Metre (m) is used for larger measurements (e.g., height of India Gate, depth of a well).
Centimetre (cm) is used for smaller measurements (e.g., length of a handkerchief, distance between buttons).
The appropriate unit is chosen based on the size of the object or distance.
Far and Near Chapter Notes | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download

Have you ever wondered how we measure the height of a tree, the length of a ribbon, or the distance to another city? We cannot use the same unit for all these!
In this chapter Far and Near, we will:
Discover which unit—mm, cm, m, or km—is best for different measurements.
Learn how to change one unit into another.
Try fun activities like measuring saris, sprout lengths, and even the tallest statues in the world.
Explore how distances are measured in real life—on playgrounds, train journeys, and even in races.
Let’s start with a quick identification
Identify the appropriate units for measuring each of the following.
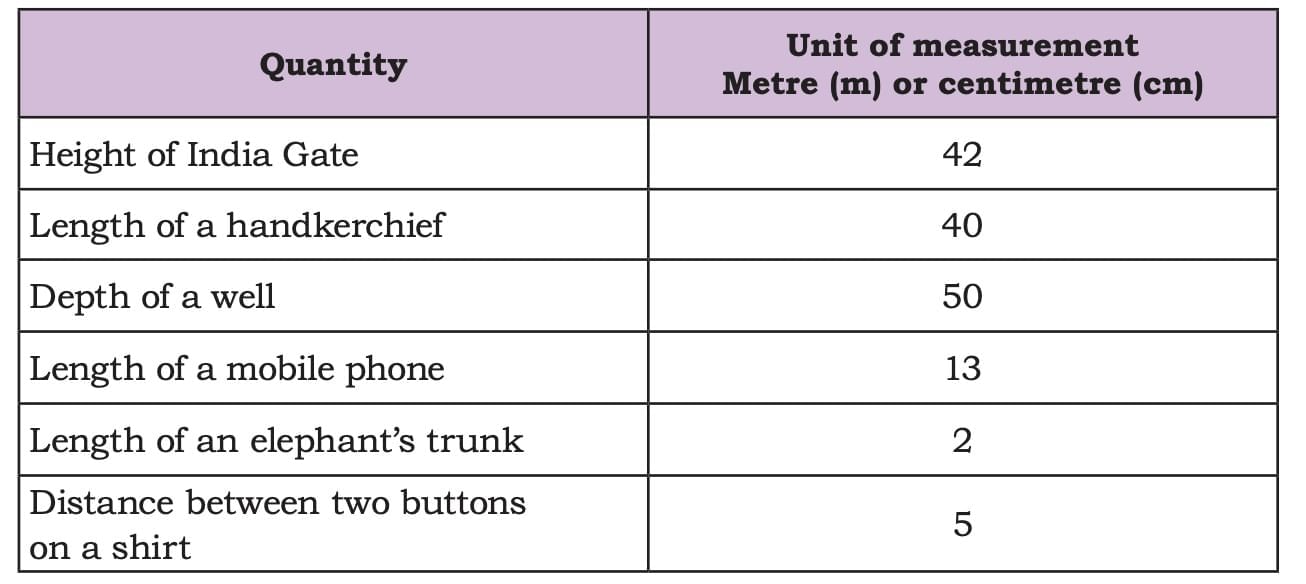
In conclusion, we can say that:
Different Units but Same Measure
We often use different units (like centimetres and metres) to measure the same length.
1 metre (m) = 100 centimetres (cm).
