CA Foundation Exam > CA Foundation Notes > Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation > Cheat Sheet: Equations
Cheat Sheet: Equations | Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Definition |

|
| Types of Equations |

|
| Methods to Solve Simultaneous Equations |

|
| Quadratic Equations |

|
| Sum and Product of Roots |

|
| Cubic Equations |

|
Definition
An equation is a mathematical statement that shows equality between two expressions, denoted by the '=' sign.
Conditional equation: True for specific values (e.g., x + 2 = 5 holds for x = 3)
Identity: True for all values of the variable (e.g., (x+1)^2 = x^2 + 2x + 1)
Types of Equations
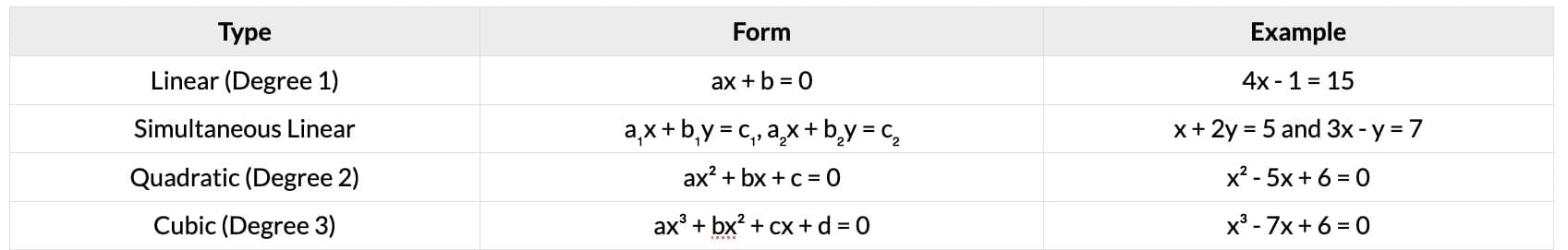
Question for Cheat Sheet: EquationsTry yourself: What type of equation is represented by ax² + bx + c = 0?View Solution
Methods to Solve Simultaneous Equations
1. Elimination Method
Example: Solve 2x + 5y = 9 and 3x - y = 5.
Multiply equations and eliminate one variable:
x = 2, y = 1
Multiply equations and eliminate one variable:
x = 2, y = 1
2. Cross Multiplication Method
For equations:
a₁x + b₁y + c₁ = 0
a₂x + b₂y + c₂ = 0
Use:
x / (b₁c₂ – b₂c₁) = y / (c₁a₂ – c₂a₁) = 1 / (a₁b₂ – a₂b₁)
Quadratic Equations
Standard Form: ax² + bx + c = 0
Roots: x = [-b ± √(b² – 4ac)] / 2a
Discriminant (D): b² – 4ac
- D = 0: Real and equal roots
- D > 0 (perfect square): Real, rational, and unequal
- D > 0 (not a perfect square): Real, irrational, and unequal
- D < 0: Imaginary roots
Sum and Product of Roots
If α and β are roots of ax² + bx + c = 0:
- Sum = –b/a
- Product = c/a
Cubic Equations
Use the factor theorem or trial & error to find one root, then reduce to a quadratic.
Example: Solve x³ – 7x + 6 = 0
Try x = 1 → LHS = 0 ⇒ (x – 1) is a factor.
Factor: (x – 1)(x – 2)(x + 3)
Roots: x = 1, 2, –3
Try x = 1 → LHS = 0 ⇒ (x – 1) is a factor.
Factor: (x – 1)(x – 2)(x + 3)
Roots: x = 1, 2, –3
The document Cheat Sheet: Equations | Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation is a part of the CA Foundation Course Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation.
All you need of CA Foundation at this link: CA Foundation
|
101 videos|209 docs|89 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Equations - Quantitative Aptitude for CA Foundation
| 1. What are the different types of equations commonly encountered in mathematics? |  |
Ans. The main types of equations include linear equations, quadratic equations, cubic equations, and higher-degree polynomial equations. Linear equations have the form ax + b = 0, quadratic equations are expressed as ax² + bx + c = 0, and cubic equations take the form ax³ + bx² + cx + d = 0. Additionally, there are also systems of equations, which consist of multiple equations that can be linear or nonlinear.
| 2. What methods can be used to solve simultaneous equations? |  |
Ans. Simultaneous equations can be solved using various methods, including substitution, elimination, and matrix methods. The substitution method involves solving one equation for a variable and substituting it into another equation. The elimination method involves adding or subtracting equations to eliminate a variable. The matrix method employs matrices and determinants to find solutions, particularly useful for larger systems of equations.
| 3. How do you find the sum and product of the roots of a quadratic equation? |  |
Ans. For a quadratic equation in the form ax² + bx + c = 0, the sum of the roots (α + β) is given by -b/a, and the product of the roots (αβ) is given by c/a. This relationship is derived from Vieta's formulas, which relate the coefficients of the polynomial to sums and products of its roots.
| 4. What are the characteristics of cubic equations, and how are they solved? |  |
Ans. Cubic equations have the general form ax³ + bx² + cx + d = 0. They can have one real root and two complex conjugate roots or three real roots. Solving cubic equations can be more complex than quadratic ones and can be approached using methods such as factoring, synthetic division, or applying Cardano's formula, which provides a systematic way to find roots.
Related Searches




















