UGC NET Paper 2: Computer Science 6th Jan 2025 Shift 1 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Consider following conditional statements if (m == 20 - 10 || n > 10). The order of execution of the following operations is
A. ==
B.-
C. ||
D. >
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, B, A, C
(b) B, D, C, A
(c) B, D, A, C
(d) A, B, D, C
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Key Points
- To determine the order of execution of the operations in the given conditional statement
if (m == 20 - 10 || n > 10), we need to consider the operator precedence in C-like programming languages. - Operator precedence determines the order in which parts of an expression are evaluated.
- Here is the precedence of the operators involved, from highest to lowest:
- Subtraction (-)
- Relational equality (==)
- Relational greater than (>)
- Logical OR (||)
Additional Information
According to the operator precedence:
- First, the subtraction operation (B) is performed:
20 - 10. - Then, the equality operation (A) is evaluated:
m == 10. - Next, the relational greater than operation (D) is evaluated:
n > 10. - Finally, the logical OR operation (C) is performed to combine the two relational results.
- Thus, the order of execution is: B, D, A, C.
- Therefore, Option 3 is the correct answer.
Q2: The characteristics of modern programming are:
A. Each module should do only one thing.
B. Communication between modules is allowed only by a calling module.
C. Communication can take place directly between modules that do not have calling - called relationship.
D. All modules are designed as single-entry, single exit systems using control structure.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B & C only
(b) A, B & D only
(c) A, C & D only
(d) C & D only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
- Each module should do only one thing: This principle is often referred to as the Single Responsibility Principle, which is a part of the SOLID principles of object-oriented design. It ensures that a module or class has only one reason to change, thereby making the code more maintainable and understandable.
- Communication between modules is allowed only by a calling module: This promotes loose coupling and high cohesion between modules, meaning that modules are independent and interactions are limited to well-defined interfaces. This makes the system more modular and easier to test and maintain.
- All modules are designed as single-entry, single-exit systems using control structure: This refers to structured programming, where the flow of control is limited to a few well-defined constructs, such as loops and conditionals. This makes the code easier to follow and reduces the risk of errors.
Additional Information
- Adhering to these principles allows for better modularization of code, making it easier to understand, maintain, and scale.
- It also helps in isolating bugs, as each module can be tested independently.
- Good module design often follows the principle of information hiding, where the internal workings of a module are hidden from other modules.
- These principles are fundamental to modern software development practices, including Agile and DevOps methodologies.
Q3: Which of the following CFG(s) is/are in Chomsky Normal form (All capital letters are variables & lower case are terminals)
A. S → ABC/AB
A → a
B → b
C → d
B. X → RT/TR
T → t
R → XT/r
C. P → qP/sQ
Q → r/s
D. M → MN/MP
N → nm/n
P→ P
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & B only
(b) B only
(c) C only
(d) B & D only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is option 1: A & B only
A grammar is said to be in Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) if:
- Every production rule is of the form: A → BC or A → a
- A, B, C are variables (non-terminals) and a is a terminal
- B and C must not be the start symbol
Analysis of each CFG:
A.
- S → ABC / AB → valid if ABC and AB are variables (allowed)
- A → a, B → b, C → d → all terminals, valid CNF form
- √ In CNF
B.
- X → RT / TR → 2 variables → valid CNF form
- T → t → terminal → valid
- R → XT / r → XT is variable pair, r is terminal → valid
- √ In CNF
C.
- P → qP / sQ → terminals followed by variable → Not CNF
- Q → r / s → terminals → valid, but since P rules are invalid → X Not in CNF
D.
- M → MN / MP → variable pairs → valid
- N → nm / n → nm has two terminals → not allowed in CNF
- P → P → unit production with same variable → invalid in CNF
- X Not in CNF
Explanation of options:
- Option 1 – A & B only: √ Correct
- Option 2 – B only: X A is also valid
- Option 3 – C only: X C is not in CNF
- Option 4 – B & D only: X D is invalid
Hence, the correct answer is: option 1: A & B only
Q4: Arrange the following in the increasing order with respect to access time.
A. Solid State Drive
B. Optical Disks
C. DRAMs
D. SRAMS
E. Registers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, C, A, B, E
(b) B, D, C, A, E
(c) A, E, B, D, C
(d) E, D, C, A, B
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
- Registers have the fastest access time as they are located within the CPU.
- SRAMs (Static Random-Access Memory) are faster than DRAMs because they do not need to be refreshed and are used for cache memory.
- DRAMs (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) are slower than SRAMs but faster than SSDs and optical disks. They are used as the main memory in computers.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs) are faster than optical disks as they use flash memory and have no moving parts.
- Optical Disks (such as CDs, DVDs) have the slowest access time due to the mechanical nature of reading and writing data.
Therefore, the increasing order with respect to access time is:
- Registers
- SRAMs
- DRAMs
- Solid State Drive (SSD)
- Optical Disks
Additional Information
- Registers are used to store data temporarily while the CPU processes instructions.
- SRAMs are used for CPU cache, providing faster access to frequently used data.
- DRAMs are used as the main memory in computers due to their cost-effectiveness and higher capacity compared to SRAMs.
- SSDs offer faster boot times and data access compared to traditional hard drives.
- Optical Disks are commonly used for media distribution and backup storage.
Q5: Which of the following is not a divide and conquer method
(a) Binary Search
(b) Merge Sort
(c) Quick Sort
(d) Heap Sort
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Heap Sort.
Divide and Conquer is a fundamental algorithmic technique where a problem is broken down into smaller sub-problems, each of which is solved independently, and then the solutions to the sub-problems are combined to form the solution to the original problem.
Binary Search, Merge Sort, and Quick Sort are all classic examples of divide and conquer algorithms:
- Binary Search: This algorithm works by dividing the search interval in half repeatedly until the target value is found or the interval is empty.
- Merge Sort: This sorting algorithm divides the array into two halves, recursively sorts each half, and then merges the sorted halves to produce the final sorted array.
- Quick Sort: This sorting algorithm selects a 'pivot' element and partitions the array into two sub-arrays according to whether elements are less than or greater than the pivot, then recursively sorts the sub-arrays.
Heap Sort, however, is not a divide and conquer algorithm. It is an efficient, comparison-based sorting algorithm that builds a heap data structure from the input data and then repeatedly extracts the maximum element from the heap to build the sorted array.
Other Related Points
- While Heap Sort is not a divide and conquer algorithm, it is still an efficient sorting algorithm with a time complexity of O(n log n) for both the average and worst cases.
- Divide and conquer algorithms are widely used due to their ability to break complex problems into simpler sub-problems, making them easier to manage and solve.
- Understanding the different types of algorithms and their characteristics is essential for choosing the right approach for a given problem.
Q6: Which of the following is the solution of the following recurrence relation T(n) = T(2n/3) + 1?
(a) θ(n2)
(b) θ(log n)
(c) θ(n log n)
(d) θ(n3/2)
Ans: b
Sol: The given recurrence relation reduces the problem size by a constant factor each time. Here’s how it works:
- Each step breaks the problem into a smaller part, specifically 2n/3.
- This type of reduction is similar to repeatedly halving the size, but with a different factor.
- Such recurrences typically result in a solution that grows logarithmically with input size.
- So, the time complexity is theta(log n).
Q7: INSERT command is used to
A. add a single tuple to a relation
B. add multiple tuples to a relation
C. add values to specific attributes
D. insert new table
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A only
(b) A, B only
(c) A, B, C only
(d) B, C, D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C only.
Key Points
The INSERT command in SQL is used to add data to tables within a database.
Specifically, the INSERT command can perform the following actions:
- Add a single tuple to a relation (or table): This allows the addition of a single row of data to the table.
- Add multiple tuples to a relation: This allows the addition of multiple rows of data to the table in one command.
- Add values to specific attributes: This allows specifying particular columns in the table to insert data into, rather than all columns.
The INSERT command does not create new tables; it only inserts data into existing tables.
Q8: The network using CSMA/CD has a bandwidth of 20 mbps. If the maximum propagation time is 25μ sec (microsecond), what is the minimum size of the frame?
(a) 500 bits
(b) 1000 bits
(c) 1500 bits
(d) 2000 bits
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 2) 1000 bits.
Key Points
The network uses CSMA/CD, which stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection.
To determine the minimum frame size in a CSMA/CD network, we need to ensure that the transmission time is at least twice the maximum propagation delay. This is to detect collisions before the entire frame is transmitted.
Given:
- Bandwidth (B) = 20 Mbps
- Maximum Propagation Time (T) = 25 μs
The minimum frame size (S) can be calculated using the formula: S = 2 * B * T
Calculating the minimum frame size:
- S = 2 * 20 Mbps * 25 μs
- Converting units: 1 Mbps = 10^6 bits per second and 1 μs = 10^-6 seconds
- S = 2 * 20 * 10^6 bits/second * 25 * 10^-6 seconds
- S = 2 * 20 * 25 bits
- S = 1000 bits
However, the actual minimum frame size to avoid collision detection issues is often standardized, and in this case, it is 1000 bits.
Additional Information
- CSMA/CD is used in Ethernet networks to manage the transmission of data and avoid collisions. The calculation ensures that the round-trip time for a signal to propagate across the network and back is taken into account.
- Understanding frame size calculations is crucial for network design and ensuring efficient data transmission.
Q9: The mathematical notation to describe logical entailment of a sentence"α entails another sentence β" is
(a) α  B
B
(b) α ⊆ β
(c) β  α
α
(d) β ⊆ α
Ans: a
Sol: The mathematical notation for logical entailment is:
The expression α ⊨ β means that the sentence α logically entails the sentence β.
This indicates that if α is true, then β must also be true in every possible case.
Q10: Software Testability is simply how easily a software program can be tested. Which one characteristics does not lead to testable software?
(a) Observability
(b) Controllability
(c) Repairability
(d) Understandability
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Repairability.
Software testability is the degree to which a software artifact supports testing in a given test context.
Several characteristics influence the testability of software, including:
- Observability: This characteristic ensures that the internal state of the software can be observed through its outputs.
- Controllability: This characteristic ensures that the software can be easily controlled by providing inputs and test conditions.
- Understandability: This characteristic ensures that the software's design and implementation are easy to understand and follow.
- Repairability does not directly lead to testable software. While it is important for software maintenance, it does not impact the ease of testing the software.
Other Related Points
- Other characteristics that contribute to software testability include simplicity, stability, and documentation.
- Improving software testability can lead to more efficient and effective testing processes.
- Testability is an important consideration during software design and development to ensure that the software can be thoroughly tested before release.
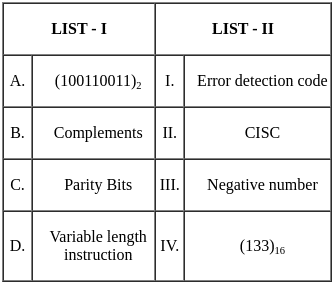
Q11: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(d) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is: Option 2
Here is the detailed explanation for the correct answer:
Therefore, the correct matching is Option 2:
- A - IV: (100110011)2 is equivalent to (133)16.
- B - III: Complements are used for representing negative numbers.
- C - I: Parity bits are used as error detection codes.
- D - II: Variable length instruction is a characteristic of CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing).
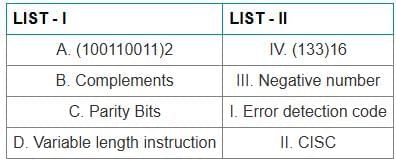
Q12: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
- Decision Tree (A) is linked with the C4.5 Algorithm (III) which is a well-known algorithm used to generate a decision tree.
- Supervised Learning (B) can be associated with Non-linear Regression Algorithm (IV) as it involves using labeled data to predict outcomes.
- Artificial Neural Network (C) is connected to the Delta Learning Rule (I) which is used to adjust the weights in the network.
- Instance base Learning (D) relates to the Self Organizing Map (II) which is a type of artificial neural network that uses unsupervised learning to produce a low-dimensional representation of the input space.
Other Related Points
- The C4.5 algorithm is an extension of the earlier ID3 algorithm and is used for generating a decision tree based on labeled input data.
- Supervised learning algorithms, including non-linear regression, are used for making predictions based on input-output pair datasets.
- The Delta Learning Rule is a gradient descent learning rule used for training artificial neural networks.
- Self Organizing Maps are used for clustering and visualizing high-dimensional data in a low-dimensional space.
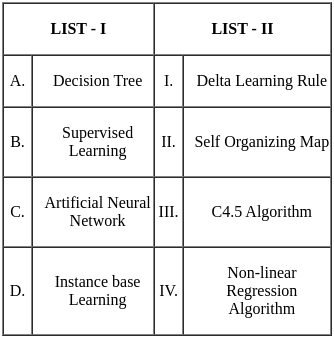
Q13: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II: Match the logical equivalence propositions
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(b) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Key Points
Let's match the logical equivalence propositions between LIST-I and LIST-II:
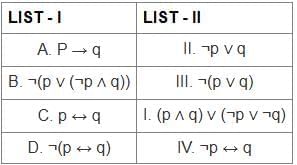
The matchings are:
- A - II: P → q is logically equivalent to ¬p ∨ q
- B - III: ¬(p ∨ (¬p ∧ q)) is logically equivalent to ¬(p ∨ q)
- C - I: p ↔ q is logically equivalent to (p ∧ q) ∨ (¬p ∨ ¬q)
- D - IV: ¬(p ↔ q) is logically equivalent to ¬p ↔ q
Therefore, the correct option is Option 3.
Q14: A linear programming problem (LPP) is as follows:
Min z = 30x - 18y, subject to the constraints; 3x + 4y ≤ 60, 5x - 3y ≥ 20 and x, y ≥ 0. In this feasible region, the solution of LPP is/are
A. (4, 0)
B. (2, 0)
C. (7, 5)
D. (0, 15)
E. (8, 5)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) B only
(c) E only
(d) D only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 1) A and C only.
To determine the solution of the given linear programming problem (LPP), we need to check which of the given points satisfy all the constraints and provide the minimum value for the objective function.
