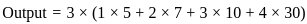UGC NET Paper 2: Computer Science 11 March 2023 | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: A relation 'R' is defined on ordered pairs of integers as:
(x, y) R (u, v) if x < u and y > v. Then R is
(a) Neither a partial order nor an equivalence relation
(b) A partial order but not a total order
(c) A total order
(d) An equivalence relation
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Neither a partial order nor an equivalence relation
Let's reevaluate the properties of the relation R :(x, y) R(u, v) if x < v and y > v.
- Reflexivity: For any ordered pair (x, y), it is not possible for both x < y and y > y to be true simultaneously. Therefore, R is not reflexive.
- Antisymmetry: If (x, y) R(u, v) and (u, v) R(x, y), then x < v and y > v imply u < v and v > y. However, this does not necessarily mean that (x, y) = (u, v). Therefore, R is not antisymmetric.
- Transitivity: If (x, y) R(u, v) and (u, v) R(w, z), then x < v, y > v, u < z, and v > z. Combining these, we can deduce x < z and y > z. Therefore, R is transitive.
- A binary relation is an equivalence relation on a nonempty set S if and only if the relation is reflexive(R), symmetric(S) and transitive(T).
- A binary relation is a partial order if and only if the relation is reflexive(R), antisymmetric(A) and transitive(T).
- From the given relation, it is neither partial order nor equivalence relation.
So, the correct answer is indeed: 1) Neither a partial order nor an equivalence relation.
Q2: Suppose you are married and you and your partner attend a party with three other married couples. Several handshakes took place. No one shook hands with himself (or herself) or with their partner, and no one shook hands with the same person more than once. After all hand shaking was completed, suppose you asked each person, including your partner, how many hands they had shaken. Each person gave a different answer. How many hands did your spouse shake?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is option 3)
There are 8 people (4 couples). Each person shakes hands with at most 6 others (excluding self and spouse).
Handshake counts are distinct: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7.
Model as a graph with 8 vertices, each with degree 0 to 7.
The person with degree 7 shakes hands with all 7 others (except their spouse). Their spouse has degree 0 (no handshakes).
The remaining 6 people form 3 couples. The person with degree 6 shakes hands with all except their spouse (degree 1).
Continuing, degrees pair as (5, 2), (4, 3).
If you have degree 4, your spouse has degree 3.
Total handshakes = (0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7) / 2 = 28 / 2 = 14.
Thus, your spouse shook 3 hands.
So, the correct answer is 3.
Q3: The negation of "Some students like hockey" is:
(a) Some students dislike hockey
(b) Every student dislike hockey
(c) Every student like hockey
(d) All students like hockey
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Every student dislike hockey
- The original statement, "Some students like hockey," is an example of a quantified statement in logic.
- The quantifier "Some" refers to the existence of at least one student who likes hockey. In symbolic logic, this statement can be represented as ∃ (there exists) student (S) such that they like hockey (H).
- Now, when we negate this statement, we are essentially saying that it is not true that there exists a student who likes hockey.
- In symbolic logic, the negation would be ¬∃S(H), which is equivalent to ∀S(¬H), where ∀ denotes "for all" or "every."
- So, the negation "Every student dislikes hockey" is expressing that for every student, it is not the case that they like hockey.
Q4: Simplify the following using K-Map
F(A, B, C, D) = ∑(0, 2, 5, 7, 8, 10, 13, 15)
(a) BD + B'D'
(b) AC + A'C'
(c) BC + B'C'
(d) AD + A'D'
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is BD + B'D'
- An pairs is a group of two adjacent 1's. An pairs reduces one variable from a Boolean equation.
- An quads is a group of four adjacent 1's. An quads reduces two variable from a Boolean equation.
- An octet is a group of eight adjacent 1's. An octet reduces three variable from a Boolean equation.
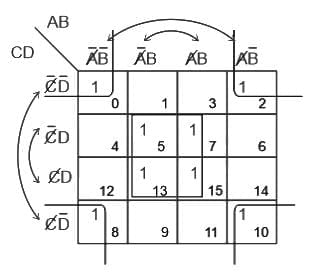
After simplification BD + B'D'
Q5: Consider an unpipelined machine with 10nsec clock cycles which uses four cycles for ALU operations and branches where as five cycles for memory operation. Assume that the relative frequencies of these operations are: 40%, 20% and 40%, respectively. Due to clock skew and setup pipeline let us consider that the machine adds one nsec overhead to the clock. How much speedup is observed in the instruction execution rate when a pipelined machine is considered.
(a) 2 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 6 times
(d) 8 times
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 4 times
Total Clock Cycle = 0.40 x 4 + 0.20 x 4 + 0.40 x 5
Total Clock Cycle = 1.6 + 0.8 + 2
Total Clock Cycle = 4.4 Clock Cycle
Here,
Non-pipeline time = 4.4 clock cycle * 10 nsec
Non-pipeline time = 44nsec
Pipeline time = Clock time + overhead time = 10nsec + 1nsec = 11nsec
Speedup= Time taken by non-pipeline machine / Time taken by pipeline machine
Speedup = 44/11 = 4
So, the correct answer is 4 times
Q6: Machine Level Language is a/an
(a) Assembly Language
(b) Low Level language
(c) High level Language
(d) Translating Language
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Low Level language
- Low-Level Language: Low-level languages are closely related to the hardware of a computer system. They operate and behave on the computer's hardware directly, making them more efficient but less portable. Machine language and assembly are both examples of low-level languages. Low-level languages are harder to read and write since they require detailed knowledge of the hardware's internal workings.
- Assembly Language: This is a low-level programming language where there is a strong correspondence between its instructions and the architecture's machine code instructions. It's one step away from machine language which is directly interpreted into the hardware. Each assembly language is specific to a particular computer architecture.
- High-Level Language: High-level languages are coding languages designed to be easy for humans to read, write, and maintain. Examples of high-level language include Python, Java, C++, and more. These languages do not require the programmer to understand the hardware's inner workings and are designed to be more user-friendly, abstracting away the complexities and details of the hardware.
Q7: Which of the following is wrong about the data types?
(a) The number is always positive when qualifier ‘unsigned' is used.
(b) The number can be positive or negative when the qualifier ‘signed' is used
(c) The range of values for signed data types is more than that of unsigned data types
(d) The left most bit in unsigned data type is used to represent the value
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is The range of values for signed data types is more than that of unsigned data types
- Signed integers can represent both positive and negative numbers because they reserve one bit for the sign of the number. For example, in an 8-bit signed integer, the leftmost bit is used as the sign bit. When this bit is set to 0, it means the number is positive, and when it is 1, the number is negative. The remaining 7 bits are used to represent the actual number value. Therefore, an 8-bit signed integer can represent values in the range of -128 (10000000 in binary) through 127 (01111111 in binary).
- On the other hand, unsigned integers can only represent positive numbers as well as zero because they do not reserve a bit for a sign. Instead, all the bits are used to represent the value of the number itself. For example, an 8-bit unsigned integer can represent values in the range of 0 (00000000 in binary) through 255 (11111111 in binary).
- So, the 'range' of signed and unsigned integers of the same bit length is technically the same, the 'scope' of the unsigned integer is larger, encompassing higher positive numbers at the cost of any negative numbers. For signed integers, the range is distributed in positive and negative directions around zero. Hence, statement 3 is incorrect.
Other Related PointsData types in programming denote the kind of value a variable can store and how much memory it requires. Different programming languages have various data types, but some common datatypes:
- Integer (int): Integers are simply whole numbers, positive, negative, or zero, without a fractional component.
- Floating-point numbers (float, double): These numbers include a decimal point and can therefore represent fractional numbers. The differences are in precision and range, with 'double' typically allowing for a larger number of significant digits and a larger range than 'float'.
- Character (char): Character data types are used to store individual characters, such as letters, numbers, punctuation marks, or other symbols.
- Boolean (bool): The Boolean data type can hold only two possible values, true or false. It's used for logical operations.
- String: A String is a sequence of characters and is typically used to store and manipulate text.
- Array: An array is a data type that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type.
- Object: In object-oriented languages, 'object' refers to an instance of a class. It can contain properties (data) and methods (functions).
- Null: This is a special type for the value which represents no value or no object.
- Unsigned integer (unsigned int): This is an integer that can only be non-negative.
- Signed integer (signed int): This is an integer that can be either non-negative or negative.
Q8: Which of the following statement is correct, according to the following instance of the relational schema R(X, Y, Z)? 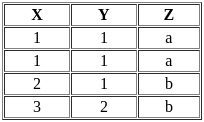
(a) X →Y, Z → X
(b) Y → Z, Z → X
(c) X → Y, X → Z
(d) Y → X, X → Z
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is X → Y, X → Z
A functional dependency, denoted X → Y, refers to a relationship between two sets of attributes. If X → Y, this means that for all tuples in a relation, if two tuples have the same value for the set of attributes X, they must also have the same value for the set of attributes Y. Similarly, for Y → X, if two tuples have the same Y value, they must have the same X value.
Let's analyze the four options:
- X → Y, Z → X: X is functionally dependent on Y because it is uniquely identify Y value but Z does not hold true because Z is not functionally dependent on X. so it is incorrect .
- Y → Z, Z → X: Y does not determine Z uniquely so it is also incorrect.
- X → Y, X → Z: X is functionally dependent on Y because it is uniquely identify Y value and X is functionally dependent on Z because it is uniquely identify Z value. So, both functional dependency are correct.
- Y → X, X → Z: Y does not determine X uniquely so it is also incorrect.
So, Correct answer is X → Y, X → Z
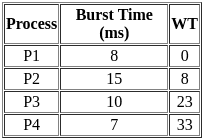
Q9: For the following set of processes scheduled using FCFS policy, determine the average waiting time. Assume that the processes arrived in the order P1, P2, P3, P4.
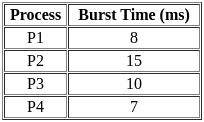
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 32
(d) 48
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 16
Gantt chart:
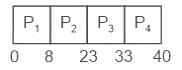



Q10: Which of the following is not a Non functional requirement?
(a) Portability.
(b) Security.
(c) Scalability
(d) User interaction
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is User interaction
- User Interaction: This is generally considered as part of the functional requirements rather than the non-functional requirements. User interaction refers to how a user will interact with the system—what functions they can perform, what outputs they yearn, how the system responses to their inputs, etc. These are tied to the tasks the system needs to perform and are usually described in use cases. User interaction can affect aspects like interface design, error handling, and overall system workflow.
- Non-functional requirements refer to the quality attributes or standards that the system must function within, such as security, scalability, or portability.
- Portability: This is a non-functional requirement that refers to the ability of software to be moved from one environment to another. For example, from one operating system to another (like Windows to Linux), or from one hardware configuration to another. The software, if designed to be portable, should require minimal adaptation to smoothly function in the new environment.
- Security: Security is another non-functional requirement and is essential for any software system. It refers to the software's ability to prevent unauthorized access, resist attacks, protect data, and recover from compromises. This encompasses aspects such as authentication, encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
- Scalability: Scalability is also a non-functional requirement. A scalable system is capable of handling an increasing amount of work by adding resources to the system. This means if the number of users increases unexpectedly, the system should be able to accommodate this increase without impacting performance or functionality. There are two main types of scalability: vertical (adding more power to existing hardware) and horizontal (adding more hardware to distribute the work).
So, the correct answer is User interaction
Q11: COCOMO stands for _______
(a) Consumed cost model
(b) Constructive cost model
(c) Common control model
(d) Composition cost model
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Constructive cost model.
The COCOMO (Constructive Cost Model) is a procedural cost estimate model for software projects that was first published by Barry W. Boehm in 1981. The model proposes an estimation of project cost, effort, and schedule when designing and developing large-scale technical projects. The COCOMO consists of a hierarchy of three increasingly detailed and accurate forms. The characteristics of the model are used for project and strategic management purposes, cost estimation, and software budgeting.
- Basic COCOMO Model: This is a static, single-valued model that computes software development effort and cost as a function of program size expressed in estimated thousands of lines of code (KLOC). It is good for quick, early, rough order of magnitude estimates of software costs, but its accuracy is limited due to its lack of factors to account for difference in project environments.
- Intermediate COCOMO Model: This model provides an estimate that is more detailed than the Basic COCOMO. It takes into account a set of "cost drivers" that reflect the characteristics of the project and can influence the effort and time required. These cost drivers include aspects like process complexity, software reliability, and personnel expertise. The impact of the cost drivers is considered for each phase of the software development process.
- Detailed COCOMO Model: This extends the Intermediate COCOMO and adds an assessment of the influence of different project parameters on each step like planning, product design, programming, testing, etc. This model emphasizes the factors contributing to the success or failure of projects at a granular level.
In essence, COCOMO is a powerful tool for predicting not just the cost but also the timeline and the effort required for software development by taking a variety of factors into account. It is often used during planning stages of a project to determine if a particular software proposal is worthwhile taking forward.
Q12: Modifying the software to match changes in the ever changing environment is called as
(a) Adaptive maintenance
(b) Corrective maintenance
(c) Perfective maintenance
(d) Preventive maintenance
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Adaptive maintenance
Adaptive maintenance involves making changes to the software in response to changes in the environment.
- This could be alterations in the operating system, the hardware, or any other external factors that the software interacts with. For instance, if a new version of a web browser is released and the software is a web application, adaptive maintenance could encompass making the necessary changes to ensure the application still works properly on the new browser version.
Other Related Points
- Software Compatibility - Software compatibility refers to the ability of a software system to run in different environments. When the environment changes, such as a new operating system, the software may need to go through adaptive maintenance to ensure it's fully compatible with this new environment.
- Software Lifecyle - This concept includes the entire lifespan of a software product, from initial development to final sunset. Adaptive maintenance falls within this lifecycle as it's an ongoing process that occurs after the deployment phase to ensure the software remains usable and effective.
- Regression Testing - After the software is modified during the adaptive maintenance process, regression testing is essential. It ensures that the previous functionalities of the software are still working correctly after the new changes are implemented, guaranteeing that the new elements haven't adversely affected the existing system.
Q13: For a function of two variables, boundary value analysis yields,
(a) 4n + 3 test cases
(b) 4n + 1 test cases
(c) n + 4 test cases
(d) 2n + 4 test cases
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 4n + 1 test cases
In this case, we consider two boundary points (the lower and upper value) for each variable under test, equating to 2n test cases. Then, we add one more test case either to handle a unique scenario, resulting in a total of 4n + 1 test cases. This might typically represent a general "nominal" case, a middle value, or another specifically important case in the context of the specific application being tested.
- The distribution of test cases being performed would be something like this:
- For each variable, there would be 2 boundary test points (low value and high value), this will result in 2n test cases for the singular functional scenarios.
- For a special or corner case, there's an additional 1 test case. The specifics of this case would depend on the function and use case under test consideration.
- In total, this gives us (2n * 2) + 1 = 4n + 1 test cases.
- This provides a comprehensive set of test cases covering both the boundaries of each individual variable as well as an additional special scenario.
Q14: Given the FFT we can have ___________ time procedure for multiplying two polynomials A(x) and B(x) of degree bound n where input and output representations are in coefficient form, assuming n is a power of 2.
(a) O(n2)
(b) O(n.log2n)
(c) O(2n)
(d) O(log2n)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is O(n.log2n)
The classical procedure for polynomial multiplication results in an O(n2) time complexity. This is because you are doing a pairwise multiplication of each coefficient from the first polynomial with each coefficient of the second polynomial. If both polynomials have n terms, that's n times n, which results in the O(n2) complexity.
However, the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)can help us improve this. Here is a high level process of polynomial multiplication using FFT:
- Convert the two polynomials from coefficient form to point-value form. For a polynomial of degree bound n, we want to evaluate it at n distinct points. This requires O(n log n) operations using the FFT.
- Now that we have the same set of n points for the two polynomials, we multiply the corresponding values together. That's just n multiplications O(n).
- Finally, we convert the resulting points back to the coefficient form using the Inverse FFT (again, O(n log n) operations).
- Adding all these up, we get O(n log n) + O(n) + O(n log n) = O(n log n) as dominant term which is significantly faster than O(n2).
- This improvement is substantial: a problem that would be computationally infeasible with the classical method may be feasible with the FFT-based method.
Q15: Consider the Graph below:
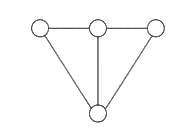
How many spanning trees can be found?
(a) 10
(b) 5
(c) 9
(d) 8
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 8
Subgraph: A subgraph is a type of graph wherein its edges and vertices are chosen as subsets from the original graph.
Spanning Tree: A spanning tree is a specific subgraph, possessing all the vertices from the original graph, and is structured as a tree (not make any loop).
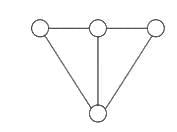
Here possible spanning tree is:
Q16: The transition function 'δ' in multi-tape Turing machine is defined as:
(a) δ : 2Q × Γk → 2Q × Γk × {L, R, S}k
(b) δ : Q × Q × Γk → Q × Q × Γk × {L, R, S}k
(c) δ : Q × Γk → Q × Γk × {L, R, S}k
(d) δ : Q × Γk × 2Q → Q × Γk × 2Q × {L, R, S}k
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is δ : Q × Γk → Q × Γk × {L, R, S}k
- The transition function for a multi-tape Turing machine should define the result of being in a certain state and reading a certain symbol or symbols from the tapes.The correct definition should be
- δ : Q × Γk → Q × Γk × {L, R, S}k
- Here is what each part of the transition function means:
- Q × Γk : The Turing machine is in a certain state from its set of states Q and reads from its k tapes symbols from the tape alphabet Γ.
