Mapping the World | Geography for Year 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a globe? |

|
| Maps and atlases |

|
| Map projections |

|
| Mercator map projection |

|
What is a globe?
From space, Earth appears as a spherical object, with approximately two-thirds of its surface covered by water and the remaining portion by land. A globe is a three-dimensional model that represents how Earth looks from space. Some globes illustrate the division of land into roughly 200 countries.
These countries are spread across seven continents:
- Europe
- Africa
- North America
- South America
- Asia
- Oceania
- Antarctica
Antarctica is unique, as it has no countries and is governed by the 1959 Antarctic Treaty, signed by 12 nations, including the United Kingdom.
Maps and atlases
Maps are essential for navigation and locating places and features. Collections of maps, often organized by country, are compiled into books called atlases. Modern technology, such as computers and tablets, displays maps and aerial photographs taken by satellites. These images are stitched together to create highly detailed views, sometimes allowing users to zoom in for a bird’s-eye perspective of specific locations, like their homes.
Historically, maps were drawn by hand using precise measurements of the terrain. Because Earth is a curved, three-dimensional object, representing it on a flat, two-dimensional map poses challenges. To address this, map-makers use different techniques called projections.
Map projections
A map projection is a method used by cartographers to depict the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane. Various projections exist, each with trade-offs:
Mercator map projection
A map projection is a method used by cartographers to represent the Earth's curved surface, or a portion of it, on a flat plane.
Cartographers have tried various projections:
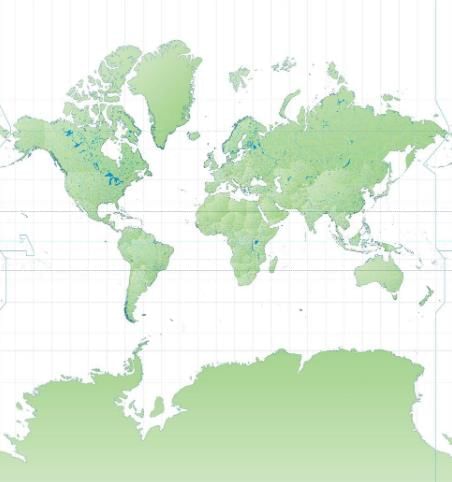
Mercator map projection
The Mercator map projection, commonly used for navigation, distorts the size of landmasses. For instance, compared to a globe, Greenland appears significantly larger, while Africa appears much smaller.
FAQs on Mapping the World - Geography for Year 6
| 1. What is a globe and how does it differ from a map? |  |
| 2. What are maps and atlases, and how are they used? |  |
| 3. What are map projections, and why are they important? |  |
| 4. What is the Mercator map projection, and what are its advantages and disadvantages? |  |
| 5. How can understanding map projections influence our perception of the world? |  |