Let’s Understand with a Story
Riya and Aman were playing in their garden. Riya had a rope that was 200 cm long.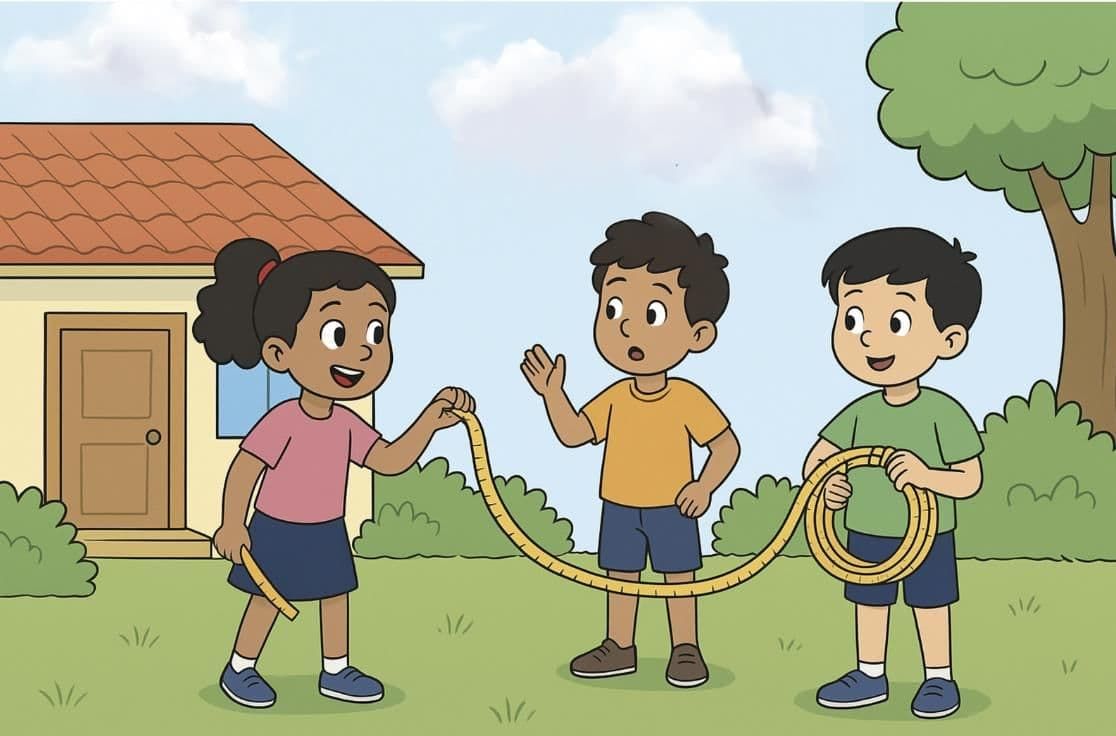 
Aman said, “200 cm sounds too big! Can we say it in metres instead?”
Riya thought for a while. She remembered what her teacher had said:
So she quickly divided 200 by 100.
“Look, Aman! 200 cm is the same as 2 metres.”
Just then, Aman brought another rope of 500 cm.
He asked, “How long is this in metres?”
Riya smiled, “That’s easy! 500 ÷ 100 = 5 metres.”
Both ropes together measured 7 metres in total!
Now, let’s connect centimetres and metres on a number line to clearly see how the conversion works.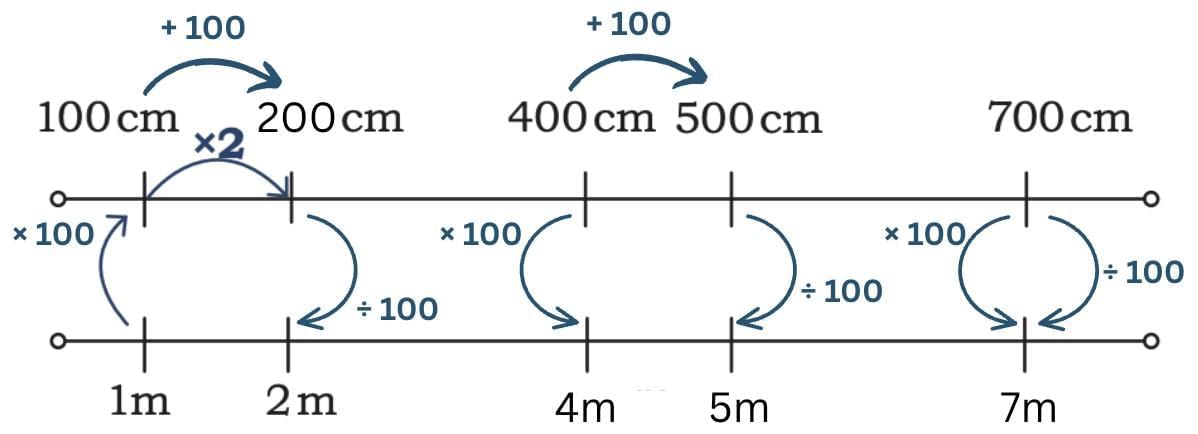
Let Us Compare
We can compare two or more lengths using the symbols < (less than), > (greater than), or = (equal to).
General Rules:
Convert units to the same form before comparing.: (Either convert everything to cm or everything to m).
