Health: The Ultimate Treasure NCERT Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Probe and Ponder
Q1: How does your body respond to an infection such as common cold?
Ans: The body responds to a common cold (caused by viruses) through the immune system. Symptoms like a runny nose, sore throat, or cough occur as the body fights the infection. The immune system produces antibodies to neutralize the virus, and white blood cells attack infected cells. Rest, hydration, and sometimes medication (e.g., for fever) help recovery.
Q2: We rarely see cases of smallpox or polio these days, but diseases like diabetes and heart problems are more common. Why?
Ans: Smallpox and polio have been nearly eradicated due to widespread vaccination programs (e.g., Edward Jenner’s smallpox vaccine, polio vaccines). In contrast, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes and heart problems are increasing due to modern lifestyle factors such as unhealthy diets (e.g., processed and junk foods like pizza, burgers, etc.), lack of exercise, stress, and longer life expectancies.
Q3: Could climate change lead to new types of diseases?
Ans: Yes, climate change can lead to new or increased disease risks. Warmer temperatures and changing weather patterns can expand the range of disease-carrying vectors like mosquitoes (e.g., malaria, dengue), alter water quality, and create conditions for new pathogens to emerge or spread more easily.
Q4: How do emotions like stress or worry affect us and make us sick?
Ans: Stress or worry can weaken the immune system by releasing hormones like cortisol, making the body more susceptible to infections (e.g., colds). Chronic stress can also contribute to non-communicable diseases like high blood pressure or diabetes by affecting sleep, diet, and mental health.
Q5: Why do some groups of people get affected more than others during disease outbreaks?
Ans: Some groups are more affected due to factors like weaker immunity (e.g., children, elderly), poor living conditions (e.g., lack of sanitation), malnutrition, or preexisting health issues. Social factors, such as crowded living spaces or limited healthcare access, also increase vulnerability.
Q6: Share your questions
1. What habits do you think are important for staying healthy every day?
Ans: The following habits are important for daily good health:
- Eating a balanced and nutritious diet (with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains)
- Maintaining personal hygiene (bathing, brushing teeth, washing hands regularly)
- Exercising or being active every day and drinking clean water
- Getting enough sleep every night
- Spending time with family and friends for a healthy mind
- Limiting screen time (phones, TV, computers)
- Staying positive and managing stress (through relaxation, hobbies, or talking to someone)
- Saying no to harmful substances like tobacco, alcohol, and drugs
2. How do your surroundings (like home, school, or playground) affect your health?
Ans: Your surroundings affect health in many ways:
- Clean surroundings (at home, school, or playground) reduce germs, insects, and the chances of getting diseases.
- Dirty or polluted places can cause illnesses like cough, asthma, and infections.
- Playgrounds that are clean and safe encourage exercise and outdoor activities, which make you physically stronger.
- Clean water and good sanitation at home and school help prevent diseases spread by germs.
- People who live or study in healthy and hygienic environments feel happier, less stressed, and get sick less often.
Keep the curiosity alive
Q1: Group the diseases shown in the images as communicable or non-communicable
Ans: Communicable Diseases
- Cold and flu: Spread from person to person (through air, droplets, etc.).
- Typhoid: Spread through contaminated food and water.
- Chickenpox: Spread from person to person (through air or direct contact).
Non-Communicable Diseases
- Diabetes: Not caused by pathogens and does not spread from person to person; usually linked to lifestyle or genetic factors.
- Asthma: Not infectious; related to environmental, genetic, or lifestyle causes.
Q2: Diseases can be broadly grouped into communicable and non-communicable diseases. From the options given below, identify the non-communicable diseases.
(i) Typhoid
(ii) Asthma
(iii) Diabetes
(iv) Measles
Options
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: The non-communicable diseases from the options are Asthma and Diabetes.
So, the correct answer is: (b) (ii) and (iii)
- Typhoid and Measles are communicable diseases (spread by germs from person to person).
- Asthma and Diabetes are non-communicable diseases (not spread from person to person; linked to genetics, lifestyle, or environment)
Q3: There is a flu outbreak in your school. Several classmates are absent, while some are still coming to school coughing and sneezing.
(i) What immediate actions should the school take to prevent further spread?
Ans: The school should close temporarily, sanitise classrooms, and encourage sick students to stay home to prevent further spread.
(ii) If your classmate, who shares the bench with you, starts showing symptoms of the flu, how can you respond in a considerate way without being rude or hurtful?
Ans: You can politely suggest that your classmate see a doctor and take a rest at home, and offer to share notes with them.
(iii) How can you protect yourself and others from getting infected in this situation?