First, we check the constraints for each point:
For point (4, 0):
- 3(4) + 4(0) ≤ 60 → 12 ≤ 60 (true)
- 5(4) - 3(0) ≥ 20 → 20 ≥ 20 (true)
- x, y ≥ 0 → true
For point (2, 0):
- 3(2) + 4(0) ≤ 60 → 6 ≤ 60 (true)
- 5(2) - 3(0) ≥ 20 → 10 ≥ 20 (false)
- x, y ≥ 0 → true
For point (7, 5):
- 3(7) + 4(5) ≤ 60 → 21 + 20 ≤ 60 → 41 ≤ 60 (true)
- 5(7) - 3(5) ≥ 20 → 35 - 15 ≥ 20 → 20 ≥ 20 (true)
- x, y ≥ 0 → true
For point (0, 15):
- 3(0) + 4(15) ≤ 60 → 60 ≤ 60 (true)
- 5(0) - 3(15) ≥ 20 → -45 ≥ 20 (false)
- x, y ≥ 0 → true
For point (8, 5):
- 3(8) + 4(5) ≤ 60 → 24 + 20 ≤ 60 → 44 ≤ 60 (true)
- 5(8) - 3(5) ≥ 20 → 40 - 15 ≥ 20 → 25 ≥ 20 (true)
- x, y ≥ 0 → true
- Only the points (4, 0), (7, 5), and (8, 5) satisfy all the constraints.
Now, we calculate the objective function z = 30x - 18y for these points:
- For point (4, 0): z = 30(4) - 18(0) = 120
- For point (7, 5): z = 30(7) - 18(5) = 210 - 90 = 120
- For point (8, 5): z = 30(8) - 18(5) = 240 - 90 = 150
- The minimum value of the objective function is 120, which is achieved by points (4, 0) and (7, 5).
Therefore, the correct answer is 1) A and C only.
Other Related Points
- Linear programming problems involve optimizing a linear objective function subject to a set of linear constraints.
- The feasible region is the set of all points that satisfy the constraints.
- The optimal solution is a point in the feasible region that minimizes or maximizes the objective function.
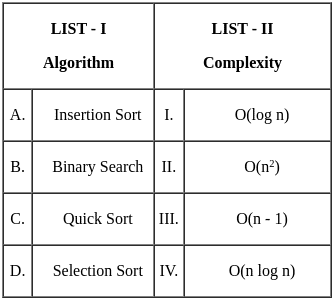
Q15: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1: A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Key Points
- Insertion Sort: The complexity is O(n-1) in the average and worst case, where n is the number of elements. This is because each element might need to be compared with all other elements in the worst-case scenario.
- Binary Search: The complexity is O(log n). This logarithmic complexity comes from the fact that the algorithm repeatedly divides the search interval in half.
- Quick Sort: The average-case complexity is O(n log n). This is because the algorithm divides the array into two parts and recursively sorts them.
- Selection Sort: The complexity is O(n²). In each iteration, the algorithm selects the smallest element and places it in the correct position, leading to quadratic time complexity.
Additional Information
- Insertion Sort: This algorithm is efficient for small datasets or nearly sorted data.
- Binary Search: This algorithm requires the dataset to be sorted before it can be applied.
- Quick Sort: Despite its average-case efficiency, its worst-case complexity is O(n²), but this can be mitigated with good pivot selection strategies.
- Selection Sort: It performs well on small lists but is inefficient on large lists compared to more advanced algorithms like Quick Sort or Merge Sort.
Q16: What will be the right sequence of the phases of database design-
A. Physical Design
B. Conceptual Design
C. Logical Design
D. Requirement collection and analysis
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, A, B, C
(b) D, B, C, A
(c) D, B, A, C
(d) D, A, C, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2: D, B, C, A.
The phases of database design typically follow a specific sequence to ensure that the database system meets user requirements and is well-structured:
- Requirement Collection and Analysis (D): This is the first phase where the requirements of the database system are gathered and analyzed. This includes understanding what data needs to be stored, how it will be used, and who will use it.
- Conceptual Design (B): In this phase, a high-level conceptual schema is created, usually using Entity-Relationship (ER) diagrams. This schema represents the overall structure of the database without worrying about specific details.
- Logical Design (C): This phase involves translating the conceptual schema into a logical schema, which describes the structure of the database in a data model of choice (e.g., relational model). This includes defining tables, columns, data types, and relationships.
- Physical Design (A): The final phase is where the logical schema is translated into a physical schema. This involves specifying the actual storage structures, indexing methods, and file organizations that will be used to store the data on a physical medium.
Additional Information
- Proper database design is critical to ensure data integrity, reduce redundancy, and improve performance.
- The use of appropriate design tools and techniques, such as ER diagrams and normalization, is essential in the design process.
- Iterative refinement and validation of the database design with stakeholders help in addressing any issues early in the development cycle.
Q17: Which of the following is not true about Global Variables:
(a) The values of the Global variables which are sent to the called function may be changed inadvertently by the called function.
(b) Functions are supposed to be independent and isolated modules. This character is lost, if they use global variables.
(c) It is not immediately apparent to the reader which values are being sent to the called function
(d) A function that uses global variables does not suffer from reusability.
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
Key Points
Global variables are variables that are declared outside of any function and can be accessed from any function within the same scope.
- The values of the global variables which are sent to the called function may be changed inadvertently by the called function. This means that any function can modify the global variable, leading to potential side effects. (Option 1 is true)
- Functions are supposed to be independent and isolated modules. This character is lost if they use global variables. Using global variables can lead to tightly coupled code, making the functions dependent on the state of global variables. (Option 2 is true)
- It is not immediately apparent to the reader which values are being sent to the called function. This can make the code harder to read and understand as the dependencies are not explicit. (Option 3 is true)
- A function that uses global variables does not suffer from reusability. This is the incorrect statement because functions using global variables indeed suffer from reusability as they rely on the global state. (Option 4 is not true)
Additional Information
- Global variables can lead to namespace pollution, where multiple variables may interfere with each other.
- They can make debugging difficult as any part of the code can change the global variable value.
- Global variables can be useful in certain scenarios, such as when maintaining state in a web application, but should be used sparingly and with caution.
- It is often better to use local variables or pass parameters explicitly to functions to maintain code clarity and modularity.
Q18: In Software Engineering Jackson's Principle based on
A. Designation
B. Definitions
C. Refutable Assertions
D. Formal Review
E. Requirement Elicitation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B & C Only
(b) B, C & D Only
(c) C, D & E Only
(d) B, D & C Only
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
Jackson's Principle in Software Engineering is based on Designation, Definitions, and Refutable Assertions.
- Designation: This involves identifying and naming the different components and elements within the software system.
- Definitions: This involves providing clear and precise definitions of the various components and elements identified.
- Refutable Assertions: This involves making assertions about the software system that can be tested and potentially refuted, ensuring the system's robustness and reliability.
Other Related Points
- Option 2, which includes Definitions, Refutable Assertions, and Formal Review, is incorrect because Formal Review is not part of Jackson's Principle.
- Option 3, which includes Refutable Assertions, Formal Review, and Requirement Elicitation, is incorrect because Requirement Elicitation and Formal Review are not part of Jackson's Principle.
- Option 4, which includes Definitions, Formal Review, and Refutable Assertions, is incorrect because Formal Review is not part of Jackson's Principle.
Q19: Definitions of ________ organized into following four categories namely, Thinking Humanly, Thinking Rationally, Acting Humanly, Acting Rationally
(a) Machine Learning
(b) Deep Learning
(c) Artificial Intelligence
(d) Neural Network
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Artificial Intelligence. Explanation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the field of study that encompasses the creation of systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
The definitions of AI can be organized into the following four categories:
- Thinking Humanly: AI systems that mimic human thought processes.
- Thinking Rationally: AI systems that use logical reasoning and decision-making.
- Acting Humanly: AI systems that exhibit human-like behaviors.
- Acting Rationally: AI systems that act in a rational manner to achieve specific goals.
AI encompasses various subfields, including machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks, which contribute to its development and applications.
Other Related Points
- AI has numerous applications across different industries, including healthcare, finance, automotive, and entertainment.
- AI technologies are continually evolving, leading to advancements in natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and more.
- AI systems can enhance productivity, improve decision-making, and provide new insights by analyzing large datasets.
- Ethical considerations and responsible AI development are critical to ensure the technology benefits society as a whole.
Q20: Which table for a dynamic pipeline become more interesting when a nonlinear pattern is followed?
(a) Reservation Table
(b) Confusion Table
(c) Inverted Table
(d) Greedy Table
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Reservation Table.
- A reservation table is used in dynamic pipelines to keep track of the usage of functional units over time.
- When a nonlinear pattern is followed, the reservation table becomes more interesting because it needs to efficiently handle the dynamic allocation and deallocation of resources.
- This dynamic nature allows the pipeline to adapt to varying workloads and optimize the performance.
- The reservation table helps in avoiding conflicts and ensuring that the functional units are utilized effectively, especially when there are dependencies among instructions.
- It is crucial in maintaining the pipeline's efficiency and preventing stalls that can occur due to resource contention.
- Reservation tables are used in various stages of instruction execution to track the availability and scheduling of resources.
- They play a vital role in superscalar and out-of-order execution architectures by managing multiple instructions simultaneously.
- In a complex pipeline, the reservation table helps in reducing latency and improving throughput by efficiently scheduling instructions.
- Understanding the reservation table is essential for optimizing the performance of modern processors and designing efficient instruction pipelines.
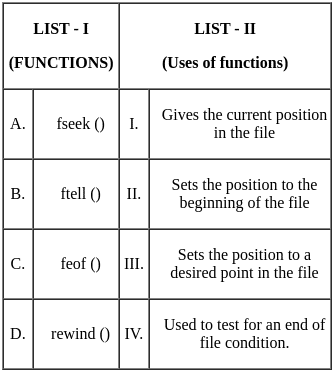
Q21: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is option 2: A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
- fseek (): This function sets the file position indicator to a specific point in the file. Hence, it matches with III.
- ftell (): This function returns the current file position indicator's value in the file. Hence, it matches with I.
- feof (): This function checks if the end of the file has been reached. Hence, it matches with IV.
- rewind (): This function sets the file position indicator to the beginning of the file. Hence, it matches with II.
The correct answer is : option 2
Q22: Yacc is which of the following parsers?
(a) Predictive Parser
(b) SLR Parser
(c) CLR Parser
(d) LALR Parser
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is LALR Parser.
Key Points
Yacc (Yet Another Compiler-Compiler) is a tool used to generate a parser in the form of a LALR (Look-Ahead LR) parser.
- A LALR parser is a type of LR parser, specifically designed to handle a larger set of grammars than SLR parsers, while being more efficient than CLR parsers.
- Yacc is widely used in compiler construction to generate the syntax analysis phase of a compiler.
- It takes a formal grammar for the source language and produces source code for a parser that can parse the language.
- Yacc generates an LALR(1) parser, which means it uses one look-ahead symbol to make parsing decisions.
Additional Information
- Yacc has been instrumental in the development of many programming languages, including C and many others.
- It is often used in conjunction with a lexical analyzer generator like Lex.
- Yacc's output is typically in the form of C source code, which can be compiled to produce the parser.
- The combination of Lex and Yacc allows for the creation of a complete compiler front end, including lexical analysis and syntax analysis.
- Yacc was developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories in the early 1970s by Stephen C. Johnson.
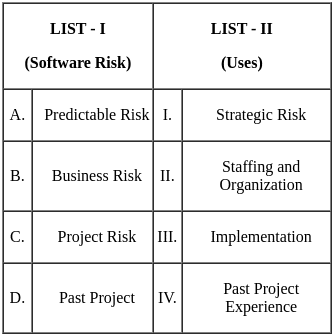
Q23: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II-, D - III
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
Key Points
Predictable Risk (A) - Past Project Experience (IV)
- Predictable risks can be identified and mitigated using knowledge and experience from past projects.
Business Risk (B) - Strategic Risk (I)
- Business risks are often tied to strategic decisions and long-term planning, affecting the overall direction of the project.
Project Risk (C) - Staffing and Organization (II)
- Project risks include issues related to staffing, resource allocation, and organizational structure, which can impact the project's success.
Past Project (D) - Implementation (III)
- Lessons learned from past projects can provide valuable insights into the implementation phase of new projects.
Additional Information
- Understanding different types of risks and their uses helps in better risk management and mitigation strategies.
- Predictable risks can often be foreseen and planned for, whereas business and strategic risks require careful consideration of the broader impact.
- Staffing and organizational risks can be mitigated by ensuring the right resources and structures are in place.
- Implementation risks can be reduced by leveraging past project experiences and applying best practices.
Q24: Which of the following description(s) is/are true:
A. Red Black Tree - Guarantees worst case of O(log n) time for search, insert & delete.
B. Trie - Used for efficient prefix - based searches.
C. AVL Tree - self balancing binary search tree with stricker balance criteria.
D. B - Tree - Allows efficient search, insert, delete operations in disk based system.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & B only
(b) C & D only
(c) B only
(d) A, B, C & D only
Ans: d
Sol: The Correct answer is : A, B, C & D are correct.
- A. Red Black Tree: ✅ True
A Red-Black Tree is a self-balancing BST that guarantees O(log n) time for search, insert, and delete operations in the worst case. - B. Trie: ✅ True
Tries (prefix trees) are used for efficient prefix-based searching and are common in applications like autocomplete and dictionary lookups. - C. AVL Tree: ✅ True
AVL Trees are also self-balancing BSTs with a stricter balancing condition than Red-Black Trees (balance factor must be -1, 0, or 1). So this statement is also true. - D. B-Tree: ✅ True
B-Trees are optimized for disk-based storage systems and support efficient search, insert, and delete operations with fewer disk reads.
Conclusion: All options A, B, C, and D are correct.
Q25: Sequence the following stages of the sliding window protocol for flow control.
A. Sender move the window to the next set of frames.
B. Sender sends a window of frames.
C. Receiver acknowledge the received frames.
D. If acknowledgment is not received, Sender retransmits the frame.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, A, C, D
(b) B, C, D, A
(c) B, D, C, A
(d) B, C, A, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
The sliding window protocol for flow control involves the following stages:
- B. Sender sends a window of frames.
- C. Receiver acknowledges the received frames.
- A. Sender moves the window to the next set of frames.
- D. If acknowledgment is not received, Sender retransmits the frame.
Therefore, the correct sequence is Option 4: B, C, A, D.
Additional Information
- In the sliding window protocol, the sender can send multiple frames before needing an acknowledgment for the first frame.
