Short Question Answer: Particulate Nature of Matter | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1: Give two reasons to justify -
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
Ans: For a temperature of <0 ⁰Cwater is in solid-state, for 0⁰C → 100⁰C → water is in a liquid state and for temperature >100 ⁰C water is in a gaseous state. Since room temperature always lies between 0 ⁰C and 100 ⁰C and within this range the physical state of water is liquid so water is liquid at room temperature.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Ans: Since the room temperature is very less than the melting point of iron hence an almirah made up of iron will be a solid at room temperature.
Q2: What happens when we apply pressure to the particles of matter?
Ans: Pressure is defined as the force applied per unit area. When we apply pressure to the particles of matter:
- The force pushes the particles closer together.
- This can lead to changes in the state of matter.
- In gases, increased pressure can compress the particles.
Overall, applying pressure affects the arrangement and movement of particles in different states of matter.
Q3: If the melting point of object A is high then what state do you expect it to be at room temperature?
Ans: If an object has a high melting point, it will remain in a solid state at room temperature. This is because:
- The melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
- At temperatures below the melting point, the substance stays solid.
Therefore, a high melting point indicates that the object will not melt at typical room temperatures.
Q4: When heat is being supplied to a solid, then what does the heat energy do to the particles of the solid?
Ans: When heat is supplied to a solid:
- The kinetic energy of the particles increases.
- This increase allows the particles to overcome the forces of attraction holding them in place.
- As a result, the particles start to move more freely.
- Eventually, the solid melts and transforms into a liquid.
Q5: Why do we say that evaporation is a surface phenomenon?
Ans: Evaporation is known as a surface phenomenon because:
- Only the particles at the surface of a liquid can absorb energy.
- These particles gain enough energy to break free from the liquid and turn into vapour.
- This process occurs without the liquid reaching its boiling point.
Q6: Which of the following matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, the smell of perfume.
Ans: As we can define matter as any ‘physical substance’, hence almonds, air, chair, the smell of perfume, cold drink and smell can be considered as matter.
Q7: What is the physical state of water at:
(a) A temperature of 250 ⁰C
Ans: The boiling point of water is 100 ⁰C, hence the physical state of water at 250⁰C will be gaseous.
(b) A temperature of 100 ⁰C
Ans: The boiling point of water is 100 ⁰C, hence at 100 ⁰C water is in the gaseous state.
Q8: What is the physical state of water at-
(a) A temperature of 25 ⁰C?
Ans: The physical state of water at 25 ⁰C is liquid.
(b) A temperature of ⁰C?
Ans: The physical state of water at ⁰C is solid.
(c) A temperature of 100⁰C?
Ans: The physical state of water at 100⁰C is gas.
Q9: Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) boiling is a bulk phenomenon and evaporation is a surface phenomenon
(b) boiling is a surface phenomenon and evaporation is a bulk phenomenon
(c) boiling and evaporation both are a surface phenomenon
(d) boiling and surface both are bulk phenomenon
Ans: The correct option is (a) boiling is a bulk phenomenon and evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
Evaporation, on the other hand, is a surface phenomenon. It occurs only at the surface of the liquid, where molecules gain enough energy to escape into the gaseous phase.
So, boiling involves the conversion of a liquid into a gas throughout its bulk, while evaporation involves the conversion of liquid into a gas at its surface.
Q10: Which of the following has the least inter atomic spacing?
(a) solid
(b) liquid
(c) gases
(d) plasma
Ans: The correct option is (a), solid.
In a solid, the atoms or molecules are closely packed together, which results in the least interatomic spacing compared to the other states of matter. In a liquid, the particles have more space between them than in a solid, while gases have even greater intermolecular spacing. Plasma is an ionized gas with very high temperatures, and it can have significant spacing between ions and electrons as well.
Q11: Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meters away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Ans: The smell of hot sizzling food travels quickly because:
- The temperature of hot food is higher, causing particles to move faster.
- Higher temperatures increase the diffusion rate of particles, allowing the aroma to spread quickly.
- In contrast, cold food has a lower temperature, resulting in a slower diffusion rate.
- Thus, the smell of hot food can reach us from several metres away, while cold food requires proximity.
Q12: Liquids generally have a lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Ans: Ice floats on the water since there is a large empty space inside the 3D structure of ice due to which it becomes less in weight as compared to water and can float on water.
Q13: Give a reason for the following observations. We can get the smell of perfume sitting several meters away.
Ans: Volatile substances such as perfumes change from liquid state to gaseous state very fast which allows them to diffuse and mix up with the air particles to reach our nostrils. Therefore we get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Q14: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Ans: Ice will be producing a more intense cooling effect as compared to water at 273 K because at 273 K ice will be absorbing latent heat of melting from the surroundings and will be getting converted into water. Therefore ice at 273 K is more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature.
Q15: What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Ans: The particles of matter have the following characteristics:
(i) The particles of matter are in continuous motion.
(ii) There are gaps between the particles of matter.
(iii) There is a force of attraction between the particles of matter which keeps them together.
