The Relationship Between Age & Crime | Sociology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Official Statistics on Age & Crime
There is a clear connection between age and criminal behavior, with younger individuals, particularly males, being more prone to offending than older individuals. Young offenders typically commit less serious crimes, such as theft and handling stolen goods.
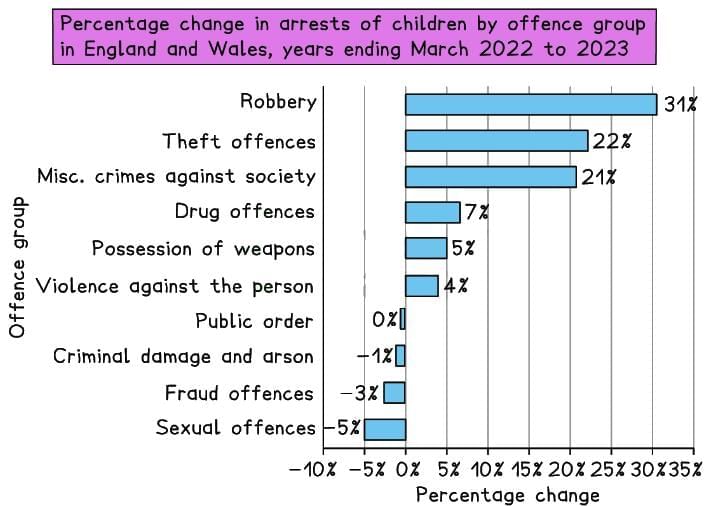 Arrests of children by offence ( Youth Justice Board for England and Wales, 2024)
Arrests of children by offence ( Youth Justice Board for England and Wales, 2024)
According to the Youth Justice Board (2024), from April 2022 to March 2023:
- Stop and searches of children aged 10–17 rose by 13%, making up over one-fifth of all stop and searches.
- Arrests of children increased by 9% compared to the previous year.
- Police cautions for children aged 10–14 increased by 6%, while those for 15–17-year-olds decreased by 7%.
- Young people are more likely to reoffend compared to adults, as reported by the Ministry of Justice (2022).
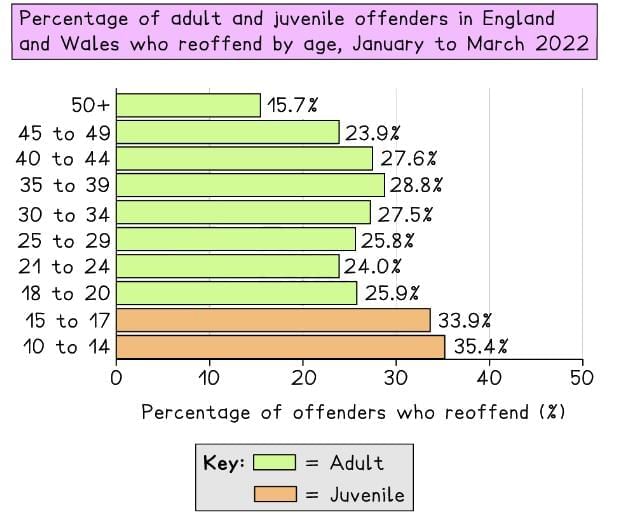 Adult and juvenile reoffenders (Ministry of Justice, 2022)
Adult and juvenile reoffenders (Ministry of Justice, 2022)
Explanations for the Link Between Age & Crime
Excitement
Young people are more inclined to engage in criminal and deviant behavior in pursuit of excitement. Breaking rules is appealing, providing an adrenaline rush and a sense of thrill.
Inadequate Socialization
Functionalist theories suggest that children who are not properly socialized into society’s norms and values are more likely to engage in crime from a young age. Ineffective primary socialization, often due to poor parenting, contributes to this issue:
- Parents may fail to take responsibility for their children’s upbringing.
- Lack of parental supervision increases the likelihood of criminal behavior.
- Fatherless families may leave children without strong male role models.
Other socialization agents, such as schools, religion, and the media, also fail to instill societal norms:
- Schools may lack effective discipline.
- The influence of religious values is waning.
- The media, including films and music, often glamorizes gun crime and violence.
This results in a breakdown of social control at home and school, leading some young people to criminal behavior. The New Right perspective, supported by Murray (1998), argues that inadequate socialization within the underclass, particularly in families without fathers, leads to criminality as young people seek role models in inappropriate places.
Key Thinker: Cohen’s (1955) Subcultural Theory
Functionalist Albert Cohen (1955) studied juvenile delinquency among working-class boys in North America and found that:
- Juvenile delinquency is primarily a group phenomenon rather than an individual one.
- Young males learn delinquent behavior by joining groups or gangs where such behavior is already established.
- In urban neighborhoods of large cities, being part of a delinquent subculture is a way of life.
- Common delinquent acts include stealing, vandalism, violence, and truancy.
Explanations for Juvenile Delinquency
Cohen argues that working-class boys share the same success goals as wider society but face barriers due to:
- Educational failure and limited job prospects caused by cultural deprivation.
- Schools, as middle-class institutions, disadvantage working-class boys through their values and expectations.
This leads to status frustration, where boys, feeling marginalized by their lack of opportunity and low social status, turn to criminality as an alternative path to success. By joining a criminal subculture, they gain status and acceptance among peers in similar social positions. Delinquent acts also serve as a way to rebel against a school system that labels them as failures.
Criticisms of Cohen’s Theory
- Cohen’s work is criticized for its middle-class bias, assuming working-class delinquents initially adopt middle-class values like educational success.
- Some argue that delinquent behavior stems from resentment toward teachers and successful middle-class students.
- Critics contend that delinquents may never have shared society’s norms, as their primary socialization fosters deviant or criminal values that are hard to break, especially with a criminal record.
- Feminists criticize Cohen for focusing solely on boys, limiting the applicability of his theory to the broader population.
- Interactionists argue that many people commit crimes, but only some, particularly young people, are caught and labeled as criminals.
|
131 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on The Relationship Between Age & Crime - Sociology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the main statistics that show the relationship between age and crime rates? |  |
| 2. What explanations exist for the link between age and crime? |  |
| 3. How does Cohen's Subcultural Theory explain youth crime? |  |
| 4. Are there any notable historical trends regarding age and crime? |  |
| 5. How do age-related crime patterns impact policy and prevention strategies? |  |