- → : This is the function mapping that describes that the left-hand side leads to the right-hand side.
- Q × Γk × {L, R, S}k : The Turing machine moves into a new state from its set of states Q, writes symbols onto its k tapes from the tape alphabet Γ, and moves its k tape heads either one cell to the left (L), one cell to the right (R), or stays stationary (S).
Q17: In Pumping Lemma for regular languages, to say a language is satisfying pumping lemma, what is the minimum length of 'y' if you consider the string as 'xyz'.
(a) n
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 0
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is option 3) 1
The Pumping Lemma for regular languages helps us to prove whether a particular language is not regular. It provides a characteristic that all regular languages must satisfy. Here is the lemma:
- If a language L is regular, there exists a constant 'p' (the pumping length) such that for any string 's' in the language L, where the length of 's' (|s|) is greater or equal to 'p', 's' can be written as 'xyz' (s = xyz), satisfying these conditions:
- For each 'i' ≥ 0, x(y^i)z is in L. This means that the string y can be "pumped" - repeated 'i' times for every nonnegative integer 'i' and the resulting string will still be in the language.
- |y| > 0: The length of the string y must be at least 1. This ensures there are some characters to repeat when "pumping".
- |xy| ≤ p: The combined length of strings x and y must be lesser or equal to the pumping length 'p'. This condition make sure we are only pumping within the first 'p' characters of 's' as we don't know what happens after 'p'.
- If a language fails to satisfy the Pumping Lemma conditions, it cannot be regular. Understanding why y's length has to be greater than 0 revolves around the concept that we are aiming to 'pump' or repeat the y section of the string. If y had no characters (|y| = 0), there would be nothing to repeat, which would make the pumping lemma concept pointless. Therefore, the minimum length of 'y' must be '1'.
Q18: In CRC coding if the data word is 111111, divisor is 1010 and the remainder is 110. Which of the following code is true?
(a) 011111101
(b) 001010110
(c) 111111110
(d) 110111111
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 111111110
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) coding involves dividing a data word by a fixed divisor to generate a remainder, which is then appended to the original data word to form the transmitted message.
In this case, the given data word is 111111, the divisor is 1010, and the remainder is 110.
To find the transmitted message, you append the remainder to the original data word. So, the transmitted message is 111111110.
Therefore, the correct option is: 3) 111111110
Q19: The A* algorithm is optimal when,
(a) It always finds the solution with the lowest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is admissible.
(b) Always finds the solution with the highest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is admissible.
(c) Finds the solution with the lowest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is not admissible.
(d) It always finds the solution with the highest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is not admissible.
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is It always finds the solution with the lowest total cost if the heuristic 'h' is admissible.
A* is a popular algorithm used in pathfinding and graph traversal, which is the process of finding a path between multiple points, called "nodes". It was introduced by Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson, and Bertram Raphael in 1968.
- The main advantage of A* is its ability to dynamically prioritize nodes that seem most likely to lead to the goal, rather than exploring all possible nodes. This is done through a combination of two cost functions, g(n) and h(n):
- g(n) is the exact cost of the path from the starting point to any node n.
- h(n) is the heuristic function that estimates the cost from node n to the goal.
- In the context of the A* algorithm, a heuristic is considered admissible if it never overestimates the cost to reach the goal.
- Suppose we are at a particular node and we want to decide which neighbouring node to visit next. A* does this by minimizing f(n) = g(n) + h(n) for the neighboring nodes. g(n) is the actual cost from the start node to the current node and h(n) is the estimated cost from the current node to the goal based on the heuristic.
The A* algorithm is guaranteed to return the shortest path to the goal if the heuristic it uses satisfies two conditions:
- It is admissible - that is, it never overestimates the actual cost to get to the goal. This is crucial because if the heuristic overestimates, A* might skip over the optimal path, making it not find the real shortest path.
- It is consistent (or monotonic) - this means that for every node n and for every successor n' of n, the estimated cost of reaching the goal from n is no greater than the cost of getting to n' plus the estimated cost of reaching the goal from n'. If the heuristic is both consistent and admissible, then A* is guaranteed to find an optimal solution while expanding the fewest nodes possible.
Therefore, the answer to your initial question is that A* is optimal when it always finds the solution with the lowest total cost if the
heuristic 'h' is admissible. The other options are not necessarily true.
Q20: Which Artificial intelligence technique enables the computers to understand the associations and relationships between objects & Events?
(a) Heuristic Processing.
(b) Cognitive Science.
(c) Relative symbolism.
(d) Pattern Matching.
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Pattern Matching.
The AI technique that primarily enables computers to understand the associations and relationships between objects & events is generally related to pattern matching.
- Pattern matching supports algorithms to understand and recognize patterns in data which may represent relationships and associations. Machine learning techniques, including both supervised and unsupervised learning, make use of pattern recognition to infer these associations.
- That being said, aspects of all the options play a role in some form. Cognitive science influences how AI is designed, heuristic processes can be used in decision-making processes, and relative symbolism could be related to how relationships are represented.
Other Related Points
- Supervised Learning: In this type of machine learning, we provide the algorithm with labeled training data. Each set of data includes the input values and the corresponding expected output. The algorithm learns from this data, creating a model that can make accurate predictions when given new, similar data. It's called "supervised learning" because the process of an algorithm learning from the training dataset can be thought of as a teacher supervising the learning process. Examples of supervised learning are Linear Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forests, and SVM (Support Vector Machines).
- Unsupervised Learning: In contrast, unsupervised learning algorithms are used when the information used to train is neither classified nor labeled. The system isn't provided with the right answers (output). The algorithm must figure out for itself how to perform the task. Essentially, the machine is shown input and is asked to find patterns, features, or relationships within that data. Clustering (grouping similar items) and Association (discovering rules that govern large portions of the data) are two main techniques in unsupervised learning. K-means and Hierarchical Clustering, as well as Apriori and FP-Growth, are examples of each respectively.
Q21: Which of the following is/are true for Dynamic RAM (DRAM)?
A. It is slower than static RAM(SRAM)
B. Packing Density is higher than Static RAM (SRAM)
C. It is faster than static RAM(SRAM)
D. It requires data refreshing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D Only
(b) A, B and C Only
(c) C and D Only
(d) B and D Only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and D Only
- A. It is slower than static RAM(SRAM) - This is correct because DRAM has longer access times than SRAM.
- B. Packing Density is higher than Static RAM (SRAM) - This is also correct. DRAM can fit more memory into a smaller space because it uses a single capacitor and transistor for each bit of data, while SRAM uses six transistors per bit.
- C. It is faster than static RAM(SRAM) - This is incorrect. SRAM is actually faster than DRAM because it does not need to refresh data like DRAM.
- D. It requires data refreshing - This is correct. DRAM uses capacitors to store each bit of data, and these capacitors gradually leak their charges over time. Because of this, DRAM requires periodic refreshing to maintain its data.
So the correct answer is A, B and D Only
Other Related Points
- SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): SRAM retains its contents as long as power is applied to the system. It does not need to be refreshed like DRAM because it uses flip-flops, which are bistable or having two stable states, to store the data. Data in SRAM remains stable as long as the memory has power. SRAM is faster and more reliable than DRAM but it's also more expensive. Therefore, it's typically used for cache memory in a system.
- DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory): DRAM, on the other hand, needs to have its storage cells refreshed periodically or else it loses the data. This is because each cell in DRAM is made of a capacitor and a transistor and the capacitors can lose their charge over time. The dynamic nature of DRAM involves constant refreshing, which leads to slower data access rates compared to SRAM. However, DRAM is cheaper and has a higher density (more storage per unit area) than SRAM, so it is used as the main system memory in computers.
Q22: Given a vector with cartesian components (x, y), if scaling is done with matrix  , which of the following are true.
, which of the following are true.
A. Decreases the vertical by three halves
B. Increases the vertical by three halves
C. Doubles the horizontal
D. Halves the horizontal
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and C only
(b) A and D only
(c) B and C only
(d) B and D only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is B and D only
In linear algebra, scaling is a linear transformation that enlarges or diminishes objects. The scaling matrix is diagonal with scaling factors on the diagonal. It appears you're giving entries of the diagonal matrix.
Let's denote the vector as V = [x, y], and the scaling matrix as M = [0.5, 1.5]. When you multiply the vector V by the matrix M, you get a new vector V' as follows:
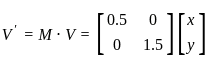
The resulting vector is:
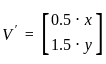
This represents a transformation that scales the width (x component) by a factor of 0.5 (which means halving) and the height (y component) by a factor of 1.5 (which means increasing by 1.5x or three halves).
Therefore, the correct answers are: Halves the horizontal and Increases the vertical by three halves.
Q23: Which of the following lists defined in HTML share similar elements?
A. Unordered lists
B. Ordered lists
C. Definition Lists
D. Corelated lists
E. Enumerated lists
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B only
(b) A, C, E only
(c) A, B, C only
(d) A, C, D only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A, B only
- These are the standard and widely used types of lists in HTML. Unordered lists use bullets, and ordered lists use numbers or letters. Definition lists, mentioned in option C, are also a valid type of list in HTML but have a different structure as they consist of terms and their definitions. Options D ("Corelated lists") and E ("Enumerated lists") are not standard terms for HTML lists.
So, to summarize, the correct options are A and B.
Q24: What are the drawbacks of using file systems to store data?
A. Data inconsistency
B. Difficulty in accessing data
C. Data isolation
D. Atomicity of updates
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, only
(b) B, C, D only
(c) A, B, C only
(d) A, B, C, D
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C, D
- Data inconsistency: This can occur in file systems because each system could have different formats and constraints, meaning the same piece of data could be stored differently in separate systems. For instance, the date could be stored in a 'dd/mm/yyyy' format in one system and 'mm/dd/yyyy' in another.
- Difficulty in accessing data: File systems do not typically have sophisticated querying capabilities, making it difficult to access data. They usually provide simple read/write operations on a per-file basis and do not provide a convenient means to retrieve subparts of a file.
- Data isolation: Data stored in a file system is not easily integrated with other data. Files can be stored in various formats (like text, binary), and on disparate systems, which can make it challenging to combine data from different sources.
- Atomicity of updates: Atomicity refers to the concept that an operation (like updating a file) either completely succeeds or completely fails, with no partial success. File systems often lack this feature. If a system crash or power failure happens during an update of a file, the file can be left in an inconsistent state.
Therefore all given options (A, B, C, D) are drawbacks of using file systems to manage data.
Other Related PointsFile systems also come with a number of advantages and are widely used due to factors like:
- Simplicity: File systems are straightforward to use. Most computer users are already familiar with file manipulation commands like create, read, update, delete, for both the file and the data within the file.
- Performance: File systems tend to be very fast and efficient for simple read/write operations. They can handle heavy data read/write traffic efficiently.
- Compatibility: They're almost universally supported across various operating systems, simplifying data sharing and migration tasks.
- Space Management: Modern file systems are good at managing space on storage devices. They can keep track of which parts of the hard disk are in use and which parts are not.
- Data Security: File systems allow you to set permissions at the file and directory levels, which provides an additional layer of data security.
- Cost: File systems are generally included with the operating system and don't require additional software cost.
Q25: Which of the following database model, we have a parent-child relationship?
A. hierarchical databases
B. network databases
C. relational databases
Choose the correct answer from the options below:
(a) A, B
(b) A, C
(c) B, C
(d) A, B, C
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A, B
- Hierarchical databases and network databases both use the concept of a parent-child relationship.
- In a hierarchical database, data are organized into a tree-like structure with a single root, to which all other data are linked in a hierarchy of parent-child relationships.
- Network databases allow multiple parent-child relationships, as the items can be accessed in multiple ways - not just from root to leave.
Other Related Points
- Relational databases, contrastingly, use a model where data are organized as a set of formally-described tables from which data can be accessed or reassembled in many different ways without having to reorganize the tables themselves. They don't use the concept of parent-child relationships explicitly, as the relationships are based on common attributes between tables and not on an individual level of records.
Q26: Which one of the following types of memory is fastest
(a) Cache Memory
(b) Register Memory
(c) Main Memory
(d) Secondary Memory
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Register Memory
- Register Memory: Register memory is a tiny unit of memory that is part of the CPU (central processing unit).
- It is the fastest and smallest form of memory.
- Because of its speed, it's used to store and quickly access the data that the CPU is currently processing.
- Register memory is significantly smaller in comparison to Cache, Main Memory or Secondary Memory due to cost and technology limitations.
Other Related Points
- Cache Memory: Cache memory is a small, fast memory that is used to store frequently accessed data by the processor. It is faster than Main Memory (RAM), but slower than Register Memory. Cache memory is used to efficiently increase the speed of data access by the processor by keeping a copy of the most frequently used data from the Main Memory. There are typically multiple levels of cache (L1, L2, L3) with different speeds and sizes.
- Main Memory: Often referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory), Main Memory is a form of computer memory that can be read from and written to by the processor. It is much larger than cache memory or register memory but it is also slower. The operating system, application programs, and data in current use are kept in RAM so that the CPU can quickly reach them.
- Secondary Memory: Also known as storage memory, this includes devices like hard disks, solid state drives, and other forms of storage that are not directly accessible by the CPU (they require I/O operations for access). Secondary memory has the highest capacity and is used to store a large amount of data and information permanently, even without power. It is the slowest type of memory discussed here, but it's also typically the least expensive per unit of storage and is non-volatile, meaning it retains data even when powered off.
Q27: If a constructor 'Date' is declared explicitly and has to be defined outside the class, which of the following is correct?
(a) Date :: Date(int dd) {/*...*/}
(b) explicit Date:: Date(int dd) {/*...*/}
(c) Such a constructor cannot be defined
(d) Constructor always has to be defined inside the class
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Date :: Date(int dd) {/*...*/}
When we declare the constructor inside the class we could use the explicit keyword to prevent implicit conversions:
class Date {
explicit Date(int dd);
};
But when defining it outside the class, we should not include the explicit keyword:
Date :: Date(int dd) {/*...*/}
So, the correct answer is Date :: Date(int dd) {/*...*/}
Other Related PointsA constructor in object-oriented programming is a special type of subroutine (function or method) called to create an object. It prepares the new object for use, often accepting arguments that the constructor uses to set member variables required.
In C++, the constructor is a special function with the same name as the class which is automatically called whenever an object of the class is created. It is used to initialize the object of its class. Here's some basic features of constructors:
- It should be declared in the public section of a class.
- It is automatically invoked whenever an object is created.
- It cannot return values and doesn't have a return type, not even void.
- An error occurs if you declare a constructor with a return type.
- It can have default arguments.
- We cannot refer to their address.
- It can be overloaded with different parameters.
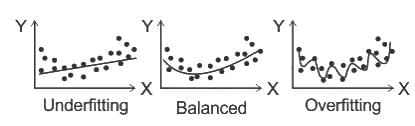
Q28: Overfitting is expected when we observe that?
(a) With training iterations error on training set as well as test set decreases
(b) With training iterations error on training set decreases but test set increases
(c) With training iterations error on training set as well as test set increases
(d) With training iterations training set as well as test error remains constant
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is With training iterations error on training set decreases but test set increases
- Overfitting model learns the training data too well, capturing noise or minor fluctuations.
- It performs well on the training data but poorly on unseen data because it has essentially 'memorized' the training set rather than understanding the underlying patterns. The option that describes overfitting is: 2) With training iterations, error on the training set decreases but the error on the test set increases.
- In overfitting, the model starts fitting the training data too closely, capturing noise and specific patterns in the training set that may not generalize well to new, unseen data.
- As a result, the model's performance on the test set deteriorates even though it continues to improve on the training set.
Other Related Points
- Underfitting: The model is too simple and fails to learn the underlying structure of the data. As a result, it performs poorly on both the training data and the new, unseen data because it doesn't capture the complexity required.
- The goal in machine learning is to find a balance between overfitting and underfitting for the model to generalize well to new data.
Q29: The main function of the microkernel is to provide a communication facility between the __________ program and the various __________ that are also running in user space.
(a) Virtual, Processes
(b) System, Processes
(c) Client, Services
(d) Virtual, Services
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Client, Services.
- The microkernel is a design approach in operating system architecture where the kernel is kept minimal, and essential functions are moved to user space as separate processes or servers. The main function of the microkernel is to provide a communication facility between the client programs and the various services that are also running in user space. Other options doesn't accurately describe the relationship in a microkernel architecture. So, correct answer is Client, Services.
Other Related Points
- A microkernel is an operating system design where the kernel is kept minimal, containing only essential functions like process scheduling, memory management, and inter-process communication.
- Additional operating system services, such as device drivers and file systems, are moved to user space as separate processes or servers.
- This design promotes modularity and flexibility, making it easier to add, update, or replace individual components without affecting the entire system.
- The microkernel approach aims to improve system reliability, security, and maintainability by reducing the complexity of the kernel and isolating critical components in user space.
Q30: Consider an operating system capable of loading and executing a single sequential user process at a time. The disk head scheduling algorithm used is first come first served (FCFS). If FCFS is replaced by shortest seek time first (SSTF) and the vendor claims 50% better benchmark results. What is the expected improvement in the I/O performance of user programs?
(a) 50%
(b) 100%
(c) 25%
(d) 0%
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 0%
- While the disk head scheduling algorithm can make a huge difference in the performance of the disk I/O operations, it does not have a direct impact on the execution of user programs. The performance of user programs depends mainly on the CPU scheduling policies and the available resources such as main memory, cache, and so on.
- Switching from FCFS to SSTF only makes the disk drive work better, but it doesn't improve the overall performance of the user program with various input and output devices. In simple terms, the user program's I/O performance stays the same, with no improvement (0% improvement).