Use 1 m = 100 cm to change units.
Simplify the numbers by adding or converting if required.
Compare the values directly using <, >, or =.
Remember:
1 m = 100 cm
If numbers are equal → use =
If one is bigger → use > or < accordingly.
Examples:
(a) 456 cm ____ 5 m
Convert 5 m = 500 cm.
Compare: 456 cm < 500 cm.
(b) 55 cm + 200 cm ____ 200 cm + 54 cm
Left side = 255 cm, Right side = 254 cm.
Compare: 255 cm > 254 cm.
Measuring Long Distances



Let Us Explore
When we walk 1,000 metres, we say we have walked 1 kilometre (1 km).
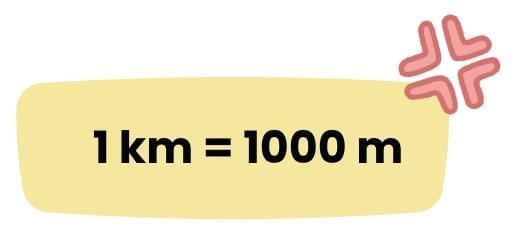
The prefix ‘kilo’ means thousand.
Kilometres are used to measure long distances like:
Distance between two cities
Length of a road
Distance travelled in a vehicle
Let’s practice some examples
1. Convert kilometres to metres
3 km = 3 × 1000 m = 3000 m
7 km = 7 × 1000 m = 7000 m
2. Convert metres to kilometres
5000 m = 5000 ÷ 1000 = 5 km
2300 m = 2300 ÷ 1000 = 2 km 300 m
The World of Small Things
Some objects, like sprouts, small screws, and nails, are very small in size.
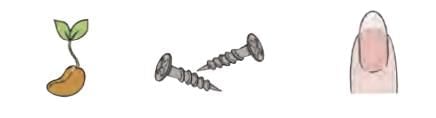
To measure such small things, we use the smaller marks on a scale (ruler).
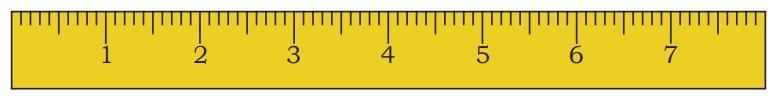
- We use a smaller unit called millimetre (mm).
Between 1 cm and 2 cm on a scale, there are 10 equal small divisions.
Each small division is called 1 millimetre (mm).
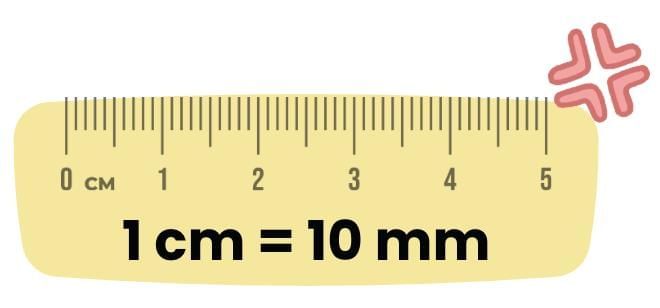
These smaller marks allow us to measure lengths more precisely.
Relationships between Different Units
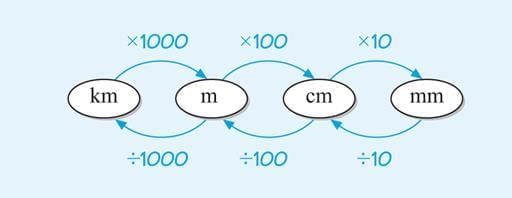
Adding and Subtracting Lengths
We can add and subtract lengths just like we add and subtract numbers. We need to be careful with units.