- The window size determines the number of frames the sender can send without receiving an acknowledgment.
- This protocol helps in efficient use of network bandwidth and reduces the waiting time for acknowledgments.
Q26: The light given off by the phosphor during exposure to the electron beam is known as
(a) Fluorescence
(b) Phosphorescence
(c) Persistence
(d) Retracing
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Fluorescence.
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation.
- It is a form of luminescence.
- In a cathode ray tube (CRT) or other similar devices, when the phosphor coating is struck by the electron beam, it emits visible light through the process of fluorescence.
- This emission of light occurs almost instantaneously with the exposure to the electron beam.
- Fluorescence ceases almost immediately when the excitation source (electron beam) is removed.
- This characteristic makes it suitable for applications requiring quick response times.
Other Related Points
- Phosphorescence, on the other hand, involves a delayed emission of light and continues to glow even after the excitation source is removed.
- Persistence refers to the duration the screen continues to emit light after the electron beam has moved on.
- Retracing is the process where the electron beam returns to the beginning of the next line or frame in a CRT display.
Q27: 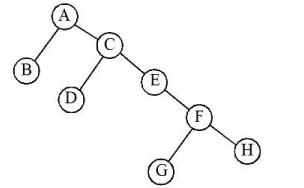
Considering above binary tree, what will be the inorder traversal
(a) B A D C E G F H
(b) G H F E D C B A
(c) B A C D E G F H
(d) G H F D E B C A
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is 1) B A D C E G F H.
- Inorder traversal of a binary tree visits nodes in the following order: left subtree, root node, right subtree.
- The provided sequence B A D C E G F H follows this rule, visiting the leftmost nodes first, then the root, and finally the rightmost nodes.
Additional Information
- Inorder traversal is used to get nodes of a binary search tree (BST) in non-decreasing order.
- This traversal method is used in many tree-related algorithms and problems.
- It is also useful in scenarios where the order of node processing matters, such as expression trees for arithmetic operations.
Q28: Which are often needed to evaluate the cache performance?
(a) Hit Ratio
(b) Latency
(c) Cache Traces
(d) Transfer Rate
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Hit Ratio.
Key Points
The Hit Ratiois a critical metric for evaluating the performance of a cache.
- It measures the percentage of cache accesses that result in a cache hit, where the requested data is found in the cache.
- A higher hit ratio indicates that the cache is effectively storing and providing the required data, reducing the need to access slower main memory.
- It is calculated as the number of cache hits divided by the total number of cache accesses.
- Improving the hit ratio can significantly enhance the overall system performance by reducing latency and increasing throughput.
Additional Information
- Other metrics such as latency, transfer rate, and cache traces can also be important for evaluating specific aspects of cache performance.
- Latency measures the time taken to access data from the cache.
- Transfer rate indicates the speed at which data can be transferred to and from the cache.
- Cache traces provide detailed records of cache accesses, which can be analyzed to optimize cache configuration and policies.
- However, the hit ratio remains a primary indicator of the cache's effectiveness in reducing memory access times.
Q29: Which of the following uses only increment operations for adding and removing element at either end?
(a) Queues
(b) Stacks
(c) Priority Queues
(d) Deques
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Deques.
A deque (double-ended queue) is a data structure that allows elements to be added or removed from both ends.
- Deques support insertion and deletion operations at both the front and the back, making them very flexible.
- Unlike stacks and queues which are restricted to adding or removing elements from only one end, deques can perform these operations at either end using only increment operations.
- This makes deques particularly useful in scenarios where elements need to be accessed, added, or removed from both ends efficiently.
Other Related Points
- Deques can be implemented using arrays or linked lists.
- They provide a more generalized version of stacks and queues, which are limited to LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) and FIFO (First-In-First-Out) operations respectively.
- Common operations in a deque include push_front(), push_back(), pop_front(), and pop_back().
- In many programming languages, deques are available as part of the standard library, making them easy to use and implement.
Q30: Which of the following is TRUE about the Pumping Lemma for regular language?
(a) It applies to all regular language
(b) It applies only to infinite regular languages
(c) It applies to all context-free languages
(d) It applies to all recursively enumerable languages
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is It applies to all regular languages.
The Pumping Lemma is a property that applies to all regular languages, and it is used to prove whether a language is not regular.
- If a language is regular, there exists some length (p) such that any string longer than p can be divided into three parts, xyz, satisfying certain conditions.
- The conditions are: for the string xyz, the length of xy is at most p, y is not an empty string, and the string xy^iz (i ≥ 0) is still in the language.
- The Pumping Lemma helps in identifying strings that cannot be pumped, thereby proving that the language is not regular.
Other Related Points
- The Pumping Lemma does not apply to finite languages, as there is no need to pump strings in such cases.
- While the Pumping Lemma provides a necessary condition for regularity, it is not a sufficient condition; that is, some non-regular languages may satisfy the lemma.
- The lemma is a fundamental concept in the theory of computation and automata theory, helping in understanding the limitations of regular languages.
- It is an essential tool in formal language theory for distinguishing between regular and non-regular languages.
Q31: Which of the following statements are true about the sets.
A. 0 ∈ Ø
B. Ø ∈ {0}
C. Ø ∈ {Ø}
D. {Ø} ∈ {Ø}
E. {Ø} ⊂ {Ø, {Ø}}
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D and E
(b) A, B, C and E only
(c) A, C only
(d) C and E only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is option 4.
A. 0 ∈ Ø
- Explanation: The empty set (
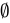 ) contains no elements.
) contains no elements. - Conclusion: False, because
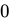 is not an element of
is not an element of 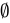 .
.
B. Ø ∈ {0}
- Explanation: The set
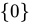 has only one element:
has only one element: 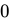 . The empty set is not listed as an element.
. The empty set is not listed as an element. - Conclusion: False, because
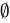 is not in
is not in 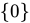 .
.
C. Ø ∈ {Ø}
- Explanation: The set
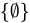 has one element: the empty set itself.
has one element: the empty set itself. - Conclusion: True, because
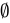 is explicitly an element of
is explicitly an element of 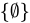 .
.
D. {Ø} ∈ {Ø}
Explanation: The set
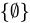 contains only
contains only 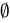 , not
, not 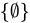 itself.
itself.Conclusion: False, because
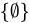 is not an element of itself.
is not an element of itself.
E. {Ø} ⊂ {Ø, {Ø}}
Explanation:
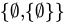 has two elements:
has two elements: 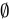 and
and 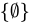 .
.- The subset
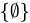 is contained within it.
is contained within it.
Conclusion: True, because every element of 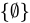 (which is just
(which is just 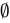 ) is also in
) is also in 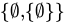
Correct Option:
Only C and E are true.
Answer: Option 4 (C and E only).
Key Concepts:
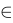 (Element of): Checks if an item is directly inside a set.
(Element of): Checks if an item is directly inside a set.Example:
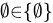 is true.
is true.
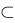 (Subset of): Checks if all elements of one set are in another.
(Subset of): Checks if all elements of one set are in another.Example:
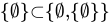 is true.
is true.
The empty set (
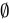 ) is not an element of every set—only when explicitly included (e.g.,
) is not an element of every set—only when explicitly included (e.g., 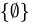 ).
).
This aligns perfectly with Option 4.
Q32: Choose the correct statement(s)
A. A problem which is NP-Complete will have the property that it can be solved in polynomial time iff all other NP-complete problems can also be solved in polynomial time.
B. All NP-complete problem are NP-hard problems.
C. If an NP-hard problem can be solved in polynomial time, then all NP-complete problem can be solved in polynomial time
D. All NP-hard problems are not NP-complete.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C only
(b) B, D only
(c) A, B, C only
(d) A, B, C, D
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
Statement A: A problem which is NP-Complete will have the property that it can be solved in polynomial time iff all other NP-complete problems can also be solved in polynomial time.
- This statement is correct. By definition, if one NP-complete problem can be solved in polynomial time, all NP-complete problems can be solved in polynomial time because they are all polynomial-time reducible to each other.
Statement B: All NP-complete problems are NP-hard problems.
- This statement is correct. NP-complete problems are a subset of NP-hard problems, meaning every NP-complete problem is also NP-hard.
Statement C: If an NP-hard problem can be solved in polynomial time, then all NP-complete problems can be solved in polynomial time.
- This statement is correct. If any NP-hard problem (which is not necessarily in NP) can be solved in polynomial time, it implies that P = NP, meaning all NP-complete problems can also be solved in polynomial time.
Statement D: All NP-hard problems are not NP-complete.
- This statement is correct. NP-hard problems include both NP-complete problems and other problems that are not in NP.
Since statements A, B, C, and D are all correct, the correct answer is Option 4.
Q33: Which of the following is not a component of the classic Planning Definition?
(a) Init
(b) Domain
(c) Action
(d) Goal
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Domain.
Key Points
In the context of classic planning in artificial intelligence, the primary components are Init, Action, and Goal.
- Init refers to the initial state from which the planning begins.
- Action refers to the set of operations or steps that can be performed to transition from one state to another.
- Goal refers to the desired end state that the planning process aims to achieve.
The term Domain does not specifically refer to a component in the classic definition of planning.
While domains can be a part of the broader context in which planning occurs, they are not considered one of the core components of the planning definition itself.
Additional Information
- Domains usually describe the environment or the problem space in which planning is performed.
- In AI planning, a domain often includes definitions of the states, actions, and goals relevant to the specific problem.
- The classic planning problem focuses on transitioning from the initial state to the goal state using a sequence of actions.
- Understanding the specific components helps in formulating effective planning algorithms and solutions in artificial intelligence.
Q34: In concurrency control, phantom problem may occur, when-
(a) records are inserted
(b) records are deleted
(c) records are modified
(d) records are indexed
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is records are inserted.
Key Points
In concurrency control, the phantom problem occurs when records are inserted into the database during the execution of a transaction.
- The phantom problem arises in a situation where a transaction reads a set of records that satisfy a certain condition, and another transaction inserts new records that also satisfy the same condition.
- For example, if Transaction A reads all records where the age is greater than 30, and Transaction B inserts a new record with age 35, Transaction A may miss this new record if it reads again.
- This leads to inconsistency because Transaction A's subsequent read operations may return a different set of records.
- To prevent the phantom problem, isolation levels like Serializable are used, which ensures that no new records can be inserted that satisfy the condition during the transaction execution.
Additional Information
- Concurrency control is essential in database management systems to ensure the correctness and isolation of transactions.
- Other common concurrency problems include lost updates, dirty reads, and unrepeatable reads.
- Different isolation levels (Read Uncommitted, Read Committed, Repeatable Read, and Serializable) provide different levels of protection against these problems.
- The Serializable isolation level is the most restrictive and ensures complete isolation but can impact performance due to its strict locking mechanisms.
Q35: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
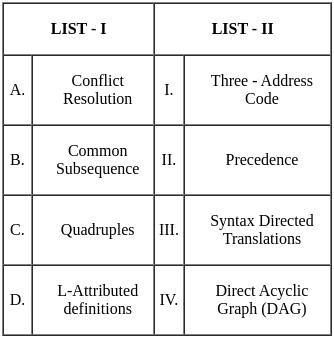
Key Points
- Conflict Resolution is associated with Precedence (A - II).
- Common Subsequence is related to Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG) (B - IV).
- Quadruples match with Three-Address Code (C - I).
- L-Attributed definitions are connected to Syntax Directed Translations (D - III).
Additional Information
- Conflict Resolution often involves determining the precedence of operators in expressions to resolve ambiguities.
- Common Subsequence problems can be effectively represented and solved using Direct Acyclic Graphs (DAGs).
- Quadruples are a format for representing intermediate code in compiler design, commonly in Three-Address Code.
- L-Attributed definitions are used in Syntax Directed Translations to specify how attributes are evaluated in parsing.
Q36: Consider the following statements
int x = 10, y = 15;
x = ((x = y) ? (y + x) : (y - x));
What will be the value of x after executing these statements?
(a) 5
(b) 25
(c) 15
(d) 30
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 30.
- Let's break down the given code to understand how the value of
xbecomes 30. - The initial values are:
int x = 10;int y = 15;
- Next, we have the statement:
x = ((x = y) ? (y + x) : (y - x));
- In the statement
(x = y),xis assigned the value ofy, so nowx = 15. - In the ternary conditional operator
((x = y) ? (y + x) : (y - x)), sincex = yresults inxbeing non-zero (true in a Boolean context), the condition is true. - When the condition is true, the expression
(y + x)is evaluated.yis 15 andxis now 15, soy + x = 15 + 15 = 30.
- Therefore,
x = 30after the assignment.
Additional Information
- The ternary conditional operator is a shortcut for the
if-elsestatement and is used to assign one of two values based on a condition. - Syntax:
condition ? value_if_true : value_if_false. - It's important to understand the order of evaluation and assignment in expressions to correctly determine the resulting values of variables.
- In this example, the assignment
(x = y)happens first, followed by the evaluation of the ternary condition and the resulting expression.
Q37: What is the correct sequence of steps used by knowledge base designing?
A. Ask questions about the intended interpretation.
B. Choose task domain or world to represent.
C. Select atoms to represent propositions of Interest.
D. Tells the system propositions that are true in the intended interpretation/axiomatizing the domain.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D
(b) B, C, D, A
(c) C, D, A, B
(d) D, A, B, C
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Knowledge base designing involves a specific sequence of steps to accurately represent a domain of interest.
- A. Ask questions about the intended interpretation: This step involves understanding the context and the specific meanings of the propositions that will be represented in the knowledge base.
- B. Choose task domain or world to represent: This step involves selecting the particular area or world that the knowledge base will cover.
- C. Select atoms to represent propositions of interest: In this step, the basic atomic elements or propositions that are relevant to the domain are identified.
- D. Tell the system propositions that are true in the intended interpretation/axiomatizing the domain: This step involves defining the truths or axioms that apply to the chosen domain.
The correct sequence of these steps is:
- B. Choose task domain or world to represent.
- C. Select atoms to represent propositions of interest.
- D. Tell the system propositions that are true in the intended interpretation/axiomatizing the domain.
- A. Ask questions about the intended interpretation.
Hence, the correct answer is Option 2.
Other Related Points
- The steps in knowledge base designing ensure that the system accurately represents the chosen domain and can effectively interpret and answer queries.