Other Related Points
- FCFS (First-Come, First-Served): FCFS is a scheduling algorithm that services tasks in the order they arrive. The first to arrive gets served first. It's simple but can lead to high waiting times if a long task arrives before short tasks.
- SSTF (Shortest Seek Time First): SSTF is a disk scheduling algorithm that services the disk I/O request closest to the current position of the disk head, thereby minimizing total seek time. It's typically more efficient than FCFS, but can lead to starvation of some requests.
Q31: Let 'n' denote a positive integer. Suppose a function F is defined as
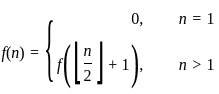
What is f(25)? and what does this function find?
(a) 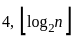
(b) 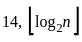
(c) 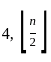
(d) 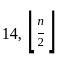
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 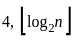
This function takes a positive integer n and recursively applies the following operation: Divide the number by 2 (taking the integer floor of the result). At n = 1, the function returns 0.
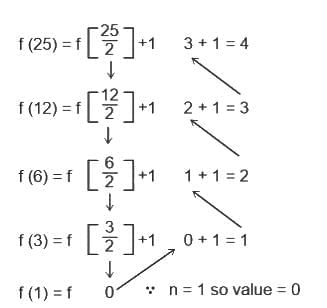
Since log₂(25) equals 4, our result is also 4. So, correct answer is 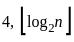
Q32: A Computer on a 10 Mbps network is regulated by a token bucket. The token bucket is filled at a rate of 2 Mbps. It is initially filled to capacity with 16 megabits. What is the maximum duration for which the computer can transmit at the full 10 Mbps?
(a) 1.6 seconds
(b) 2 seconds
(c) 5 seconds
(d) 8 seconds
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 2 seconds
The maximum duration for which the computer can transmit at the full 10 Mbps can be calculated using the concept of token bucket.
- Token rate into bucket = 2 Mbps
- Output rate of bucket = 10 Mbps
- Effective rate = 10-2 = 8 Mbps
- Bucket capacity is full, 16 Mb
- So, at effective rate bucket will drain in 16/8 = 2s
Q33: In the standard Ethernet with transmission rate of 10Mbps, assume that the length of the medium is 2500m and size of a frame is 512 bytes. The propagation speed of a signal in a cable is normally 2 × 108 m/s. Calculate Transmission delay and propagation delay.
(a) 25.25μs and 51.2μs
(b) 51.2μs and 12.5μs
(c) 10.24μs and 50.12μs
(d) 12.5μs and 51.2μs
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 51.2μs and 12.5μs
The delay in Ethernet transmission, which is measured by the duration required to send a single frame over the physical medium, is determined by dividing the frame size by the speed of transmission. In this case, the transmission delay is:
Transmission delay = Frame size / Transmission rate
⇒ 512 bytes / 10 Mbps = 51.2 microseconds
In Ethernet, the propagation delay denotes the time duration for a single bit to traverse from source to destination over the physical network medium. It's assessed by dividing the medium's length by the transmission speed of the signal. In this case, the propagation delay is:
Propagation delay = Length of medium / Propagation speed
⇒ 2500 m/2 x 10^8 m/s 12.5 microseconds
Consequently, in a standard Ethernet setup featuring a transmission rate of 10 Mbps, a medium length of 2500 m, and a frame size of 512 bytes, the correspondingly calculated transmission delay and propagation delay are 51.2μs and 12.5μs, respectively.
Q34: A 4-input neuron has weights 1, 2, 3, 4. The transfer function is linear with the constant of proportionality being equal to 3. The inputs are 5, 7, 10, 30, respectively
Then the output will be,
(a) 120
(b) 213
(c) 410
(d) 507
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 507
A linear neuron is a basic type of artificial neuron or node in a neural network that performs a linear transformation on its inputs. It is a fundamental building block in the field of neural networks. The output of a linear neuron is computed by taking a weighted sum of its input values and applying a constant factor called the bias or constant of proportionality.
To calculate the output of the neuron, you can use the formula for a linear neuron:

In this case:
- Constant of Proportionality = 3
- Weights = [1, 2, 3, 4]
- Inputs = [5, 7, 10, 30]
- So, the output would be:
Now, calculate the values:
Therefore, the correct answer is: 4) 507
Q35: Consider the following statements:
A. There exists a Boolean algebra with '5' elements.
B. Every element of Boolean algebra has unique complement.
C. If a Lattice 'L' is a Boolean algebra then 'L' is not relatively complemented.
D. The direct product of two Boolean Algebras is also a Boolean algebra
Choose the correct answer about the four statements given above.
(a) Only A and D are correct
(b) Only B and D are correct
(c) All statements are NOT correct
(d) All statements are correct
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Only B and D are correct
A. There exists a Boolean algebra with '5' elements.
- This statement is false. A Boolean algebra will have 2n elements, where n is a positive integer (as it consists of all subsets of a set of size n). Therefore, if it has 5 elements, then it is not a Boolean algebra because 5 is not a power of 2.
B. Every element of Boolean algebra has a unique complement.
- This statement, however, is true. In Boolean algebra, for every element A, there exists a unique element B such that A ^ B = 0 (the zero element, or "false") and A v B = 1 (the one element, or "true"). Thus, every element does have a unique complement.
C. If a Lattice 'L' is a Boolean algebra then 'L' is not relatively complemented.
- This statement is false. A lattice 'L' is called complemented if for every element a there is an element b such that a ∨ b = 1 and a ∧ b = 0. And these elements are called complements of each other. If these complements are unique then the lattice is called relatively complemented. A Boolean algebra is a special kind of lattice where the complement for each element is unique. So, actually, if 'L' is a Boolean algebra, then 'L' is relatively complemented.
D. The direct product of two Boolean Algebras is also a Boolean algebra.
- This statement is true. The direct (or Cartesian) product of two Boolean algebras produces a new Boolean algebra. For any two Boolean algebras A and B, their Cartesian product A × B, equipped with componentwise operations, is also a Boolean algebra.
Based on the above analysis, the correct answer is: 2) Only B and D are correct
Q36: Consider the following conditional code, which returns a Boolean values
if ((x > 25) && (y >100))
return 'false';
else if((x ≤ 25) && (y ≤ 100))
return 'true';
else if((x > 25) && (y ≤ 100))
return 'false';
else
return 'true';
Simplify it by filling in the following blank with a single Boolean expression without changing the behaviour of the conditional code.
if (__________)
return 'true';
else
return 'false';
(a) x > 25
(b) x ≤ 25
(c) y >100
(d) y ≤ 100
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is x ≤ 25
Here the code:
if ((x ≤ 25) || (y > 100))
return 'true';
else
return 'false';
This code aims to achieve the same result as the above code provided. Let's analyze the conditions:
- (x ≤ 25): This condition is true when x is less than or equal to 25.
- (y > 100): This condition is true when y is greater than 100.
- The || (logical OR) operator is used between these conditions. In the simplified code:
- If either (x ≤ 25) is true or (y > 100) is true (or both), the entire expression evaluates to true.
- If neither condition is true, the entire expression evaluates to false.
(x ≤ 25) ∧ (y ≤ 100)
(x ≤ 25) ∧ (y > 100)
This simplifies to x ≤ 25. The answer (b) is correct.
So, the code essentially says: Return 'true' if either x is less than or equal to 25 or y is greater than 100. Return 'false' otherwise.
Q37: Which one of the following allows the session to continue?
(a) When a user quits a browser
(b) When the user logs out and is invalidated by the servlet
(c) When the session is timed out due to inactivity
(d) When the user refreshes the browser and there is a persistent cookie
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is When the user refreshes the browser and there is a persistent cookie
Persistent cookies are stored on the user's device and can persist across browser sessions.
- When the user refreshes the browser, the persistent cookie allows the server to recognize and associate the user with an existing session, thus allowing the session to continue.
- Persistent cookies are not affected by actions like quitting the browser or logging out, and they can help maintain session state even if there is some inactivity that would otherwise lead to a timeout.
Other Related Points
- Closing a browser often ends the session, especially if it relies on session cookies.
- When a user is logged out and invalidated by a servlet, the session also ends, as the 'logout' action generally terminates the session.
- A session timeout due to inactivity would definitely lead to the end of the active session.
Q38: Consider the two relations below. The primary keys are underlined. Identify all possible foreign key(s) from the options based only on the two relations.
EMP (eid, ename, did)
DEPT (did, dname)
(a) eid
(b) did
(c) eid, did
(d) eid, did, ename
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is did
- Foreign Key: A foreign key in a database is a field or collection of fields in one table, that is a primary key in another, related table. The purpose of the foreign key is to ensure referential integrity of the data.
- In the relation provided, 'did' in the EMP relation can be a foreign key that refers to the 'did' in the DEPT relation. The column 'did' in the EMP relation identifies the department to which an employee belongs, and it's reasonable to think that each 'did' in EMP corresponds to a 'did' in DEPT.
Other Related Points
- Primary Key: The primary key is a distinct type of candidate key chosen by the database designer to make a row unique in a table. It can neither have null values nor duplicate values.
- Super Key: A super key is a set, or any subset of, one or more columns (attributes) that can be used to uniquely identify a record in a database table. It can include extraneous attributes.
- Candidate Key: A candidate key is a minimal set of columns (that is, a super key reduced to its irreducible minimum) which can uniquely identify a record. There can be more than one candidate key, but they each must be able to uniquely identify a record without any extraneous data.
Q39: In Linux Operating System, when _________ is invoked, it is passed a set of flags that determine how much sharing is to take place between the parent and child tasks.
(a) fork()
(b) clone()
(c) pthread()
(d) thread()
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is clone()
- clone(): This system call creates a new process, similar to fork(), but it also allows the child process to share parts of its execution context with the calling process.
- The execution context includes resources like memory space, file descriptor tables, etc.
- The degree of sharing is controlled by a set of flags passed when invoked, which defines a spectrum between traditional processes and threads.
Other Related Points
- fork(): This is a system call used in Unix and Linux-based systems that creates a new process. The new process, called the child process, is an exact copy of the calling process, which is the parent process. It gets a new process ID (PID) and inherits most of the properties of the parent process, but they do not share the same memory space.
- pthread_create(): This function is used to create a new thread in the context of the current process in POSIX-compliant operating systems (like Unix or Linux). Threads created by pthread_create share the same memory space but get their own stack memory.
- There is no thread() system call in Linux.
Q40: Given Ethernet address 01011010 00010001 01010101 00011000 10101010 00001111 in binary, what is the address in hexadecimal notation?
(a) 5A ∶ 88 ∶ AA ∶ 18 ∶ 55 ∶ F0
(b) 5A ∶ 81 ∶ BA ∶ 81 ∶ AA ∶ 08
(c) 5A ∶ 18 ∶ 5A ∶ 18 ∶ 55 ∶ 0F
(d) 5A ∶ 11 ∶ 55 ∶ 18 ∶ AA ∶ 0F
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 5A ∶ 11 ∶ 55 ∶ 18 ∶ AA ∶ 0F
To convert the given Ethernet address from binary to hexadecimal, we can group the binary digits into sets of four (from right to left) and then convert each group into its equivalent hexadecimal representation. The given Ethernet address in binary is:
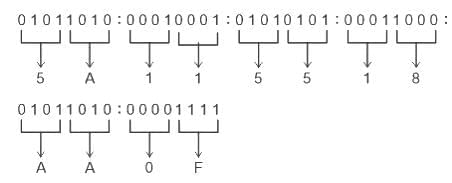
After the grouping 5A ∶ 11 ∶ 55 ∶ 18 ∶ AA ∶ 0F, Hence, correct answer is 5A ∶ 11 ∶ 55 ∶ 18 ∶ AA ∶ 0F
Other Related PointsMedia Access Control (MAC) address, also known as an Ethernet address, is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on a physical network. These addresses are assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface card (NIC) and are stored in its hardware. Here are a few key points about MAC addresses:
- Uniqueness: Every device that can connect to a network (such as computer, smartphones, servers, networking equipment, and Internet of Things devices) has a unique MAC address. This is essential for network operations, as it allows packets to be delivered to the precise device for which they are intended even in a complex network with many devices.
- Physical Storage: MAC addresses are "burned" into the NIC during the manufacturing process and typically cannot be changed. They are a combination of manufacturer identification number and a unique number assigned by the manufacturer.
- Structure of MAC Addresses: MAC addresses are typically represented as six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by colons, hyphens, or without a separator. This results in a 48-bit number (6 bytes), allowing for a vast number of unique addresses.
- Usage in Networking: MAC addresses operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) networking model, which is responsible for network node-to-node data transfer. When a network packet is sent across the internet, its destination IP address gets it to the right network, and then the MAC address ensures the packet is delivered to the correct device on that network.
Q41: Consider the following statements:
P: There exists no simple, undirected and connected graph with 80 vertices and 77 edges.
Q: All vertices of Euler graph are of even degree.
R: Every simple, undirected, connected and acyclic graph with 50 vertices has at least two vertices of degree one.
S: There exits a bipartite graph with more than ten vertices which is 2-colorable.
What is the number of correct statements among the above statements.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Option 4) 4
Statement P: There exists no simple, undirected, and connected graph with 80 vertices and 77 edges.
- This is true. A simple, undirected, and connected graph with 'n' vertices must contain at least 'n-1' edges to be connected. However, with exactly 'n-1' edges, the graph would be a tree with no cycles. Adding further edges would introduce cycles (assuming we’re considering simple graphs -- that is, no loops or multiple edges). A graph with 80 vertices would require at least 79 edges to be connected, so it's not possible to have a simple, undirected, and connected graph with 80 vertices and 77 edges.
Statement Q: All vertices of an Euler graph are of even degree.
- This is true. An Eulerian graph is one where every vertex has an even degree. This condition is both necessary and sufficient for the graph to have an Eulerian cycle (a cycle that covers every edge exactly once).
Statement R: Every simple, undirected, connected, and acyclic graph with 50 vertices has at least two vertices of degree one.
- This is true. Such a graph with 'n' vertices is called a tree and, in any tree, there are at least two vertices of degree one (the endpoints of the longest path in the tree), no matter the number of vertices.
Statement S: There exists a bipartite graph with more than ten vertices which is 2-colorable.
- This is true. If a graph is bipartite, it is 2-colorable. This means that the vertices can be colored using only two colors in such a way that no two adjacent vertices share the same color. Any graph with two or more vertices can be bipartite (split into two sets, where vertices in the same set are not adjacent), so a bipartite graph with more than ten vertices that is 2-colorable certainly exists.
A simple, undirected, connected graph with n = 80 vertices requires at least n - 1 = 79 edges (e.g., a tree). With 77 edges, the graph cannot be connected (it has at least two components). Thus, P is true. Q, R, and S are correctly explained.
Therefore, all the statements P, Q, R, and S are correct. The number of correct statements is 4.
Q42: Which of the statement is not true in regards to virtual memory?
(a) The main objective for using virtual memory is to increase the effective capacity of the memory system
(b) Size of the program can be as large as the size of the secondary memory
(c) Program and data are stored in the secondary memory
(d) None of these
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is None of these
The all three statements are correct.
- The main objective for using virtual memory is indeed to increase the effective capacity of the memory system by allowing programs to operate as if there is more main memory available than is physically installed.
- The size of the program can be as large as the size of the secondary memory because virtual memory allows a program to run as if the entire operating system's memory is available to it, while in actuality it may be stored on secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive.
- With virtual memory, program and data are indeed often stored in secondary memory. They are only loaded into the primary memory (such as RAM) as necessary, which enables efficient memory usage.
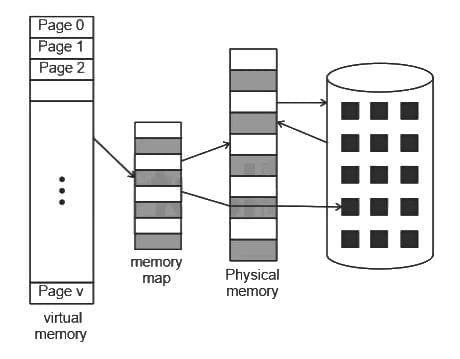
So, correct answer is None of the above.
Other Related Points
- Memory Management: Virtual memory serves as a technique for memory management by an operating system (OS).
- Simulates Physical Memory: It allows a computer to compensate for physical memory shortages by using a portion of the hard drive space to act as or imitate physical memory (RAM).
- Virtual Address Space: It creates a "virtual address space" which is an artificial set of addresses.
- Paging: The OS uses a method known as "paging" to map these virtual addresses to physical addresses on the computer's storage.
- Page Swapping: When physical memory resources run low, pages are moved (swapped) to the hard drive from the RAM, freeing up some physical memory. When the processor needs the data from these pages, they are moved back into the RAM from the hard drive, a process referred to as "page swapping".
- Performance Trade-off: There is a performance trade-off with virtual memory due to slower access times when reading from the hard drive as compared to physical memory. However, the overall system performance generally improves as more programs can be run simultaneously.
- Large Applications: Virtual memory allows for efficient execution of large, complex, and memory-intensive applications by making them believe there is more memory available than there really is.
- Program Size: With virtual memory, the size of programs can be larger than physical memory.
- Increased Capacity: The primary objective of virtual memory is to increase the effective capacity of the system's memory, letting users run more applications at the same time more efficiently.
 Q43: Which of the following statement is/are false?
Q43: Which of the following statement is/are false?