1. Adding Lengths
Example 1: Saji walked 3 km 450 m in the morning and 4 km 650 m in the evening. How much did he walk in total?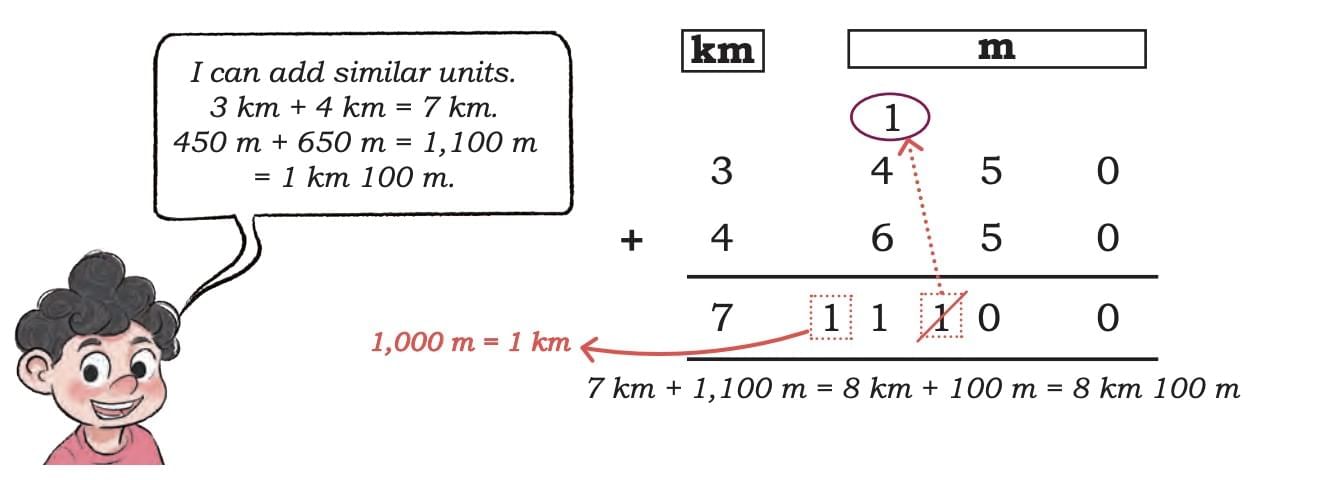
Let's take a look at both the methods
Method 1: Adding km and m separately
- Add kilometres: 3 km + 4 km
= 7 km. - Add metres: 450 m + 650 m
= 1100 m. - Convert 1100 m to km and m
= 1000 m + 100 m
= 1 km 100 m. - Add the converted metres to kilometres
7 km + 1 km 100 m
= 8 km 100 m.
Method 2: Convert everything to metres and then add
- Convert 3 km 450 m
= 3 x 1000 m + 450 m
= 3000 m + 450 m
= 3450 m. - Convert 4 km 650 m
= 4 x 1000 m + 650 m
= 4000 m + 650 m
= 4650 m. - Total distance = 3450 m + 4650 m = 8100 m.
- Convert 8100 m to km and m
= 8000 m + 100 m
= 8 km 100 m.
2. Subtracting Lengths
Example 2: Electricians are changing the cables in a house. They need 63m of cable for this purpose. They used 16m 75cm cable in the first room. What is the length of the cable left?
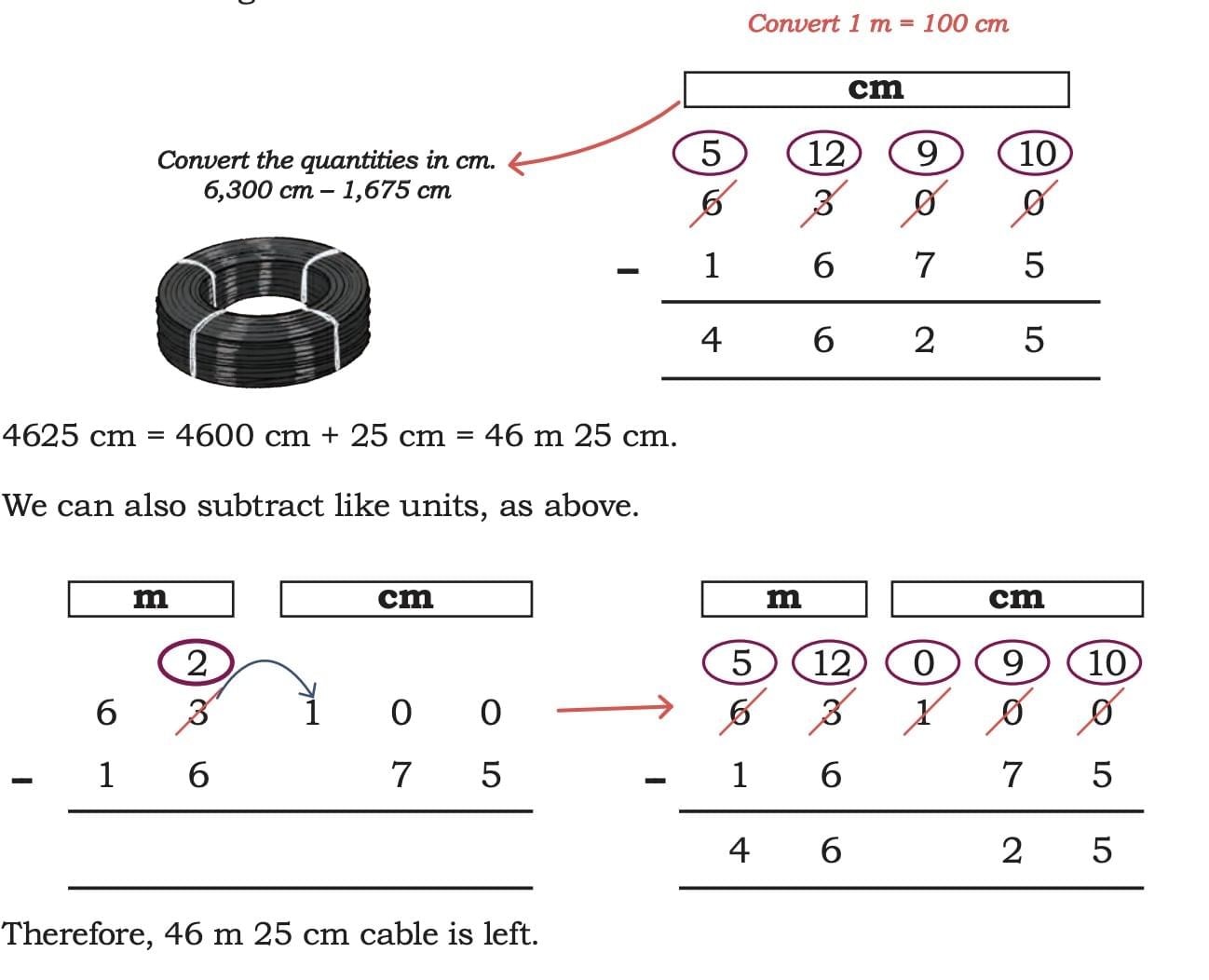
Let's take a look at both the methods
Electricians need 63 m of cable. They used 16 m 75 cm in the first room.Method 1: Convert everything to cm and then subtract
- Total cable needed: 63 m
= 63 x 100 cm
= 6300 cm. - Cable used: 16 m 75 cm
= 16 x 100 cm + 75 cm
= 1600 cm + 75 cm
= 1675 cm. - Cable left
= 6300 cm - 1675 cm
= 4625 cm. - Convert 4625 cm to m and cm
