HOTS Questions: Forces and laws of Motion | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Q1: Match the following with the correct response.

(a) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
(b) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
(c) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
(d) 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
Ans: (a)
1) A cart is pulled by the horse as the horse applies a force on earth and earth applies a equal and opposite force. this is stated in Newton third law of motion.
2) We get a backwards jerk due to inertia as the car speeds up, and our body tends to move backwards and resist the change.
3) Sole of the shoe wears out due to friction.
4) The spring in the gun transfers the momentum to the bulletand according to law of conservation of momentum the gun recoils.
Q2: Dust particles come out of a hanging carpet when we strike it with a stick because-
A. Carpet starts moving forward and backwards due to the inertia of motion
B. Dust particles remain at rest
C. Dust particles start moving forward due to the inertia of motion
D. Carpet remains at rest
(a) A, B, and C are correct
(b) A and B are correct
(c) B and C are correct
(d) All of these
Ans: (b)
This is because when we hit a carpet the carpet starts moving forward and its inertia of rest changes into the inertia of motion but the dust particles which are there with the carpet they move just because of the carpet but actually the particles remain at rest that is why these particles fall of due to the change of inertia.
Q3: Find the incorrect statement about Newton’s law of action and reaction.
Action and reaction
(a) Action and reaction are equal in magnitude
(b) Action and reaction act on the same bodies
(c) Action and reaction act simultaneously
(d) Action and reaction are different in direction
Ans: (b)
Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that the forces are equal in magnitude (a), act simultaneously (c), and are opposite in direction (d). However, they act on different bodies, not the same one.
Q4: If an object experiences a net zero unbalanced force, then the body
(a) moves with constant velocity
(b) cannot remain at rest
(c) can be accelerated
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
If an object experience a net zero unbalanced force, than the body moves with constant velocity. Zero unbalanced force due to produce acceleration in the body.
Q5: Match the following with the correct response.
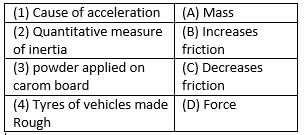
(a) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
(b) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
(c) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
(d) 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
Ans: (d)
D is the correct option.Force is the cause of acceleration. Mass Is the quantitative measure Of inertia. We apply powder on the carrom board to decrease friction. Tyres of vehicles made rough to increase friction.
Q6: A force of 7 kg-wt acts on a body of mass 10 kg. Calculate the acceleration produced.
(a) 7 ms−2
(b) 8 ms−2
(c) 10 ms−2
(d) 6 ms−2
Ans: (a)
1 kg-wt = 9.8 N
7 kg-wt = 7 × 9.8 = 68.6 NForce = Mass x Acceleration
68.6 = 10 x Acceleration
a = 6.86 ≈ 7 m s-2
Q7: Which is the incorrect statement about action and reaction referred to Newton’s third law of motion?
A. They are equal
B. They are opposite
C. They act on the same object
D. They act simultaneously
(a) A and C are correct
(b) B and C are correct
(c) A, B, and C are correct
(d) option c
Ans: (d)
Newton’s Third Law of Motion states:
"For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction."Now, evaluate each statement:
A. They are equal – This is true. Action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude.
B. They are opposite – This is true. They act in opposite directions.
C. They act on the same object – This is false. Action and reaction forces always act on different objects.
D. They act simultaneously – This is true. Action and reaction occur at the same instant.
Q8: Statement A: A passenger falls forward when a bus suddenly starts moving in the forward direction.
Statement B: A gun recoils backwards with a smaller speed than the bullet moving forward.
(a) Statement B is true
(b) Statement A is true
(c) Both statements A and B are true
(d) Neither Statement A nor Statement B is true
Ans: (a)
A passenger falls backward when a bus suddenly start moving in the forward direction due inertia of rest. A gun recoils backward with small speed than the bullet moving forward due to law of conservation of momentum.
Q9: When a force is exerted on an object, it can change its-
A. State
B. Position
C. Shape
D. Direction
(a) A, B, and C are correct
(b) B and C are correct
(c) A and B are correct
(d) All of these
Ans: (d)
D is the correct option.A force acting on an object causes the object to change its shape or size, to start moving, to stop moving, to accelerate or decelerate. When there's the interaction between two objects they exert a force on each other, these exerted forces are equal in size but opposite in direction.
Q10: The physical quantity which is equal to the rate of change of momentum is
(a) force
(b) energy
(c) power
(d) impulse
Ans: (a)
Force is the equal to the rate of change of momentum. Force = final momentum-initial momentum/time , f = mv-mu/t.
Q11: Which of the following is not used to reduce friction?
(a) using oil between contact surfaces
(b) using a ball bearing
(c) making scratches on the contact surfaces
(d) using grease between contact surfaces
Ans: (c)
To reduce the friction, oiling between contact surface, using ball bearing and using grease between contact surfaces. Making scratches between contact surfaces increase the friction.