A. The processor has direct access to both primary and secondary memory
B. Primary memory stores the active instructions and data for the program being executed on the process
C. Secondary memory is used as a backup memory
D. Memory system is implemented on a single level memory
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) B and C only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) A and D Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A and D Only
- Statement A is false because the processor does not have direct access to secondary memory. It directly interacts with primary memory (also called main memory) and cache memory. For information on the secondary storage, it goes through input/output routines.
- Statement D is false because memory system is not implemented on a single level memory. Computer systems have a memory hierarchy which includes various levels like registers inside CPU, cache memory, main memory and secondary memory. Each level in the hierarchy represents a trade-off between speed and size, with the memory getting slower and larger as one moves from registers to secondary memory. This structure helps in optimizing system performance.
- Statements B and C are true, B is true because primary memory (like RAM) indeed stores the active instructions and data for the program being executed on the processor.
- C is true because secondary memory (like hard disks, SSDs) is often used for long-term storage and can serve as a backup. It stores the data and instructions that are not actively being used by the processor.
Other Related Points
Primary Memory: Primary memory, also known as main memory, is the component in a computer that holds data while it is being processed. Its main characteristics are:
- It is directly accessible by the CPU.
- Stores data temporarily.
- It is volatile, which means data is lost when power is turned off.
- It contains information that's currently being used by the computer, such as operating system instructions, applications in use, and the data they use.
- Examples include Random Access Memory (RAM), and cache memory.
Secondary Memory: Secondary memory, also referred to as external memory or auxiliary storage, is where a computer permanently stores data, until it is deliberately removed. Its main characteristics are:
- It is not directly accessible by the CPU. The computer uses I/O channels to access secondary memory.
- Stores data permanently, even when the computer is powered off.
- It is non-volatile, which implies that it retains information even when not powered.
- Used for storing the bulk of the computer's data, such as operating system files, applications, and user files.
- Examples include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and external hard drives.
Q44: How many different binary trees are possible with 'n' nodes?
(a) n-1
(b) 2n - 1
(c) 2n
(d) 2n - n
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 2n - n
- A binary tree allows for a maximum of two child nodes per parent node.
- The formula (2n - n) can be used to ascertain the number of different binary trees that can be drawn given 'n' number of nodes.
- As an example, when 'n' is equal to 1, applying the formula yields (21 - 1), which equals 1.
- As an example, when 'n' is equal to 2, applying the formula yields (22 - 1), which equals 2.
- As an example, when 'n' is equal to 3, applying the formula yields (23 - 1), which equals 5.
- Therefore, when 'n' nodes, we can draw (2n - n) unique binary tree.
Q45: The item generated by the production A → ɛ is :
(a) A → .
(b) A → ε.
(c) A → .ε
(d) A → ε
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A → .
- In the context of LR parsing in the field of computer science, an 'item' of a grammar rule represents a partially recognized rule. The dot in the item is used to indicate how much of a rule has been seen at a particular point in the parse process.
- For example, if we have a rule such as A -> BCD, when parsing begins, no part of the right side has been recognized, so the initial item is A -> .BCD. As parsing proceeds and B, C, and D are recognized, the dot moves rightward: A -> B.CD, A -> BC.D, and A -> BCD. respectively.
- Now, let's consider your rule A -> ε, which means that A can produce an empty string (epsilon). In the context of recognizing this rule, initially we've seen none of it, hence the item is A -> .. After recognizing the ε (meaning, recognizing that there's nothing to recognize), the item would be A -> ε..
- So, where we haven't parsed any symbols yet, the correct representation would be A -> .. The 'ε' isn't generally shown in the item because the dot alone indicates that no part of the right hand side has been seen, which is appropriate for a production that generates the empty string.
Q46: Where does the values of alpha-beta search get updated?
(a) Along the path of search.
(b) Initial state itself.
(c) At the end.
(d) None of these.
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Along the path of search.
- Alpha-beta pruning is an algorithm that seeks to minimize the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. The alpha-beta values get updated as the search algorithm delves deeper into the game tree, i.e., along the path of search.
- Alpha is the best value that the algorithm can guarantee at that level or above, while beta is the best value that the algorithm can guarantee at that level or below. As the algorithm searches through the game tree, alpha and beta are continually updated, hence providing bounds on the values that can be obtained by sections of the tree remaining to be analysed. This allows branches which cannot possibly influence the final decision to be pruned, hence making the algorithm more efficient.
- The initial state introduces alpha and beta values, typically initialized to negative and positive infinity respectively. The end state does provide definite alpha-beta values, but these aren't updated at the end - they are updated along the path as the search progresses.
Therefore option 1 is the correct answer.
Q47: Identify the incorrect statement(s).
(a) A candidate key is minimal set of one or more attributes that, taken collectively, allows us to uniquely identify any entity in the entity set.
(b) A candidate key for which no proper subset is also a candidate key is called a super key.
(c) A super key is a set of one or more attributes that, taken collectively, allows us to uniquely identify any entity in the entity set.
(d) A super key for which no proper subset is also a super key is called a candidate key.
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A candidate key for which no proper subset is also a candidate key is called a super key.
A candidate key for which no proper subset is also a candidate key is called a super key. This statement is incorrect because a candidate key is a minimal set of one or more attributes that can uniquely identify records in the entity set, and for a candidate key, no proper subset of it is a candidate key. However, this does not make it a super key. A super key is a set of one or more attributes that can uniquely identify records, but it may not be minimal. That is, a super key has a property that some subsets of it are still super keys.
Other Related Points
- Super Key: A super key is a set, or any subset of, one or more columns (attributes) that can be used to uniquely identify a record in a database table. It can include extraneous attributes.
- Candidate Key: A candidate key is a minimal set of columns (that is, a super key reduced to its irreducible minimum) which can uniquely identify a record. There can be more than one candidate key, but they each must be able to uniquely identify a record without any extraneous data.
- Primary Key: The primary key is a distinct type of candidate key chosen by the database designer to make a row unique in a table. It can neither have null values nor duplicate values.
- Foreign Key: A foreign key in a database is a field or collection of fields in one table, that is a primary key in another, related table. The purpose of the foreign key is to ensure referential integrity of the data.
(a): True (candidate key is minimal).
(b): False (a candidate key is already minimal; it’s a super key, but the statement’s phrasing is incorrect).
(c): True (super key uniquely identifies).
(d): True (a minimal super key is a candidate key).
Q48: The memory size for n address lines and m data lines is given by
(a) 2m × n
(b) m × n2
(c) 2n × m
(d) n × m2
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 2n × m
In a basic memory unit (like RAM), the number of address lines determines the number of memory locations, and the number of data lines determines the size of each memory location.
- The number of memory locations is given by 2n, where n is the number of address lines. This is because each address line can be either 0 or 1 - two possibilities. So with n lines, we have 2n possible combinations, each representing a different memory location.
- The size of each memory location is determined by m, the number of data lines. Each data line can carry one bit of data. So, m data lines can carry m bits of data.
- Combining these two considerations, the total size of the memory is the number of memory locations multiplied by the size of each location in bits.
- So, total memory size = 2n memory locations × m bits/location
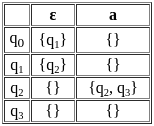
Q49: In the ε-NFA, M = ({q0, q1, q2, q3}, {a}, δ, q0, {q3}) where 'δ' is given in the transition table below, what is the minimum length of string to reach to the final state?
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is option 2) 1
An ε-NFA or epsilon-NFA is a type of non-deterministic finite automaton that includes epsilon or empty string transitions.
- To find the minimum length of a string to reach the final state in the given ε-NFA, you can analyze the transitions and the epsilon (ε) transitions. The ε-NFA has states q0, q1, q2, and q3.
- Starting from the initial state q0, you need to follow the transitions and epsilon transitions until you reach the final state q3. Let's go step by step:
- Start at q0.
- Use the ε-transition to go from q0 to q1.
- Use the ε-transition to go from q1 to q2.
- Use the 'a' transition to go from q2 to q3.
- Now, you have reached the final state q3. The minimum length of the string to reach q3 is 1, as there is one 'a' transition from q2 to q3.
- Therefore, the minimum length of the string to reach the final state q3 is 1.
Q50: Identify the correct operation which produces the below given output based on two relations R1 and R2.
R1
R2
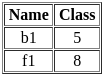
Output:
Choose the correct answer from the options below:
(a) R1 ⋂ R2
(b) R1 - R2
(c) R1 - (R1 - R2)
(d) Option 1 and 3 both
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is R1 ⋂ R2 and R1 - (R1 - R2)
Key Points
Intersection, Union and Difference operations are basic set operations that are used in many areas of mathematics and computer science, including databases and programming. For the , let's think of sets (or relations, in database terms) as collections of distinct items (or tuples).
Intersection (⋂):The intersection of two sets, R1 and R2, denoted as R1 ⋂ R2, is a set that contains all the tuples that are in both R1 and R2.
- For instance, if R1 contains the elements {a, b, c} and R2 contains the elements {b, c, d}, the intersection of R1 and R2 would be {b, c} because these are the elements common to both sets.
Union (⋃): The union of two sets, R1 and R2, denoted as R1 ⋃ R2, is a set that contains all the tuples that are in R1 or R2 or in both.
- Continuing with the previous example, the union of sets R1 {a, b, c} and R2 {b, c, d} would be {a, b, c, d}. This includes all unique elements from both sets.
Difference (-):The difference operation between two sets, R1 and R2, denoted as R1 - R2, results in a set that contains all the tuples that are present in R1 but not in R2.
- So, if we take the difference between R1 {a, b, c} and R2 {b, c, d}, we would have {a}, which is the element present in R1 but not in R2.
- In the context of relational databases, these operations act on tables or relations where tuples are equivalent to set elements. For instance, for the "difference" operation, the resulting relation includes all rows that are in the first relation (R1) and not in the second (R2).
Let's break it down:
Operation 1: Intersection (R1 ⋂ R2)
- The intersection of two sets is a set containing all the elements that are common to both sets.
- So, in the case of R1 and R2, the intersection operation ⋂ will look at both relations (or sets of tuples), and return a new relation that contains only the tuples that appear in both R1 and R2. In this case, the tuple containing ("b1", 5) is the only one that appears in both relations, hence it is the result of the intersection.
Operation 3: R1 - (R1 - R2)
- "R1 - R2" stands for set difference, which is a set of elements that exists in one set but not the other. So, "(R1 - R2)" gives us all tuples that exist in R1 but not in R2.
- But the operation we are looking at is "R1 - (R1 - R2)". This operation will give us all tuples from R1 that also exist in R2, which in terms of set theory, is the exact definition of intersection.
- So "R1 - (R1 - R2)" is essentially a long approach to defining an Intersection operation which is simply written as R1 ⋂ R2.
So, with the given data, both options 1) and 3) will provide us the common tuples between R1 and R2, which in this case is just ("b1", 5).
Q51: Which of the following statements are true?
A. Shortest remaining time first scheduling may cause starvation
B. Preemptive scheduling may cause starvation
C. Round robin is better than FCFS in terms of response time
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A only
(b) B, C only
(c) A, B only
(d) A, B, C
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C
- Shortest remaining time first scheduling may cause starvation: True. In the shortest remaining time first scheduling policy, the process with the shortest remaining time gets the CPU next. However, if short processes keep coming, a long process may never get the CPU, causing starvation.
- Preemptive scheduling may cause starvation: True. In preemptive scheduling, if a process with higher priority arrives, the current running process might be preempted. This can lead to a situation where a low-priority process may never get a chance to execute, which could potentially cause starvation.
- Round robin is better than FCFS in terms of response time: True. In Round Robin scheduling, each process gets a small unit of CPU time (time quantum), usually 10-100 milliseconds. After this time has elapsed, the process is preempted and added to the end of the queue. If there are n processes in the queue and the time quantum is q, then each process gets 1/n of the CPU time in chunks of at most q time units at once. This reduces the average waiting time and improves the response time compared to FCFS (First Come First Serve) where the process that arrives first is executed first and subsequent processes have to wait for the prior process to complete execution.
Q52: In design protocol of critical section problem, each process must ask permission to enter critical section in __________ code; it then executes in the critical section; once it finishes executes in the critical section it enters the __________ code. The process then enters the __________ code.
(a) entry section, remainder section, exit section
(b) entry section, exit section, remainder section
(c) remainder section, entry section, exit section
(d) remainder section, exit section, entry section
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is entry section, exit section, remainder section
The critical section problem is a set of rules or protocols for managing concurrent access to a resource that is shared among several processes. The protocols define that:
- Each process must ask permission to enter the critical section in the "entry section" code.
- It then executes in the "critical section" where it has exclusive access to the shared resource.
- Once it finishes execution in the critical section, it enters the "exit section" code where it signals that it has finished with the shared resource.
- The process then enters the "remainder section" code where it executes the non-critical part of its code that doesn't involve the shared resource.
So, the flow is: Entry section -> Critical section -> Exit section -> Remainder section.
The correct sequence is: entry section (request permission), critical section (execute), exit section (release), remainder section (non-critical code). The question asks for entry, critical, exit, remainder, but options omit critical section. Assuming “executes in the critical section” implies critical section, the correct order is entry, critical, exit, remainder. Option (b) is closest but misleading without critical section.
Q53: How do you create agile processes to manage unpredictability?
A. Requirements gathering must be conducted very carefully.
B. Risk analysis must be conducted before planning takes place.
C. Software increments must be delivered in short time periods.
D. Software processes must not adapt to changes incrementally.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A only
(b) B only
(c) C only
(d) D only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is C only
Agility in project management typically refers to the ability to rapidly and flexibly respond to change, which is particularly important in environments marked by uncertainty and unpredictability.
- Option C "Software increments must be delivered in short time periods" accurately represents this concept. Agile frameworks, such as Scrum and Kanban, rely on iterative development, where solutions evolve through the collaborative effort of self-organizing cross-functional teams.
- Delivering software in increments or iterations, often in short time periods (usually ranging from a week to a month), allows teams to incorporate feedback and make necessary adjustments as the project progresses.
- This practice helps handle unpredictability as it encourages continuous improvement and adaptation to change.
So, only Option C accurately reflects a key element of creating agile processes to manage unpredictability.
Other Related Points
- Option A "Requirements gathering must be conducted very carefully" is relevant to every software project irrespective of it being agile or not. Agile methodology doesn't abandon careful requirements gathering, but rather it promotes the idea of building a product incrementally and refining requirements throughout the project lifecycle instead of trying to define all requirements upfront.
- Option B "Risk analysis must be conducted before planning takes place" is again an essential part of every project but not specific to agile. Furthermore, agile methodology encourages continuous risk analysis throughout the project rather than only at the beginning.
- Option D "Software processes must not adapt to changes incrementally" contradicts the essence of agile. Agile methods are built specifically to adapt and respond to changes incrementally. It's about learning and adjusting through each iteration based on empirical feedback, rather than sticking to a rigidly defined plan from the start.
Q54: Software project manager is responsible for the following tasks:
A. Project Planning
B. Project status tracking
C. Resource management
D. Risk management
E. Project delivery within time & budget.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) All the statements are correct.
(b) Only B & C are correct.
(c) Only A & D are correct
(d) All the statements are not correct.
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is
Project planning:
- Project managers are responsible for creating a detailed project plan which includes defining project goals, establishing tasks and timelines, deciding upon project resources, setting budget and outlining project communication strategy.
Project status tracking:
- A key responsibility of a project manager is to track the progress of the project against its planned objectives. They need to ensure things are staying on track and to update stakeholders on the project's progress and changes.
Resource management:
- Project managers allocate resources (which can be team members, tools, technology, budget, and time) to the various tasks and roles involved in a project. They ensure the optimal use of resources to accomplish the project goals.
Risk management:
- Part of a project manager's job is to identify potential risks in the project and plan mitigation or contingency strategies, and manage and control the risks if they occur.
Project delivery within time & budget:
- Project managers are responsible for ensuring that projects are delivered within the scope, timeline, and budget defined during the planning phase. They need to manage any changes required to keep the project on track.
Hence, all the statements are part of the responsibilities of a software project manager.
Other Related Points
Stakeholder management:
- Project managers are responsible for communicating with stakeholders to keep them informed about the project's progress and to manage their expectations. This may involve negotiating with stakeholders to address their concerns and ensure their needs are met.
Quality management:
- They need to ensure the outputs of the project meet the required quality standards. This includes setting up appropriate procedures and controls for quality assurance.
Change management:
- During a project, change is inevitable. A project manager handles requested changes and their impact on the project in an organized way to avoid any chaos and unnecessary disruptions.
Conflict Resolution:
- Conflicts or disagreements may arise among team members or different stakeholders. The project manager must mediate and resolve these disputes to maintain a smooth workflow.
Project closure:
- At the end of a project, the project manager is responsible for closing out all aspects of the project, including conducting post-project evaluation, releasing project resources, and ensuring all project documentation is finalized and stored.
Learning and Development:
- It's essential for project managers to encourage continuous learning within the project team, from both successes and failures, and to instill best practices for future projects. They should also be focused on their own professional development to keep up with new project management trends and techniques.
Q55: Mr. X designed open source software which must comply with some criteria. Choose the false statement in respect of above.
A. No restriction on redistribution of the software as part or whole.
B. The integrity of the author's source code must be maintained.
C. The software can be sold after distribution.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A only
(b) B only
(c) C only
(d) All statements are false
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is C only
Open source software is a type of software where the source code is open and available to the general public. This means that anyone is welcomed to view, use, modify, and distribute the project's source code.
- The idea behind open source is rooted in the philosophy of freedom, collaboration, transparency, and community-oriented development. Here is a more detailed of the primary characteristics:
- Freedom to Use: Open source software can be used by anyone for any purpose. There are no restrictions on how or where it can be used.
- Open Source Code: The source code of the software is made widely available to the public. Anyone can examine or modify the source code, which can lead to better code quality due to the possibility of community review.