= 4600 cm + 25 cm
= 46 m 25 cm.
Method 2: Subtracting m and cm separately (with borrowing)
Step 1: Arrange in Columns
Step 2: Notice the Borrowing
We cannot directly subtract 75 from 00 cm.
So, we borrow 1 metre (m) = 100 cm.
Now, 63 m becomes 62 m, and centimetres become 200 cm (100 already + borrowed 100).
Step 3: Subtract Normally
Centimetres: 200 - 75 = 125 cm
Metres: 62 - 16 = 46 m
Step 4: Convert if Needed
Since 100 cm = 1 m,
125 cm = 1 m 25 cm
So,
46 m 125 cm = 46 m 25 cm
Multiplying and Dividing Lengths
We can also multiply and divide lengths to find total or equal parts.
Multiplying lengths helps when the same length is used many times, like cloth for several shirts or ribbon pieces.
Dividing lengths helps when we need to share a length into equal parts, like cutting a rope into equal pieces.
1. Multiplying Lengths
Example 1: We need a 1 m 80 cm cloth to make a shirt for a 10-year-old child. How much cloth will be needed to make shirts for 20 such children?
Given:
Cloth for 1 child’s shirt = 1 m 80 cm
For 20 children, we multiply.
Let's take a look at the methods to solve
Method 1: Break and Multiply
Step 1: Break into metres and centimetres.
1 m 80 cm = 1 m + 80 cm
Step 2: Multiply separately.
20 × 1 m = 20 m
20 × 80 cm = 1600 cm
Step 3: Convert cm into metres.
1600 cm = 16 m
Step 4: Add together.
