Past Year Questions: Bills of Exchange and Promissory Notes | Accounting for CA Foundation PDF Download
Q 1. State with reasons, whether the following statements are True or False: (2 Marks)
(i) A Promissory Note can be made payable to the Bearer. (Sep 2024)
Answer: False. A promissory note should not be made payable to the bearer. The payee must be to a certain person.
(ii) Promissory Note is different from Bill of Exchange because the amount is paid by the maker in case of former and by the acceptor in the later. (Jun 2024)
Answer: True. In case of the promissory note, it is generally the maker who makes the payment, but in case of the bill of exchange, the person accepting the bill shall be liable to make the payment to the holder of the bill.
Q 2. For mutual accommodation of himself and Gagan, Aman drew upon Gagan a bill of ₹ 7,500 at 3 months on 01.04.2024. Gagan accepted the bill and returned to Aman who discounted it immediately @ 8% p.a. According to agreement, Aman and Gagan shared the proceeds as 2:1. On the date of Maturity Aman remitted his share to Gagan who honoured the bill by payment.
Show journal entries in the books of Aman and Gagan. (5 Marks, May 2025)
Answer:
In the books of Aman
Journal Entries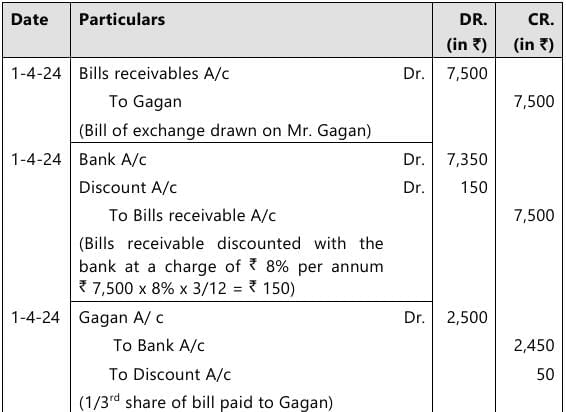

In the books of Gagan
Journal Entries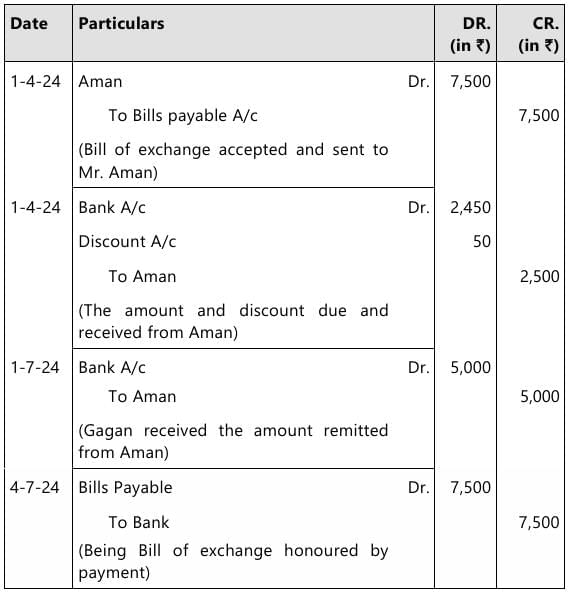
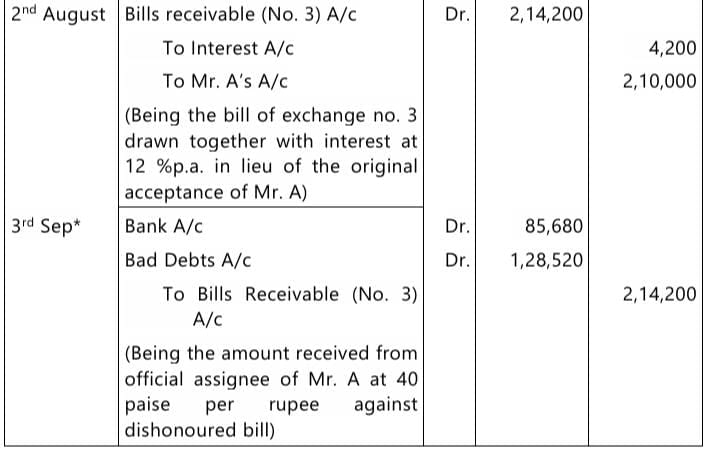
Q 3. Mr. A accepts two bills of exchange on June 1, 2024 for ₹ 1,50,000 and ₹ 60,000 drawn on him by Mr. B. The bill of exchange for ₹ 1,50,000 is for two months while the bill of exchange for ₹ 60,000 is for three months. Mr. B got the first bill discounted with the bank for ₹ 1,49,000 on June 3, 2024. On August 2, 2024, Mr. A requested Mr. B to cancel both the bills and drew a new bill on him with the combined amount of both the bills along with interest @ 12% per annum for a period of two months. Before the due date of the renewed bill on September 3, 2024, Mr. A becomes insolvent and only 40 paise in a rupee could be recovered from his estate.