- Free Redistribution: Users have the right to freely distribute copies of the software, in original or modified form. Redistribution rights allow software to be shared and spread quickly.
- Derived Works: Users can modify the software and create derivative works. This means that open source software can be customised to meet specific needs, or can serve as a basis for a completely new project.
- Community-Oriented Development: Open source software is typically developed in a public and collaborative manner. This collaboration often leads to more robust, innovative, and rapidly developing software, as multiple individuals contribute their expertise to the project.
- A large number of open source licenses exist, such as the MIT License, the GNU General Public License (GPL), and the Apache License, each of which have slightly different rules and requirements.
- Software can range from operating systems (like Linux), databases (like MySQL), web servers (like Apache), programming languages (like Python), and even games. The software is generally considered reliable because it's been tested and improved by a large number of users and developers from the community.
Let's break down each statement according to above .
- A. No restriction on redistribution of the software as part or whole. This statement is consistent with many open source licenses, which indeed allow the free redistribution of the software.
- B. The integrity of the author's source code must be maintained. This statement is also in line with some open source licenses, which may require that any modifications to the original source code be clearly indicated or that derivative works also be open source.
- C. The software can be sold after distribution. This statement is typically true for open source software. Open source licenses generally allow users to sell the software or include it in a commercial product. The key is that they cannot restrict others from redistributing it freely.
So, based on the provided options, C is the false statement. Open source software can indeed be sold after distribution, as long as the terms of the open source license are adhered to, such as allowing others to freely redistribute the software.
- A: True (no restriction on redistribution).
- B: True (some licenses, e.g., GPL, require maintaining source code integrity).
- C: True (software can be sold).
- The correct answer is (d).
Q56: Circuit satisfiability problem: Given a Boolean combinatorial circuit composed of AND, OR and NOT gates, is it satisfiable? A one output Boolean combinatorial circuit is satisfiable means for the given inputs the output will be 1.
A. The circuit satisfiability problem belongs to class NP
B. The circuit satisfiability problem is at least as hard as any language in NP
C. The circuit satisfiability is NP - Complete
D. The size of the circuit is Θ(K2 + 1)
E. If P ≠ NP, this situation would contradict the NP - Completeness of the problem.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C, D Only
(b) B, D, E Only
(c) A, B, C Only
(d) B, C, D Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A, B, C Only
A. The circuit satisfiability problem belongs to class NP:
- This is true. The class NP (Nondeterministic Polynomial time) consists of decision problems for which a given solution can be verified as correct or incorrect in polynomial time. A Boolean circuit satisfiability problem is indeed in NP because an assignment of the variables that makes the output of the circuit true can be checked efficiently.
B. The circuit satisfiability problem is at least as hard as any language in NP:
- This is true. In complexity theory, problems that are as least as hard as the hardest problems in NP are known as NP-hard problems. The circuit satisfiability problem (or SAT problem in general) is known to be NP-hard.
C. The circuit satisfiability is NP - Complete:
- This is true. NP-Complete problem class is a subset of NP, so all NP-Complete problems are in NP, but they also have the property that every problem in NP is reducible to them in polynomial time, hence the circuit satisfiability problem can be classified as NP-Complete.
D. The size of the circuit is Θ(K2 + 1):
- This statement is not necessarily true. The size of the circuit could be depicted with different factorial complexities, and it doesn't necessarily have a relationship with Θ(K2 + 1).
E. If P ≠ NP, this situation would contradict the NP - Completeness of the problem:
- This statement is false. The question of whether P = NP or P ≠ NP is one of the most significant unsolved questions in computer science. If P ≠ NP, it does not contradict the NP-Completeness of the problem, and NP-Complete problems like circuit satisfiability would still exist.
Q57: Match the following based on the language accepted by using brute force method of parsing. 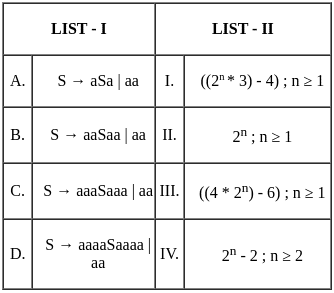
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - I, B - IV, C - III, D - II
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
- List I describes grammar productions while List II describes the lengths of the strings generated by those grammars. Looking at the grammar productions, they generate strings of specific lengths by inserting 'a's at specific positions. Let's interpret each grammar:
- A. (S → aSa | aa), everytime you recursively descend, you add an 'a' on both sides of the string. This step doubles the length, starting from the base string 'aa' which has length of 2. Therefore, it matches with II. 2n ; n ≥ 1. Example: aa, aaaa, aaaaaa, .....
- B. (S → aaSaa | aa), you add 'aa' on both sides upon each recursive descend, effectively adding 4 to the length each iteration, starting from the base string 'aa' which has length of 2. So it generates strings with lengths of (4n - 2) for n ≥ 1 this matches with IV. 2n - 2 ; n ≥ 2. Example: aa, aaaaaa,aaaaaaa, ....
- C. (S → aaaSaaa | aa), each recursive step adds 'aaa' on both sides, essentially adding 6 to the length on each recursion, starting from 'aa' with length of 2. So it generates strings of lengths (6n - 4) for n ≥ 1, this matches with I. ((2n * 3) - 4) ; n ≥ 1. Example: aa, aaaaaaaa, aaaaaaaaaaaaaa, ......
- D. (S → aaaaSaaaa | aa), each recursion results in 'aaaa' on either side of the string, leading to an increase of 8 characters, starting from 'aa' which has length of 2. So it generates strings of lengths (8n - 6) for n ≥ 1, due to 4 base characters added on each side, this matches with III. ((4 * 2n) - 6) ; n ≥ 1. Example: aa, aaaaaaaaaa, .....
Q58: Match List I with List II
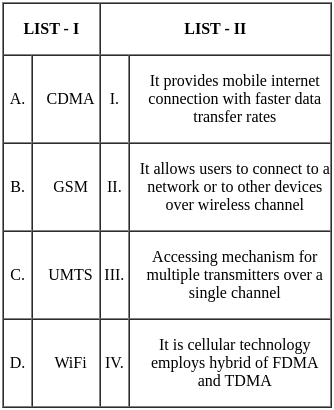
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
(c) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
A. CDMA - III. Accessing mechanism for multiple transmitters over a single channel
B. GSM - IV. It is cellular technology employs hybrid of FDMA and TDMA
C. UMTS - I. It provides mobile internet connection with faster data transfer rates
D. WiFi - II. It allows users to connect to a network or to other devices over wireless channel
The correct answer is : A – III, B – IV, C – I, D – II
Other Related Points
- CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access): This cellular technology uses a spread spectrum technique, enabling multiple users to share a single frequency channel. Its primary purpose is to provide mobile voice and data services.
- GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications): GSM is a digital cellular technology that helps devices connect to the internet.
- UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System): This is a 3G cellular technology providing faster data transfer rates than GSM.
- Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity): Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that permits devices to connect to the internet or to each other over a short distance.
Q59: Match List I with List II
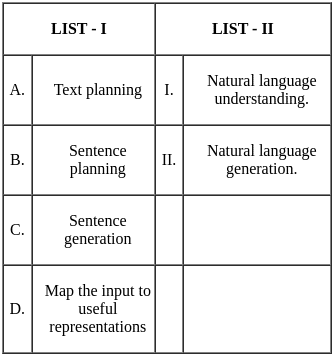
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - I, D - II
(b) A - II, B - II, C - I, D - II
(c) A - I, B - II, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - II, C - II, D - I
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - II, C - II, D - I
A. Text planning -> II. Natural language generation:
- Text planning is a step in the natural language generation process. It involves deciding what content to include in a text, as well as the order in which that content should be presented. This includes planning the main points, arguments, or messages that the text will communicate.
B. Sentence planning -> II. Natural language generation:
- Sentence planning is another step in the language generation process. This involves deciding how individual sentences will be structured, including the ordering of words and phrases, and the selection of appropriate vocabulary. It generally comes after text planning, so that each sentence supports the overall textual structure.
C. Sentence generation -> II. Natural language generation:
- Sentence generation is the final step in the natural language generation process, where the structured sentences (from the planning phase), are actually generated in specific chosen language (like English, Spanish etc.). This is where the planned elements from text and sentence planning come together to create cohesive, comprehensible output.
D. Map the input to useful representations -> I. Natural language understanding:
- Mapping the input to useful representations is a step in natural language understanding. This means converting raw input (which is usually in the form of human language text) into a form that a machine can 'understand' and process. This could be, for example, a vector representation of a sentence in a high-dimension space, or a parse tree that represents the grammatical structure of a sentence. This process aids in interpreting the meaning of the input.
Q60: Consider the statements:
A. There does not exist a polynomial time algorithm to solve integer linear programming problem.
B. Main focus of PERT is 'minimizing time'.
Choose the correct option about the statements A and B.
(a) A is True; B is True
(b) A is True; B is False
(c) A is False; B is True
(d) A is False; B is False
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A is True; B is True
The statement "There does not exist a polynomial time algorithm to solve the integer linear programming problem" is true.
- The integer linear programming problem is known to be NP-hard, there is no known polynomial-time algorithm for solving it in the general case.
The statement "Main focus of PERT is 'minimizing time' " is true.
- The Project Evaluation and Review Technique, or PERT, is a tool used to plan and manage projects. It lets us organize and plan all the tasks needed to complete a project, and figure out the quickest way to do it. PERT was created back in the 1950s to help figure out how much time and money a project might need.
Q61: The correct sequence in fetch-execute cycle is ______
A. Decode
B. Fetch
C. Execute
Chose the correct answer from the following
(a) A - B - C
(b) B - C - A
(c) C - B - A
(d) B - A - C
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is B - A - C
The fetch-execute cycle, also known as the instruction cycle, is the basic operational process of a computer. It is the process by which a computer retrieves a program instruction from its memory, determines what actions the instruction requires, and carries out those actions. This cycle is repeated continuously by the central processing unit (CPU), from bootup to when the computer is shut down.
- Here's a detailed of each step:
- Fetch: At this stage, the computer retrieves the instruction from its memory. The CPU uses the program counter to determine the location of the next instruction. The program counter holds the memory address of the "next" instruction that is going to be executed.
- Decode: During this phase, the fetched instruction is broken up into parts that have different meanings. It interprets the instruction that was fetched, i.e., what operation needs to be performed, and on what data.
- Read Address: Accessing or reading an address from memory is an important operation performed by a CPU during the fetch-execute cycle of a program
- Execute: Finally, the CPU performs the instruction that was fetched and decoded. For example, if the instruction was to add two numbers, the CPU will perform the addition at this stage.
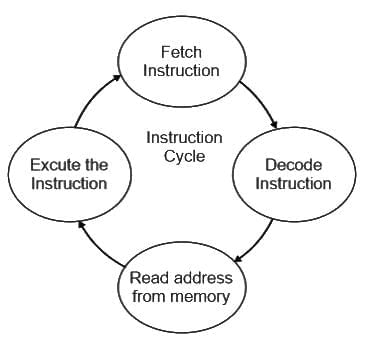
Q62: In what sequence the initialization, testing and execution of body is done while using do-while loop?
A. Commenting
B. Execution of the body
C. Initialisation
D. Testing the condition
Choose the correct answer from the following
(a) D, B, C
(b) D, C, B
(c) C, A, B
(d) C, B, D
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is C, B, D
Initialization (C):
- This is the first step that usually takes place before entering the loop. We initialize the variables in this step. For instance, let's say we have a counter or iterator; we define and set it to an initial value (like int i = 0;) before we start the loop. Note that this step may not always be 'inside' the loop construct but is logically the first step related to the loop.
Execution of the Body (B):
- After initialization step, control enters the loop. In the case of the 'do-while' loop, the loop’s body gets executed at least once, regardless of whether the condition is true or false. This is because the condition is tested after the execution of the loop's body. So the 'do' part of 'do-while' is actually executing the body of the loop.
Testing the Condition (D):
- After the body of the loop has been executed, the condition in the 'while' part is tested. If this condition evaluates to true, the control jumps back to the start of the loop and executes the loop's body again. If it evaluates to false, the loop is exited, and the control moves to the next part of the program following the loop.
Q63: Select the correct order of DBSCAN algorithm.
A. Find recursively all its density connected points and assign them to the same cluster as the core point.
B. Find all the neighbor points with eps and identify the core points with more than MinPts neighbors.
C. Iterate through the remaining unvisited pointed in the dataset.
D. For each core point if it is not already assigned to a cluster, create a new cluster.
Choose the correct answer from the following:
(a) B, D, C, A
(b) D, B, C, A
(c) B, D, A, C
(d) D, B, A, C
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is B, D, A, C
The correct order of the DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise) algorithm is:
- Find all the neighbor points within 'eps' and identify the core points with more than 'MinPts' neighbors.
- For each core point, if it is not already assigned to a cluster, create a new cluster.
- Find recursively all its density connected points and assign them to the same cluster as the core point.
- Iterate through the remaining unvisited pointed in the dataset.
Other Related Points
DBSCAN, which stands for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise, is a popular clustering algorithm used in data mining and machine learning.
The algorithm works by defining clusters as dense regions in the data space, separated by regions of lower object density (which are often noise). DBSCAN can find arbitrary shaped clusters, and it's less influenced by the initialization parameters compared to other clustering techniques, like K-means. The algorithm works as follows:
- Identify Core, Border, and Noise Points: The algorithm begins by identifying the type of data points. A point can be a core point, a border point, or a noise point. This categorization is achieved by looking if there are at least a minimum number of points (MinPts) within a certain radius (eps) of the examined point.
- Core Point: If there are at least MinPts within the eps radius, then the data point of interest is labeled as a core point.
- Border Point: If there are fewer than MinPts within the eps radius, but the point lies within the eps radius of another core point, then it’s a border point.
- Noise Point: If a point is neither a core point nor a border point, it is considered a noise point.
- Grow Clusters: The algorithm proceeds by growing a cluster for each core point, connecting it to other core points within the eps radius. Points that are within the eps distance of each other are placed in the same cluster. This can be a recursive procedure because, as each additional core point is added, it might bring border points into the cluster if they fall inside the eps radius.
- Assign Border Points to Clusters: If a border point falls inside the eps radius of a core point, it’s assigned to the cluster of that core point, else it's considered as a noise point.
- Iterate Until All Points Assigned: The algorithm iterates over all points in the dataset until all points are assigned to a cluster or labeled as noise.
- Some of the advantages of DBSCAN are that it does not require the user to set the number of clusters a priori, it can find arbitrarily-shaped clusters and it has a notion of noise. On the other hand, it might struggle with clusters of varying densities.
Q64: Select the correct order of events after power is initialized on a system.
A. Bootstrap loader is loaded from the disk
B. Kernel is loaded onto the memory
C. Firmware ROM loads boot block
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, A
(b) C, A, B
(c) A, B, C
(d) A, C, B
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is C, A, B
C. Firmware ROM loads boot block:
- When you turn the power on in a computing system, a built-in piece of software called firmware, which is stored in ROM (Read-Only Memory), is activated first.
- This firmware includes a program called BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) in modern systems.
- These programs start the boot process by performing a power-on self-test (POST) to check the health of the system's hardware.
- Then, they look for a bootable device (like a hard disk, USB drive, etc.). From this device, it loads the boot block, also known as the Master Boot Record (MBR) or GUID Partition Table (GPT) in UEFI systems. This boot block contains information about the layout of the storage device and points to the location of the bootloader.
A. Bootstrap loader is loaded from the disk:
- The boot block points to the location of the bootloader in secondary storage (hard disk, SSD, USB, etc.). The firmware loads this bootloader, known as a bootstrap loader, into memory. The job of the bootloader is to load and initiate the operating system.
B. Kernel is loaded onto the memory:
- Once the bootloader is in memory, it loads the operating system kernel into memory.
- The kernel is the core component of an operating system and interacts directly with the system's hardware. When the kernel is ready, it starts the operating system – bringing us to a state where the system is ready to run applications.
Q65: Given below are two statements: one is labeled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Cohesion is a qualitative indication of the degree to which a module can be written more compactly and is able to complete its function in a timely manner.
Reason R: Cohesion is a qualitative indication of the degree to which a module is connected to other modules and the outside world.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is NOT the correct of A.
(c) A is correct but R is not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A is correct but R is not correct.
- Assertion A: Cohesion in software engineering is the measure of how closely the responsibilities of a module or a component are related to each other. It's about how focused a module is on what it should do. Modules that perform one very specific task are considered highly cohesive. This statement is correct as more cohesive modules tend to be more compact and efficient.
- Reason R: The statement is incorrect. The definition provided in this statement describes 'coupling', not 'cohesion'. Coupling is the degree to which one module depends on other modules. In contrast, cohesion refers to how closely all tasks performed by a module are related to each other.
So, "A is correct but R is not correct" which corresponds to option 3 is the right answer.
Q66: Given the graph below which one of the following edges cannot be added in that order to find a minimum spanning tree algorithm.
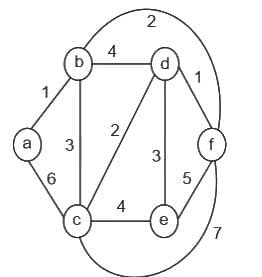 A. a - b
A. a - b
B. d - f
C. b - f
D. d - c
E. d - e
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B, C, D, E
(b) A, B, D,C, E
(c) B, A, C, E, D
(d) B, A, D, C, E
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is B, A, C, E, D
In Kruskal's algorithm, the edges are incorporated in the order of their increasing weights. Nonetheless, in Option 3, edge E bearing a weight of 4 is added prior to edge D with a weight of 2. Therefore, Option 3 is an incorrect representation.