- Each step builds upon the previous ones, creating a robust and reliable knowledge base.
- Properly asking questions about the intended interpretation helps in refining the knowledge base and ensuring it accurately reflects the domain.
Q38: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
Ans: b
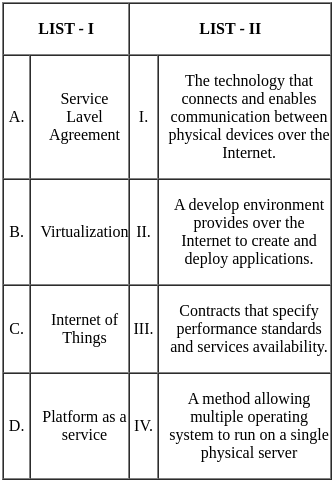
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is:
- Contracts that specify performance standards and services availability.
Virtualization is:
- A method allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is:
- The technology that connects and enables communication between physical devices over the Internet.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is:
- A development environment provided over the Internet to create and deploy applications.
Additional Information
- SLAs are crucial for ensuring that service providers meet the agreed-upon performance standards.
- Virtualization helps in optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs by allowing multiple virtual instances on a single physical machine.
- IoT enables smart devices to collect and share data, leading to improved automation and efficiency in various sectors.
- PaaS offers developers a platform with tools and services to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Q39: Regarding the code optimization, choose the correct sequence
A. Algebraic Simplification
B. Use of machine idioms
C. Redundant - instruction elimination
D. Flow of control optimization
E. Improved target code
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, B, D, E
(b) B, C, D, A, E
(c) C, D, A, B, E
(d) D, B, A, C, E
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3: C, D, A, B, E.
- Code optimization is an important aspect of improving the efficiency and performance of code. The sequence provided in the correct answer represents a logical flow for optimizing code.
- Redundant-instruction elimination (C) should be performed first. This step removes any unnecessary instructions, reducing the code size and improving its efficiency.
- Flow of control optimization (D) follows. This step focuses on improving the control flow within the code, such as optimizing loops and conditional branches to make the code run faster.
- Algebraic simplification (A) is the next step. This involves simplifying algebraic expressions within the code to make them more efficient and easier to compute.
- Use of machine idioms (B) comes after. This step involves using specific machine-level instructions that are more efficient than their higher-level counterparts, which can improve the performance of the code on a given architecture.
- Finally, improved target code (E) is generated. This involves producing the final optimized machine code that is more efficient and runs faster on the target machine.
Other Related Points
- Code optimization is typically performed by compilers, which can automate many of these steps to produce efficient machine code from higher-level programming languages.
- The goals of code optimization include reducing the execution time, minimizing memory usage, and improving the overall performance of the software application.
- Advanced optimization techniques may also consider factors such as power consumption and code maintainability.
- Different optimization techniques may be more or less effective depending on the specific context and the nature of the code being optimized.
Q40: Which of the following does not interrupt a running process?
(a) Device
(b) Timer
(c) Scheduler
(d) Power Failure
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Scheduler.
Key Points
The scheduler is a system software that manages process scheduling in the operating system.
- It determines which process runs at any given time based on a specific scheduling algorithm.
- Schedulers do not interrupt running processes but instead manage the execution sequence of processes.
- There are three types of schedulers: long-term (job scheduler), short-term (CPU scheduler), and medium-term.
- The short-term scheduler (CPU scheduler) selects a process from the ready queue and allocates the CPU to it.
- Schedulers ensure that all processes get a chance to execute and manage the allocation of system resources efficiently.
Additional Information
- Interrupts are signals sent to the CPU by hardware or software indicating an event that needs immediate attention.
- Common types of interrupts include device interrupts, timer interrupts, and power failure interrupts.
- Device interrupts occur when an I/O operation completes, timer interrupts occur at regular intervals, and power failure interrupts occur during power outages.
- Schedulers work in conjunction with interrupts to manage process execution and resource allocation.
Q41: Which of the following do not represent memory reference instruction.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B & C only
(b) B & D only
(c) A & D only
(d) A & E only
Ans: a
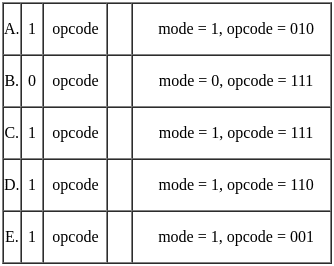
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
Memory Reference Instructions:
Typically, in basic computer architecture (like the one used in many educational models), memory reference instructions have:
A mode bit = 1 (indicating it's a memory reference)
An opcode that belongs to a set of defined memory operations (like
000,001,010,011, etc.)
But certain opcodes (like 111) are usually reserved for non-memory reference instructions, such as:
Register reference
Input/output instructions
Or other system-level operations
Let’s evaluate each option
A. mode = 1, opcode = 010
Mode = 1 → √ Memory reference
Opcode 010 → √ Valid (e.g., could be LDA, STA etc.)
→ √ Memory reference instruction
B. mode = 0, opcode = 111
Mode = 0 → X Not a memory reference (could be register or I/O reference)
→ XNOT a memory reference instruction
C. mode = 1, opcode = 111
Mode = 1 → suggests memory reference
But opcode = 111 is usually not assigned to memory reference — used for I/O or register reference
→ X NOT a valid memory reference instruction
D. mode = 1, opcode = 110
Mode = 1 → √
Opcode = 110 → could still be memory reference depending on the architecture
→ √ Likely a memory reference instruction
E. mode = 1, opcode = 001
Mode = 1 → √
Opcode = 001 → √ Likely memory instruction (e.g., ADD, AND etc.)
→ √ Memory reference instruction
X So, the ones that are NOT memory reference instructions are: B and C
Correct Answer: (b) B & C only
Q42: Which of the following command can be used to modify data in an SQL Table?
A. INSERT
B. DELETE
C. UPDATE
D. SELECT
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, D only
(b) A, C, D only
(c) B, C, D only
(d) A, B, C only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 4) A, B, C only.
- INSERT: This command is used to add new rows of data to a table. It allows you to insert new records into an existing table.
- DELETE: This command is used to remove existing records from a table. It allows you to delete rows from a table based on specified conditions.
- UPDATE: This command is used to modify existing records in a table. It allows you to update values in specified columns for rows that meet certain conditions.
Other Related Points
- SELECT: This command is used to retrieve data from a table. It allows you to query the database and retrieve specific data based on the conditions provided. However, it does not modify the data in the table.
- Therefore, the correct answer includes INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE commands, as they are all used to modify data in a table.
Q43: Consider a noiseless channel with a bandwidth of 5000Hz transmitting a signal with two signal levels. The maximum bit rate is
(a) 2500 bps
(b) 10000 bps
(c) 5000 bps
(d) 20000 bps
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 10000 bps.
According to the Nyquist formula for a noiseless channel, the maximum bit rate can be calculated as:
- Bit Rate = 2 * Bandwidth * log2(L)
- Where L is the number of signal levels.
- In this case, the bandwidth is 5000 Hz and there are 2 signal levels.
- Substituting the values, we get:
- Bit Rate = 2 * 5000 * log2(2)
- log2(2) is 1.
- Therefore, Bit Rate = 2 * 5000 * 1 = 10000 bps
- Hence, the maximum bit rate is 10000 bps.
Other Related Points
- The Nyquist theorem is fundamental in digital communications for determining the maximum data rate of a noiseless channel.
- This theorem is particularly useful in understanding the limitations of signal transmission in various communication systems.
- Practical implementations may achieve lower bit rates due to various factors such as noise and signal attenuation.
- The number of signal levels (L) directly influences the bit rate; higher levels can increase the bit rate, but also increase complexity and potential error rates.
Q44: Which of the following/s is/are FALSE statement?
A. An all key relation is always in BCNF since it has no FDs.
B. A relation that is not in 4NF due to nontrivial MVD must be decomposed to convert it into a set of relations in 4NF.
C. The decomposition removes the redundancy by the MVD.
D. 3NF is stronger than BCNF.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A only
(b) A, B only
(c) D only
(d) C only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is: option 3: D only
Concept & Statement Analysis:
Statement A: ✅ True
An all-key relation means every attribute is part of the candidate key. Hence, no non-trivial Functional Dependencies (FDs) exist. Since BCNF only cares about non-trivial FDs and their compliance with superkeys, the relation is automatically in BCNF.
Statement B: ✅ True
If a relation is not in 4NF due to the presence of a non-trivial Multivalued Dependency (MVD) that violates 4NF, it must be decomposed to eliminate redundancy and achieve 4NF compliance.
Statement C: ✅ True
Yes, the decomposition in 4NF removes redundancy that arises due to MVDs. That's the goal of 4NF: to eliminate non-trivial MVDs that are not supported by superkeys.
Statement D: ❌ False
This is incorrect. In fact, BCNF is stronger than 3NF. Every relation in BCNF is in 3NF, but not every 3NF relation is in BCNF. 3NF allows some redundancy in special cases where BCNF does not.
Explanation of options:
- Option 1 – A only: ❌ A is true.
- Option 2 – A, B only: ❌ A and B are true.
- Option 3 – D only: ✅ Correct. Only D is false.
- Option 4 – C only: ❌ C is true.
Hence, the correct answer is: option 3: D only
Q45: Consider a pipeline unit for fixed - point multiplication of 8-bit integers. Arrange the following stages in a correct sequence.
Stage A : Consists of two CSAS and it merges four numbers from previous stage.
Stage B : is a CPA, which adds up the two numbers
Stage C : is made up of two levels of four CSAS.
Stage D : Generates eight partial products.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C, A, B, D
(b) D, C, A, B
(c) B, D, C, A
(d) A, C, D, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2: D, C, A, B
The correct sequence of stages for fixed-point multiplication of 8-bit integers is as follows:
- Stage D: Generates eight partial products. This stage is the initial step where the multiplicand and multiplier are combined to produce partial products.
- Stage C: Consists of two levels of four CSAS (Carry Save Adders). This stage processes the partial products to reduce the number of operands.
- Stage A: Consists of two CSAS and it merges four numbers from the previous stage. This further reduces the operands.
- Stage B: Is a CPA (Carry Propagate Adder), which adds up the two numbers. This final stage produces the final product by adding the last two numbers.
Q46: The entire set of parameters, including return address that is stored for a procedure invocation is referred to
(a) stack frame
(b) stack base
(c) stack limit
(d) stack record
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is stack frame.
Key Points
A stack frame is a data structure that contains information about the function or procedure invocation.
- It includes the return address, which is the point to which control should return after the function completes.
- The stack frame also contains parameters passed to the function, local variables, and other important data for the function execution.
- Each function call creates a new stack frame, which is pushed onto the call stack.
- When the function completes, its stack frame is popped from the stack, and control returns to the return address.
- Managing stack frames is crucial for maintaining the correct flow of control and data during program execution.
Additional Information
- The stack base is the starting point of the stack memory region, not specific to an individual function call.
- The stack limit refers to the maximum allowed size of the stack memory region.
- The term stack record is less commonly used but can be synonymous with stack frame in some contexts.
- Understanding stack frames is important for debugging and performance optimization in software development.
Q47: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: a
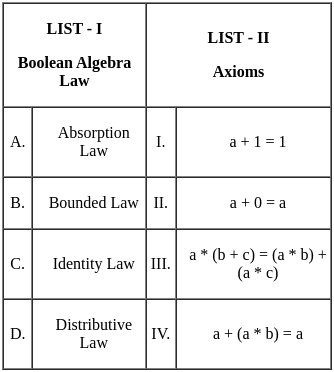
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
The correct matching of Boolean Algebra Laws with their corresponding Axioms is as follows:
- Absorption Law: a + (a * b) = a
- Bounded Law: a + 1 = 1
- Identity Law: a + 0 = a
- Distributive Law: a * (b + c) = (a * b) + (a * c)
Based on this, the correct matching is:
- A - IV (Absorption Law - a + (a * b) = a)
- B - I (Bounded Law - a + 1 = 1)
- C - II (Identity Law - a + 0 = a)
- D - III (Distributive Law - a * (b + c) = (a * b) + (a * c))
Other Related Points
- Understanding Boolean Algebra is essential in digital electronics and computer science for designing and analyzing digital circuits.
- Boolean Algebra allows for the simplification of logic expressions, making it easier to implement and optimize digital systems.
- These fundamental laws and axioms provide the foundation for more complex theorems and applications in Boolean logic and digital design.
Q48: Which one of the following is not the part of requirement management?
(a) Features Traceability Table
(b) Dependency Traceability Table
(c) Interface Traceability Table
(d) Page Traceability Table
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Page Traceability Table.
Key Points
- Requirement management involves tracking and managing changes to the requirements of a system.
- It ensures that all requirements are met and that the development process aligns with the specified needs.
- Common elements of requirement management include:
- Features Traceability Table: Tracks the implementation of various features.
- Dependency Traceability Table: Manages dependencies between different requirements.
- Interface Traceability Table: Tracks interfaces and their specifications.
- Page Traceability Table is not typically part of requirement management. It does not relate to tracking or managing requirements but may instead pertain to documentation or web page tracking.
Additional Information
- Requirement management tools often integrate with other systems to provide a comprehensive view of the project status.
- Effective requirement management can lead to better project outcomes by ensuring all stakeholder needs are addressed.
- Tools like JIRA, IBM DOORS, and HP ALM are commonly used for requirement management.
- Proper documentation and traceability are crucial for audit and compliance purposes.
Q49: Which of the following algorithm are based on the Breadth First Search (BFS)?
A. Prim's algorithm
B. Kruskal algorithm
C. Dijkstra algorithm
D. Greedy algorithm
E. Dynamic Programming
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & B only
(b) A, C & D only
(c) D & E only
(d) A & C only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
Key Points
Prim's Algorithm:
- Prim's Algorithm is used to find the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for a weighted undirected graph.
- It starts from an arbitrary node and explores all the adjacent nodes using BFS to find the edge with the smallest weight that connects the tree to a new vertex.
- It continues this process until all vertices are included in the MST.
Dijkstra's Algorithm:
- Dijkstra's Algorithm is used for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph.
- It starts from the source node and uses BFS to explore all possible paths to other nodes, selecting the path with the smallest cumulative weight.
- It is particularly useful for graphs with non-negative weights.