Ans: To protect yourself and others, wash your hands frequently, avoid close contact, and wear a mask.
Q4: By following these steps, you show care for yourself and everyone around you while strengthening good habits for health and kindness. Your family is planning to travel to another city where malaria is prevalent.
(i) What precautions should you take before, during, and after the trip?
Ans: To protect our family from malaria during travel, focus on preventing mosquito bites and taking prescribed preventative medication.
- Before travel, consult a doctor, get necessary vaccinations, and pack mosquito repellent and protective clothing.
- During the trip, continue using repellent, wear long sleeves and pants, and sleep under mosquito nets.
- After returning, monitor for any symptoms like fever, and seek immediate medical attention if they occur.
(ii) How can you explain the importance of mosquito nets or repellents to your sibling?
Ans: Explain to your sibling that mosquitoes spread malaria and that nets or repellents protect by blocking bites.
(iii) What could happen if travellers ignore health advisories in such areas?
Ans: If travellers ignore health advisories in such areas, they risk malaria infection, severe illness, or even death.
Q5: Your uncle has started smoking just to fit in with his friends, even though it is well known that smoking can seriously harm health and even cause death.
(i) What would you say to him to make him stop, without being rude?
Ans: Dear Uncle, I care about your health and well-being, and I want to talk to you about smoking. It’s well-known that smoking can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and lung cancer. Quitting smoking can greatly improve your health and quality of life.
(ii) What would you do if your friend offers you a cigarette at a party?
Ans: Politely decline the cigarette at the party and explain the health risks to your friend.
Remember: It's okay to say NO and you don’t need to do something just to fit in.
(iii) How can schools help prevent students from indulging in such harmful habits?
Ans: Schools can help prevent students from indulging in such habits by educating them about the health risks and organizing awareness programs regularly.
Q6: Saniya claims to her friend Vinita that “Antibiotics can cure any infection, so we don’t need to worry about diseases.” What question(s) can Vinita ask her to help Saniya understand that her statement is incorrect?
Ans: Why Saniya’s Statement is Wrong:
- Antibiotics only work against bacterial infections, not viral ones like the flu or common cold.
- Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance, making them less effective in the future.
- Some diseases are caused by fungi, protozoa, or viruses, which require different treatments.
Vinita can ask Saniya, Did you know that antibiotics don’t work on viruses like the flu or measles? They’re only useful for bacterial infections. Also, if we take antibiotics when we don’t need them, they might stop working when we really do. That’s why doctors are careful about prescribing them.”