Q67: What is the safest order while simplifying Context Free Grammar?
(a) Elimination of ε-productions, Unit productions and then Useless symbols & productions.
(b) Elimination of useless symbols & productions, ε-productions and then Unit productions.
(c) Elimination of Unit productions, ε-productions and then Useless symbols and productions.
(d) Elimination of ε-productions, Useless symbols and productions and then Unit productions.
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Elimination of ε-productions, Unit productions and then Useless symbols & productions.
The order for simplifying a context-free grammar (CFG) is:
- Elimination of ε-productions.
- Elimination of unit productions.
- Elimination of useless symbols & productions.
The reasoning behind this order is:
- First, eliminate ε-productions: ε-productions can potentially introduce new unit productions into the grammar, so it’s usually better to eliminate these first.
- Second, eliminate unit productions: The removal of unit productions could potentially make a previously useful production into a useless one, so it's better to handle unit productions before dealing with useless ones.
- Third, eliminate useless symbols and productions: This is typically done last, as the previous elimination steps could potentially create new useless symbols or productions that need to be eliminated.
Therefore, the safest order according to the options provided would be: Elimination of ε-productions, Unit productions, and then Useless symbols & productions. So, your first option is the preferred one.
Q68: Rearrange the following sequence in the context of OSI Layers:
A. Transforming the raw bits in the form of frame for transmission
B. Transmission of raw bits over communication channel
C. Handling user interfaces
D. Control and monitoring of subnet
E. Transmission data through connection oriented or connection less using datagrams
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - B - C - D - E
(b) B - C - D - E - A
(c) B - A - D - E - C
(d) A - B - D - E - C
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is B - A - D - E - C
A. Transforming the raw bits in the form of frame for transmission:
- This activity belongs to the Data Link Layer (Layer 2). This layer performs the function of formatting the data into a frame - a package that contains the necessary syntax or structure for transmission.
- Each frame includes the data to be transmitted as well as control information such as error checking and the physical address of the destination.
B. Transmission of raw bits over communication channel:
- The Physical Layer (Layer 1) is responsible for this. The main function is to transmit raw bitstreams over the physical medium (the communication channel). This includes setting voltages for '0' and '1' bits, defining how devices can transmit, defining the physical network layout, and dealing with the actual connector interfaces in hardware.
C. Handling user interfaces:
- This is the Application Layer (Layer 7). This layer provides a user interface and facilitates interaction between the user (or the user's software) and the network. For example, this might be a web browser interacting with a web server.
D. Control and monitoring of subnet:
- That's a responsibility of the Network Layer (Layer 3). This layer handles operations such as routing packets through a network, addressing devices on the network, and managing network traffic congestion. Functions also include subnet traffic control, packet sequencing, and logical network layout and design.
E. Transmission data through connection-oriented or connection-less using datagrams:
- The Transport Layer (Layer 4) deals with this. This layer is responsible for delivering messages between devices over the network and manages error checking and retransmission of packets as necessary. It handles issues like flow control (ensuring that data is sent at a rate that the receiver can handle) and multiplexing (combining multiple signals for transmission).
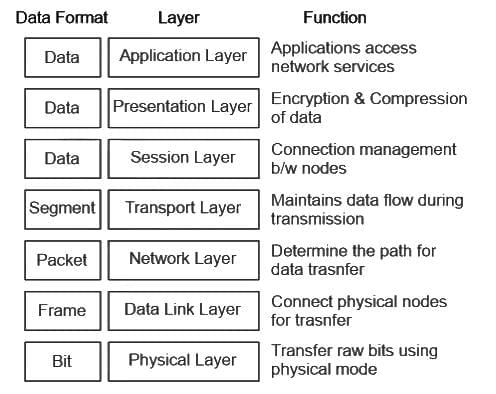
Q69: Choose the correct option describing the features of Artificial neural network
A. It is essentially machine learning algorithm.
B. It is useful when solving the problems for which the data set is very large.
C. They are able to extract features without input from the programmer.
D. These are systems modeled on the human brain and nervous system
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) All the statements are correct.
(b) Only B & C are correct.
(c) Only A & D are correct.
(d) All the statements are not correct.
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is All the statements are correct.
A. "It is essentially a machine learning algorithm."
- This is true because artificial neural networks (ANNs) are indeed a type of machine learning algorithm. These are a set of algorithms, modeled loosely after the human brain, that are designed to recognize patterns. They interpret sensory data through a type of machine perception, labeling or clustering raw input.
B. "It is useful when solving the problems for which the data set is very large."
- Again, this is true. ANNs have proven highly useful in situations where the dataset is large and complex, as they can learn directly from the data and make predictions or classifications.
C. "They are able to extract features without input from the programmer."
- This is also true. One of the significant strengths of ANNs is their ability for feature learning or automatically discovering the representations needed for feature detection or classification from raw data. This replaces manual feature engineering and allows a machine to both learn the features and use them to perform a specific task.
D. "These are systems modeled on the human brain and nervous system."
- This is correct as well. ANNs indeed take inspiration from the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely mirror the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection can transmit a signal from one artificial neuron to another. An artificial neuron that receives a signal can process it and then signal additional artificial neurons connected to it.
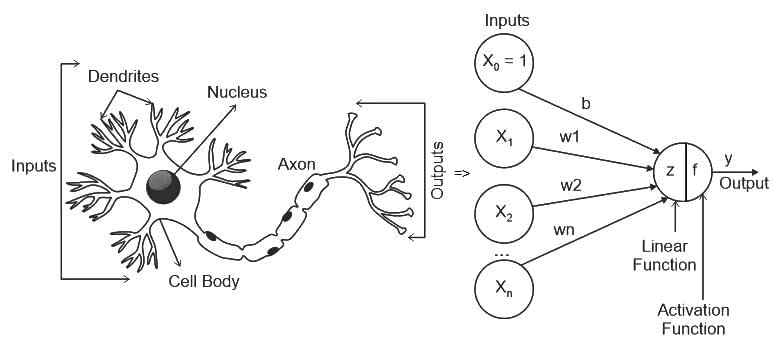
Q70: Four persons: P, Q, R and S are in police custody and one of them has committed a crime. They confess as follows:
A. Person P : Q did it.
B. Person Q : S did it.
C. Person R : I did not do it.
D. Person S : Q lied.
If exactly one of the statements is false, which of the following is the guilty person.
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is option 2) Q
If only one statement is false, then consider the following:
- If P's statement is false (meaning Q did not do it), it would suggest that S's statement is true. However, this creates a conflict because if Q did not do it, then Q didn't lie when he said S did it. This conflict means that P's statement cannot be the one that is false.
- If Q's statement is false (meaning S did not do it), then S's statement that 'Q lied' is indeed true. No conflict arises here. So, this situation is possible.
- If R's statement is false (R actually did it), that would mean Q's and S's statements are both true - a contradiction. So, this can't be the case.
- If S's statement is false (meaning Q did not lie), then Q's statement that 'S did it' is true. This is a contradiction, so S's statement cannot be the one that's false.
So the only situation where only one statement is false is if Q's statement is false. Based on that, S is innocent, and Q is the one who lied which also means Q is the guilty person.
Other Related Points
Decision-making process:
- Identify the decision: You realize that you need to make a decision. Your first step is to clearly define what the decision is and why it needs made.
- Gather relevant information: Collect some pertinent information before you make your decision: what information is needed, the best sources of information, and how to get it. This step could involve seeking advice and opinions from others, studying, or doing research.
- Identify alternatives: As you collect information, you will probably identify several possible paths of action, or alternatives. You can also brainstorm for new solutions.
- Weigh the evidence: This step involves analyzing your alternatives by their potential impact on your established goals or objectives. You can choose the alternative that seems to best meet your needs, or you can employ more sophisticated techniques like a decision matrix or SWOT analysis.
- Choose among alternatives: Once you have weighed all the evidence, you are ready to select the alternative that seems to be best suited to you.
- Take action: You now have to implement the alternative you selected.
- Review decision and consequences: Evaluate whether the decision was the best one you could have made or if there's room for improvement. This is where you learn from your previous decision making and apply it to future ones.
This decision-making process can be applied to a wide range of scenarios, such as personal decisions, managerial decisions, strategic decisions, etc. It's crucial in different aspects of life as it allows individuals to choose the most fitting solution in different scenarios.
Q71: Assertion A: A Raster scan device is a CRT graphic device and can use a television monitor for display
Reason R: In Raster scan display the picture is composed of a series of dots. These dots are traced out as a series of horizontal lines. Television works in a similar fashion.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A
Statement A: "A Raster scan device is a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) graphic device and can use a television monitor for display."
- This is true since raster scan devices do utilize CRT technology, which is the same technology used in older television monitors. Raster scan devices create images by illuminating individual pixels in a grid (raster), which is similar to the way an old CRT television would display its image.
Statement R: "In Raster scan display the picture is composed of a series of dots. These dots are traced out as a series of horizontal lines. Television works in a similar fashion."
- This is also true. When producing an image, a raster scan device does so by drawing out a series of horizontal lines composed of individual dots/pixels--this is also known as scanning. This method of drawing an image is similar to older CRT televisions which produce an image through a similar scan process.
Therefore, as both statements are accurate and Statement R relates directly to the matter raised in Statement A, Both A and R are true and R is the correct of A.
Other Related Points
- Raster Scan: In raster scan systems, the image is composed of a matrix (grid) of small squares, known as pixels. The electron beam produced by the cathode ray tube (CRT) of the monitor sweeps horizontally from left to right, top to bottom, across the screen. This happens very rapidly - on the order of 60 times per second or more - and each pixel is illuminated when the beam hits it, with the brightness level corresponding to the specific image detail at that pixel. Television monitors and most computer monitors display graphics this way.
- Random Scan: In random scan systems (also known as vector graphics or stroke graphics systems), images are drawn by directly specifying the lines that comprise the image, rather than illuminating individual pixels. The picture is stored as a set of line drawings, and the electron beam of the CRT directly draws these lines. This approach is more efficient for images composed mostly of lines, as opposed to complex, filled shapes, which is why it's more common in certain specific applications like oscilloscopes or some CAD systems.
Q72: An OS follows round-robin scheduling with time quantum of 4ms. Assuming that the CPU is free now and there are 20 processes waiting in the ready queue, the maximum amount of time that a process waits before getting into the CPU is _________.
(a) 80 ms
(b) 76 ms
(c) 84 ms
(d) None of the above
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 76 ms
- In round-robin scheduling, every process gets an equal share of CPU time, which is defined by the time quantum or time slice. Assuming there's no context switching time, each process will get to use the CPU for the duration of the time quantum then get placed at the end of the ready queue.
- In this case, the time quantum is 4 ms and there are 20 processes in total.
- Since one cycle for all the processes to get CPU once equals to "number of processes" times "time quantum", this means one cycle will take 20*4 = 80 ms.
- Given that CPU is free now, the first process doesn't have to wait, so it gets the CPU immediately. But the last process, i.e., the 20th process has to wait for 19 processes (not full 20, because the first process didn't wait) to complete their quanta before getting CPU. That means
- Maximum wait time = (Number of processes - 1) * Time quantum
- Maximum waiting time for a process is 19*4 = 76 ms.
Therefore, option 2), 76ms is correct.
Q73: Statement 1: Given a graph G = (V, E) in which each vertex v ∈ V has an associated positive weight w(v), we can use linear programming to find the lower bound on the weight of the minimum-weight vertex cover.
Statement 2: The lower bound can be found by maximizing the following
subject to
x(u) + x(v) ≥ 1 for each (u, v) ∈ V
x(v) ≤ 1 for each v ∈ V
x(v) ≥ 0 for each v ∈ V
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect and Statement II is correct
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
I'll break down the two statements and explain why they are both considered correct:
Statement 1:
- Given a graph
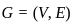 in which each vertex
in which each vertex  has an associated positive weight
has an associated positive weight 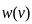 , we can use linear programming to find the lower bound on the weight of the minimum-weight vertex cover.
, we can use linear programming to find the lower bound on the weight of the minimum-weight vertex cover. - This statement is correct. Linear programming can be used to find the lower bound on the weight of the minimum-weight vertex cover by formulating it as an optimization problem.
Statement 2:
- The lower bound can be found by maximizing the following
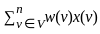
- subject to
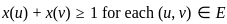
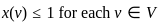
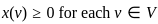
- : This is incorrect. For the minimum weight vertex cover problem, the objective function should be minimized, not maximized. Also, the constraint x(u) + x(v) ≥ 1 should be for each edge (u, v) ∈ E (not V). With these corrections, the model will be like this: It should be instead of
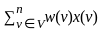 .
. - So, the corrected objective function should be:
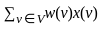
The correct LP for vertex cover minimizes Σ w(v)x(v), subject to x(u) + x(v) ≥ 1 for (u, v) ∈ E, x(v) ≥ 0, x(v) ≤ 1. The solution correctly identifies the errors in II. The answer (c) is correct.
Q74: A TCP Server application is programmed to listen on port P on Host S. A TCP Client is connected to the TCP Server over the network. Considered that while TCP Connection is active the server is crashed and rebooted. Assume that the client does not use TCP keepalive timer. Which of the following behaviours is/are possible?
Statement I: If client is waiting to receive a packet, it may wait indefinitely
Statement II: If the client sends a packet after the server reboot, it will receive the FIN segment
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is true but Statement II is false
Statement I: If a client is waiting to receive a packet, it may indeed wait indefinitely.
- This is because, without using a TCP keepalive timer, the client can't detect that the server has crashed and rebooted. It has no mechanism to determine the server's state so it waits for a packet that will never arrive. So, it is true statement.
Statement II: If the client sends a packet after the server reboot, it will not receive a FIN segment.
- In normal operation, a FIN (Finish) segment is sent by a host to indicate that it has no more data to send. However, in this circumstance, since the server has crashed and rebooted, it likely wouldn't remember the previous connection and hence wouldn't send a FIN segment in response to a packet for that connection. Instead, the client would likely receive a RST (reset) segment, indicating that the connection does not exist on the server's side. So, it is false statement.
Q75: An organization is granted the block 130.56.0.0/16. The administrator wants to create 1024 subnets. Find the number of addresses in each subnet
(a) 32
(b) 64
(c) 128
(d) 16
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 64
- The organization has been granted an IP block of 130.56.0.0/16. If the administrator wants to create 1024 subnets, they need to figure out how many bits are required to create those subnets.
- To find this, we calculate log base 2 of the required number of subnet, which is log21024 = 10. This means we need 10 bits to represent 1024 subnets.
- The original IP block was a /16, which means that there were 16 bits left for host addresses in the subnet (since an IPv4 address is 32 bits, 32-16 = 16). If 10 of these are being used for subnetting, that leaves 6 bits for host addresses within each subnet. 26 = 64
So there will be 64 addresses in each subnet. So your answer is 2) 64.
Please note that the first and last addresses in each subnet are typically reserved for network and broadcast addresses respectively, thus they aren't usually assigned to hosts. That means in practice, there would be 62 usable IP addresses in each subnet.
Q76: An organization is granted the block 130.56.0.0/16. The administrator wants to create 1024 subnets. Find the subnet prefix.
(a) 130.56.0.0/26
(b) 136.0
(c) 136.255
(d) 136.56.255
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 130.56.0.0/26
- To find the subnet prefix, we can take the given IP address (130.56.0.0) and combine it with the subnet mask to determine the range of IP addresses in each subnet.
- The organization was granted the block 130.56.0.0/16, and then 10 bits were borrowed for subnetting. So, the new subnet mask is /26 (16 original network bits + 10 subnet bits).
- Let's calculate the subnet prefix:
A /16 network with 1024 subnets uses 10 bits, yielding a /26 mask (255.255.255.192). "
The prefix for the first subnet is 130.56.0.0/26.
The correct answer is: 130.56.0.0/26.
Q77: An organization is granted the block 130.56.0.0/16. The administrator wants to create 1024 subnets.
Find first and last addresses of First subnet.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 2
The IP address block is 130.56.0.0/16 and the administrator wants to create 1024 subnets, subnets would have a /26 subnet mask, meaning there are 64 addresses in each subnet.
- Therefore, the first and last addresses of the first subnet would be:
- The first address (network address) would be the first address of the granted block, that is: 130.56.0.0.
- Since there are 64 addresses in each subnet, the last address (broadcast address) would be the 63rd increment from the first address, that is: 130.56.0.63.
So the correct answer would be:
First address = 130.56.0.0, Last address = 130.56.0.63
Please note that the first and last addresses in each subnet are typically reserved for network and broadcast addresses respectively, thus they aren't usually assigned to hosts. That means in practice, there would be 62 usable IP addresses in each subnet.
Q78: An organization is granted the block 130.56.0.0/16. The administrator wants to create 1024 subnets. Find first and last addresses of last subnet.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 4
- Based on the previous question where we established the new subnet mask as /16 resulting in 64 addresses in each subnet:
- The first address of each subnet is a multiple of 64 in the last octet, and the last address is 63 greater than the first address (because we start at 0).
- The last subnet can be calculated by subtracting 64 (one subnet's worth of addresses) from the entire address space. So the last subnet's first address can be calculated as 256 - 64 = 192 (the "256" being representative of the total number of addresses accessible by 8 bits in the last section of the IP address), with the "192" being the starting point of the final subnet in the /26 partitioning.
- Hence, the first address of the last subnet is: 130.56.255.192
- The last address in the subnet is the first address plus 63, because there are 64 addresses in each subnet. That would be: 130.56.255.255
So, the answer is: 4) First address = 130.56.255.192, Last address = 130.56.255.255.
