Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects NCERT Solutions | Science Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Probe and Ponder (Page 46) |

|
| InText (Page 49 - 56) |

|
| Keep the curiosity alive (Pages 58-61) |

|
| Discover, design, and debate (Page 61) |

|
Probe and Ponder (Page 46)
Q1: If we don’t have an electric lamp while making an electric circuit with an electric cell, is there any other way to find out if current is flowing in the circuit?
Ans: Yes, there are other ways to check if current is flowing. One way is to use a magnetic compass. If you place a compass near the wire and close the circuit, the needle of the compass will deflect when the current flows through the wire. This shows that electricity is passing through the circuit. Another way is to use a device like an electric bell or buzzer, which will make a sound if current is present.
Q2: Is it possible to make temporary magnets? How can these be made?
Ans: Yes, temporary magnets can be made easily. Wrapping a long insulated wire around an iron nail and connecting both ends of the wire to a battery turns the nail into an electromagnet (a temporary magnet). When electric current flows through the wire, the nail acts like a magnet and can attract magnetic materials. When the current is switched off, the nail loses its magnetism.
Q3: We can generate heat by burning fossil fuels and wood; but how is heat generated in various electrical appliances?
Ans: In electrical appliances, heat is generated due to the heating effect of electric current. When electric current passes through a wire or coil (often made of materials like nichrome), the wire offers resistance to the current. This resistance causes some electrical energy to change into heat energy, making the wire hot. That’s why devices like heaters, irons, and toasters become warm when switched on.
Q4: How do we know if a cell or a battery is dead? Can all cells and batteries be recharged?
Ans: A cell or battery is considered dead if it can no longer provide enough current to light a bulb, move a motor, or run any electrical device. Sometimes the device works weakly or not at all, which signals that the battery is dead. Not all cells and batteries can be recharged. Dry cells, like those used in TV remotes, are single-use and cannot be recharged. Rechargeable batteries, such as those in mobile phones and laptops, can be used again and again by recharging them with a charger.
Q5: Share your questions __________
Ans: Questions are as follows:
- Why does reversing the battery terminals in a coil change the direction of the compass needle?
- What happens if we use longer wires to make an electromagnet?
- Which fruit or vegetable makes the strongest electric cell?
- How does a rechargeable battery work differently from a single-use battery?
- What materials are best for making heating elements in electric appliances?
InText (Page 49 - 56)
Q1: Can we use electric current to make a magnet? (Page No. 49)
Ans: Yes, the magnetic effect of the electric current is used to make a magnet. If an electric current is passed through a long conducting wire coiled around a metal nail or rod, the nail or rod becomes a magnet during the flow of the current. When the electric current flow stops, the nail or the rod does not have a magnetic force.
Q2: Does an electromagnet also have two poles like a bar magnet? (Page No. 50)
Ans: Electromagnets also have two poles like a bar magnet. When an electric current is passed through a conducting wire coiled around an iron nail, one end of the nail becomes the North pole of the magnet, and the other end of the nail becomes the South pole of the magnet. This can be shown by bringing the North pole of a compass needle near two ends (one by one) of the nail, while current is flowing, and observing its deflection in each case. The property of magnets that ‘like poles repel each other’ shows that the electromagnets also have two poles like a bar magnet.
Q3: Are electromagnets also used in real life, for lifting objects? (Page No. 52)
Ans: Electromagnets are widely used in factories and scrap yards to move, lift, and sort heavy metal items. These electromagnets are hung to the cranes. The crane operator moves the hanging magnet with the crane to heavy metal items and switches ON the current. The magnet lifts all magnetic items from the pile of heavy metal items. The crane operator controls and moves the magnet to the other position where these items are to be released. He then switches OFF the current, and the magnetic field disappears; the items are released. CraneQ4: While doing the activity for the electromagnet, did you also notice that the wire ends got warm? Why would that happen? (Page No 52)
CraneQ4: While doing the activity for the electromagnet, did you also notice that the wire ends got warm? Why would that happen? (Page No 52)
Ans: The wire ends get warm when current flows through the wires for some time. This happens due to the heating effect of electric current. Depending on the nature of the metals used as conductors, the conductors offer some resistance to the flow of the current. In the process, a part of the electric energy is converted into heat energy that warms the ends of the wires.
