NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Gynaecology and Obstetrics > Mind Map: Endocrine Physiology
Mind Map: Endocrine Physiology | Gynaecology and Obstetrics - NEET PG PDF Download
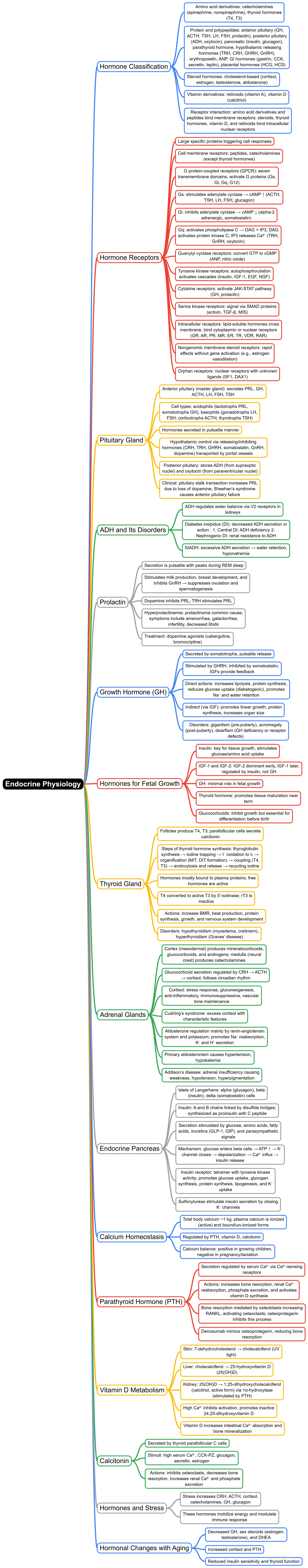
The document Mind Map: Endocrine Physiology | Gynaecology and Obstetrics - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Gynaecology and Obstetrics.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
76 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Endocrine Physiology - Gynaecology and Obstetrics - NEET PG
| 1. What are the main hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland and their functions? |  |
Ans.The anterior pituitary gland produces several key hormones, including Growth Hormone (GH), which stimulates growth and cell reproduction; Prolactin (PRL), which promotes milk production in lactating women; Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which regulates the thyroid gland; Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH), which stimulates cortisol production from the adrenal cortex; and Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), which are critical for reproductive function.
| 2. How do feedback mechanisms regulate hormone secretion in the endocrine system? |  |
Ans.Feedback mechanisms are crucial for maintaining homeostasis in the body. There are two primary types: negative and positive feedback. Negative feedback occurs when the output of a process inhibits its own production; for example, high levels of cortisol inhibit ACTH secretion. Positive feedback amplifies a response; an example is oxytocin during childbirth, where its release leads to increased contractions, prompting more oxytocin release until delivery.
| 3. What is the role of insulin and glucagon in glucose metabolism? |  |
Ans.Insulin and glucagon are hormones produced by the pancreas that play opposing roles in glucose metabolism. Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells and promoting its storage as glycogen in the liver and muscle. In contrast, glucagon raises blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogenolysis (the breakdown of glycogen) and gluconeogenesis (the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources) in the liver when blood sugar levels drop.
| 4. What are the effects of thyroid hormones on metabolism? |  |
Ans.Thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T₄) and triiodothyronine (T₃), have a profound impact on metabolism. They increase the basal metabolic rate, enhance protein synthesis, promote the breakdown of fats, and stimulate carbohydrate metabolism. These hormones are essential for normal growth and development, particularly in the nervous system and skeletal system.
| 5. How does the adrenal gland respond to stress, and what hormones are involved? |  |
Ans.The adrenal gland responds to stress through the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. In response to stress, the hypothalamus secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release ACTH. ACTH then acts on the adrenal cortex to produce glucocorticoids, primarily cortisol, which helps to mobilize energy stores and suppress non-essential functions during stressful situations. Additionally, the adrenal medulla releases catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that prepare the body for a "fight or flight" response.
Related Searches