Q79: An organization is granted the block 130.56.0.0/16. The administrator wants to create 1024 subnets.
Find subnet mask.
(a) 130.255.255.255
(b) 130.56.255.255
(c) 130.56.0.255
(d) 255.255.255.192
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 255.255.255.192
When the IP address block 130.56.0.0/16 is divided into 1024 subnets, it means that we require 10 more bits for subnetting, which means we need to extend the subnet mask by 10 bits.
The original subnet mask for the /16 network was 255.255.0.0. When we extend by 10 bits, we get a /26 network.
In dotted decimal format, a /26 network's subnet mask is 255.255.255.192. So, our new subnet mask will not have any prefix of the 130.56 network block because those are separate parts of the IP addressing scheme.
For standard subnet masks, first octet would be 255, 255, 255, or 192 (for /26 network).
Here, the subnet mask related to /26 is 255.255.255.192.
Q80: Which of the following are correct on regular expressions?
A. φ + L = L + φ = L
B. εL = Lε = L
C. φL = Lφ = φ
D. φL = Lφ = L
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and D only
(b) A, B and C only
(c) B and D only
(d) A and D only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and C only
A. φ + L = L + φ = L
This expression pertains to the union operation with an empty set φ and a language L.
- φ + L: This operation takes the union of an empty set φ with a language set, L. Since there are no elements in the set φ, the union operation with L simply yields the set L. It's basically L union nothing, which is L itself.
- L + φ: This is the same scenario as above but the order of sets is reversed. The union operation doesn't depend on the order of sets. It's just L union with nothing, which is still L.
- L + φ = φ + L = L simply means that the union of set L with the empty set φ (in either order) gives us L. This is a known property in set theory: the union of any set with the empty set is the set itself.
B. εL = Lε = L
- This expression pertains to the concatenation operation involving an empty-string ε and a language L.
- εL: An empty string can be thought of as the "zero" of string operations. Concatenating it in the front of any language L does not alter the language, hence the result is L.
- Lε: Similarly, concatenating an empty string at the end of any language L also does not change the language, resulting in L.
- εL = Lε = L simply means that concatenating either at the start or the end of language L with an empty string ε, does not change L.
C. φL = Lφ = φ
- This expression pertains to the concatenation operation involving an empty set φ and a language L.
- φL: Concatenating empty set φ in front of (or with) any language L yields an empty set. This is because there are no strings in φ to concatenate with strings in L.
- Lφ: Similarly, concatenating empty set φ at the end of any language L, also gives empty set, as there are no strings in φ to concatenate with strings in L.
- φL = Lφ = φ simply means that concatenating either at the start or the end of a language L with an empty set, yields an empty set.
D. φL = Lφ = L
- φL and Lφ: As explained above, concatenating an empty set φ (at the start or the end of a language) with any language L will result in an empty set, not L.
- Therefore, the claim φL = Lφ = L is incorrect. The correct equation would be φL = Lφ = φ.
Q81: Consider the following Learning algorithms.
A. Logistic regression.
B. Back propagation.
C. Linear regression.
D. Forward propagation.
Which of the following options represents classification algorithm?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A & C only
(b) B & D only
(c) A & B only
(d) C & D only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A & B only
Learning algorithms: These algorithms are used in machine learning to help technology in human learning process. It is used to process data to extract patterns appropriate for application in a new system.
From above given options, only a) and b) are learning algorithms.
- Logistic regression: It is used for binary classification problems. It is used to examine and describe the relationship between a binary variable and set of predicator variables. The primary objective of logistic regression is to model the mean of the response variables, given a set or predicator variables.
- Back propagation: It is the essence of neural net training. It is the method of fine tuning the weights of a neural net based on the error rate obtained in the previous iteration. It is a standard method of training artificial neural networks.
Other Related Points
- Linear regression and forward propagation are not typically considered classification algorithms. Linear regression is a regression algorithm used for predicting continuous numeric values, while forward propagation is a step in the training process of neural networks and is not a standalone algorithm for classification.
Q82: Which Boolean operation on two variables can be represented by a single perception layer?
A. X1 AND X2
B. X1 OR X2
C. X1 NOR X2
D. X1 XOR X2
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B Only
(b) B and C Only
(c) A, B and C Only
(d) A, B, C and D Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A, B and C Only
A perceptron can solve boolean functions that are linearly separable. A problem is linearly separable if you can draw a line (or, more generally, a hyperplane) to separate inputs of different classes.
Here's how it can represent AND, OR, and NOR:
- AND Operation: Mapping each set of inputs (0,0), (0,1), (1,0), (1,1) can be solved linearly. The points can be separated into two classes, one for outputs that should be 0 and one for outputs that should be 1.
- OR Operation: Just like the AND operation, the OR operation is also linearly separable. The (0,0) inputs which yield 0 can be separated from (1,0), (0,1), (1,1) inputs that yield 1.
- NOR Operation: Similar to the OR operation, the NOR operation is also linearly separable. The NOR operation is simply the inverse of the OR operation.
However, XOR operation is not linearly separable, that is, there is no straight line that can separate the data for 0s and 1s. So, it can't be represented by a single-layer perceptron.
Whereas a single layer perceptron can represent only linear separable Boolean functions, a multi-layer perceptron or a deeper neural network model can represent more complex lineraly inseperable functions, such as XOR. This is because layers beyond the first can account for inputs from previous layers, allowing for complex decision boundaries beyond a simple straight line.
Q83: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
In Assembly programming language, there are different types of address modes:
- Direct Addressing: Also known as absolute addressing, is when the instruction specifies the memory address of the operand.
- Indirect Addressing: The instruction specifies a register that contains the memory address of the operand.
- Register Addressing: The instruction specifies the register which contains the operand.
- Immediate Addressing: The instruction contains the operand.
Matching each mode with the corresponding example:
- Direct Addressing would be "STA FFFFH" because the instruction specifies the exact memory address to store an accumulator.
- Indirect Addressing would be "MOV A, M" because the instruction specifies a memory location using an indirect reference which indirectly points to the operand's location.
- Register Addressing would be "MOV A, B" because the instruction defines that the value in register B is to be moved to register A.
- Immediate Addressing would be "MVI A, FFH" because the instruction contains the data directly (in this case, FFH is the immediate data).
Therefore, the matching is: A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Other Related Points
- Indexed Addressing Mode: Some architectures provide indexed addressing modes where the final address is calculated by adding a base register and an index value. This is particularly useful in array traversals.
- Relative Addressing Mode: The effective address of the operand is generated by adding an offset value from the instruction to the program counter or a base register.
- Base Register Addressing Mode: In this mode, a base register holds a base address and the address field of the instruction holds displacement. The effective address is calculated by adding the base address to the displacement.
Q84: Match List I and List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is
A. Apache Kafka - Open-source platform that was created by Linkedin.
- Apache Kafka is an open-source stream-processing software platform developed by LinkedIn and was donated to the Apache Software Foundation. It is designed for high-volume real-time data ingestion and processing. It is used in scenarios where high throughput, reliable delivery and horizontal scalability are necessary.
B. Pig - Platform for constructing data flows for extract, transform, and load (ETL) processing and analysis of large datasets.
- Pig is an open-source platform that provides a high-level mechanism for the parallel execution of map-reduce jobs executed on Hadoop clusters. Pig simplifies the use of Hadoop by allowing SQL-like commands for data extract-transform-load (ETL) operations, as well as large data set analysis.
C. Apache Mahout - Open-source platform used for creating scalable machine learning algorithms.
- Apache Mahout is a project of the Apache Software Foundation with the goal of creating scalable machine learning algorithms. The algorithms focus primarily in the areas of collaborative filtering, clustering, and classification, and are designed to be scalable and robust.
D. MapReduce - General-purpose computing model and runtime system for distributed data analytics.
- MapReduce is a computational model and software framework for writing applications that rapidly process vast amounts of data in parallel on large clusters of compute nodes. It is a core component of the Apache Hadoop software framework which allows processing huge amounts of data.
Q85: Given an expression
(A + B * D)/(E - F) + G
A. The prefix notation is +/+A*DB - EFG
B. The prefix expression is the reverse of the postfix expression
C. The order of operands in infix expression and postfix expression are the same.
D. The order of operands in infix expression, prefix expression and postfix expression are the same.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D Only
(b) C and D Only
(c) A and B Only
(d) A and D Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is C and D Only
Let's analyze each option:
The prefix notation is +/+A*DB - EFG
- This is incorrect. The correct prefix notation for the given expression (A + B * D)/(E - F) + G is: + / + A * B D - E F G
The prefix expression is the reverse of the postfix expression
- The postfix expression for the given expression is: A B D * + E F - / G +
- If we reverse this, we get: + G / - F E + * D B A
This is not the same as the correct prefix notation, so option B is not correct.
The order of operands in infix expression and postfix expression are the same.
- This statement is true. In infix notation (the typical mathematical notation), the operands are placed between the operators. In postfix notation, the order of operands remains the same as in infix notation.
The order of operands in infix expression, prefix expression, and postfix expression are the same.
- The order of operands in infix expression, prefix expression and postfix expression are the same" is true. Even though the arrangement of operators varies between these notation formats, the occurrence of operands remains the same.
So, the correct answer is 2) C and D Only.
Q86: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(c) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
A. If the implementation of generated or derived classes differ only through a parameter we have - III. to use templates
- Templates in C++ allow functions and classes to operate with generic types, enabling a higher degree of code reuse. If we have classes that differ only by the type of data they operate on, templates are an excellent way to optimize that.
B. If the actual types of objects used cannot be known at compile time, then we have - I. to use class hierarchy
- A class hierarchy allows us to use the principle of polymorphism where a base class reference can point to any derived class object. This feature is helpful when we don't know the exact type of objects at compile time.
C. If inline operations are essential and templates are used then we have - II. improved run-time efficiency
- Inline functions and templates can help improve runtime efficiency by eliminating the overhead of repeated function calls and allowing different data types to be handled by the same functions or classes.
D. To gain access to differing instances for derived classes through base we have - IV. to use explicit casting
- Casting allows us to convert one object type to another. To access the specific implementation of a derived class from something that is only aware of the base class, we would typically use casting. This allows us to recover the specific type of the derived class and access its specifics.
Q87: Match List I with List II
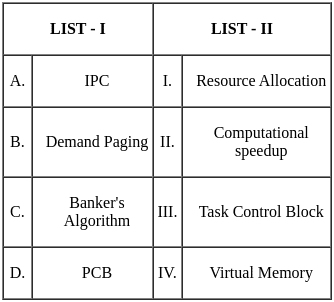
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(c) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(d) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
A. IPC - Computational speedup:
- IPC stands for Inter-Process Communication. It's a mechanism that allows processes to communicate and synchronize their actions. This communication can ensure efficient use of resources, avoid conflicts and can also lead to computational speedup if communication between processes is done efficiently.
B. Demand Paging - Virtual Memory:
- Demand Paging is a strategy for managing computer memory. In this system, only the necessary pages of a program are loaded into physical memory, the rest are kept in virtual memory. This happens on demand, i.e., when the specific page is required.
- Virtual Memory is a feature of an operating system (OS) that enables a computer to be able to compensate shortages of physical memory by transferring pages of data from random access memory (RAM) to disk storage. This process is invisible to the user. Demand Paging is a strategy used in virtual memory systems.
C. Banker's Algorithm - Resource Allocation:
- The Banker's Algorithm is an approach to managing computer resources so that deadlock conditions can be rigorously avoided. It's used in operating systems that manage multiple processes. It helps to determine the safe sequence for allocating resources to the processes.
- Resource Allocation is the assignment of available resources to various uses. In the context of an operating system, these resources include things like CPU time, memory space, and I/O devices. The Banker's Algorithm is one method of managing resource allocation in a way that avoids deadlocks.
D. PCB - Task Control Block:
- PCB stands for Process Control Block. It is a data structure in the operating system kernel containing the information needed to manage a particular process. It contains details like process state, process identification number, program counter, priority, registers, etc.
- A Task Control Block—as the name implies—is a similar structure, except it's often used in the context of scheduling and managing "tasks" (essentially processes). So, a Process Control Block (PCB) can be considered a kind of Task Control Block.
Q88: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
The correct match for each algorithm to its description is as follows:
- Dijkstra's Algorithm - III. Stores the total cost from a source node to the current node: Dijkstra's Algorithm is used to find the shortest paths from a source node to all other nodes in a weighted graph. It uses a data structure, often a priority queue, to keep track of the minimum distance from the source node to each node in the graph.
- Prim's Algorithm - II. Stores minimum cost edge: Prim's Algorithm is a greedy algorithm used to find the minimum spanning tree of a connected, undirected graph. It works by adding the smallest edge that connects a vertex from the growing minimum spanning tree to a vertex outside the tree.
- Warshall's Algorithm - I. Calculates path matrix: Warshall's Algorithm is used to find the transitive closure of a directed graph. It determines the reachability between pairs of vertices in a graph and represents the results in the form of a path matrix.
- Kruskal's algorithm - IV. Finds Minimum Spanning Tree: Kruskal's Algorithm is also used to find the minimum spanning tree of a connected, undirected graph. It works by sorting all the edges in ascending order of their weights and adding them to the growing minimum spanning tree as long as they do not form a cycle.
Q89: A Turing Machine for the language L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1} is designed. The resultant model is M = ({q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7, qf}, {a, b, c, d}, {a, b, c, d, X1, X2, Y1, Y2}, δ, q0, B, {qf}) and part of 'δ' is given in the transition table. You need to write the following questions based on design of Turing Machine for the given language. Note that, while designing the Turing Machine X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's and Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's of the given string.
 What is the Move in the cell with number 'M1' of the resultant Table?
What is the Move in the cell with number 'M1' of the resultant Table?
(a) (q2, X2, R)
(b) (q2, X2, L)
(c) (q3, X2, L)
(d) Error Entry
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (q2, X2, L)
State Diagram: L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1}
- X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's
- Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's
- q0 is initial state.
- q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7 are internal states.
- qf is final state.
According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M1 is (q2, X2, L)
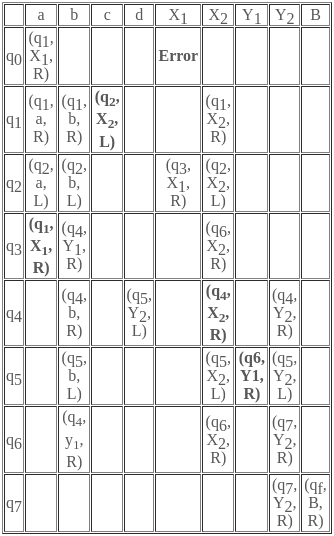
Q90: A Turing Machine for the language L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1} is designed. The resultant model is M = ({q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7, qf}, {a, b, c, d}, {a, b, c, d, X1, X2, Y1, Y2}, δ, q0, B, {qf}) and part of 'δ' is given in the transition table. You need to write the following questions based on design of Turing Machine for the given language. Note that, while designing the Turing Machine X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's and Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's of the given string
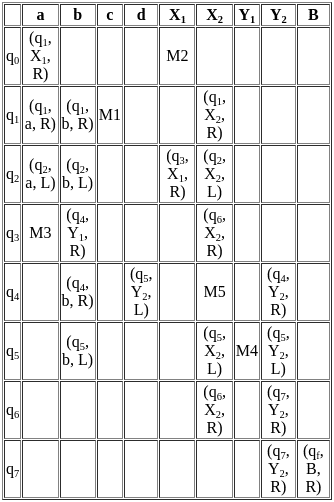 What is the Move in the cell with number 'M2' of the resultant Table?
What is the Move in the cell with number 'M2' of the resultant Table?
(a) (q1, X1, R)
(b) (q1, a, R)
(c) (q2, X1, R)
(d) Error Entry
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Error Entry
:
State Diagram: L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1}
- X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's
- Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's
- q0 is initial state.
- q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7 are internal states.
- qf is final state.
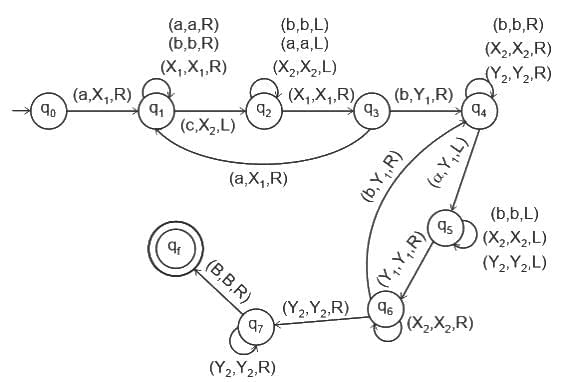
According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M2 is Error Entry
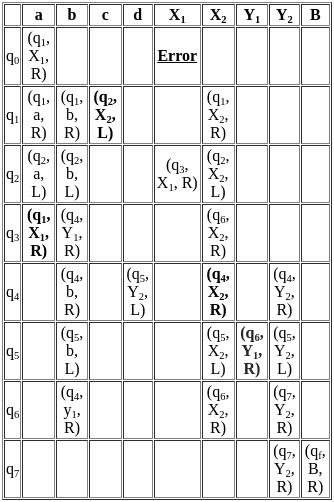
Q91: A Turing Machine for the language L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1} is designed. The resultant model is M = ({q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7, qf}, {a, b, c, d}, {a, b, c, d, X1, X2, Y1, Y2}, δ, q0, B, {qf}) and part of 'δ' is given in the transition table. You need to write the following questions based on design of Turing Machine for the given language. Note that, while designing the Turing Machine X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's and Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's of the given string.