Q5: Can we also make our Voltaic cell using easily available materials? (Page No. 56)
Ans: We can make our Voltaic cell using fresh lemon pieces, iron nails, copper wires or thin strips and an LED lamp to check the current of the cell. Five iron nails and five copper strips have to be inserted, one in each lemon piece. The copper strip of the first lemon piece should be connected to the iron nail of the second lemon. The copper strip of the second lemon should be connected to the iron nail of the third lemon, and so on.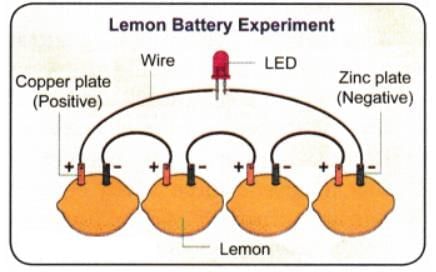
The first iron nail is to be connected to the negative terminal of the LED, and the last copper strip to the positive terminal of the LED. The LED will glow to show that the Voltaic cell is ready.
Keep the curiosity alive (Pages 58-61)
Q1: Fill in the blanks:
(i) The solution used in a Voltaic cell is called ________.
(ii) A current carrying coil behaves like a _______ .
Ans:
(i) The solution used in a Voltaic cell is called electrolyte.
(ii) A current-carrying coil behaves like a magnet.
Q2: Choose the correct option:
(i) Dry cells are less portable compared to Voltaic cells. (True/False)
(ii) A coil becomes an electromagnet only when electric current flows through it. (True/False)
(iii) An electromagnet, using a single cell, attracts more iron paper clips than the same electromagnet with a battery of 2 cells. (True/False)
Ans:
(i) False
Dry cells are more portable as they use a paste electrolyte and are compact.
(ii) True
A coil becomes an electromagnet only when electric current flows through it.
(iii) False
More cells provide stronger current, leading to a stronger magnetic field and more attraction.
Q3: An electric current flows through a nichrome wire for a short time.
(i) The wire becomes warm.
(ii) A magnetic compass placed below the wire is deflected.
Choose the correct option:
(a) Only (i) is correct
(b) Only (ii) is correct
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are correct
(d) Both (i) and (ii) are not correct
Ans: (c) Both (i) and (ii) are correct
When current flows through a nichrome wire:
(i) The wire gets warm — due to the heating effect of current.
(ii) The compass needle deflects — due to the magnetic effect of current.
Q4: Match the items in Column A with those in Column B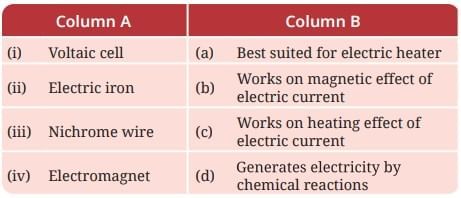
Ans: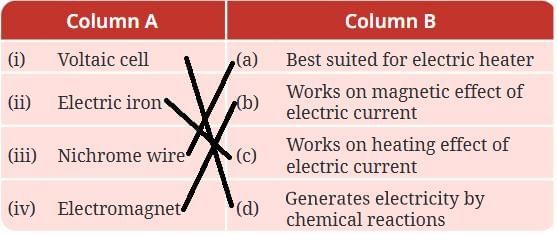
Q5: Nichrome wire is commonly used in electrical heating devices because it
(i) is a good conductor of electricity.
(ii) generates more heat for a given current.
(iii) is cheaper than copper.
(iv) is an insulator of electricity.
Ans: (ii) generates more heat for a given current
Nichrome is used in heating devices because it has high electrical resistance and can withstand high temperatures without melting.
So, it produces more heat for the same current compared to low-resistance metals like copper.
Q6: Electric heating devices (like an electric heater or a stove) are often considered more convenient than traditional heating methods (like burning firewood or charcoal). Give reason(s) to support this statement considering societal impact.
Ans: Traditional methods like burning firewood or charcoal are NOT convenient because:
(i) More space in the household is required to store dry firewood or charcoal.
(ii) The smoke arising from the burning of firewood or charcoal is a health hazard. It gives a burning sensation to the eyes and makes breathing difficult.
(iii) The burning of firewood or charcoal releases harmful gases like carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. These gases pollute the air we breathe and, therefore, are not good for our environment.
Electric heating devices, like an electric heater or stove, are more convenient as they need less space and do not cause pollution.
Q7: Look at the Fig. 4.4a. If the compass placed near the coil deflects:
(i) Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the path of the electric current.
(ii) Explain why the compass needle moves when current flows.
(iii) Predict what would happen to the deflection if you reverse the battery terminals.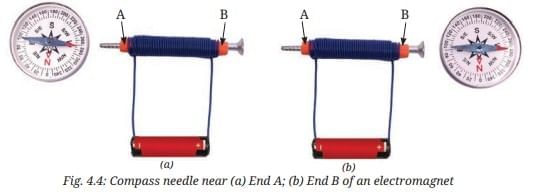 Ans: (i) The current flows from the positive terminal of the cell to end marked A of the coil, then through the coil to end marked B, and then to the negative terminal of the cell as shown by the red arrows in the Figure.