Additional Information
- Both Prim's and Dijkstra's algorithm rely on the BFS approach to explore nodes level by level, ensuring that the shortest path or smallest weight edge is chosen at each step.
- Prim's Algorithm is specifically used for creating MSTs, whereas Dijkstra's is for shortest path problems.
- While BFS is a fundamental concept, both algorithm incorporate additional logic, such as priority queues, to optimize their respective goals.
Q50: The primary function of firewall in network security is
(a) To monitor network traffic and detect anomalies.
(b) To create virtual private networks for secure communication.
(c) To filter incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules
(d) To encrypt data before Transmission.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is To filter incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
Key Points
The primary function of a firewall in network security is to filter incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
- Firewalls establish a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the Internet.
- They inspect incoming and outgoing traffic and allow or block traffic based on predefined security rules.
- Firewalls can help prevent unauthorized access, monitor network traffic, and protect against various types of cyber attacks.
- They can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both.
- Firewalls are essential components in maintaining network security and ensuring data integrity.
Additional Information
- Firewalls can also provide additional features such as VPN support, intrusion detection and prevention, and content filtering.
- They help protect against common threats such as malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks.
- Modern firewalls may include advanced features like application-level filtering and user authentication.
- The concept of a firewall has evolved over time to adapt to new types of network threats and security requirements.
Q51: Which of the following is the simplified form of the given function.
f(A, B, C) = ∑m(0, 1, 3, 7)
(a) A'B'C' + A'B'C + A'BC + ABC
(b) A'B' + A'BC + ABC
(c) A'B' + BC
(d) A'B' + BC'
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is A'B' + BC.
Key Points
To simplify the given function f(A, B, C) = Σm(0, 1, 3, 7), we use the Karnaugh map method.
We place the minterms in the Karnaugh map:
- m(0): A'B'C'
- m(1): A'B'C
- m(3): A'BC
- m(7): ABC
Grouping the 1s in the Karnaugh map:
- Group 1: A'B' (covers m(0) and m(1))
- Group 2: BC (covers m(3) and m(7))
Therefore, the simplified form is A'B' + BC.
Additional Information
- The simplification process helps to reduce the complexity of the Boolean function, making it easier to implement in digital circuits.
- The Karnaugh map is a visual method used to simplify Boolean expressions without using Boolean algebra theorems and properties.
- Minimizing Boolean functions is essential in designing efficient digital systems with fewer gates and reduced power consumption.
Q52: Arrange the following graph on the basis of number of edges in increasing order [for n > 3]
A. Kn (Complete Graph)
B. Cn (Cycle graph)
C. Wn (Wheel graph)
D. Kn, n (Complete Bipartite Graphs)
E. Qn (n-cubes graph)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, A, D, E
(b) B, A, C, D, E
(c) A, B, C, E, D
(d) E, D, C, A, B
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
- Complete Graph (Kn): Has n(n−1)/2 edges.
- Cycle Graph (Cn): Has n edges.
- Wheel Graph (Wn): Has 2(n−1) edges.
- Complete Bipartite Graph (Kn,n): Has n2 edges.
- n-Cube Graph (Qn): Has n × 2n−1 edges.
- Let us verify using n = 5:
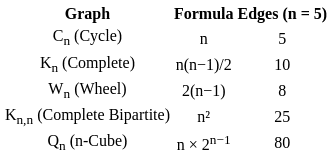
- Now arranging based on increasing number of edges:
- → Cycle (5) < Wheel (8) < Complete (10) < Complete Bipartite (25) < n-Cube (80)
- So, the correct answer is: B,C,A,D,E.
Q53: Correct the order of instruction cycle:
A. Read the effective address
B. Fetch the information
C. Execute the instruction
D. Decode the instruction
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D
(b) B, D, A, C
(c) B, A, D, C
(d) A, B, D, C
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2: B, D, A, C.
The instruction cycle is the process by which a computer retrieves, decodes, and executes an instruction.
The correct sequence of operations is:
- Fetch the information (B): The instruction is fetched from memory.
- Decode the instruction (D): The fetched instruction is decoded to understand the operation to be performed.
- Read the effective address (A): The effective address of the data required for the operation is determined.
- Execute the instruction (C): The instruction is executed and the desired operation is performed.
Other Related Points
- The instruction cycle is fundamental to the operation of all computers and involves multiple steps to ensure that the correct operations are performed accurately.
- Each step in the cycle is crucial for the correct execution of instructions, ensuring that the computer processes data efficiently.
- Understanding the instruction cycle is important for those studying computer architecture and assembly language programming.
Q54: Which of the following is the correct sequence with regard to service routine?
A. Save contents of processor registers
B. Turn the interrupt facility on
C. Service the device whose flag is set
D. Check which flag is set
E. Restore contents of processor registers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) D, B, C, A, E
(c) D, C, B, E, A
(d) A, D, C, E, B
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
To understand the correct sequence of a service routine, it is essential to follow the logical order of operations when handling an interrupt:
- Save contents of processor registers (A): This ensures that the current state of the processor is preserved, so it can be restored later.
- Check which flag is set (D): Determine which device or event caused the interrupt.
- Service the device whose flag is set (C): Perform the necessary actions to handle the interrupt.
- Restore contents of processor registers (E): Restore the processor to its previous state.
- Turn the interrupt facility on (B): Re-enable interrupts to allow further interrupt handling.
The correct sequence is: A, D, C, E, B.
Other Related Points
- This sequence ensures that the system correctly handles the interrupt without losing any critical information or causing inconsistencies.
- Each step is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the processor state and ensuring that the system can continue to operate correctly after the interrupt is serviced.
Q55: Consider the following statements regarding multiple access techniques & identify the CORRECT ones.
A. ALOHA is used for multiple access on a shared medium
B. TDMA uses WALSH TABLES for time slot allocation
C. CSMA/CD was invented for wireless networks
D. CDMA codes are sequence of number generated by orthogonal codes
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & B only
(b) B & C only
(c) C & D only
(d) A & D only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4.
Statement A: ALOHA is used for multiple access on a shared medium.
- ALOHA is a simple communication scheme in which each source in a network sends data whenever there is a frame to send. If the frame collides with another frame, the sender waits for a random amount of time before resending the frame.
- Statement D:CDMA codes are sequences of numbers generated by orthogonal codes.
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) uses orthogonal codes to separate different users. These codes are unique and enable multiple users to share the same frequency without interference.
- Statement B: TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) does not use WALSH TABLES for time slot allocation. TDMA allocates distinct time slots to different users, but the allocation is not managed by Walsh tables, which are used in CDMA for spreading codes.
- Statement C: CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) was not invented for wireless networks. It was designed for wired Ethernet networks. Wireless networks typically use CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) due to the hidden node problem.
Q56: Find the correct sequence of prototype software development model.
A. Start
B. Develop Prototype
C. Deliver to customer
D. Quick Design
E. Quick Play
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) A, E, D, B, C
(c) A, B, D, E, C
(d) A, B, E, D, C
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
- The correct sequence of the prototype software development model is Option 2: A, E, D, B, C.
- This sequence follows a logical progression in the prototype development process.
Explanation
- Step A: Start - The process begins with starting the project.
- Step E: Quick Play - A quick play or initial interaction with the idea or requirement gathering.
- Step D: Quick Design - A quick design is created based on the initial interactions and requirements.
- Step B: Develop Prototype - The prototype is developed based on the quick design.
- Step C: Deliver to Customer - The prototype is then delivered to the customer for feedback and further iterations.
Q57: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that provides increased storage reliability through redundancy.
- Different RAID levels use different methods to improve performance and reliability.
Other Related Points
- RAID level 1: Disk mirroring (II) - In this level, data is duplicated (mirrored) across two or more disks. This provides high data reliability but reduces the storage capacity by half.
- RAID level 2: ECC organization (IV) - This level uses error-correcting codes (ECC) to improve data reliability. It is not commonly used in practice.
- RAID level 3: Bit-interleaved parity organization (I) - This level uses byte-level striping with a dedicated parity disk. It offers good performance for large read and write operations.
- RAID level 4: Block-interleaved parity organization (III) - This level uses block-level striping with a dedicated parity disk. It improves performance for large read operations but can be a bottleneck for write operations.
Q58: Which of the following are not data manipulation instructions?
A. Call
B. Load
C. And
D. Increment
E. Shift
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) C & E only
(b) A & B only
(c) D & E only
(d) A & C only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is 2) A & B only.
- Call: This instruction is typically used in assembly language to call a subroutine or function. It is not a data manipulation instruction as it deals with program control flow.
- Loud: This seems to be a typographical error or a non-standard instruction and does not correspond to any known data manipulation operation.
In contrast, the other options are data manipulation instructions:
- And: This is a logical operation that performs a bitwise AND between two operands, manipulating the data.
- Increment: This instruction increases the value of a variable or register by one, directly manipulating the data.
- Shift: This instruction shifts the bits of a register or memory location left or right, manipulating the data.
Other Related Points
- Data manipulation instructions are used to perform operations on data stored in registers or memory. These operations include arithmetic, logical, and bit manipulation instructions.
- Control flow instructions like Call are used to manage the execution flow of programs and do not directly modify data.
Q59: Arrange the 2-D viewing transformation pipeline.
A. Convert world-coordinates to viewing coordinates
B. Map viewing coordinates to normalized viewing coordinates using window-viewport specifications
C. Construct world - coordinates scene using modeling - coordinates transformations
D. Map normalized viewpoint to device coordinates
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, C, B, A
(b) D, C, A, B
(c) D, A, B, D
(d) B, C, A, D
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
Key Points
The correct sequence for the 2-D viewing transformation pipeline is:
- D. Map normalized viewpoint to device coordinates
- C. Construct world-coordinates scene using modeling-coordinates transformations
- B. Map viewing coordinates to normalized viewing coordinates using window - viewpoint specifications
- A. Convert world-coordinates to viewing coordinates
- This sequence ensures that the scene is first constructed in world coordinates, then converted to viewing coordinates.
- Next, the coordinates are mapped to normalized viewing coordinates, and finally, they are mapped to device coordinates for display.
Additional Information
- Understanding the 2-D viewing transformation pipeline is essential for computer graphics and visualization.
- This process helps in accurately rendering a 2-D scene from world coordinates to device coordinates.
- Each step in the pipeline ensures that the transformations are applied correctly to maintain the integrity of the visual representation.
- Proper handling of transformations avoids distortions and maintains the correct aspect ratio of the graphical objects.
Q60: An alternate key in database table is also called
(a) Primary key
(b) Candidate key
(c) Super key
(d) Foreign key
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Candidate key.
A candidate key is an attribute or a set of attributes that can uniquely identify a row in a table.
- It is an alternative to the primary key in the table.
- Each table can have multiple candidate keys, but only one primary key.
- Candidate keys must contain unique values and cannot contain NULL values.
- Examples of candidate keys include a combination of fields such as a person's social security number and email address.
Additional Information
- Candidate keys are essential in ensuring data integrity and preventing duplicate records in a database.
- While primary keys are often used as references for foreign keys, candidate keys provide flexibility in database design.
- In SQL, you can define candidate keys using unique constraints on the columns.
- Understanding candidate keys is crucial for database normalization and efficient query performance.
Q61: If the virtual memory size is 32 MB and a physical memory size is 4MB with a page size of 2KB, Calculate the number of frames available in physical memory
(a) 1024
(b) 2048
(c) 3072
(d) 4096
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
If the virtual memory size is 32 MB and the physical memory size is 4 MB with a page size of 2 KB, we need to calculate the number of frames available in physical memory.
Calculation:
First, convert the physical memory size into kilobytes (KB):
- 4 MB = 4 * 1024 KB = 4096 KB
Next, divide the physical memory size by the page size to get the number of frames:
- Number of frames = Physical Memory Size / Page Size
- Number of frames = 4096 KB / 2 KB = 2048 frames
Therefore, the number of frames available in physical memory is 2048.
Other Related Points
Virtual Memory:
- Virtual memory allows a computer to compensate for shortages of physical memory by temporarily transferring data from random access memory (RAM) to disk storage.
- It uses both hardware and software to enable a computer to run larger applications or multiple applications simultaneously.
Physical Memory:
- Physical memory refers to the actual RAM installed in a computer.
- It is a volatile memory that temporarily stores data and machine code currently being used.
Page Size:
- Page size is the size of a page in memory management schemes. It is a fixed-length contiguous block of virtual memory.
- Page sizes are typically a power of 2, ranging from 512 bytes to several megabytes.
Q62: The major adverse side effects of scan conversion are ;-
A. Staircase appearance
B. Unequal brightness of slanted lines
C. Picket fence problem
D. Rasterization
E. Pre-filtering and Post-filtering
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & B only
(b) A, B & C only
(c) B, C & D only
(d) C, D & E only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
The major adverse side effects of scan conversion are:
- Staircase appearance: This is a visual artifact that occurs when diagonal or curved lines are rendered as a series of small steps, rather than smooth lines.
- Unequal brightness of slanted lines: This effect happens when the brightness of slanted lines is not consistent, often due to the way pixels are illuminated on the screen.
- Picket fence problem: This is an issue where alternating lines or patterns are not displayed correctly, resembling a picket fence.
Additional Information
- Rasterization: The process of converting vector graphics into a raster image (pixels or dots).
- Pre-filtering and Post-filtering: Techniques used to improve image quality before and after scan conversion.
Q63: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Hadoop Distribution File System is related to the Name-Node in Hadoop architecture.
- The Name-Node is the centerpiece of an HDFS file system. It keeps the directory tree of all files in the file system, and tracks where across the cluster the file data is kept.
Veracity is associated with Trust.
- In the context of big data, veracity refers to the quality and trustworthiness of the data.
Apache Pig is developed by Yahoo.
- Apache Pig is a platform for analyzing large data sets that consists of a high-level language for expressing data analysis programs, coupled with infrastructure for evaluating these programs. Yahoo! developed and contributed Apache Pig to the open-source community.
Apache Hive is developed by Facebook.
- Apache Hive is a data warehousing tool developed by Facebook for querying and managing large datasets residing in distributed storage.
Therefore, the correct matches are:
- A - III (Hadoop Distribution File System - Name-Node)
- B - I (Veracity - Trust)
- C - IV (Apache Pig - Yahoo)
- D - II (Apache Hive - Facebook)
Other Related Points
- These tools and concepts are fundamental in the field of big data and data analysis, each serving a specific purpose and developed by major tech companies.