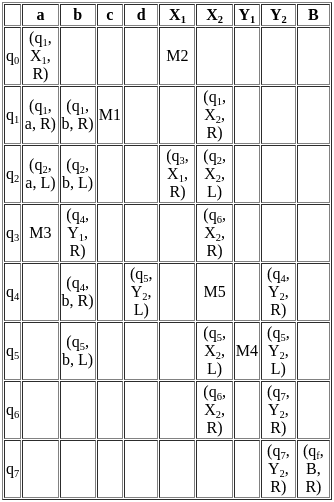 What is the Move in the cell with number 'M3' of the resultant Table?
What is the Move in the cell with number 'M3' of the resultant Table?
(a) (q1, X1, L)
(b) (q4, X1, R)
(c) (q1, X1, R)
(d) Error Entry
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (q1, X1, R)
State Diagram: L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1}
- X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's
- Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's
- q0 is initial state.
- q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7 are internal states.
- qf is final state.
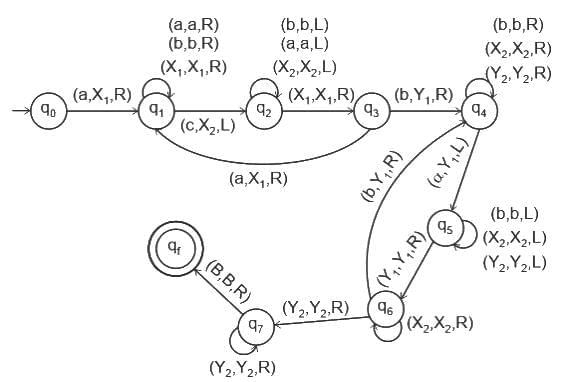 According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M3 is (q1, X1, R)
According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M3 is (q1, X1, R)
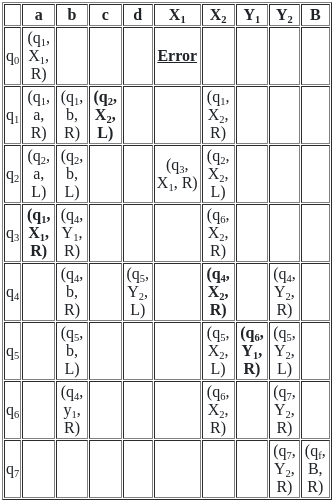
Q92: A Turing Machine for the language L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1} is designed. The resultant model is M = ({q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7, qf}, {a, b, c, d}, {a, b, c, d, X1, X2, Y1, Y2}, δ, q0, B, {qf}) and part of 'δ' is given in the transition table. You need to write the following questions based on design of Turing Machine for the given language. Note that, while designing the Turing Machine X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's and Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's of the given string.
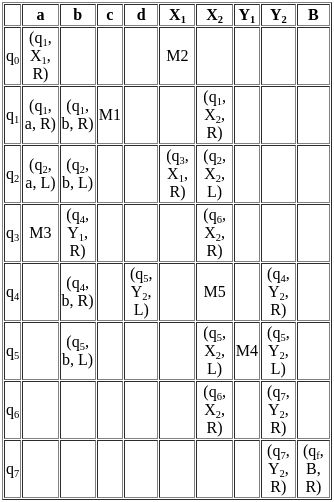 What is the Move in the cell with number 'M4' of the resultant Table?
What is the Move in the cell with number 'M4' of the resultant Table?
(a) (q6, Y1, R)
(b) (q3, Y1, R)
(c) (q4, Y1, L)
(d) (q3, Y1, L)
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is (q6, Y1, R)
State Diagram: L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1}
- X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's
- Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's
- q0 is initial state.
- q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7 are internal states.
- qf is final state.
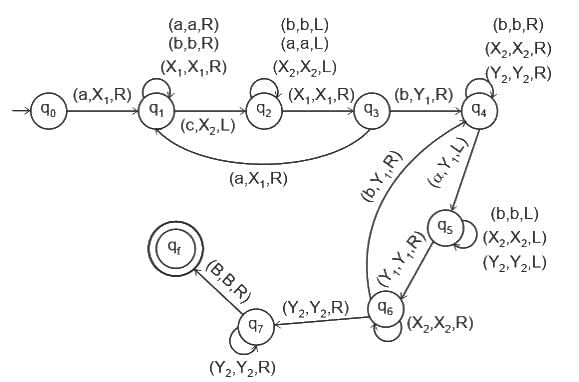
According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M4 is (q6, Y1, R)
Q93: A Turing Machine for the language L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1} is designed. The resultant model is M = ({q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7, qf}, {a, b, c, d}, {a, b, c, d, X1, X2, Y1, Y2}, δ, q0, B, {qf}) and part of 'δ' is given in the transition table. You need to write the following questions based on design of Turing Machine for the given language. Note that, while designing the Turing Machine X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's and Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's of the given string.
What is the Move in the cell with number 'M5' of the resultant Table?
(a) (q4, X2, R)
(b) (q5, X2, R)
(c) (q5, X2, L)
(d) Error Entry
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is (q4, X2, R)
:
State Diagram: L= {anbmcndm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1}
- X1 and X2 are used to work with 'a's and 'c's
- Y1 and Y2 are used to handle 'b's and 'd's
- q0 is initial state.
- q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6, q7 are internal states.
- qf is final state.
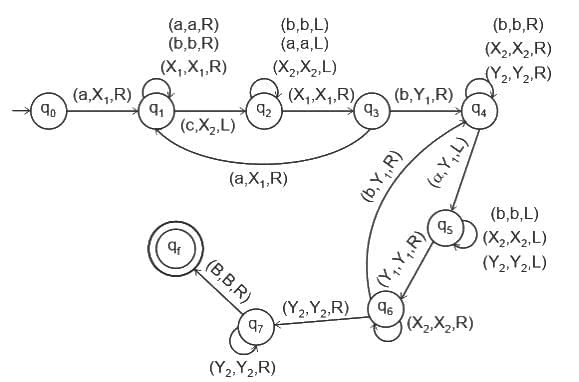 According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M5 is (q4, X2, R)
According to State Diagram We fill the transition table: So M5 is (q4, X2, R)
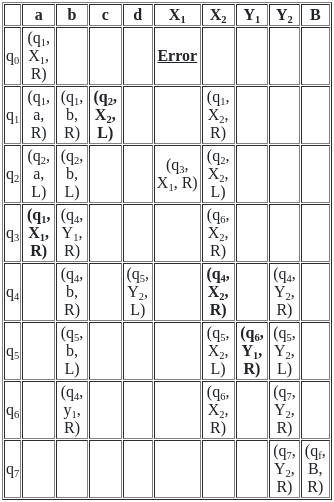
Q94: The Solution to Silly Window Syndrome problem is/are:
A. Nagle's Algorithm
B. Clark's Algorithm
C. Jacobson's Algorithm
D. Piggy backing Algorithm
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B Only
(b) A and C Only
(c) C and D Only
(d) B and D Only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A and B Only
A. Nagle's Algorithm:
- This algorithm addresses the issue of inefficient transmission of small packets of data (known as 'small' or 'silly' windows in TCP/IP parlance), especially over large networks with high bandwidth-delay products (like the internet).
- Rather than sending each packet as it becomes ready, Nagle's Algorithm groups small outgoing messages into larger packets before sending them out to improve efficiency.
B. Clark's Algorithm:
- The statement clarifies that Clark's Algorithm, also known as the "Clark-Wilson algorithm," is typically associated with integrity constraints in database systems and not directly linked to addressing the Silly Window Syndrome.
If there is specific context or materials connecting Clark's Algorithm to the Silly Window Syndrome, option 1 (A and B Only) might be correct; otherwise, in a general networking context, Nagle's Algorithm (Option A) is the primary solution for mitigating the Silly Window Syndrome.
Other Related Points
- C. Jacobson's Algorithm: Van Jacobson (VJ) developed an algorithm to tackle congestion control in TCP. Jacobson's algorithm doesn't directly address the Silly Window Syndrome, but it does play a pivotal role in overall traffic control, making data transport more reliable over the network by reducing congestion.
- D. Piggybacking Algorithm: In the context of networking, piggybacking refers to the practice of sending a data packet (ACK or NAK) along with a data frame, rather than separately, to improve overall efficiency. This also doesn't directly address the Silly Window Syndrome, but it contributes to increased efficiency in network communications.
Q95: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - I, D - II
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
A. Product Complexity - Software cost estimation:
- Product complexity refers to the number of components in a product and the intricacy of their interconnections.
- As the complexity of the product increases, it becomes harder to estimate costs accurately since many factors like development time, testing, debugging, documentation etc., increase exponentially. Therefore, it is directly related to software cost estimation.
B. Structured System Analysis - System Requirements Design:
- Structured system analysis is a traditional method of systems analysis and design that involves a sequence of activities – data flow diagramming, data dictionary, process decomposition and system flowcharting – all of which aim to create a blueprint of the existing system and propose enhancements.
- This approach goes hand in hand with System Requirements Design, where the requirements for a new system are defined. Structured system analysis would typically be used to guide and inform this design process.
C. Coupling & Cohesion - Software Design:
- Coupling and Cohesion are fundamental software design principles.
- Cohesion refers to how closely the responsibilities of a module or a class are related to each other.
- High Cohesion is generally preferred as it promotes the maintainability and understandability of the system.
- Coupling, on the other hand, relates to the degree to which one class knows about another class.
- If a change in one class forces a change in another class, the classes are said to be tightly coupled.
- Minimizing coupling is a key aspect of software design, as it enhances modularity and independence between the sections of software.
D. Symbolic Execution - Validation Techniques:
- Symbolic Execution is a software testing technique in which programs are executed with symbolic values rather than actual data input.
- The aim is to calculate the output on given symbolic values and then solving those expressions in order to have all possible values for testing.
- As such, it is often used as a validation technique to ensure the accuracy and quality of software during testing phase, making it an important part of the software development process.
Q96: Which of the following statements are correct?
A. The first three-address instruction in the intermediate code is a leader.
B. The instruction which is exactly at the middle of the given three address code is a leader.
C. Any instruction that is the target of a conditional or unconditional jump is a leader.
D. Any instruction that immediately follows a conditional or unconditional jump is a leader.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C
(b) B, C and D
(c) A, C and D
(d) A, B, C and D
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A, C and D
A. The first three-address instruction in the intermediate code is a leader.
- Leaders, in programming, are the first instructions of a ‘basic block’ in the control-flow graph.
- A basic block is a straight-line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit.
- The first instruction of a basic block is known as a leader. So, in context, the first three-address instruction would be a leader as it's the first instruction in the block. This statement is correct.
B. The instruction which is exactly at the middle of the given three address code is a leader.
- A leader doesn't get determined by its position in the middle of the given intermediate code. It becomes a leader if it's the first instruction in the block, or if it's the target of a conditional or unconditional jump, or if it immediately follows a jump. Just being at the "middle" doesn't qualify an instruction as a leader. Therefore, this statement is incorrect.
C. Any instruction that is the target of a conditional or unconditional jump is a leader.
- This is correct. An instruction becomes a leader if it becomes the target of a jump - whether that jump is conditional or unconditional. That's because it marks a new possible entry point into a block of code, and thus starts a new basic block.
D. Any instruction that immediately follows a conditional or unconditional jump is a leader.
- This statement is also correct. The instruction immediately following a conditional or unconditional jump also starts a new basic block. This is because the jump could transfer control elsewhere, and so the next instruction potentially starts a new sequence of code with no prior branches in.
So, summarizing, the correct statements here are A, C, and D, option 3.
Q97: Consider two hosts P and Q are connected through a router R. The maximum transfer unit (MTU) value of the link between P and R is 1500 bytes and between R and Q is 820 bytes. A TCP segment of size of 1400 bytes is transferred from P to Q through R with IP identification value of 0x1234. Assume that IP header size is 20 bytes. Further the packet is allowed to be fragmented that is Don't Fragment (DF) flag in the IP Header is not set by P. which of the following statement is/are true
A. Two fragments are created at R and IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes
B. If the second fragment is lost then R resend the fragment with IP Identification value of 0x1234
C. If the second fragment lost then P required to resend the entire TCP segment
D. TCP destination port can be determined by analyzing the second fragment only
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C Only
(b) A and C Only
(c) C and D Only
(d) B and D Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A and C Only
A. Two fragments are created at R and IP datagram size carrying the second fragment is 620 bytes: TRUE
- Since the TCP segment is of size 1400 bytes and the MTU between P and R is 1500 bytes, P can send it to R without fragmentation. However, when the router R tries to forward them to Q, it will not be able to do so because the MTU between R and Q is 820 bytes.
- Since the IP header size is 20 bytes, the maximum payload that can be carried in one IP datagram on the R-Q link is 800 bytes.
- The first fragment will have 800 bytes and the second fragment will have the remaining 600 bytes of the TCP segment. But, we must consider that both fragments will have their own 20 bytes IP header. So, the total size of the second IP datagram will be of 620 bytes (600 + 20 bytes of IP header).
B. If the second fragment is lost then R resend the fragment with IP Identification value of 0x1234: FALSE
- In case the second fragment is lost, R does not resend the fragment because the retransmission responsibility belongs to the end systems (here, P), not the routers.
C. If the second fragment lost then P required to resend the entire TCP segment: TRUE
- As B, it's the end system's (P) responsibility to detect the loss (via TCP mechanisms) and retransmit the entire TCP segment.
D. TCP destination port can be determined by analyzing the second fragment only: FALSE
- Only the first fragment has the entire TCP header because IP fragmentation does not duplicate the TCP headers in the fragments.
- The TCP header contains information such as source port, destination port, sequence number, and acknowledgment number. The later fragments only contain IP headers and the remaining portion of the data. So, it's not possible to determine TCP port by analyzing the second fragment.
Q98: Match List I with List II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A - IV; B - III; C - I; D - II
(b) A - III; B - IV; C - II; D - I
(c) A - II; B - IV; C - I; D - III
(d) A - III; B - IV; C - I; D - II
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A - III; B - IV; C - I; D - II
A. Planar Graph - III. 4-Colorable.
- The four-color theorem states that any map in a plane can be colored using four-colors in such a way that regions sharing a common boundary (other than a single point) do not share the same color.
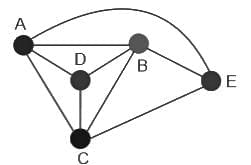
B. Bipartite Graph - IV. 2-Colorable.
- A bipartite graph can be divided into two sets of vertices such that all edges connect a vertex in one set to a vertex in the other set. Therefore, they are 2-colorable.
C. PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) - I. Probabilistic Model.
- PERT is a statistical tool, used in project management, designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project. It uses probabilistic time estimates.
D. CPM (Critical Path Method) - II. Deterministic Model.
- CPM is a method used in project management for planning and scheduling the different steps in the project. It's a deterministic model because it assumes a fixed time duration for each task.
Q99: Which of the following is (are) correct about the regular expression?
aa*bb*cc*dd*
A. The language for the given expression is:
L = {anbncmdm | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1} U {anbmcmdn | n ≥ 1, m ≥ 1}
B. The Context Free Language for the given expression is:
S → AB | C
A → aAb | ab
B → cBd | cd
C → aCd | aDd
D → bDc | bc
C. The language generated by this expression is equal number of 'a's, followed by equal number of 'b's, followed by equal number of 'c's and followed by equal number of 'd's.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Only A is correct
(b) Only B is correct
(c) Both A and B are correct
(d) All the three A, B and C are correct
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Both A and B are correct
Let's analyze the given regular expression and the options:
The given regular expression is aa*bb*cc*dd*, where:
- a* denotes zero or more occurrences of 'a'
- b* denotes zero or more occurrences of 'b'
- c* denotes zero or more occurrences of 'c'
- d* denotes zero or more occurrences of 'd'
Now, let's evaluate the options:
A. The language for the given expression is:
Example: abcd, aabcdd, ....
This is correct. The regular expression generates strings with an equal number of 'a's followed by an equal number of 'b's, and then an equal number of 'c's followed by an equal number of 'd's.
B. The Context Free Language for the given expression is:
Example: abcd, aabcdd, ....
This is correct. The context-free grammar represents the same language as the regular expression.
So, the correct answer is: 
Q100: Which AI System mimics the evolutionary process to generate increasingly better solutions to a process to a problem?
A. Self organizing neural network.
B. Back propagation neural network.
C. Genetic algorithm.
D. Forward propagation neural network.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A Only
(b) B Only
(c) C Only
(d) D Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is C only
- Genetic algorithms mimic the process of natural selection and evolution to generate increasingly better solutions to a problem.
- They involve the use of populations of potential solutions, where individuals (potential solutions) undergo genetic operations such as mutation, crossover, and selection to produce new generations of individuals.
- Over successive generations, the algorithm tends to converge towards better solutions.
Other Related Points
- Self-organizing neural network: This refers to neural networks that can organize themselves based on the input data. They learn to form internal representations without explicit supervision.
- Backpropagation neural network: Backpropagation is a supervised learning algorithm used for training artificial neural networks. It involves calculating the gradient of the error with respect to the weights of the network and adjusting the weights to minimize the error.
- Forward propagation neural network: Forward propagation is the process of passing input data through the neural network to generate an output. In this phase, input signals are processed layer by layer until the final output is produced without adjusting the weights.
FAQs on UGC NET Paper 2: Computer Science 11 March 2023 - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam, and what is its purpose? |  |
| 2. What subjects are covered in the UGC NET Paper 2 for Computer Science? |  |
| 3. How can candidates prepare effectively for UGC NET Paper 2 in Computer Science? |  |
| 4. What is the marking scheme for UGC NET Paper 2? |  |
| 5. Are there any eligibility criteria for appearing in UGC NET Paper 2 for Computer Science? |  |