Assignment: Conditional & Iteration | Computer Application: Class 10 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which of the following are invalid conditional statements of Python?
(a) IF
(b) Test if
(c) if-else
(d) if-elif
Ans. (a,b) IF and Test if
IF and Test if are invalid conditional statements of Python.
Q2. Which of the following is/are not a valid Python loop ?
(a) for
(b) while
(c) iter
(d) repeat
Ans. (c,d) iter, repeat
iter and repeat are not valid Python loop. for and while are valid loop statements.
Q3. Which of the following is used to define a block of code (e.g., body of if or body of a loop) in Python ?
(a) { }
(b) ( )
(c) indentation
(d) Quotation
Ans. (c) indentation
Indentation is used to define a block of code in Python.
Q4. What is the output of following code ?
if None :
print "Up"
else:
print "Down"
(a) Up
(b) Down
(c) No output
(d) Up Down
Ans. (b) Down
Since None is treated as false, the if condition results in false. The block of if will be ignored and the else block will be executed and Down will be printed on the output screen.
Q5. What will be the output of following code ?
for i in range(1) :
print i
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) No output
(d) Error in code
Ans. (a) 0
The range(n) function generates a list as [0, 1, 2..., n - 1]. Thus, the range(1) function will generate a list as [0]. Thus the for loop will execute only one time and print 0 on the output terminal.
Q6. What will the output of following code ?
for i in range(1, 0) :
print i
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) No output
(d) Error in code
Ans. (c) No output
The function range(1, 0) will return return an empty list [] as no number falls in the arithmetic progression beginning with 1 and ending with 0. Thus, the for loop will not execute even once and hence, no output will be generated on the output screen.
Q7. What is the output of following code ?
while 3 >= 3 :
print 3
(a) 3 is printed once
(b) 3 is printed three times
(c) 3 is printed infinitely until program is closed
(d) Error in code
Ans. (c) 3 is printed infinitely until program is closed
Since the given condition (3 >= 3) will always remain true, the while loop will execute indefinitely and keep on printing 3 on the output screen till the program is closed.
Theoretical Questions
Q1. What are selection statements ? How are they useful ?
Ans. A statement that carries out a set of instructions depending upon a condition's result is known as a selection or conditional statement. Python provides selection statements in the form of if and if-else statements.
These statements enable a program to carry out a set of instructions depending upon a condition's result. For example,
num = 5
if num >= 0 :
print "Positive"
else :
print "Negative"
Q2. What are looping statements ? How are they useful ?
Ans. A statement that allows a set of instructions to be performed repeatedly is known as a looping or iteration statement. Python provides looping statements in the form of for and while loop.
These statements enable a program to perform a set of instructions repeatedly. For example,
num = 3
while num > 0 :
print num
num = num - 1
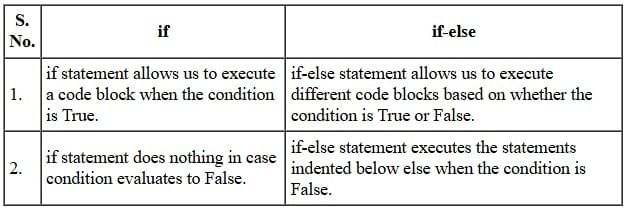
Q3. Differentiate between if and if-else statements.
Ans. Difference between if and if-else statements in Python:
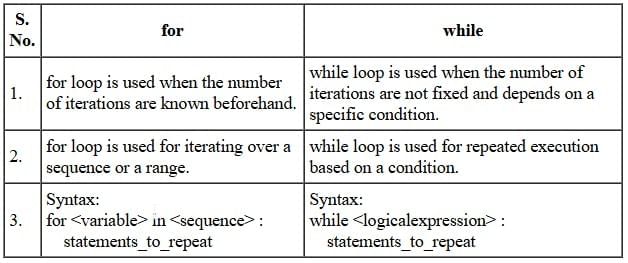
Q4: Differentiate between for and while statements.
