Forms of Social Stratification | Sociology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Social Stratification & Inequality
Social stratification refers to the hierarchical organization of society into distinct layers or strata, where each layer holds varying degrees of power and privilege.
A social hierarchy resembles a pyramid, with each level possessing greater authority than the one beneath it. The most advantaged group occupies the top, while the least advantaged resides at the bottom.
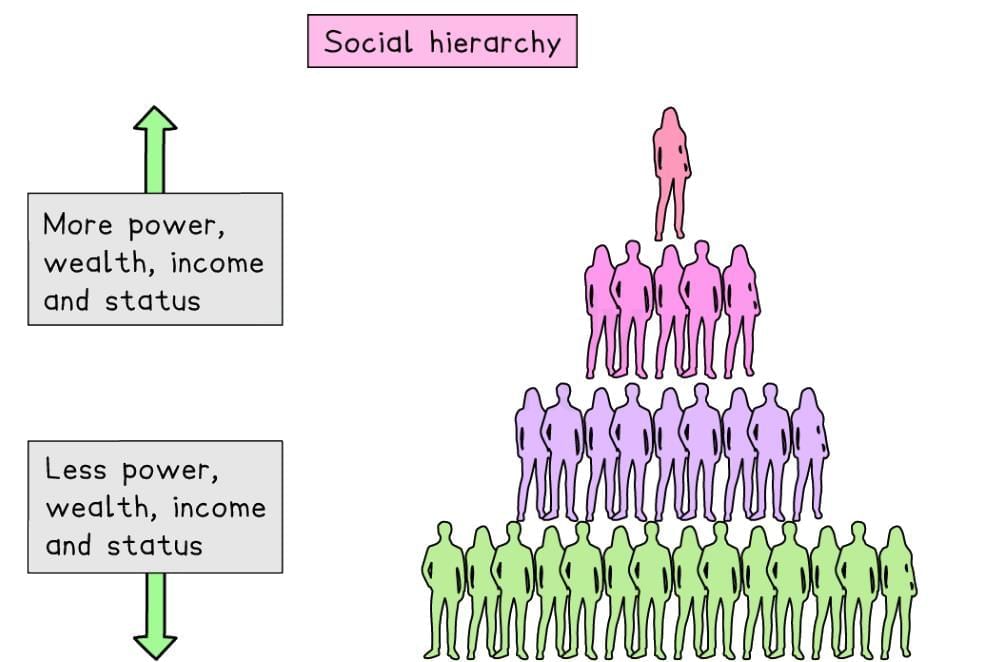 Social stratification hierarchy
Social stratification hierarchy
Social inequality involves the unequal allocation of:
- Resources, such as wealth and influence.
- Opportunities (or life chances), including access to education or jobs.
Studies of inequality examine:
- The scope and nature of inequality.
- Reasons why certain individuals or groups receive more resources and opportunities.
- How disparities in resources and opportunities manifest across individuals and groups based on social class, gender, ethnicity, and age.
Stratification entails disparities in the distribution of resources like wealth, income, status, and power among groups. The top tier enjoys significantly greater wealth, income, status, or power compared to the bottom tier.
Key Concepts
- Wealth: Ownership of assets, such as real estate, land, stocks, or savings.
- Income: Monetary earnings, such as wages or benefits like access to a company vehicle.
- Status: An individual’s social rank or standing in society, influenced by wealth, occupation, or social influence.
- Power: The capacity of an individual or group to achieve their objectives despite resistance, such as influencing legislation.
In contemporary UK society, social class, determined by economic factors like occupation and income, is the primary form of stratification.
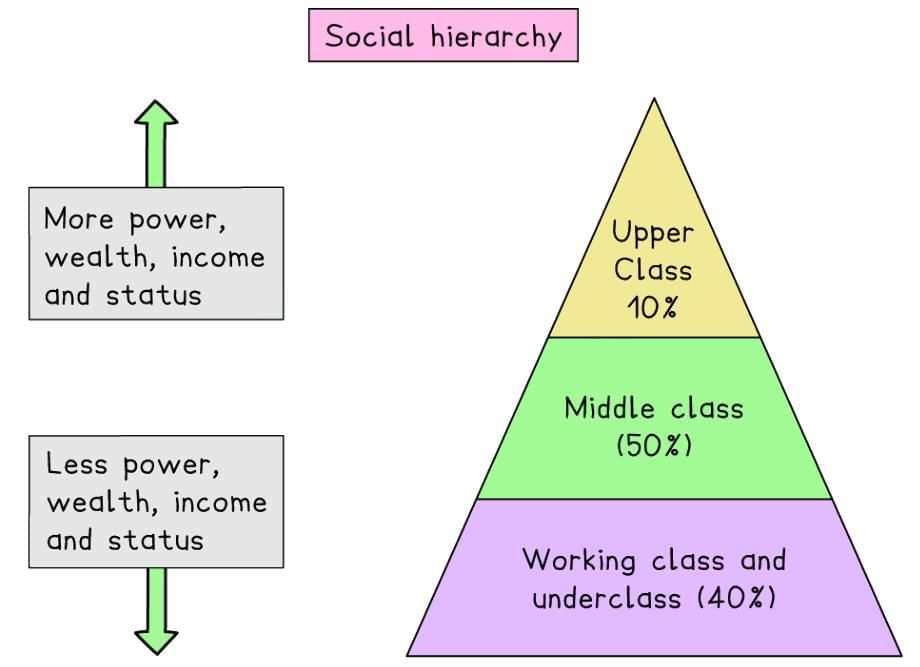 Social class as a stratification system
Social class as a stratification system
Types of Social Stratification
Stratification systems vary based on whether a person’s status is ascribed or achieved:
- Ascribed status: A fixed social position assigned at birth, unchangeable over time, e.g., being born into royalty.
- Achieved status: A social position earned through personal effort or merit, e.g., achieving top grades in GCSEs through ability and hard work.
Stratification systems also differ in terms of openness, i.e., the potential for social mobility:
- Open system: Status is achieved, allowing social mobility, such as movement between social classes.
- Closed system: Status is ascribed, restricting social mobility, as seen in systems like the Indian caste system.
Slavery
- Slavery was a race-based stratification system in Ancient Greece, Rome, and the 19th-century southern United States.
- White slave owners claimed ownership over Black slaves, treating them as property (chattel).
- Social status was ascribed at birth, with children of slaves automatically inheriting slave status, making the system closed.
- Racial stratification persisted in the U.S. through segregation laws, which were repealed in 1964 following the Civil Rights Movement.
Feudalism
- The feudal system in medieval Europe was a stratified social structure divided into four estates.
- Loyalty was pledged to the king, whose authority was considered divinely ordained.
- Social positions were ascribed, offering little to no opportunity for mobility between estates, rendering the system closed.
- Marriage across estates or social classes was generally inconceivable.
The Caste System in Traditional India
- The caste system in India, tied to Hindu religious beliefs, is another example of stratification. Individuals are born into a specific caste, determining their social position in a closed system.
- Each caste was historically linked to specific occupations, and inequalities between groups were justified by religious doctrines.
Apartheid
- Apartheid in South Africa (1948–1994) enforced racial segregation as a government policy, using ethnicity as the basis for stratification.
- Social positions were ascribed at birth, creating a closed system with minimal social mobility.
- Racial segregation permeated all aspects of life, restricting access to employment, housing, healthcare, and education based on race.
|
172 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Forms of Social Stratification - Sociology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is social stratification and why is it important to understand? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of social stratification? |  |
| 3. How can social stratification lead to inequality? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of social stratification in modern societies? |  |
| 5. How does social mobility relate to social stratification? |  |




















