English Colonies in North America Chapter Notes | Social Studies for Grade 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Jamestown |

|
| Plymouth |

|
| New England Colonies |

|
| Middle Colonies |

|
| Southern Colonies |

|
| Thirteen Colonies |

|
Introduction
Long ago, people from England came to North America to start new homes. They built settlements called colonies. These colonies grew over time and became important places where people lived, worked, and made rules. This chapter tells the story of how these colonies started, how people lived, and what made each group of colonies special. We will learn about Jamestown, Plymouth, and the Thirteen Colonies, including their governments, religions, economies, and challenges.
Jamestown
The Early Years
Jamestown was the first permanent English settlement in North America, started in 1607.
- It was built in Virginia, near a river, by a group called the Virginia Company.
- The settlers wanted to find gold and get rich, but they faced many problems.
- The land was swampy, and there was not enough food or clean water.
- Many settlers got sick or died because of diseases and hunger.
- The settlers fought with the Native Americans who lived nearby, like the Powhatan people.
- John Smith became a leader and made rules to help the settlers work together.
- He told everyone, "If you don’t work, you don’t eat," which helped them survive.
- The early years were very hard, and many settlers did not survive the first winters.
- Help from Native Americans, like trading for food, saved some settlers.
Growth of a Colony
Jamestown started to grow after the early hard years.
- A crop called tobacco became very important because people in England wanted it.
- John Rolfe, a settler, learned to grow tobacco, which made the colony money.
- Farmers planted more tobacco, and the colony became richer.
- More people came to Jamestown to live and work on farms.
- The Virginia Company sent women to Jamestown so settlers could start families.
- In 1619, the House of Burgesses was created, which was a group that made laws.
- This was one of the first times settlers helped make their own rules in America.
- People from Africa were brought to Jamestown in 1619 to work on farms.
- The colony grew, but there were still fights with Native Americans over land.
Plymouth
Plymouth was started in 1620 by a group called the Pilgrims.
- The Pilgrims were people who wanted to practice their religion freely.
- They sailed from England on a ship called the Mayflower.
- They landed in what is now Massachusetts, in a cold and rocky area.
- The first winter was very hard, and many Pilgrims got sick or died.
- Native Americans, like Squanto and the Wampanoag, helped the Pilgrims.
- Squanto taught them how to grow corn, fish, and survive in the new land.
- The Pilgrims signed the Mayflower Compact, a set of rules to work together.
- In 1621, the Pilgrims and Native Americans had a big feast called the First Thanksgiving.
- Plymouth grew slowly but became a strong community based on religion.
New England Colonies
Religion and Government
The New England colonies included Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire.
- Religion was very important in these colonies, especially for the Puritans.
- Puritans wanted to make their church pure and followed strict religious rules.
- They built churches and made laws based on their religious beliefs.
- Only church members could vote or help make laws in some colonies.
- Town meetings were held where people talked about rules and problems.
- Leaders like ministers and governors made important decisions.
- Rhode Island was different because it allowed religious freedom for everyone.
- People who disagreed with Puritan rules, like Roger Williams, started Rhode Island.
- Government and religion worked closely together, but some people wanted more freedom.
Economy and Conflict
The New England colonies had a rocky land, so farming was hard.
- People grew crops like corn and raised animals for food.
- They also fished, built ships, and traded goods with other places.
- The ocean helped them make money by fishing for cod and whales.
- They traded furs, lumber, and fish with England and other colonies.
- Some people worked as blacksmiths, carpenters, or shopkeepers.
- There were conflicts with Native Americans over land and resources.
- Wars, like King Philip’s War in 1675, happened between colonists and Native Americans.
- Many people died in these wars, and some Native American tribes lost their land.
- The economy grew, but conflicts made life hard for both settlers and Native Americans.
Middle Colonies
Founding and Government
The Middle colonies were New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware.
- These colonies were started by different groups, like the Dutch and English.
- New York was first called New Netherland, started by the Dutch, but the English took it over.
