Unit Test (Solutions): Life Lines of National Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
M.M.: 30
Instructions: Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1. Which organization is responsible for constructing and maintaining border roads in India?
a) Central Public Works Department (CPWD)
b) National Highway Authority of India (NHAI)
c) Border Roads Organisation (BRO)
d) State Public Works Department (PWD)
Ans: c) Border Roads Organisation (BRO)
The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is specifically tasked with the construction and maintenance of border roads, ensuring connectivity in remote areas.
Q2. Which of the following is NOT a National Waterway in India?
a) Ganga River (Allahabad to Haldia)
b) Brahmaputra River (Sadiya to Dhubri)
c) Mandavi River
d) West-Coast Canal in Kerala
Ans: c) Mandavi River
The Mandavi River is not designated as a National Waterway, unlike the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers, which are significant for navigation.
Q3. Which port is known as the largest port with a spacious natural harbor?
a) Kandla Port
b) Mumbai Port
c) Chennai Port
d) Paradip Port
Ans: b) Mumbai Port
Mumbai Port is recognized for its large natural harbor, making it the largest port in India in terms of cargo handling.
Q4. What is the primary role of pipelines in India’s transport network?
a) Transporting passengers
b) Carrying crude oil, petroleum products, and natural gas
c) Delivering food grains to markets
d) Connecting rural roads to highways
Ans: b) Carrying crude oil, petroleum products, and natural gas
Pipelines primarily serve to transport crude oil, petroleum products, and natural gas, which is essential for energy supply in India.
Q5. Which mode of transport is most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods?
a) Airways
b) Railways
c) Waterways
d) Roadways
Ans: c) Waterways
Waterways are the most efficient mode for transporting heavy and bulky goods due to their cost-effectiveness and capacity.
Q6. Explain the importance of transport in the economy of a country.
Ans: Transport is crucial for a country's economy because it:
- Facilitates the movement of raw materials to factories and finished goods to consumers.
- Connects supply and demand locations, enabling trade at local, national, and global levels.
- Reduces costs and improves accessibility.
- Boosts economic activities, contributing to national development and enhancing the quality of life.
Q7. What are the advantages of roadways over railways in India?
Ans: Roadways offer several advantages over railways:
- Cost-effective: Cheaper to construct and maintain.
- Short distances: More economical for transporting small loads.
- Convenience: Provides door-to-door service, reducing loading and unloading costs.
- Feeder service: Acts as a link to other transport modes like railways and airports.
Q8. Describe the role of the Indian postal network in communication.
Ans: The Indian postal network, the largest in the world, plays a vital role in communication by managing both parcels and personal written messages. It categorises mail into:
- First-class mail: Includes airlifted cards and envelopes.
- Second-class mail: Comprises surface-transported book packets, newspapers, and periodicals.
To enhance delivery speed in major towns and cities, the network has introduced six mail channels:
- Rajdhani Channel
- Metro Channel
- Green Channel
- Business Channel
- Bulk Mail Channel
- Periodical Channel
This comprehensive system strengthens communication across India.
Q9. What is the significance of the Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways?
Ans: The Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways form a major road network connecting Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, and Mumbai through six-lane highways. This project includes:
- The North-South Corridor from Srinagar to Kanyakumari.
- The East-West Corridor from Silchar to Porbandar.
Implemented by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI), these highways:
- Reduce travel time and distance between major cities.
- Enhance trade and economic connectivity.
Q10. Discuss the challenges faced by road transportation in India and suggest measures to address them.
Ans: Road transportation in India faces several challenges:
- Inadequate Network: The existing road network is not enough to support the high volume of traffic, causing significant congestion, particularly in urban areas.
- Unmetalled Roads: Nearly half of the roads are unmetalled, which restricts their usability during the rainy season.
- Inadequate National Highways: The current National Highways are unable to accommodate heavy traffic efficiently.
- Old Infrastructure: Many bridges and culverts are outdated and narrow, leading to delays and safety issues.
Measures to Address These Issues:
- Expand and upgrade the road network, ensuring the construction of all-weather roads.
- Increase funding for National Highways and modernise existing bridges and culverts.
- Promote initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana to enhance rural road connectivity.
- Implement smart traffic management systems to alleviate urban congestion.