- Understanding the role and origin of these tools can significantly enhance one's knowledge and capability in handling large-scale data processing and analysis.
Q64: Identify the correct statements from the following regarding spiral model.
A. Spiral model is an incremental process model.
B. Spiral model is a risk - driven process model.
C. Spiral model is an acyclic balancing approach.
D. Spiral model involves a set of anchor point milestone.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & B Only
(b) B & C Only
(c) A & D Only
(d) B & D Only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is 4) B & D Only.
Key Points
- The Spiral model is a risk-driven process model (Statement B). It focuses on identifying and mitigating risks at each iteration of the model.
- The Spiral model involves a set of anchor point milestones (Statement D) which are used to ensure that the project stays on track and meets its objectives.
Additional Information
- The Spiral model is indeed an incremental process model (Statement A), but that is not the only characteristic; hence, option 4 is more comprehensive.
- The Spiral model is not an acyclic balancing approach (Statement C); it involves repeating cycles, or iterations, to progressively refine the project.
- Each cycle in the Spiral model includes planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation phases.
- The model is particularly effective for large, complex, and high-risk projects where changes are expected during the development process.
Q65: Which one of the following is not related to the feed forward networks on the Backpropagation Algorithm
(a) Boolean function
(b) Continuous function
(c) Arbitrary function
(d) Greedy function
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is Greedy function.
- Feedforward networks and the Backpropagation algorithm are used in training neural networks.
- These algorithms can learn to approximate Boolean functions, continuous functions, and even arbitrary functions.
- Greedy algorithms, on the other hand, are a different class of algorithms that build up a solution piece by piece, always choosing the next piece that offers the most immediate benefit.
- Therefore, Greedy function is not directly related to the feedforward networks on the Backpropagation algorithm.
Other Related Points
- Feedforward networks process data in one direction from input to output.
- Backpropagation is a supervised learning algorithm used for training artificial neural networks.
- It minimizes the error by adjusting the weights in the network based on the error gradient.
- Greedy algorithms are typically used in optimization problems and are not used in neural network training.
- Examples of greedy algorithms include Dijkstra's algorithm for shortest paths, Prim's algorithm for minimum spanning trees, etc.
Q66: Which of the following statement is not True?
(a) A data member of a class can be declared as static and is normally used to maintain values common to the entire class.
(b) A friend function can be invoked like a normal function without the help of any object.
(c) The scope resolution operator (::) can be overloaded like normal operators
(d) Multiple inheritance may lead to duplication of inherited members from a "Grandparent" base class. This may be avoided by making the common base class a virtual base class.
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Key Points
- A data member of a class can be declared as static and is normally used to maintain values common to the entire class.
- A friend function can be invoked like a normal function without the help of any object.
- The scope resolution operator (::) cannot be overloaded like normal operators.
- Multiple inheritance may lead to duplication of inherited members from a "Grandparent" base class. This may be avoided by making the common base class a virtual base class.
Additional Information
- The scope resolution operator (::) is used to define the scope of a function or a variable in C++.
- While most operators can be overloaded in C++, the scope resolution operator (::) is one of the few exceptions that cannot be overloaded.
- This restriction helps in maintaining the clarity and unambiguous usage of the scope resolution operator.
Q67: Which of the following table contains the primary information in the data warehouse?
(a) Dimension table
(b) Fact table
(c) Lookup table
(d) Primary table
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Fact table.
A Fact table contains the primary information in a data warehouse.
- The fact table stores quantitative data for analysis and is often denormalized.
- It usually contains foreign keys to dimension tables which describe the context of the facts.
- The fact table is central to the star schema and snowflake schema of data warehousing.
- It typically includes measures (numeric values) and keys to associated dimension tables.
- Examples of measures in a fact table include sales amount, quantity sold, and transaction count.
Other Related Points
- Fact tables are optimized for query performance and are often indexed to speed up data retrieval.
- They are typically large in size and grow quickly as more transactional data is added over time.
- Fact tables can be categorized into different types such as transactional, periodic snapshot, and accumulating snapshot fact tables.
- Unlike dimension tables, which store descriptive attributes, fact tables focus on storing measurable, quantitative data.
Q68: Arrange the following steps of the Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree in the correct order.
A. Visit the Left subtree
B. Visit the Root node
C. Visit the Right subtree
D. Start traversing by visiting the nodes in rooted tree
E. Repeat the above three steps.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) E, A, B, C, D
(c) D, A, B, C, E
(d) D, A, E, B, C
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is option 3: D, A, B, C, E
In order traversal of a binary tree is a type of depth-first traversal where nodes are visited in the following order:
- Step 1: Start traversing by visiting the nodes in the rooted tree.
- Step 2: Visit the Left subtree.
- Step 3: Visit the Root node.
- Step 4: Visit the Right subtree.
- Step 5: Repeat the above three steps for each subtree.
Q69: Arrange the following steps of the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) process in the correct - sequence.
A. DHC PACK
B. DHCP DISCOVER
C. DHCP OFFER
D. DHCP REQUEST
E. Client receives IP configuration
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) B, C, D, A, E
(c) C, B, A, E, D
(d) D, A, E, C, B
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network management protocol used to automate the process of configuring devices on IP networks.
- The DHCP process consists of several steps to assign an IP address to a client.
- The correct sequence of the DHCP process is as follows:
- DHCP DISCOVER: The client sends a broadcast message to discover a DHCP server.
- DHCP OFFER: The DHCP server responds with an offer message containing an IP address and configuration details.
- DHCP REQUEST: The client requests the offered IP address and configuration from the DHCP server.
- DHCP ACK: The DHCP server acknowledges the request and assigns the IP address to the client.
- Client receives IP configuration: The client receives the IP configuration and can now use the network.
Other Related Points
- DHCP simplifies network management by automatically assigning IP addresses and reducing manual configuration efforts.
- DHCP can also provide other network configuration information such as default gateway, subnet mask, and DNS servers.
- DHCP leases IP addresses to clients for a specific duration, after which the client must renew the lease.
- DHCP can be used in both small and large networks, including home networks, enterprise networks, and service provider networks.
Q70: Which one of the following is the correct estimation model based on software equation?
(a) E = [LOC × B0.222/P]2 × (1/t4)
(b) E = [LOC × B0.333/p]3 × (1/t4)
(c) E = [LOC × B0.444/p]4 × (1/t3)
(d) E = [LOC × B0.111/p]6 × (1/t3)
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
- The correct estimation model based on software equation is:
- E = [LOC × B0.333/P]3 × (1/t4)
- This model is used to estimate the effort required for software development.
- LOC stands for Lines of Code, B is a constant, P stands for productivity, and t represents time.
- In this model, the effort is proportional to the cube of the size of the code divided by productivity and inversely proportional to the fourth power of time.
Additional Information
- Estimation models help project managers and developers to predict the time and cost required to complete a software project.
- They are crucial for planning and resource allocation.
- Different models may be used based on the type and complexity of the software project.
- Understanding and using the correct estimation model can significantly impact the success of a software project.
Q71: Consider the following Graph of disk scheduling and identify the disk scheduling algorithm representing by this graph.
Queue 84, 125, 11, 36, 170, 20, 172, 45
(a) SSTF
(b) SCAN
(c) C-SCAN
(d) C-LOOK
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is C-LOOK.
- C-LOOK (Circular LOOK) is a disk scheduling algorithm that is an optimized version of the LOOK algorithm.
- In C-LOOK, the disk arm only goes as far as the last request in each direction, then immediately reverses direction without going to the end of the disk.
- This minimizes the movement of the disk arm and reduces the total seek time.
- When the disk arm reaches the end of the queue in one direction, it jumps to the other end of the queue and starts servicing requests in the opposite direction.
- This is different from the C-SCAN algorithm, where the disk arm goes to the end of the disk and then starts from the beginning.
Other Related Points
- The queue given is: 84, 125, 11, 36, 170, 20, 172, 45.
- Assume the initial position of the disk arm is at 50.
- Using the C-LOOK algorithm, the disk arm will first service requests in one direction until it reaches the last request, then it will jump to the other end of the queue and continue servicing requests.
- Here’s how the sequence looks like: 84, 125, 170, 172, then jump back to the start and service: 11, 20, 36, 45.
- This minimizes the seek time compared to other algorithms like SCAN or C-SCAN.
Q72: The hamming distance between 10101 and 11110 is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
- The Hamming distance between two strings of equal length is the number of positions at which the corresponding symbols are different.
- To calculate the Hamming distance between the binary strings 10101 and 11110, compare each corresponding position:
- Position 1: 1 vs 1 (no difference)
- Position 2: 0 vs 1 (difference)
- Position 3: 1 vs 1 (no difference)
- Position 4: 0 vs 1 (difference)
- Position 5: 1 vs 0 (difference)
- There are 3 positions where the corresponding bits differ.
Hence, the Hamming distance between 10101 and 11110 is 3.
Other Related Points
- The Hamming distance is used in error detection and correction in data transmission.
- It is named after Richard Hamming, an American mathematician and computer scientist.
- It is particularly useful in coding theory for designing error-correcting codes.
- The concept can be extended to other types of data, such as text strings and DNA sequences.
Q73: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
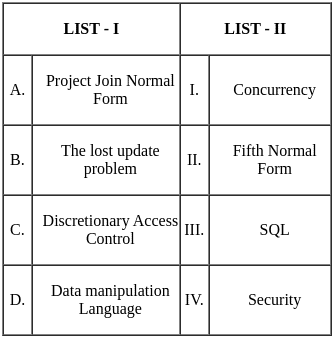
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
Project Join Normal Form (PJNF) is associated with Fifth Normal Form(II).
- Fifth Normal Form (5NF), also known as PJNF, is used to eliminate redundancy in relational databases.
The lost update problem is associated with Concurrency(I).
- The lost update problem occurs when multiple transactions are updating the same data concurrently, leading to incorrect or lost updates.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC) is associated with Security(IV).
- Discretionary Access Control is a type of access control where the owner of the data or resource determines who can access it, enhancing security.
Data Manipulation Language (DML) is associated with SQL(III).
- DML is a subset of SQL that includes commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, used for data manipulation in databases.
Other Related Points
- Understanding the relationships between database concepts and their applications is essential for database management and security.
- Ensuring proper normalization and access control mechanisms are crucial for maintaining data integrity and security.
Q74: The kind of symbols for basic syntactic elements of first-order logic are
A. Constant
B. Domain
C. Predicate
D. Temporal
E. Function
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D only
(b) A, B, C only
(c) A, C, E only
(d) C, D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 3) A, C, E only.
Key Points
First-order logic includes several basic syntactic elements that are essential for its formulation and interpretation.
The correct symbols involved are:
- Constant (A): Represents specific objects in the domain of discourse.
- Predicate (C): Represents properties of objects or relationships between objects in the domain.
- Function (E): Represents mappings from tuples of objects to objects within the domain.
Additional Information
- Domain (B) is not a symbol but rather the set of all objects under consideration in a particular interpretation.
- Temporal (D) is related to temporal logic, not first-order logic, and involves time-dependent statements.
- First-order logic is also known as predicate logic or first-order predicate calculus.
- It is a formal system used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science.
Q75: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
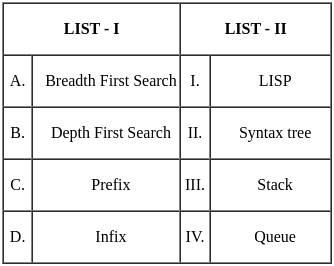
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is option 4.
Key Points
Breadth First Search (A) uses a Queue (IV).
- BFS explores all nodes at the present depth level before moving on to nodes at the next depth level, making use of a queue data structure to keep track of nodes to be explored.
Depth First Search (B) uses a Stack (III).
- DFS explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking, making use of a stack data structure to keep track of the path.
Prefix (C) is associated with LISP (I).
- In LISP and other prefix notation systems, operators precede their operands.
Infix (D) is related to the Syntax tree (II).
- Infix notation is commonly used in arithmetic expressions and can be represented by a syntax tree where each node represents an operator and its children represent operands.
Additional Information
- Breadth First Search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) are fundamental algorithms used in graph theory and have applications in various fields such as AI, network analysis, and more.
- Prefix notation, also known as Polish notation, and Infix notation are different ways of writing arithmetic expressions used in computer science and mathematics.
- Understanding the differences between these notations and their implementations is crucial for fields like compiler design and expression evaluation.
Q76: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
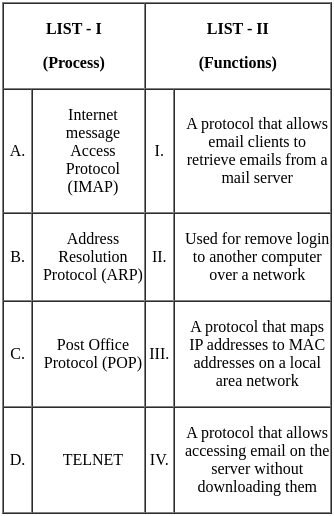
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP): A protocol that allows accessing email on the server without downloading them. (IV)
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): A protocol that maps IP addresses to MAC addresses on a local area network. (III)
- Post Office Protocol (POP): A protocol that allows email clients to retrieve emails from a mail server. (I)
- TELNET: Used for remote login to another computer over a network. (II)
- IMAP allows users to access and manage their email directly on the mail server, making it possible to access the same inbox from multiple devices.
- ARP is essential for local area network communication as it translates IP addresses into MAC addresses, allowing devices to locate each other on the same network.
- POP downloads emails from the mail server to the local device, making it accessible without an internet connection but not synchronizable across multiple devices.
- TELNET is one of the oldest network protocols used to establish a remote connection to another computer, typically for managing devices or systems.
Q77: Collaborative document inspection technique used for?
(a) Requirement Validation Process
(b) Requirement Verification Process
(c) Integration Testing
(d) Blackbox Testing
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Requirement Validation Process.
Key Points
- Collaborative document inspection is a technique used in the requirement validation process.
- It involves stakeholders and team members reviewing and discussing requirements to ensure they are complete, accurate, and feasible.
- This technique helps identify any ambiguities, inconsistencies, or missing information in the requirements.