Q12: Match the following with the correct response.
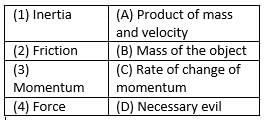
(a) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
(b) 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
(c) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
(d) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
Ans: (d)
Inertia → (B) Mass of the object
Explanation: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion, which depends on its mass.Friction → (D) Necessary evil
Explanation: Friction opposes motion but is necessary for everyday activities like walking and driving.
Momentum → (A) Product of mass and velocity
Explanation: Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity (p=mvp = mvp=mv).
Force → (C) Rate of change of momentum
Explanation: According to Newton's Second Law, force is the rate of change of momentum.
Q13: Which of the following physical quantities is associated with Newton’s second law of motion?
(a) velocity
(b) time
(c) mass
(d) all of these
Ans: (d)
Newton’s second law of motion states that rate of change in momentum is equal to force applied. Momentum is the product of mass and velocity. So, mass, velocity and time all are associated with Newton’s second law of motion.
Q14: What is the momentum of an object of mass 1/2 m, moving with a velocity 2v?
(a) mv
(b) mv2
(c) 1/2 mv2
(d) (mv)2
Ans: (a)
Momentum of a body is equal to product of mass and velocity. Momentum
Q15: Match the following with the correct response.

(a) 1-B, 2-A, 3-C, 4-D
(b) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
(c) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
(d) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
Ans: (a)
- Newton’s first law of motion → (B): It states that an object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
- Newton’s second law of motion → (A): It states that force is directly proportional to the product of mass and acceleration (F=maF = maF=ma).
- Newton’s third law of motion → (C): It states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
- Galileo’s law of inertia → (D): It states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless an external force acts on it.
Q16: An Object moving along a straight path with an accelerated motion. The correct statement about the object-
A. Its velocity keeps changing
B. Its speed keeps changing
C. A force is always acting on it
D. Its mass keeps on changing
(a) A and B are correct
(b) B and C are correct
(c) A, B and C are correct
(d) All of these
Ans: (c)
The correct option is Option C.
This is because when acceleration increases so will speed and velocity. As acceleration is a type of accelerated force a force will always act on the body.
Q17: State whether the following statement is true or false “force can be measured using first law of motion”
(a) true
(b) false
(c) partially true
(d) partially false
Ans: (b)
The force can be measured by newton’s second law of motion. First law of motion states that object in rest or uniform motion tends to remain in its state.
Q18: “Internal forces are forces which bodies exert on each other when the bodies are part of the system” is
(a) false
(b) true
(c) partially true
(d) partially false
Ans: (b)
Internal forces are those forces which exert on each other when the bodies are part of the system. The forces acting between the atoms of molecules that keep them together are example of internal force.
Q19: Match the following with the correct response.
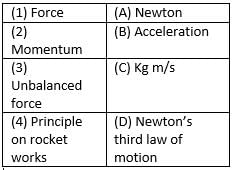
(a) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
(b) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
(c) 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
(d) 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
Ans: (b)
Force → (A) Newton
Explanation: The SI unit of force is Newton (N), named after Sir Isaac Newton.
Momentum → (C) kg m/s
Explanation: Momentum is the product of mass and velocity, and its unit is kg·m/s.
Unbalanced force → (B) Acceleration
Explanation: An unbalanced force causes a change in motion, resulting in acceleration according to Newton’s Second Law.
Principle on which rocket works → (D) Newton’s third law of motion
Explanation: Rockets work based on Newton’s Third Law, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Q20: The passenger feels a jerk forward when a bus moving at a high speed suddenly stops. This happens due to
(a) gravitational pull of the Earth
(b) Inertia of the bus
(c) Inertia of the passenger
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
When a moving bus at high speed suddenly stops, the passenger feels a jerk in the forward direction due to the inertia of motion, which tends to keep the moving body in motion.
Q21: A body moves with a constant speed of 5m/s. This shows that no unbalanced forces are acting on the body is a
(a) false statement
(b) partially true
(c) true statement
(d) partially false
Ans: (c)
If no unbalanced force acts on the body, the speed of the body remains constant. So, a body moving with a constant speed of 5m/s does not have any unbalanced force acting on it.
Q22: The Weight of a body due to the Earth acts
(a) vertically downwards
(b) horizontal
(c) in any direction
(d) vertically upwards
Ans: (a)
The weight of the body is the measure of force by which an object is attracted towards the centre of the Earth. It always acts vertically downwards.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on HOTS Questions: Forces and laws of Motion - Science Class 9
| 1. What are the basic laws of motion formulated by Newton? |  |
| 2. How does friction affect motion according to the laws of motion? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of mass in Newton's second law of motion? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of inertia and its relation to Newton's first law? |  |
| 5. What is the role of action and reaction forces in everyday life? |  |
