- Conduct regular maintenance and quality checks to ensure the durability of roads.
Q11. Explain the role of railways in India’s economy and the challenges they face.
Ans: Railways are a vital mode of transport in India, playing a crucial role in the movement of both freight and passengers across long distances. They facilitate various activities such as Business, Tourism, Pilgrimage, Transport of goods. This extensive network, which spans 63,221 km and includes 7,031 stations, has been integral to India's economy for over 150 years, promoting industrial and agricultural growth. Challenges faced by Indian Railways include:
- Ticketless Travel: This leads to revenue loss and operational disruptions.
- Theft and Damage: Vandalism affects railway infrastructure and safety.
- Unnecessary Stops: Chain pulling and unnecessary halts cause delays.
- Terrain Difficulties: Construction is challenging in hilly, sandy, or swampy areas.
Possible Solutions:
- Enhance security measures.
- Implement stricter ticketing systems.
- Utilise technology for real-time monitoring.
- Invest in infrastructure to address terrain challenges.
Q12. Analyze the importance of international trade and tourism in India’s economic growth.
Ans: International Trade:
- International trade is crucial for economic growth, serving as an indicator of prosperity.
- India's trade includes exports such as software and IT services, and imports like fertilizers and edible oils.
- A positive balance of trade (more exports than imports) strengthens the economy.
- India's rise as a software giant has significantly increased foreign exchange earnings.
Tourism:
- Tourism plays a vital role, attracting over 2.6 million foreign tourists annually and generating Rs 21,828 crore in foreign exchange (2004 data).
- It employs over 15 million people and supports local handicrafts and cultural understanding.
- Tourism types include heritage, eco, adventure, cultural, medical, and business tourism.
- Both trade and tourism enhance living standards and drive economic growth by creating jobs.
Challenges:
- Key challenges include developing infrastructure and ensuring safety standards.
- Investment and policy reforms can help address these issues.
Q13: Features are marked by numbers in the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
1. Southern terminal of North-South Corridor
2. The northern terminal of North-South Corridor
3. The place where North-South and East-West Corridor meet
4. The easternmost point of East-West Corridor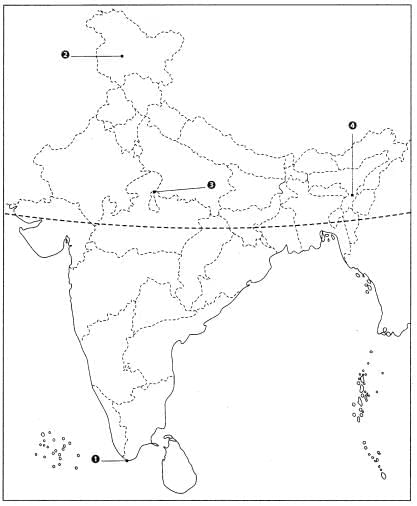
Ans:
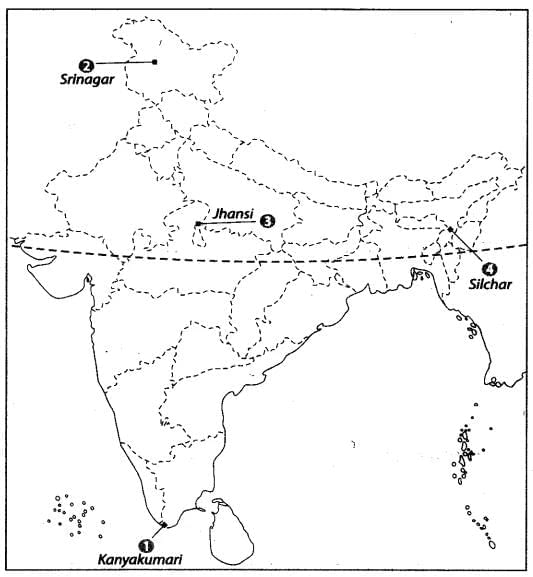
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Life Lines of National Economy - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the primary sectors of the national economy, and how do they contribute to economic development? |  |
| 2. How does transportation play a vital role in the national economy? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of communication in the context of the national economy? |  |
| 4. How do banking and financial institutions support the national economy? |  |
| 5. What are some challenges faced by the national economy, and how can they be addressed? |  |
