- It ensures that all stakeholders have a common understanding of the requirements before they are finalized.
- Collaborative inspections often involve meetings, reviews, and feedback sessions to validate requirements.
Additional Information
- Requirement validation is a critical step in the software development lifecycle to ensure project success.
- It helps prevent costly changes and rework by catching issues early in the process.
- Other techniques used in requirement validation include prototyping, simulation, and formal methods.
- Effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders are key to successful requirement validation.
Q78: If x and y are elements in a group G and if x5 = y3 = e, where e is the identity of G, then the inverse of x2yx4y2 must be
(a) y2xy2x4
(b) yxy2x3
(c) yx6y6x3
(d) x4y2x2y
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is: Option 2
Concept:
The inverse of a product of elements in a group is the reverse product of their inverses. Given 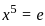 and
and 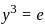 , we use:
, we use:
1. 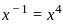 (since
(since 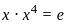 ).
).
2. 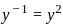 (since
(since 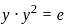 ).
).
Given:
Element to invert: 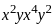
Conditions: 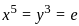 (identity).
(identity).
Steps:
1. Apply the inverse property 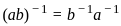 in reverse order:
in reverse order: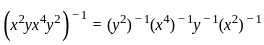 .
.
2. Compute each inverse:
- 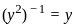 (since
(since 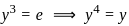 ).
).
- 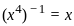 (since
(since 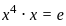 ).
).
- 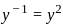 .
.
- 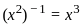 (since
(since 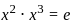 ).
).
3. Substitute and simplify: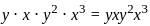 .
.
Verification:
Multiply  by
by  :
:
-  ,
, 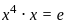 ,
,  ,
,  .
.
Result:  (identity), confirming correctness.
(identity), confirming correctness.
Final Answer: Option 2 - yxy2x3
Q79: Which one of the following is not a basic solution of system of linear equation
x1 + 2x2 + x3 = 4
2x1 + x2 + 5x3 = 5
(a) x1 = -1, x2 = 2, x3 = 1
(b) x1 = 2, x2 = 1
(c) x1 = 5, x3 = -1
(d) x2 = 5/3, x3 = 2/3
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1.
To determine if a given set of values is a basic solution for a system of linear equations, we need to check if the values satisfy all the equations in the system.
The given system of linear equations is:
x1 + 2x2 + x3 = 4 2x1 + x2 + 5x3 = 5
Let's evaluate each option:
Option 1: x1 = -1, x2 = 2, x3 = 1
- Substitute into the first equation: -1 + 2(2) + 1 = -1 + 4 + 1 = 4 (satisfies)
- Substitute into the second equation: 2(-1) + 2 + 5(1) = -2 + 2 + 5 = 5 (satisfies)
Option 2: x1 = 2, x2 = 1
- Missing x3 value, so this option cannot satisfy both equations simultaneously. This is the correct answer as it is incomplete.
Option 3: x1 = 5, x3 = -1
- Missing x2 value, so this option cannot satisfy both equations simultaneously.
Option 4: x2 = 5/3, x3 = 2/3
- Missing x1 value, so this option cannot satisfy both equations simultaneously.
Other Related Points
- In a system of linear equations, a basic solution typically involves having the same number of independent equations as unknowns, with each unknown having a unique value.
- Basic solutions can be found using methods such as substitution, elimination, or matrix operations.
- Consistency of the system needs to be checked to ensure that there are no contradictions in the equations.
Q80: The probability that A hits a target is 1/4, and the probability that B hits the target is 2/5. Both shoot at the target, what is the probability that at least one of them hits the target, i.e., that A or B (or both) hit the target?
(a) 3/5
(b) 11/9
(c) 2/20
(d) 11/20
Ans: d
Sol: The probability that at least one of A or B hits the target can be found using these steps:
- The probability that A misses the target is 1 - 1/4 = 3/4.
- The probability that B misses the target is 1 - 2/5 = 3/5.
- The probability that both miss is (3/4) × (3/5) = 9/20.
- So, the probability that at least one hits the target is 1 - 9/20 = 11/20.
Additional Information
- This problem involves the concept of complementary probability, which is useful when calculating the probability of at least one event occurring.In probability theory, the complement rule is used to determine the probability of an event not occurring.
- Option 4 is indeed correct as the final probability calculation matches the probability required.
Q81: Which of the following represents the output of the transition function(δ)
δ(q0,a) = (q1, x, R)
δ(q1,a) = (q1, a, R)
δ(q1, y) = (q1, y, R)
δ(q1, b) = (q2, y, L)
δ(q2, y) = (q2, y, L)
δ(q2, a) = (q2, a, L)
δ(q2, x) = (q0, x, R)
δ(q0, y) = (q3, y, R)
δ(q3, y) = (q3, y, R)
δ(q3, ◻) = (qf, ◻, R)
(a) L = {anbn|n ≥ 0}
(b) L= {anbn|n ≥ 1}
(c) L = {anbn|n > 0}
(d) L = {anbn|n > 1}
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is L = {anbn|n ≥ 1}.
Key Points
This Turing machine recognizes the language L = {anbn|n ≥ 1} which means it accepts strings where the number of 'a's is equal to the number of 'b's, and there is at least one 'a' and one 'b'.
The transition functions describe how the machine processes the input:
- δ(q0,a) = (q1, x, R): When in state q0 and reading 'a', it replaces 'a' with 'x' and moves right, transitioning to state q1.
- δ(q1,a) = (q1, a, R): When in state q1 and reading 'a', it keeps 'a' and moves right, staying in state q1.
- δ(q1, y) = (q1, y, R): When in state q1 and reading 'y', it keeps 'y' and moves right, staying in state q1.
- δ(q1, b) = (q2, y, L): When in state q1 and reading 'b', it replaces 'b' with 'y' and moves left, transitioning to state q2.
- δ(q2, y) = (q2, y, L): When in state q2 and reading 'y', it keeps 'y' and moves left, staying in state q2.
- δ(q2, a) = (q2, a, L): When in state q2 and reading 'a', it keeps 'a' and moves left, staying in state q2.
- δ(q2, x) = (q0, x, R): When in state q2 and reading 'x', it keeps 'x' and moves right, transitioning to state q0.
- δ(q0, y) = (q3, y, R): When in state q0 and reading 'y', it keeps 'y' and moves right, transitioning to state q3.
- δ(q3, y) = (q3, y, R): When in state q3 and reading 'y', it keeps 'y' and moves right, staying in state q3.
- δ(q3, ◻) = (qf, ◻, R): When in state q3 and reading blank (◻), it keeps the blank and moves right, transitioning to final state qf.
Additional Information
- In state q0, the machine starts by marking an 'a' with 'x' and then searches for the corresponding 'b' to mark it with 'y'.
- In state q1, the machine skips over 'a's and 'y's until it finds a 'b'.
- In state q2, the machine moves left to revisit and check the marked 'x' and continues the process until all 'a's and 'b's are marked.
- When all 'a's and 'b's are marked, the machine moves to state q3, where it verifies the marking and then transitions to the final state qf.
Q82: Given the following processes with their times and priority (lower number indicates higher priority)
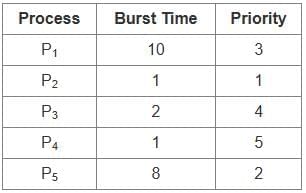
Which of the following is a value of average waiting time using priority scheduling algorithm?
(a) 9.2
(b) 6.8
(c) 7.6
(d) 10.0
Ans: d
Sol: The priority scheduling algorithm executes processes based on their priority, with lower numbers meaning higher priority. To find the average waiting time, follow these steps:
- List processes in order of priority (from highest to lowest).
- Calculate the waiting time for each process by adding up the burst times of all previous processes.
- Add all waiting times and divide by the number of processes to get the average.
For the given data, the calculated average waiting time is 10.0.
Q83: The degree of a relation in database is
(a) the number of tuples in the relation
(b) the number of attribute in the relation
(c) the number of values in domain
(d) the number of keys in a relation
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is the number of attributes in the relation.
The degree of a relation (or table) in a database refers to the number of attributes (or columns) that the relation contains.
- Each attribute represents a property or characteristic of the entity that the relation describes.
- For example, in a student relation, attributes could include student ID, name, age, and major.
- The degree of the student relation would be 4 if there are four attributes.
- This term is different from the cardinality of a relation, which refers to the number of tuples (or rows) in the relation.
Additional Information
- Understanding the degree of a relation is essential in database design, as it impacts how data is structured and accessed.
- Database schemas define the structure of relations, including their degree and the data types of their attributes.
- Normalization techniques in database design aim to optimize the degree and minimize redundancy.
- Relational database management systems (RDBMS) use the schema to enforce data integrity and support query optimization.
Q84: Which of the following are correct for the neural network?
A. The training time depends upon the size of network.
B. Neural network can be simulated on the conventional computer.
C. Neural network mimic the same way as that of the humans brain.
D. A neural network include feedback.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) A, C and D only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) A and C only
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2.
Key Points
Training Time and Network Size:
- The training time of a neural network depends upon the size of the network. Larger networks typically require more time to train due to the increased number of parameters that need to be adjusted.
Neural Network Simulation:
- Neural networks can be simulated on conventional computers. Various software frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras allow for the simulation and training of neural networks on standard computing hardware.
Neural Network Mimicry:
- Neural networks are designed to mimic the way the human brain processes information. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process inputs in a manner similar to the synapses in a human brain.
Feedback in Neural Networks:
- Some neural networks include feedback mechanisms, particularly in recurrent neural networks (RNNs), where outputs from previous steps are fed back into the network as inputs for future steps.
Additional Information
- Neural networks are a key component of deep learning, which is a subset of machine learning.
- They are used in various applications such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems.
- Training a neural network involves adjusting the weights of the connections between neurons to minimize the error in predictions.
- Neural networks can be categorized into different types, such as feedforward neural networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), each suited for specific types of tasks.
Q85: Which of the following is the complement of the boolean function.
A'B + CD' + A'B + CD'
(a) A'B + CD'
(b) (A + B)(C + D')
(c) (A + B')(C' + D)
(d) AB' + CD'
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3) (A + B')(C' + D).
Given Boolean function: A'B + CD' + A'B + CD'
First simplify the given expression:
- A'B + A'B = A'B (redundant term)
- CD' + CD' = CD' (redundant term)
So, the simplified function = A'B + CD'
Now, we are asked to find the complement of this function:
Let F = A'B + CD'
Then the complement is: F' = (A'B + CD')'
Apply De Morgan’s Law:
- (A'B + CD')' = (A'B)' · (CD')'
- (A'B)' = A + B'
- (CD')' = C' + D
Therefore, F' = (A + B')(C' + D)
Hence, the correct answer is: Option 3) (A + B')(C' + D)
Q86: Which of the following are key features of Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANETs)
A. Self-Organizing and decentralized.
B. High Mobility of nodes.
C. Requires fixed Infrastructure for operation.
D. Network Topology is dynamic and constantly changing.
E. It requires a central controller to manage network traffic.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B & E only
(b) B, C, D & E only
(c) A, B & D only
(d) A, B & C only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is 3) A, B & D only.
- Self-Organizing and decentralized: MANETs are self-configuring networks without the need for a centralized control. Nodes organize themselves dynamically.
- High Mobility of nodes: Nodes in MANETs are often mobile, leading to frequent changes in the network topology.
- Network Topology is dynamic and constantly changing: Due to the mobility of nodes, the network topology in MANETs changes frequently.
Other Related Points
- MANETs do not require fixed infrastructure for their operation. They can function independently of any pre-existing infrastructure.
- There is no central controller required to manage network traffic in MANETs, which is a characteristic contrary to option E.
- MANETs are used in various applications such as military operations, disaster recovery, and mobile communication where a fixed infrastructure is not feasible.
Q87: Choose the correct statements from the following
A. In connection oriented service, the destination address is to be specified only during the setup.
B. Packet sequencing is not guaranteed in connection oriented service
C. Flooding is method in which every incoming packet is sent out on every outgoing line except the one by which it arrived.
D. Presentation layer performs detection and recovery from errors in the transmitted data.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B & C only
(b) B, C & D only
(c) A & C only
(d) A, C & D only
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Statement A: In connection-oriented service, the destination address is to be specified only during the setup.
- This statement is correct because, in a connection-oriented service, a connection is first established between the sender and receiver before data is transmitted. The destination address is specified during the setup phase.
Statement C: Flooding is a method in which every incoming packet is sent out on every outgoing line except the one by which it arrived.
- This statement is correct. Flooding is a network routing technique where every incoming packet is sent to all outgoing lines except the one it arrived on, ensuring that packets reach their destination by multiple paths.
Other Related Points
Statement B: Packet sequencing is not guaranteed in connection-oriented service.
- This statement is incorrect. Connection-oriented services, such as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), guarantee packet sequencing, ensuring that packets are delivered in the correct order.
Statement D: Presentation layer performs detection and recovery from errors in the transmitted data.
- This statement is incorrect. Error detection and recovery are typically handled by the transport layer, not the presentation layer. The presentation layer is responsible for data translation, encryption, and compression.
Q88: Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
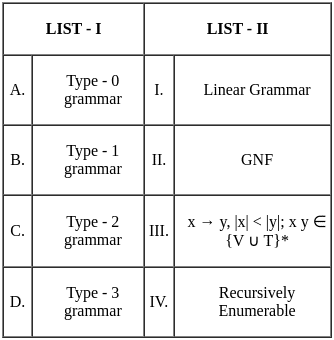
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - lI, D - I
Ans: d
Sol: Type-0 Grammar: Also called Unrestricted Grammar. Recognized by Turing Machines. These languages are Recursively Enumerable. → IV
Type-1 Grammar: Context-Sensitive Grammar. Rules are of the form x → y where |x| ≤ |y| and both sides are strings over variables and terminals. → III
Type-2 Grammar: Context-Free Grammar. Can be converted into Greibach Normal Form (GNF). → II
Type-3 Grammar: Regular Grammar. A subset of CFGs where production rules are linear. → I
Correct Matching:
- A → IV
- B → III
- C → II
- D → I
Correct Answer: Option 4) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Q89: Which of the following Graph is/are planar?
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) B only
(c) A only
(d) A and B only
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is A and B only.
- A planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges intersect only at their endpoints.
