Assignment: Particulate Nature of Matter | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Short Question/Answer (Q&A) |

|
| Activity-Based Question |

|
| Research-Based Question |

|
| Think & Explain |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. What happens to the particles of matter when the temperature increases?
(a) They become larger
(b) They move faster
(c) They become denser
(d) They stop moving
Ans: (b)
As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of particles increases, causing them to move faster.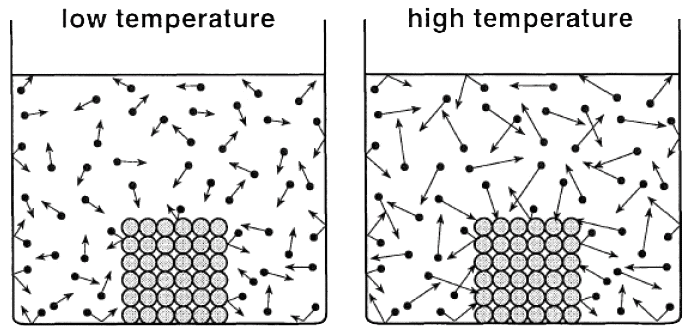
Q2. Which of the following is an example of sublimation?
(a) Ice melting
(b) Water boiling
(c) Camphor turning into gas
(d) Water freezing
Ans: (c) Camphor turning into gas
Sublimation is the direct change of a solid to gas without passing through the liquid state, as seen in camphor.
Q3. What state of matter is water at 0°C?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) Plasma
Ans: (a) Solid
Water freezes into solid ice at 0°C.
Q4. What is the change of state from liquid to gas called?
(a) Melting
(b) Condensation
(c) Boiling
(d) Freezing
Ans: (c) Boiling
Boiling is the change of a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
Short Question/Answer (Q&A)
Q1. What is the physical state of water at 100°C?
Ans: Water is in the gas state (steam) at 100°C.
Q2. What is diffusion?
Ans: Diffusion is the process where particles of one substance mix with particles of another substance, moving into spaces between the particles of the other.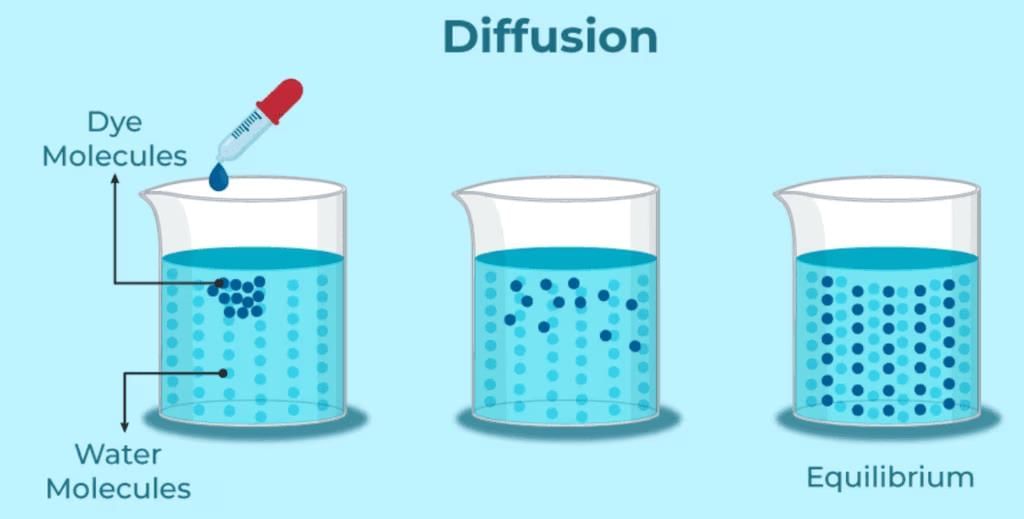
Q3. Why do ice cubes melt when taken out of the freezer?
Ans: Ice melts when it absorbs heat from the surrounding air, increasing the kinetic energy of its particles until they break free from their fixed positions.
Q4. Why does a balloon fill up with air?
Ans: Gases have high compressibility, meaning they can be packed into small spaces, like inside a balloon.
Activity-Based Question
Q. Take one spoon of salt and add it to one glass of water. What happened when you dissolved salt in water? Which property of matter is concluded from this activity?
Ans: When salt is added to water, it dissolves, meaning its particles break apart and spread out evenly between the water particles. As a result, the water level may rise slightly, but the salt becomes invisible as it dissolves. This demonstrates that matter is made up of tiny particles that can interact and mix with each other.
Property of Matter: This activity shows that matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that can mix with other substances, which is an example of the intermolecular interactions property of matter.
Research-Based Question
Q. Research and submit a research paper: How can the state of the matter be changed?
Ans: Matter exists in various states—solid, liquid, gas, and plasma—each characterized by distinct physical properties. The transformation between these states, known as phase transitions, is fundamental to numerous natural processes and technological applications. This paper explores the mechanisms underlying these transitions, focusing on the roles of temperature, pressure, and energy changes. Additionally, it examines recent discoveries of novel states of matter resulting from extreme conditions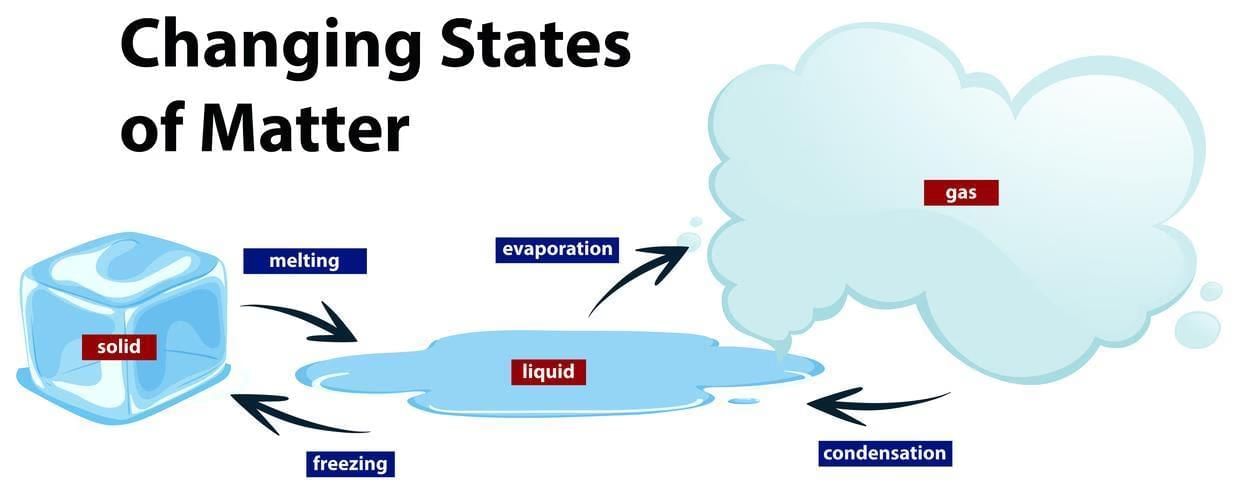
Introduction
The study of matter's states and their transitions is a cornerstone of physical science, influencing fields ranging from material engineering to cosmology. Understanding how matter changes state provides insights into both everyday phenomena and exotic cosmic events.
Fundamental States of Matter