Q16: Give reasons
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
Ans: The particles of gas have negligible attraction force between them because of which the particles move freely in all directions filling the whole container the gas is kept in.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Ans: The particles of gas move freely due to which they collide with the container walls continuously and randomly. Therefore the collision of particles on the container walls exerts pressure on the walls.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
Ans: Solids have rigid and fixed particles and have a definite shape and clear boundaries. Since a wooden table possesses all the qualities of a solid, it should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in the air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Ans: Since air is a gas and the forces of attraction between the particles of gas are very less which makes it easy to separate the particles with the help of an external force and hence we can easily move our hand in the air. Whereas in the case of solids the forces of attraction are very strong and we need a very high force to separate the particles of a solid and hence we need a karate expert for it.
Q17: Are the three states of matter inter-convertible? How can they interconnect?
Ans: Yes, the three states of matter can be converted into each other.
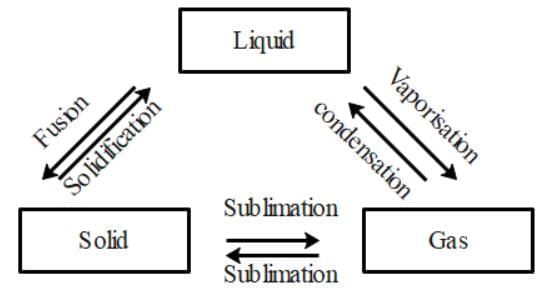
The three states of matter are interconvertible as shown below:
(a) By heating we can convert solids into liquids and by cooling we can convert liquids into solids.
(b) We can convert liquids into gases by vaporization and we can convert gases to liquids by condensation.
(c) Using sublimation we can convert solids into gases and vice versa and using condensation we can convert liquids into solids.
Q18: Why is it that to smell cold food, we have to go close but the smell of hot food reaches us several meters away?
Ans: When the particles are at higher temperature, their movements are fast and therefore they can travel up to several meters. Hence the hot food’s smell will be reaching us several meters away.
At lower temperatures, the movements of particles are not very fast and particles do not have enough kinetic energy to travel a distance of several meters. Therefore we have to go close to smell cold food.
Q19: What is the state of inter particle distance inside a solid, liquid, and gas?
Ans: In a solid, the forces of attraction between the particles are very high and hence the particles of a solid will be very close to each other and the inter particle distance is the least.
- In a liquid, the forces of attraction between the particles are very weak, and therefore the particles of a liquid will not be closely packed with each other and the inter-particle distance is large.
- In a gas, the forces of attraction between the particles are almost negligible or extremely weak and therefore the particles of a gas are very loosely packed and are very far from each other and the inter particle distance is largest.
Q20: (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
Ans: Tabular differences in characteristics of matters are given below: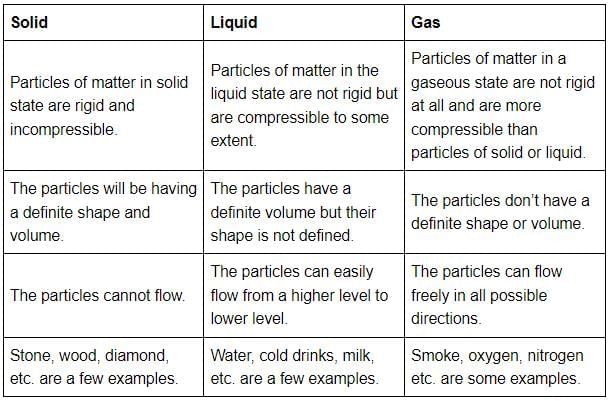 (b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Ans:
- Rigidity → The property of matter to maintain its shape when external forces are applied to it is known as rigidity. Solids have this property.
- Compressibility → The property of matter to allow compression when high pressure is applied to it is known as compressibility. Some Liquids and all gases have this property.
- Fluidity → The property of matter to flow and change in its shape when external forces are applied to it is known as fluidity. Both liquids and gases have this property.
- Filling a gas container → Gases are fluid in nature and are highly compressible which allows them to be filled within a vessel at high pressure. A large volume of gas can be filled in a container of less volume making it suitable and more cost-efficient for transportation.
- Shape → Only solid objects have well-defined shapes while liquids can acquire any shape depending on the container they are kept in and gases don’t have any shape.
- Kinetic energy → The particles of a matter are continuously in motion and thus have kinetic energy. As the particles in solids have the least movement, the kinetic energy of solids is the least. The particles of gases have the freest movements and hence they have the highest kinetic energy. The order of kinetic energies for different types of matters is: solid < liquid < gas
- Density → Density of any substance can be explained as Mass per unit volume i.e. density = mass/volume.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short Question Answer: Particulate Nature of Matter - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the particulate nature of matter? |  |
| 2. How does the particulate nature of matter explain the states of matter? |  |
| 3. What are some characteristics of particles in different states of matter? |  |
| 4. Who were some key scientists in the development of the particulate theory of matter? |  |
| 5. How does temperature affect the movement of particles in matter? |  |
