Ans. Difference between for and while statements in Python:
Q5. Rewrite the following code fragments using for loop
while num > 0 :
print num % 10
num = num/10
Ans.
l = [1]
for x in l:
l.append(x + 1)
if num <= 0:
break
print (num % 10)
num = num/10
Q6. Rewrite the following code fragments using for loop
i = 100
while (i > 0) :
print i
i -= 3
Ans.
for i in range(100, 0, -3) :
print (i)
Q7. What is following code doing ? What would it print for input as 3 ?
n = input( "Enter an integer:" )
if n < 1 :
print "invalid value"
else :
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print i * i
Ans.
The code will print the square of each number from 1 till the number given as input by the user if the input value is greater than 0. Output of the code for input as 3 is shown below:
Enter an integer:31
4
9
Q8. Rewrite following code fragments using while loops
min = 0
max = num
if num < 0 :
min = num
max = 0
# compute sum of integers from min to max
for i in range(min, max + 1):
sum += i
Ans.
min = 0
max = num
if num < 0 :
min = num
max = 0
# compute sum of integers from min to max
i = min
while i <= max:
sum += i
i += 1
Q9. Rewrite following code fragments using while loops
for i in range(1, 16) :
if i % 3 == 0 :
print i
Ans.
i = 1
while i < 16:
if i % 3 == 0 :
print (i)
i += 1
Q10. Write a short program to print the following series :
1 4 7 10 ........... 40.
Ans.
for i in range(1, 41, 3) :
print(i, end = ' ')
Output:
1 4 7 10 13 16 19 22 25 28 31 34 37 40
Q11. Write a short program to print the following series :
1 -4 7 -10 .......... -40
Ans.
x = 1
for i in range(1, 41, 3) :
print(i * x, end = ' ')
x *= -1
Output:
1 -4 7 -10 13 -16 19 -22 25 -28 31 -34 37 -40
Q12. Predict the output of the following code fragments :
count = 0
while count < 10:
print "Hello"
count += 1
Ans.
Output:
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Hello
Explanation: The while loop executes 10 times so "Hello" is printed 10 times.
Q13. What will be output of the following code if the user enters Principal amount as 20000 and Time as 10 years.
#Considering Python 2.7
P = input("Enter Principal amount:")
T = input("Enter Time:")
if T > 10:
SI = P*T*10/100
else:
SI = P*T*15/100
print("Simple Interest = ", SI)
Ans.
Output:
Enter Principal amount:20000
Enter Time:10
Simple Interest = 30000
Explanation: This Python program calculates the Simple Interest (SI) based on the given Principal amount (P) and Time (T) values. For time value of more than 10 years, the program takes the rate of interest as 10% and for 10 years or less it takes the rate of interest as 15%.
Q14. Write a Python script that asks the user to enter a length in centimetres. If the user enters a negative length, the program should tell the user that the entry is invalid. Otherwise, the program should convert the length to inches and print out the result. There are 2.54 centimetres in an inch.
Ans.
len = int(input("Enter length in cm: "))
if len < 0:
print("Invalid input")
else:
inch = len / 2.54
print(len, "centimetres is equal to", inch, "inches")Output:
Enter length in cm: 150
150 centimetres is equal to 59.05511811023622 inches
Q15. Write a program that asks the user for two numbers and prints Close if the numbers are within .001 of each other and Not close otherwise.
Ans.
Output:
Enter first number: 10.12345
Enter second number: 10.12354
Close
|
10 videos|97 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Assignment: Conditional & Iteration - Computer Application: Class 10
| 1. What is the role of conditional statements in programming? |  |
| 2. How does iteration work in programming, and why is it important? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the difference between 'if', 'else if', and 'else' in conditional statements? |  |
| 4. What are some common programming constructs used for iteration? |  |
| 5. How can conditional and iterative constructs improve code readability and maintenance? |  |