Q7: The following table contains information about the number of dengue cases reported in a hospital over a period of one year: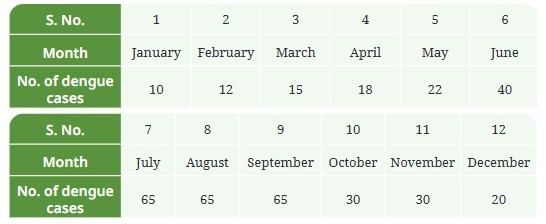
Make a bar graph of the number of cases on the Y-axis and the month on the X-axis. Critically analyse your findings and answer the following:
Ans: 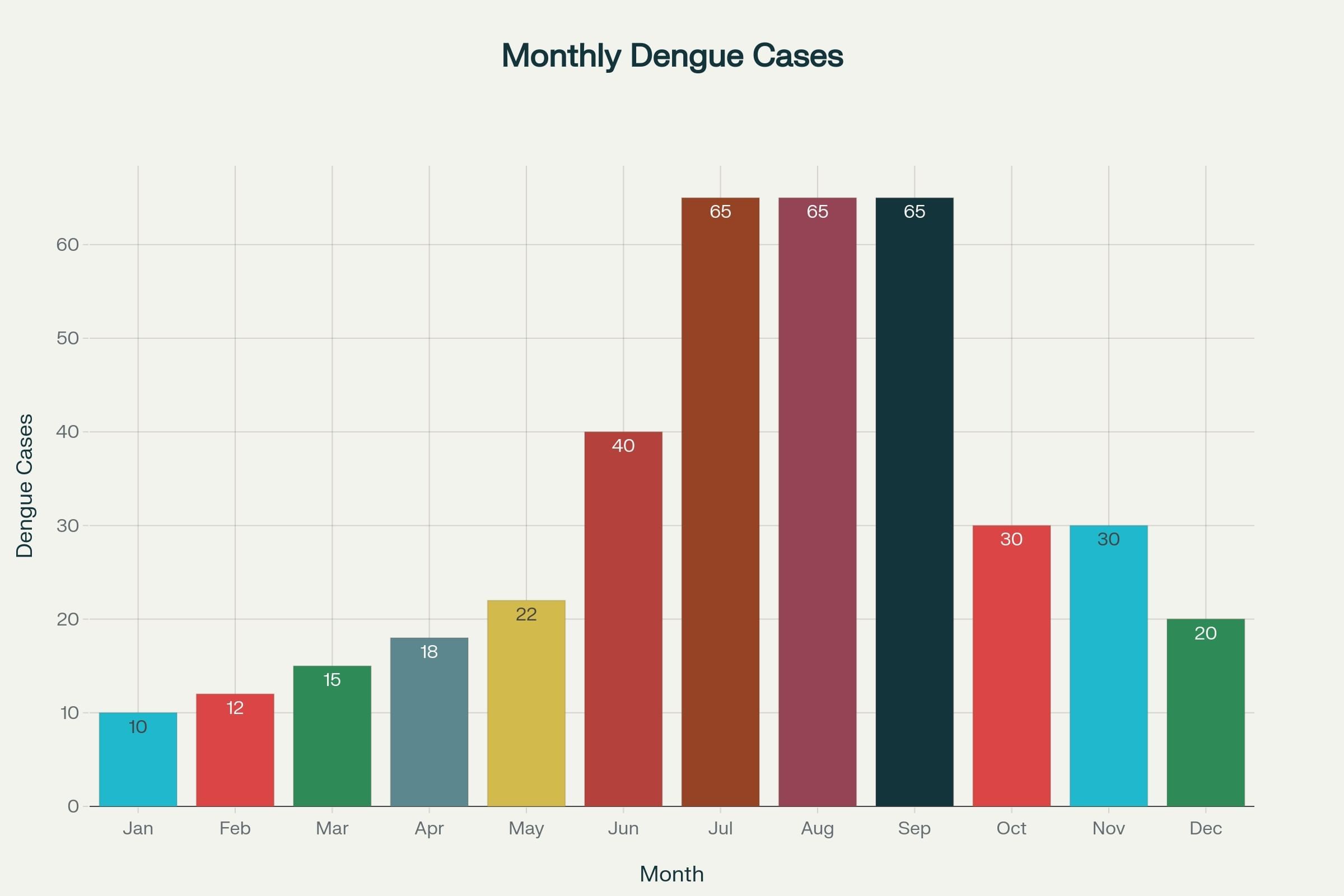
(i) In which three months were the dengue cases highest?
Ans: The three months with the highest number of dengue cases are:
- July: 65 cases
- August: 65 cases
- September: 65 cases
These are the peak months where the number of cases remained the same and were the highest for the year.
(ii) In which month(s) were the cases lowest?
Ans: The lowest number of dengue cases was reported in January (10 cases). February (12 cases) and March (15 cases) are also low, but January is the lowest.
(iii) What natural or environmental factors during the peak months might contribute to the increase in dengue cases?
Ans: Natural or environmental factors during the peak months, such as the rainy season and standing water for mosquito breeding, might contribute to the increase in dengue cases.
(iv) Suggest a few preventive steps that the community or government can take before the peak season to reduce the spread of dengue.
Ans: The community or government can take preventive steps like removing stagnant water, using mosquito nets, and spraying insecticides during this period regularly to reduce the spread of dengue.
Q8: Imagine you are in charge of a school health campaign. What key messages would you use to reduce communicable and non-communicable diseases?
Ans: Key Health Messages
- Personal Hygiene: Wash hands with soap, keep body, clothes, and surroundings clean.
- Healthy Eating: Eat balanced meals with fruits, vegetables, whole grains; avoid junk food.
- Physical Activity: Play or exercise daily to stay fit.
- Prevent Disease Spread: Cover mouth/nose when sneezing or coughing, stay home when sick, avoid sharing personal items.
- Avoid Harmful Habits: Say no to tobacco, alcohol, and drugs.
- Good Sanitation: Use toilets, keep water covered, prevent mosquito breeding.
- Mental & Social Well-being: Share worries, manage stress, and build positive relationships.
Q9: It is recommended that we should not take an antibiotic for a viral infection like a cold, a cough, or flu. Can you provide the possible reason for this recommendation?
Ans: The recommendation to avoid antibiotics for a viral infection like a cold, cough, or flu is because antibiotics do not work on viruses, which cause these illnesses.
Q10: Which disease(s) among the following may spread if drinking water gets contaminated by the excreta from an infected person? Hepatitis A, Tuberculosis, Poliomyelitis, Cholera, Chickenpox
Ans: The diseases that may spread if drinking water gets contaminated by the excreta from an infected person are Hepatitis A, Poliomyelitis, and Cholera.