Ans: (i) The current flows from the positive terminal of the cell to end marked A of the coil, then through the coil to end marked B, and then to the negative terminal of the cell as shown by the red arrows in the Figure.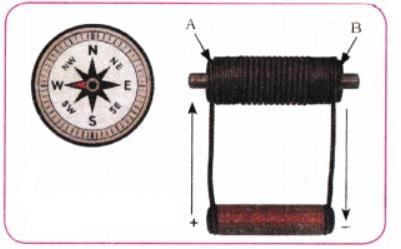 (ii) The compass needle moves as the coil becomes a magnet on passing the current through it, and the compass needle in its magnetic field moves.
(ii) The compass needle moves as the coil becomes a magnet on passing the current through it, and the compass needle in its magnetic field moves.
(iii) When we reverse the battery terminals, the poles of the coil electromagnet change. Therefore, the deflection in the compass needle also changes accordingly. The pole of the compass needle that was earlier attracted to the coil will move away from it, and the other pole of the compass needle will get attracted towards the coil.
Q8: Suppose Sumana forgets to move the switch of her lifting electromagnet model to OFF position (in introduction story). After some time, the iron nail no longer picks up the iron paper clips, but the wire wrapped around the iron nail is still warm. Why did the lifting electromagnet stop lifting the clips? Give possible reasons.
Ans: A conducting coil becomes a magnet ONLY when the electric current is flowing through it (magnetic effect of electric current). When the flow of electric current is stopped, the coil loses its magnetic effect. The magnetic effect of electric current remains in the conducting wire (coil) during the current flow only. The heating effect of electric current converts a part of the electric energy to heat energy. This heat energy makes the current-carrying wire warm. When the current stops flowing the heating effect of the electric current stops, but the wire that has become warm takes some time before cooling to the normal temperature.
Q9: In Fig. 4.11, in which case the LED will glow when the switch is closed?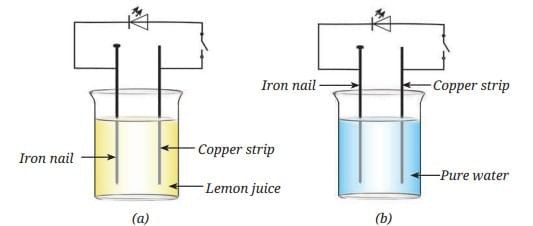
Ans: The LED will glow when the switch is closed in case of (a). Here, the electrolyte is the lemon juice. Copper and iron plates properly placed in a weak acid or salt solution and connected in a circuit, produce electricity. In case of (b), the liquid used is pure water that does not become an electrolyte.
Q10: Neha keeps the coil exactly the same as in Activity 4.4 but slides the iron nail out, leaving only the coiled wire. Will the coil still deflect the compass? If yes, will the deflection be more or less than before?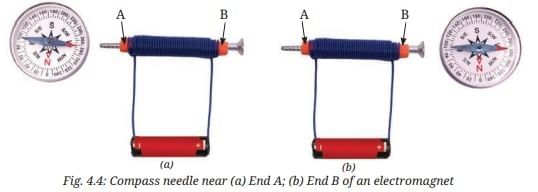 Ans: Yes, the coil will deflect the compass even after the iron nail has been slid out. The coil gets a magnetic force when current flows through it. If iron nail is inserted inside the coil, the strength of the magnet increases. Deflection in the compass will be less when Neha slides the iron nail out, due to less strong electromagnet formed by the coil alone.
Ans: Yes, the coil will deflect the compass even after the iron nail has been slid out. The coil gets a magnetic force when current flows through it. If iron nail is inserted inside the coil, the strength of the magnet increases. Deflection in the compass will be less when Neha slides the iron nail out, due to less strong electromagnet formed by the coil alone.
Q11: We have four coils, of similar shape and size, made up from iron, copper, aluminium, and nichrome as shown in Fig. 4.12. When current is passed through the coils, compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection.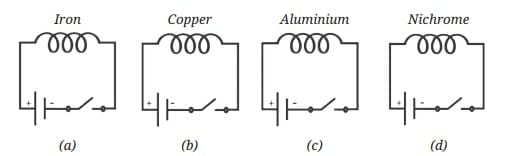 When current is passed through the coils, compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection.
When current is passed through the coils, compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection.
