times. You can write an expression for the number of miles Shannon drives to visit her grandmother v times.
8v
The document Independent and dependent variables Chapter Notes | Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8 is a part of the Grade 8 Course Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8.
All you need of Grade 8 at this link: Grade 8
|
796 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Independent and dependent variables Chapter Notes - Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8
| 1. What are independent and dependent variables? |  |
Ans. Independent variables are the factors that are changed or controlled in a scientific experiment to test their effects on the dependent variables. Dependent variables are the outcomes or responses that are measured in the experiment. For example, if you are studying how sunlight affects plant growth, the amount of sunlight is the independent variable, while the growth of the plant is the dependent variable.
| 2. How do you identify independent and dependent variables in an experiment? |  |
Ans. To identify independent and dependent variables, first look at the hypothesis or question being tested. The independent variable is what you change, while the dependent variable is what you observe or measure. For instance, in an experiment where you test different amounts of water on plant height, the amount of water is the independent variable, and the height of the plant is the dependent variable.
| 3. Can a variable be both independent and dependent in different experiments? |  |
Ans. Yes, a variable can be independent in one experiment and dependent in another. It all depends on the context of the experiment. For example, if you are studying the effect of temperature on the solubility of salt, temperature would be the independent variable. However, if you then study how solubility affects the rate of a chemical reaction, solubility would become the independent variable in that case.
| 4. Why is it important to distinguish between independent and dependent variables? |  |
Ans. Distinguishing between independent and dependent variables is crucial because it helps to clarify the relationship being tested. It allows scientists to design experiments accurately, analyze data effectively, and draw valid conclusions. Understanding this distinction also helps in replicating experiments and ensuring that results are consistent and reliable.
| 5. What are some examples of independent and dependent variables in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Examples of independent and dependent variables in everyday life include:
1. In cooking, the amount of time food is cooked (independent) affects how well it is done (dependent).
2. In exercise, the amount of weight lifted (independent) can influence muscle growth (dependent).
3. In gardening, the type of fertilizer used (independent) may affect the number of flowers produced (dependent).
Related Searches















