Solved Question and Answer: Particulate Nature of Matter | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1. Why can you smell the perfume of incense sticks?
Ans. The particles of the perfume from incense sticks are not still; they are always moving. This movement allows them to drift through the air, making it possible for us to smell the fragrance. Incense Stick
Incense Stick
Q2. Why can not you smell its perfume at a short distance when the incense stick is not lighted ?
Ans. The particles of the perfume do not have enough energy to move through the air when the incense stick is unlit. As a result:
- The scent cannot be detected from a distance.
- Only when the stick is lit do the particles gain energy.
- This allows the fragrance to spread and be smelled from farther away.
Q3. Why is the smell of the perfume of incense stick fill the whole room in a few minutes, when lighted?
Ans. When the incense stick is lighted, the heat energy makes the particles of the perfume to move rapidly. Thus, they easily drift through the air in the room and hence we can smell it anywhere in the room.
Q4. When salt or sugar are poured into different kinds of vessels, why do they take the shape of vessels ?
Ans. Salt or sugar takes the shape of a containing vessel, but does not change its individual shape. For example, sugar crystals are cubical, and they remain cubical in any vessel.
Q5. Arrange the following substances in the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles water, sugar and oxygen.
Ans. In terms of the forces of attraction between particles, the substances can be arranged as follows:
- Oxygen - has the weakest attraction between particles.
- Water - has a moderate attraction.
- Sugar - has the strongest attraction among the three.
Thus, the increasing order is: Oxygen > Water > Sugar.
Q6. Give two reasons to justify.
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is solid at room temperature.
Ans.
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid because:
- The temperature of 25°C is above the freezing point of water, which is 0°C. At this temperature, water molecules have enough energy to move freely, allowing it to exist as a liquid.
- In its liquid state, water maintains a definite volume but takes the shape of its container, which is characteristic of liquids.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature because:
- It has a fixed shape and volume, which are typical properties of solids.
- The particles in an iron almirah are closely packed together, providing it with structural integrity and rigidity.
 Iron almirah
Iron almirah
- Thus, the molecules are held very, very tightly, with the result, the iron almirah has a definite shape and definite shape and definite volume, and hence, is a solid.
Q7. State your observation immediately after adding the blue ink drop.
Ans. After adding the drop of blue ink, the following observations can be made:
- The ink begins to trickle down the sides of the beaker.
- As it moves, the blue colour starts to diffuse into the water.
- This creates wavy blue streaks throughout the liquid.
 Diffusion of ink in water
Diffusion of ink in water
Q8. What happens around each crystal of solid on introducing it to water ?
Ans. When a crystal is introduced to water, a dense and deep violet colour forms around it. The size of this violet area is larger in hot water compared to cold water.
Q9. What happens as the time passes, and why?
Ans. The dense violet colour begins to diffuse into cold water, forming coloured streaks. Over time, the solution turns pink, with a darker hue near the base of the beaker. In contrast, when added to hot water, the violet colour diffuses rapidly, resulting in a more homogeneous pink solution compared to that in cold water.
Q10. What do you observe when force is applied and then removed on the plunger of the syringe containing water ? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans. The plunger does not move inward on the application of force. When the force is removed, the plunger does not move backward.
Reason: The liquids have small intermolecular spaces. Thus, they cannot be compressed.
Q11. What do you observe when force is applied and then removed on the plunger of the syringe containing air ? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans. The plunger moves downward on the application of force to a considerable length. When the force is removed, the plunger moves backward and takes its original position.
Reason: The gases have large intermolecular spaces. Thus, they easily get compressed on the application of force. The compressed gases are under high pressure. When the force is removed, this high pressure forces the plunger back to its original position.
Q12. Give reasons:
(a) A gas fills the vessel in which it is kept completely.
Ans. The molecules of a gas have large intermolecular spaces and kinetic energy, but extremely small intermolecular forces. Thus, the molecules of the gas spread in the entire space of the containing vessel on account of high kinetic energy and practically to intermolecular forces, hence filling entire space of the vessel.
(b) A wooden table should be called a solid.
Ans. Solids are rigid, incompressible, and have definite shape and volume. Since the table has all the above mentioned properties, therefore, it it solid.
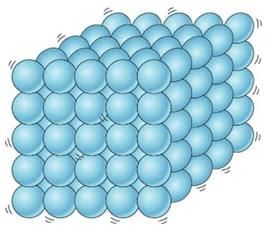 Particles in solids
Particles in solids
(c) We can easily move our hand in the air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Ans. The intermolecular forces between the molecules of a gas are almost negligible and intermolecular spaces are very large. Thus, we can easily move our hand in air, without any appreciable force.
The intermolecular forces between the molecules of a solid are very large and intermolecular spaces are very small. Thus, a lot of force is required to separate the molecules of a solid. It is for the same reasons that we need karate expert to break a block of wood.
Q13. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. (Density = Mass / Volume). Arrange the following in the order of increasing density: air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Ans. Exhaust from chimneys, air, cotton, water, honey and iron.
Example:
(i) CNG (compressed Natural gas) is used as fuel in internal combustion engines.
(ii) Oxygen in compressed form is supplied to hospitals for serious patients in cylinders.
(iii) LPG (Liquefied petroleum gas) which is used in home for cooking.
Q14. The diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool.
Ans. The diver can cut through water in a swimming pool due to the following reasons:
- The particles in water are not tightly packed; there are spaces between them.
- The attractive forces between water molecules are relatively weak.
- When the diver applies force, they displace the water, allowing them to move through it.
Q15. Why does ice float on water?
Ans. Ice floats on water because of its unique structure. Here are the key points:
- Typically, solids are denser than liquids.
- However, ice has a specific structure that creates larger spaces between its particles.
- This structure results in a lower density compared to liquid water.
- As a result, ice is able to float on water.
 Ice floats on water
Ice floats on water
Q16. Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid why
Ans. Naphthalene balls disappear over time without leaving any solid residue because they are volatile and sublime.
- Volatile: Naphthalene easily transitions from solid to gas at room temperature.
- Sublimation: This process allows the solid to change directly into vapour without becoming a liquid.
 Naphthalene Balls
Naphthalene Balls
Therefore, it changes into vapors completely, which disappear into the air, and no solid is left.
|
54 videos|256 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Solved Question and Answer: Particulate Nature of Matter - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the particulate nature of matter? |  |
| 2. How does temperature affect the movement of particles in matter? |  |
| 3. What are the different states of matter, and how do they differ in terms of particle arrangement? |  |
| 4. Can you explain how diffusion occurs at the particle level? |  |
| 5. What experiments support the theory of the particulate nature of matter? |  |
















