Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Mind Map: Foreign Exchange Rate
Mind Map: Foreign Exchange Rate | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
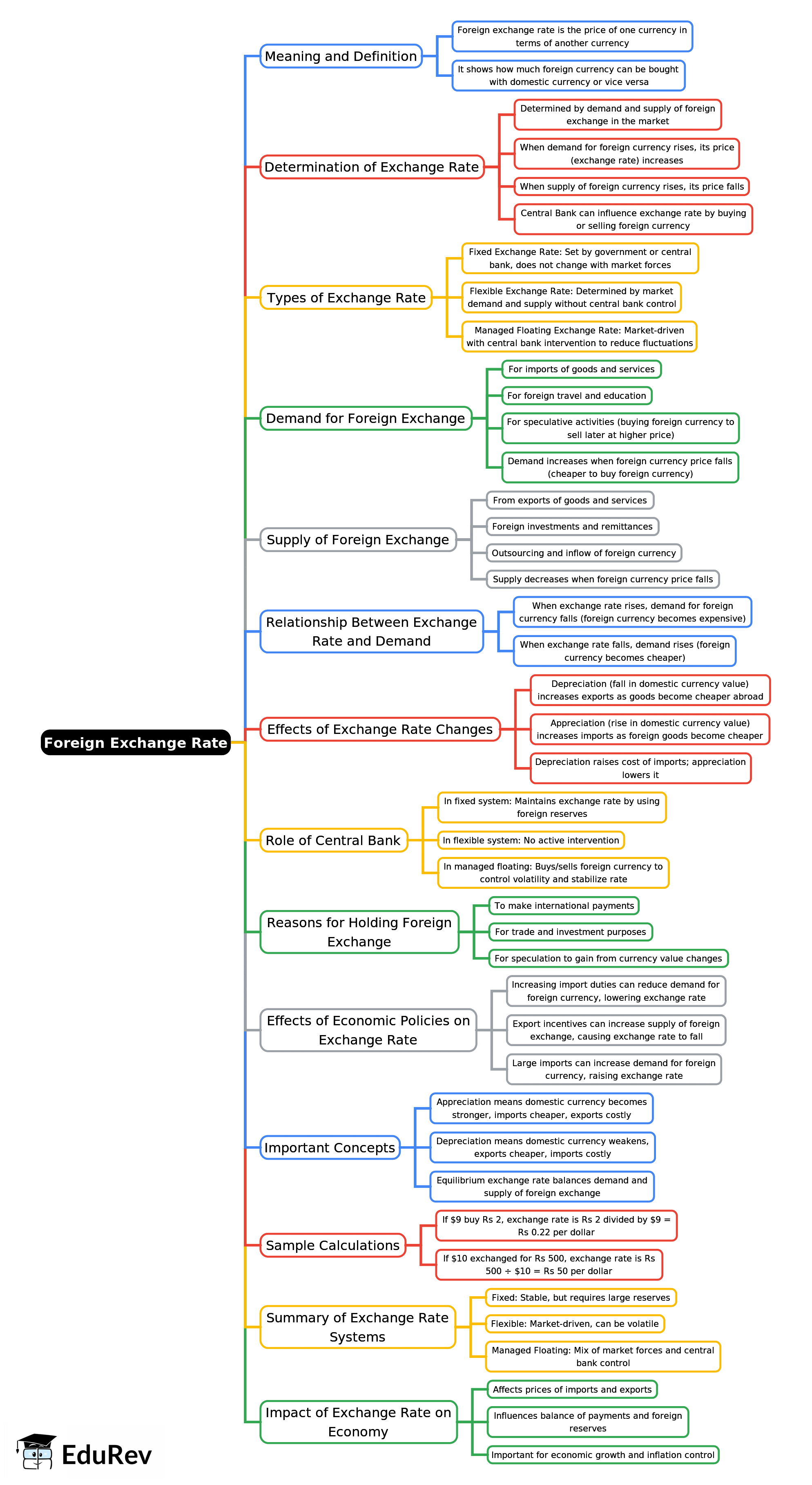
The document Mind Map: Foreign Exchange Rate | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
57 videos|110 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Foreign Exchange Rate - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the definition of a foreign exchange rate? |  |
Ans. A foreign exchange rate is the price at which one currency can be exchanged for another. It indicates how much of one currency is needed to purchase a unit of another currency. This rate is influenced by various factors including interest rates, inflation, and economic stability.
| 2. How do changes in foreign exchange rates affect international trade? |  |
Ans. Changes in foreign exchange rates can significantly impact international trade by affecting the price competitiveness of goods and services. For example, if a country's currency appreciates, its exports may become more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially reducing demand. Conversely, if the currency depreciates, exports may become cheaper and more attractive, boosting sales abroad.
| 3. What are the main factors that influence foreign exchange rates? |  |
Ans. The main factors influencing foreign exchange rates include interest rates, inflation rates, political stability, economic performance, and market speculation. Changes in these factors can lead to fluctuations in currency values, affecting trade balances and investment flows.
| 4. What is the difference between fixed and floating exchange rate systems? |  |
Ans. A fixed exchange rate system maintains a currency's value against another currency or a basket of currencies, often through government intervention. In contrast, a floating exchange rate system allows currency values to fluctuate according to market forces without direct government control. Each system has its advantages and disadvantages regarding economic stability and trade competitiveness.
| 5. How do central banks intervene in foreign exchange markets? |  |
Ans. Central banks may intervene in foreign exchange markets to stabilize or influence their currency's value. They can do this by buying or selling currencies, adjusting interest rates, or using foreign reserves. These interventions aim to prevent excessive volatility and maintain economic stability, which can be crucial for trade and investment.
Related Searches