(i) Only in circuit (a)
(ii) Only in circuits (a) and (b)
(iii) Only in circuits (a), (b), and (c)
(iv) In all four circuits
Ans: Option (iv) In all four circuits.
The compass needles placed near the coils will show deflection in all four cases. The deflection, however, will not be equal in all four cases. The magnetic strength of the electromagnet depends on the nature of the material used. Some magnetic substances like iron, nickel, and cobalt make strong electromagnets, while aluminium and nichrome may be of the same shape and size may not make equally strong magnets. Therefore, the deflection of the compass needles will vary depending on the strength of the electromagnet.
Discover, design, and debate (Page 61)
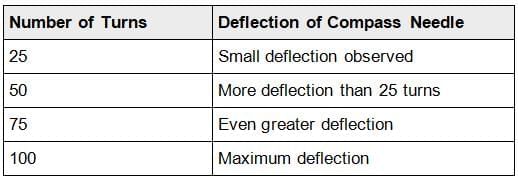
Q1: Make coils of turns 25, 50, 75, and 100. Connect them to the same cell one by one. Note the deflection in a magnetic compass placed in the same position in all the cases. Report your observations. Draw conclusion of the effect of number of turns of the coil on the strength of the electromagnet.
Ans: Activity and Observations: Coils are made with 25, 50, 75, and 100 turns, and each is connected to the same electric cell. A magnetic compass is placed near the end of each coil, and the deflection of the compass needle is observed.
Q2: Take two thin nichrome wires of equal length and different thickness (approximately one of these wire thickness to be double of the other, say 0.3 mm and 0.6 mm). Connect them one by one in a circuit which has a switch and a cell, and allow the current to flow for 30 s in each case. Momentarily touch these wires. Which wire heats up more? Now repeat the same activity with two nichrome wires of same diameter but of different lengths. Prepare a brief report of your activity.
Ans: Part 1: Same Length, Different Thickness
Two nichrome wires of the same length (example: 10 cm) but different thickness (0.3 mm and 0.6 mm) are used one by one in a circuit, and current flows for 30 seconds.
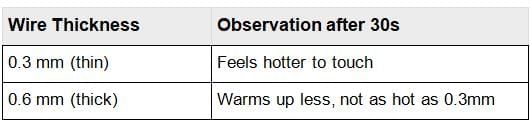
Result: The thinner nichrome wire (0.3 mm) becomes hotter than the thicker wire (0.6 mm), because thinner wires have higher resistance and produce more heat when current flows.
Part 2: Same Thickness, Different Lengths
Two wires of same thickness but different lengths (10 cm and 20 cm) are tested the same way.
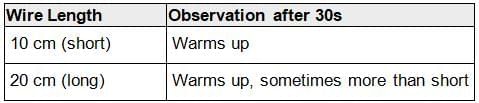
Result: The longer wire can become warmer because it has more resistance than the shorter wire.
Brief Report: Nichrome wires with more resistance (thinner or longer) heat up more when electric current flows through them. That is why thin and long wires are used as heating elements in appliances.
Q3: Try to make an electric cell using various fruits and vegetables. Also try with electrodes of different metals. Prepare a brief report.
Ans: Activity: Fruits like lemon, potato, and tomato are tried as electric cells by inserting two different metal strips (such as copper and zinc, or copper and iron) into them. Several fruits or vegetables may be connected in series to increase the power, and an LED or small bulb is connected to check if electricity is produced.
Observations:
- When copper and zinc metals are used in a lemon, the LED glows dimly.
- More lemons connected together make the LED glow brighter.
- With other fruits and vegetables such as potatoes and tomatoes, electricity is still produced, but lemons usually work the best because of their sour and acidic juice.
- If two metals that are far apart in reactivity (like zinc and copper) are used, the electricity produced is more.
- If plain water is tried instead of fruit, almost no electricity is produced.
Brief Report: Fruits like lemon or tomato, when combined with different metals, can act as simple electric cells and produce a small amount of electricity. The acidic juice in fruits helps in carrying the current. The choice of metals is important—combinations like zinc and copper are the best for making a fruit cell. This type of cell can glow a small bulb or LED if several are connected together, but they do not provide as much electricity as common batteries.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects NCERT Solutions - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the key differences between magnetic and heating effects of electricity? |  |
| 2. How does Ohm's law relate to the heating effect of electricity? |  |
| 3. What are some practical applications of the magnetic effects of electricity? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of electromagnetic induction and its significance? |  |
| 5. What safety measures should be taken to prevent accidents due to the heating effect of electricity? |  |