- Pennsylvania was started by William Penn, a Quaker, who wanted a place for religious freedom.
- Quakers believed everyone should be treated equally and did not like fighting.
- The Middle colonies had governments that let more people help make laws.
- They had assemblies where people voted for leaders and discussed rules.
- Pennsylvania had a charter that gave people rights, like fair trials.
- The colonies welcomed people from different countries, like Germany and Ireland.
- Their governments were more open to different ideas than other colonies.
Economy and Society
The Middle colonies were called the "breadbasket" because they grew a lot of wheat.
- Farmers grew crops like wheat, barley, and oats to feed people.
- They also raised animals like cows and pigs for food.
- Cities like Philadelphia and New York grew as places for trade.
- People worked as merchants, traders, and craftsmen, like making furniture.
- The Middle colonies had people from many countries, so they had different cultures.
- They had schools, churches, and markets where people came together.
- Some people owned small farms, while others worked in busy cities.
- Slavery existed, but it was not as common as in the Southern colonies.
- The economy was strong because of farming, trade, and different kinds of work.
Southern Colonies
Founding and Government
The Southern colonies were Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.
- Virginia was the first, started with Jamestown in 1607.
- Maryland was started by Lord Baltimore for Catholics to have religious freedom.
- The Carolinas were split into North and South Carolina over time.
- Georgia was started by James Oglethorpe to help poor people and protect against enemies.
- Governments were run by wealthy landowners who made laws.
- They had assemblies, but only people who owned land could vote.
- Governors were chosen by the English king or colony owners.
- The Southern colonies had fewer towns, so people lived far apart on farms.
- Laws often protected the interests of rich farmers who owned large lands.
Economy and Slavery
The Southern colonies had warm weather and good soil for farming.
- They grew crops like tobacco, rice, and indigo to sell to England.
- Plantations were large farms where these crops were grown.
- Plantations needed a lot of workers, so they used enslaved people from Africa.
- Enslaved people were forced to work hard and had no freedom.
- Slavery became a big part of the Southern economy, especially in South Carolina and Georgia.
- Some people also worked as small farmers, but plantations made the most money.
- Trade with England and other colonies helped the Southern colonies grow rich.
- Enslaved people lived in hard conditions and were treated unfairly.
- The economy depended on farming and slavery, which caused many problems.
Thirteen Colonies
Identify the Thirteen Colonies
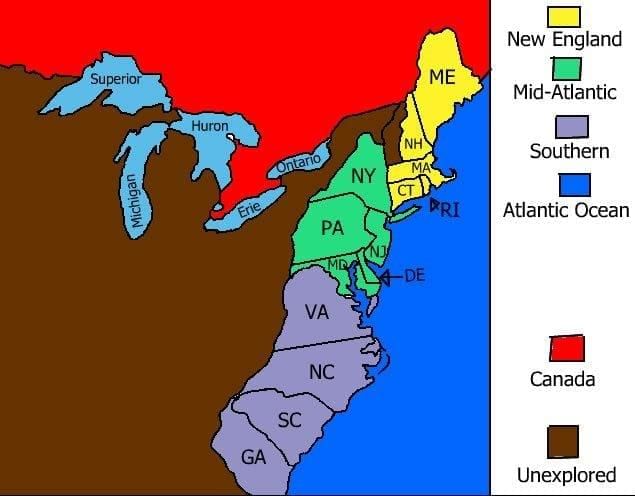
The Thirteen Colonies were the English settlements that became the United States.
- They were divided into three groups: New England, Middle, and Southern colonies.
- New England colonies: Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire.
- Middle colonies: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware.
- Southern colonies: Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia.
- Each colony had its own government, economy, and way of life.
- People in the colonies came from England and other countries for different reasons.
- Some came for religious freedom, others for land or money.
- The colonies worked together over time to fight for freedom from England.
- Knowing the Thirteen Colonies helps us understand how the United States began.
Name the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were: Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.
- These colonies were along the eastern coast of North America.
- Each colony was started at different times by different people.
- Some were started for religious reasons, like Massachusetts and Maryland.
- Others were started for farming or trade, like Virginia and New York.
- People in the colonies built homes, farms, and towns.
- They traded with each other and with England for goods.
- Naming the Thirteen Colonies helps us remember the places that became the United States.
- All 13 colonies worked together later to form one country.
FAQs on English Colonies in North America Chapter Notes - Social Studies for Grade 4
| 1. What was the significance of Jamestown in the early years of English colonization? |  |
| 2. How did the economy of the New England Colonies develop, and what role did religion play in it? |  |
| 3. What were the main factors that contributed to the founding of the Middle Colonies? |  |
| 4. How did slavery shape the economy of the Southern Colonies? |  |
| 5. What were some of the conflicts that arose in the New England Colonies, and what were their causes? |  |