- Planar graphs follow Kuratowski's theorem, which states that a graph is planar if and only if it does not contain a subgraph that is a subdivision of K5 (complete graph on five vertices) or K3,3 (complete bipartite graph on six vertices).
- To determine if a graph is planar, one can try to draw it in such a way that no edges cross each other, except at the vertices.
- Graphs A and B are determined to be planar by verifying that they can be drawn without any edge crossings.
- Graph C is not planar because it contains a subgraph that is homeomorphic to K5 or K3,3, which means it cannot be drawn without edge crossings.
- Planar graphs are useful in various fields such as computer networking, geography, and circuit design, where planar embeddings help to minimize complexity and avoid intersections.
- Graph theory provides various algorithms to check for planarity, such as the Hopcroft and Tarjan planarity testing algorithm.
Q90: As per the Software Engineering Institute (SEI), the correct sequence is
A. Initial
B. Repeatable
C. Managed
D. Optimizing
E. Defined
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) A, B, E, C, D
(c) A, E, C, D, B
(d) A, E, B, C, D
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is : option 2
As per the Software Engineering Institute (SEI), the correct sequence for the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) levels is:
- Initial
- Repeatable
- Defined
- Managed
- Optimizing
This sequence reflects the stages of maturity that organizations go through as they improve their software engineering processes. Therefore, the correct answer, which aligns with option 2, is:
Option 2: A, B, E, C, D
Q91: A machine is represented by states Q, input alphabet Σ, transition function δ. Initial state qo and final state F. The machine accepts all the strings over Σ = {a,b}, which starts and ended with any combination of all alphabet and abb works/lies in all the strings to be accepted
For the above specified passage, which of the following is DFA for the language represented/accepted by machine?
(a) 
(b) 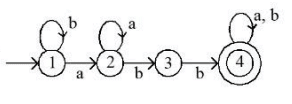
(c) 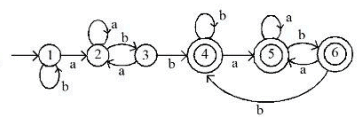
(d) 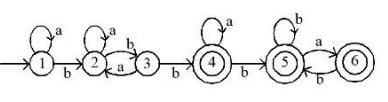
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is : Option 3
Option 1: This DFA starts with state 1 looping on a and b. Then from 1 --a--> 2, 2 --b--> 3, and 3 --b--> 4. After reaching state 4, it loops on a and b and accepts. Looks promising, but lacks rejection for incorrect sequences like “aba”. It accepts too many patterns and has no trap state to reject wrong combinations. Incorrect.
Option 2: This DFA takes a → b → a → b → final. This structure doesn’t track “abb” correctly; it adds unnecessary transitions and doesn’t form the required substring properly. Incorrect.
Option 3: This DFA clearly implements the pattern detection:
- q1 --a--> q2
- q2 --b--> q3
- q3 --b--> q4 (final)
- q4 is the accepting state, loops on all inputs (a, b)
- Other transitions (like wrong 'a' or 'b') push to dead states
This structure correctly captures the presence of “abb” as a substring.
Correct Answer is Option 3
Q92: A machine is represented by states Q, input alphabet Σ, transition function δ. Initial state qo and final state F. The machine accepts all the strings over Σ = {a,b}, which starts and ends with any combination of all alphabet and abb works/lies in all the strings to be accepted
For the above specified passage, which of the following represents the regular expression?
(a) (a + b)* aab
(b) aba(a + b)*
(c) b(a + b)* b(a + b)* a(a + b)*
(d) (a + b)* abb(a + b)*
Ans: d
Sol: The correct answer is (a + b)* abb(a + b)*.
Key Points
The given regular expression (a + b)* abb(a + b)* matches any string that has "abb" in between any combination of 'a' and 'b' characters.
- The part (a + b)* indicates any combination (including none) of 'a' and 'b' characters before "abb".
- The part abb is the fixed substring that must appear in the string.
- The part (a + b)* after "abb" indicates any combination (including none) of 'a' and 'b' characters after "abb".
This regular expression ensures that "abb" is always present in the string, surrounded by any number of 'a' and 'b' characters.
Additional Information
- Regular expressions are powerful tools used for pattern matching and string manipulation.
- They are widely used in various programming languages and tools for searching, replacing, and validating text.
- Understanding the components and structure of regular expressions is essential for effectively utilizing them in different applications.
- Common operations using regular expressions include searching for specific patterns, validating input data, and parsing text.
Q93: A machine is represented by states Q, input alphabet Σ, transition function δ. Initial state qo and final state F. The machine accepts all the strings over Σ = {a,b}, which starts and ends with any combination of all alphabet and abb works/lies in all the strings to be accepted
For the above mentioned passage which of the following is correct?
(a) 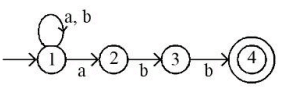
(b) 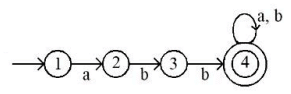
(c) 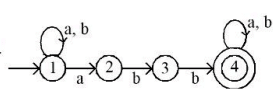
(d) 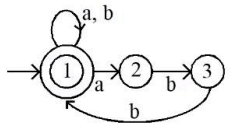
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Option 1: The DFA transitions a → b → b directly to final state. But it lacks proper looping logic to verify intermediate characters. No trap state. Incorrect.
Option 2: Accepts strings only if they end with “abb”. But the question states the string can have “abb” anywhere. Incorrect.
Option 3: The DFA clearly detects “abb” and loops over further inputs. So, even strings like “aabb”, “baabbab”, “abba” will be accepted. Correct ✔
Q94: A machine is represented by states Q, input alphabet Σ, transition function δ. Initial state qo and final state F. The machine accepts all the strings over Σ = {a,b}, which starts and ends with any combination of all alphabet and abb works/lies in all the strings to be accepted
For the above specified passage, which of the following represent the grammar for the language accepted the machine?
(a) S → AabbB, A → aA|∈, B → bB|∈
(b) S → abbA, A → aA|∈|bA
(c) S → AabbA, A → aA|bA|∈
(d) S → Aabb, A → aA|bA|∈
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Option 3.
Option 3 specifies the grammar for the language accepted by the machine as follows:
- S → AabbA
- A → aA | bA | ε
This grammar generates strings where:
- The start symbol S derives a string with 'A', followed by 'aabb', followed by 'A'.
- The non-terminal A can be replaced by 'aA', 'bA', or ε (the empty string).
This allows for the generation of strings with 'a' and 'b' characters appropriately placed in the structure defined by the grammar.
- Grammar rules (productions) define how strings in a language can be generated from the start symbol.
- The symbol 'ε' denotes the empty string, which means a non-terminal can be replaced by nothing.
- The use of non-terminals like A allows for recursive definitions, enabling the generation of complex strings.
- Correct grammar formulations are essential in parsing and generating strings in programming languages and compilers.
Q95: A machine is represents by states Q, input alphabet Σ, transition function δ. Initial state qo and final state F. The machine accepts all the strings over Σ = {a,b}, which starts and ended with any combination of all alphabet and abb works/lies in all the strings to be accepted
Which of the following represents the minimum state DFA for the above specified passage?
(a) 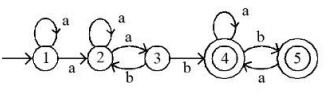
(b) 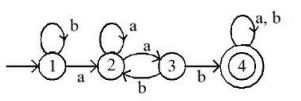
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: a
Sol: The correct answer is: Option 1
To detect “abb”, we need at least 4 states:
- q0 — Start state
- q1 — After seeing 'a'
- q2 — After seeing 'ab'
- q3 — After seeing 'abb' → Accepting
We also need a dead state to trap wrong transitions. So the **minimum** DFA needs at least 5 states.
Option 1: This DFA uses 5 states correctly and has transitions:
- q1 → q2 (on a)
- q2 → q3 (on b)
- q3 → q4 (on b) → final
- Final state loops on a, b
This is a proper minimal DFA. Correct
Option 2: Incorrect transitions. Accepts some but not all “abb” variants. Incorrect
Option 3: Uses 6 states, which is not optimal/minimal. Incorrect
Q96: Consider the following set of processes with the arrival time and length of CPU burst time given in milliseconds (ms)
Find the average weighted turnaround time for these process using Highest Response Ratio Next (HRN) Algorithm?
(a) 3.2 ms
(b) 2.834 ms
(c) 1.632 ms
(d) 6.721 ms
Ans: b
Sol: The correct answer is option 2.
CONCEPT:
Highest Response Ratio Next (HRN):
HRN is a non-preemptive scheduling algorithm where the process with the highest response ratio is selected next. The response ratio is calculated as:
Response Ratio = (Waiting Time + Burst Time) / Burst Time
Formula:
Turnaround Time (TAT) = Completion Time (CT) - Arrival Time (AT)
Weighted TAT = Turnaround Time / Burst Time
Steps:
- Select the process with the highest response ratio among all arrived processes.
- Compute completion time, TAT, and weighted TAT.
- Repeat until all processes are scheduled.
Calculated weighted turnaround times:
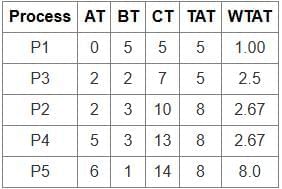
Average Weighted Turnaround Time = 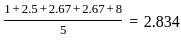
∴ Hence, the correct answer is 2.834 ms
Q97: Consider the following set of processes with the arrival time and length of CPU burst time given in milliseconds (ms)
What is the average turnaround time for these Processes with First Come First Serve (FCFS) scheduling Algorithm?
(a) 5.3 ms
(b) 6.4 ms
(c) 7.0 ms
(d) 8.2 ms
Ans: c
Sol: To find the average turnaround time using the FCFS scheduling algorithm, follow these steps:
- List the processes in the order they arrive.
- For each process, calculate its completion time by summing the burst times of all previous processes, including itself.
- Turnaround time for each process = Completion time - Arrival time.
- Find the average by adding all turnaround times and dividing by the number of processes.
After calculation, the average turnaround time for these processes is 7.0 ms.
Q98: Consider the following set of processes with the arrival time and length of CPU burst time given in milliseconds (ms)
What is the average waiting time for these processes with non-preemptive Shortest Job First (SJF) scheduling Algorithm?
(a) 3.0 ms
(b) 2.1 ms
(c) 4.6 ms
(d) 3.2 ms
Ans: d
Sol: Scheduling Algorithm: Non-preemptive Shortest Job First (SJF)
Gantt chart:
0 5 7 8 11 14
Process Table:
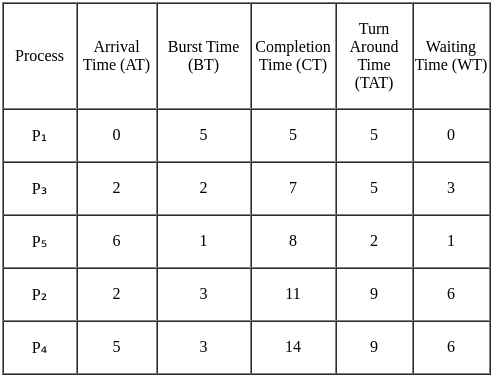
Average waiting time = 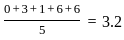
Q99: Consider the following set of processes with the arrival time and length of CPU burst time given in milliseconds (ms)
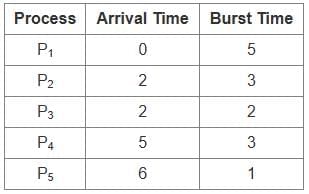
When we apply Shortest Job First (SJF) scheduling Policy/algorithm, Process (P2) faces partial starvation and waits for the longer time to execute. Which one of the following algorithms addresses this problem?
(a) Round Robin
(b) Priority
(c) Highest Response ratio Next
(d) Least Completed next
Ans: c
Sol: The correct answer is Highest Response Ratio Next.
- Shortest Job First (SJF) scheduling algorithm selects the process with the smallest execution time. This can lead to issues such as starvation, where longer processes keep getting delayed by shorter processes.
- The Highest Response Ratio Next (HRRN)algorithm addresses the starvation problem by considering the waiting time of the processes. It calculates the response ratio for each process using the formula:
- Response Ratio = (Waiting Time + Burst Time) / Burst Time
- The process with the highest response ratio is selected next for execution. This ensures that even processes with longer burst times get a chance to execute after waiting for a sufficient period.
- By considering both the waiting time and the burst time, HRRN balances the needs of both short and long processes, mitigating the risk of starvation.
Other Related Points
- The HRRN algorithm dynamically adjusts the priority of processes based on their waiting time, making it more flexible and fair compared to static scheduling algorithms.
- This algorithm is particularly useful in systems where processes have varying burst times, as it ensures a more equitable distribution of CPU time.
- Other scheduling algorithms like Round Robin and Priority Scheduling also aim to address different aspects of process scheduling, but HRRN specifically targets the starvation problem in SJF.
- HRRN is a non-preemptive scheduling algorithm, meaning once a process starts executing, it runs to completion before the next process is selected.
Q100: Consider the following set of processes with the arrival time and length of CPU burst time given in milliseconds (ms)
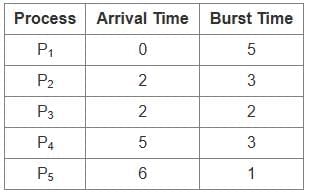
Calculate the average response time for these processes with a nonpreemptive Priorities Scheduling algorithm? Priority of the process are as follows and consider that all the processes came at zero (0) time. (Note low numbers represent high priority).
(a) 5.8 ms
(b) 5.2 ms
(c) 4.7 ms
(d) 3.8 ms
Ans: a
Sol: Scheduling Algorithm: Non-preemptive Priority Scheduling (Low number = High Priority)
Gantt chart:
0 2 7 8 12 15
Process Table:
Average response time = 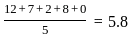 ms
ms
Answer: The corrected average response time is 5.8 ms.
Note: The Priority column is essential to justify the scheduling order. The correct formula for response time is Response Time = Start Time − Arrival Time.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Computer Science 6th Jan 2025 Shift 1 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and what subjects does it cover? |  |
| 2. How is the UGC NET exam structured? |  |
| 3. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the UGC NET exam for candidates? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Computer Science paper? |  |
