20 m + 16 m = 36 m
Method 2: Convert everything to cm and then multiply
Step 1: Convert to cm:
- 1 m 80 cm = 100 cm + 80 cm
= 180 cm
Step 2: Multiply by 20 shirts:
- Total cloth = 20 × 180 cm = 3600 cm
Step 3: Convert cm to metres:
- 3600 cm = 36 × 100 cm = 36 m
2. Dividing Lengths
Example 2: A shop sells cloth for making bags at ₹100 for 5 m. How much money is needed to buy a 1 m cloth?
If 5 m cloth costs ₹100, then a 1 m cloth costs 100 ÷ 5 = ₹20.
- A shop sells cloth for ₹100 for 5 m. How much money is needed to buy 1 m cloth?
- Cost of 5 m cloth = ₹100.
- Cost of 1 m cloth = ₹100 ÷ 5
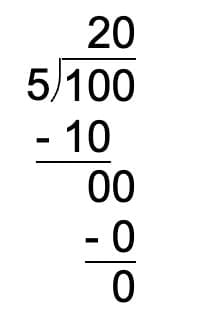
- Therefore, the cost of 1m of cloth is 20m
Let Us Estimate
- Estimating means making a good guess about a measurement without actually measuring it.
- We use things we already know as a reference.
Let's understand this with the help of an example:
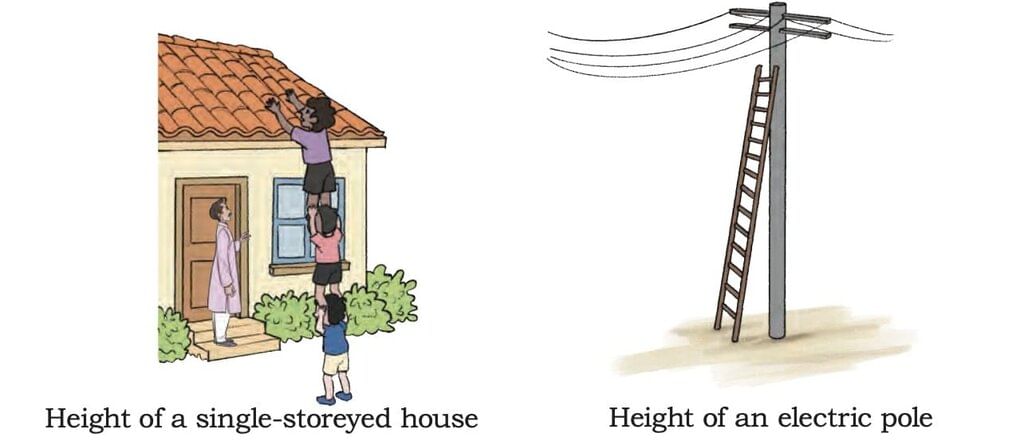
Height of a single-storeyed house: You can estimate it to be around 3-4 metres.
Height of an electric pole: You can estimate it to be around 8-10 metres.
Practice Questions
Tallest building in your neighbourhood
If one floor ≈ 3 metres, then a 5-storey building ≈ 15 metres.
Reference: single-storeyed house.
Tallest tree in your neighbourhood
Compare with electric pole (about 8–10 m).
If tree is a little taller, estimate ≈ 12–15 metres.
Quick Tip: Always compare with something you already know (like your own height or a nearby house) to estimate correctly.
Let Us Explore (Feet and Inches)
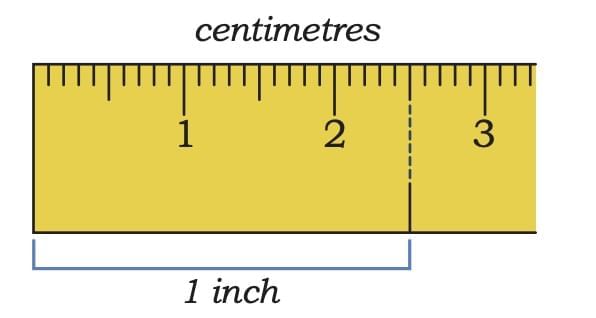
|
35 videos|318 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Far and Near Chapter Notes - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are different units used to measure lengths and distances? |  |
| 2. How do we convert between different units of length? |  |
| 3. Why is it important to measure long distances accurately? |  |
| 4. How do we add and subtract lengths in different units? |  |
| 5. What are some practical examples of measuring small things and their significance? |  |
