You are required to give the journal entries in the books of Mr. B. (5 Marks,Jan 2025)
Answer:
Journal Entries in the books of Mr. B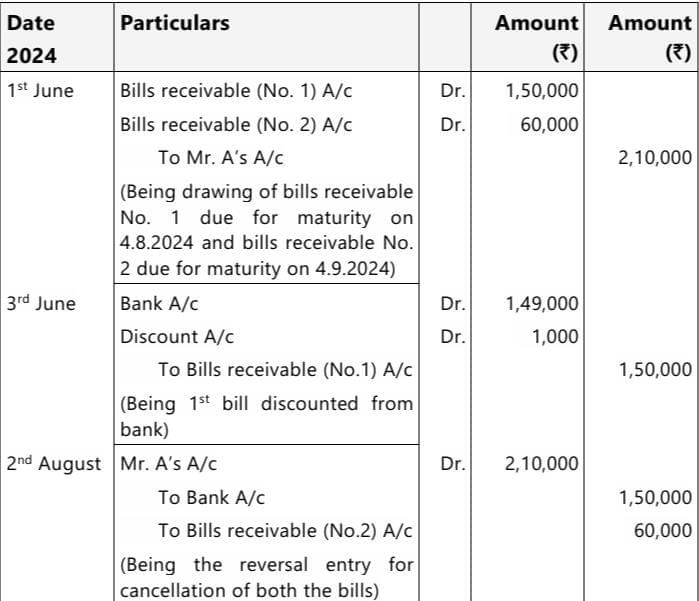
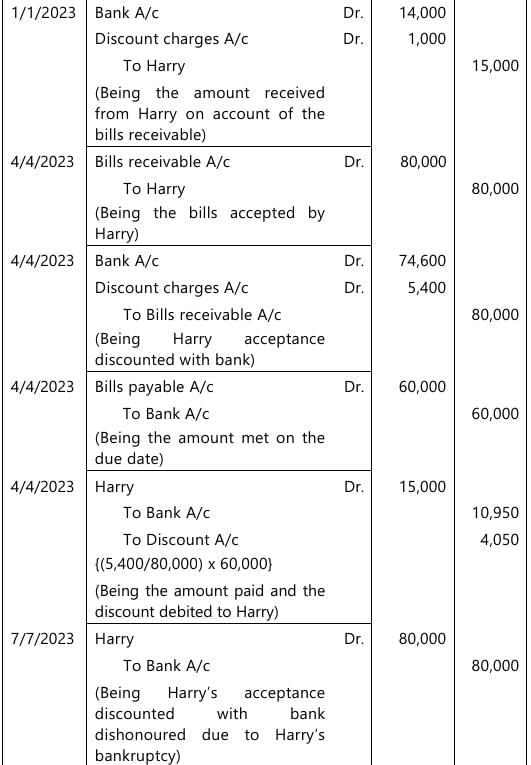
Q 4. Harry draws a bill on Sejal for ₹ 60,000 on 01.01.2023 for 3 months. Sejal accepts the bill and sends it back to Harry to get it discounted for ₹ 56,000. Harry remits 1/4th amount to Sejal. On the due date, Harry was unable to remit his share to Sejal, rather accepts a bill of ₹ 80,000 for 3 months. This bill was discounted by Sejal for ₹ 74,600. Sejal after making the payment of first bill sent 3/4th of the amount remaining to Harry. On maturity of the bill, Harry became bankrupt and his estate paying 40 paise in the rupee.
Give journal entries in the books of Sejal. Also, prepare the ledger account of Harry. All workings should form part of the answer. (10 Marks, 13 Sep 2024)
Answer:
In the books of Sejal
Journal Entries 

Harry's A/c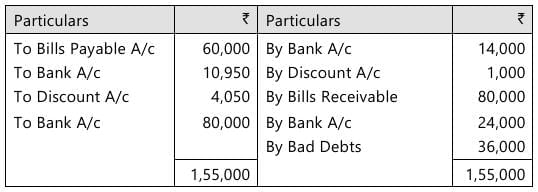
|
68 videos|265 docs|83 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Bills of Exchange and Promissory Notes - Accounting for CA Foundation
| 1. What is a bill of exchange and how does it function in financial transactions? |  |
| 2. What are the key differences between a bill of exchange and a promissory note? |  |
| 3. What legal requirements must be met for a bill of exchange to be considered valid? |  |
| 4. How can a promissory note be enforced if the maker fails to pay? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of using bills of exchange and promissory notes in business transactions? |  |
