- Solids: Characterized by fixed shapes and volumes due to closely packed particles with limited movement.
- Liquids: Have defined volumes but no fixed shapes, with particles that are close together but can flow.
- Gases: Lack both fixed shape and volume, with widely spaced particles moving freely.
- Plasma: An ionized state of matter found naturally in stars, consisting of free electrons and ions.
Mechanisms of State Transitions
- Melting (Solid to Liquid): Occurs when a solid absorbs heat, causing particles to vibrate more vigorously until they overcome their fixed positions, transitioning into a liquid state.
- Freezing (Liquid to Solid): Involves the removal of heat from a liquid, allowing particles to slow down and arrange into a structured, fixed lattice.
- Vaporization (Liquid to Gas): Occurs through evaporation or boiling when liquid particles gain sufficient energy to escape into the gaseous phase.
- Condensation (Gas to Liquid): The process by which gas particles lose energy and aggregate to form a liquid.
- Sublimation (Solid to Gas): A direct transition from solid to gas without passing through the liquid phase, observed in substances like dry ice (solid CO₂).
- Deposition (Gas to Solid): The reverse of sublimation, where gas particles directly form a solid without becoming liquid first.
Influence of Temperature and Pressure
Temperature and pressure are critical factors influencing state transitions:
- Temperature: An increase in temperature generally provides the energy needed for particles to overcome intermolecular forces, leading to transitions like melting and vaporization. Conversely, lowering the temperature can cause condensation and freezing.
- Pressure: Altering pressure can induce state changes. For example, increasing pressure can cause gases to liquefy, while decreasing pressure can allow solids to sublimate.
Think & Explain
Q: Imagine you have a cup of ice and a cup of hot water. Both are placed in a room at the same temperature. Why do you think the ice melts while the hot water cools down to room temperature?
Ans: When you place the ice in a room, it starts melting because the heat from the surroundings (the room temperature) flows into the ice. The ice is initially very cold, and the particles in the ice are tightly packed and do not move much. But when the heat energy from the surroundings enters the ice, it makes the particles in the ice vibrate more and more, eventually causing them to break free from their fixed positions. This causes the solid ice to turn into liquid water.
On the other hand, when hot water is placed in the same room, its particles are moving quickly, meaning they have a lot of energy. The surrounding air (which is at room temperature) transfers heat away from the hot water. As the heat leaves the water, the particles slow down, causing the water to cool down to room temperature. Both processes happen because energy moves from the warmer object (the hot water or the ice) to the cooler surroundings until everything reaches the same temperature.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Assignment: Particulate Nature of Matter - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the particulate nature of matter? |  |
| 2. How do particles behave in different states of matter? |  |
| 3. What role does temperature play in the behavior of particles? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of diffusion in relation to the particulate nature of matter? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding the particulate nature of matter important in science? |  |