Q11: When our body encounters a pathogen for the first time, the immune response is generally low but on exposure to the same pathogen again, the immune response by the body is much more compared to the first exposure. Why is it so?
Ans: When our body faces a pathogen (like a virus or bacteria) for the first time, our immune system needs time to:
- Identify the invader
- Create specific antibodies
- Build memory cells that remember the pathogen
This first reaction is called the primary immune response, and it’s usually slow and weak.
When the same pathogen enters our body again:
- Our memory B cells quickly produce the correct antibodies
- Our memory T cells help destroy infected cells faster
This is called the secondary immune response, and it’s faster, stronger, and more effective.
Discover, design, and debate (Page: 45)
Q1: Students maintain a health diary for at least a month to track food, hygiene, exercise, sleep, screen time, and emotional state.
Ans: Purpose: To understand our daily health habits.
Record daily for a month:
- Food: What you ate (healthy/junk)
- Hygiene: Bath, brushing, handwashing
- Exercise: Type and time
- Sleep: Bedtime, wake time
- Screen Time: Hours on phone/TV
- Mood: Happy, tired, sad, etc.
Discuss:
- What habits make you feel good?
- Do food, sleep, or screen time affect your mood?
Q2: Read about Indian scientists like Suniti Solomon, Asima Chatterjee, Dr. Yellapragada Subbarao, Dr. Mary Poonen Lukose for their contributions in the field of health and diseases
Ans:
- Suniti Solomon: Found first HIV cases in India; worked on AIDS care.
- Asima Chatterjee: Made medicines for malaria and epilepsy.
- Dr. Yellapragada Subbarao: Discovered antibiotics and cancer drugs.
- Dr. Mary Poonen Lukose: One of the first women doctors; improved child and mother health in Kerala.
Q3: The deadly disease smallpox was eradicated by vaccination. Discover how this was done and why it worked. Debate whether everyone should be required to get vaccinated to protect others.
Ans: Do it Yourself!
Suggestive Ans:
- How Smallpox Ended: People all over the world were vaccinated, and the virus had no place to spread.
- Why It Worked: Vaccine gave lifelong protection; smallpox spread only among humans.
Debate: “Should everyone be vaccinated?”
- For: Protects all, prevents outbreaks.
- Against: Personal choice, side effects (rare).
Q4: According to current guidelines, learn the correct sequence of steps for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on an adult in case of sudden stoppage of breathing. School may invite a doctor or a professional to demonstrate a mock drill.
Ans: CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) — Adult, latest steps (as per international guidelines):
- Check responsiveness: Tap and shout to see if the person responds.
- Call for help: Shout for assistance and ask someone to call emergency services (like 108 in India).
- Open airway: Tilt the head back and lift the chin.
- Check breathing: Look, listen, and feel for normal breathing for 10 seconds.
- Chest compressions: Place heel of one hand on the center of the chest, other hand on top. Push hard and fast (at least 100–120 compressions per minute). Allow the chest to rise fully between compressions.
- Rescue breaths (if trained and willing): Give 2 breaths after 30 compressions; pinch the nose, give a full breath by mouth. If not trained, do hands-only CPR (compressions only).
Q5: Invite a doctor to the school. Students may be encouraged to interact with the doctor on the issues of malnutrition, under-nutrition, and over-nutrition.
Ans: Ask questions like:
- What causes malnutrition or over-nutrition?
- Why is breakfast important?
- Which foods should we avoid?
- How are food needs different for children and elders?
After Discussion: Share what you learned about eating healthy.
Q6: If you are given an opportunity to create a health card, what all would you like to include in it. Create your own health card and have discussion about it.
Ans: Include:
- Name, age, class, blood group
- Emergency contact
- Vaccination record
- Height, weight
- Allergies or diseases
- Doctor’s remarks
Activity: Design and fill your health card; discuss its importance.
Q7: Have a debate on ‘Are there ill-effects of fast food on companion animals?
Ans: Do it Yourself!
Hint: Topic: “Does fast food harm pets?”
For: Causes obesity, stomach problems, and can be toxic.
Against: Small amounts may not harm.
Conclusion: Fast food is unhealthy for animals; pets should eat proper pet food.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Health: The Ultimate Treasure NCERT Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key components of health as described in the article? |  |
| 2. How can curiosity contribute to better health according to the article? |  |
| 3. What strategies are suggested for fostering creativity in health-related discussions? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to engage in debates about health topics? |  |
| 5. In what ways can individuals discover and design their own health improvement plans? |  |

















