Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT > NCERT Solutions: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions
The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions NCERT Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Probe and Ponder (Page 134) |

|
| InText (Pages 135-145) |

|
| Keep the curiosity alive (Pages 149 - 151) |

|
| Discover, design, and debate (Page 151) |

|
Probe and Ponder (Page 134)

Q1: What do you think is happening in the picture above?
- The picture shows Mahatma Gandhi obtaining salt from the sea during the Salt March, accompanied by followers.
- This illustrates the historical process of extracting salt from seawater through evaporation, where seawater acts as a natural solution with salt as the solute and water as the solvent, highlighting concepts of solubility and traditional salt production.
Q2: What happens when you add too much sugar to your tea and it stops dissolving? How can you solve this problem?
Ans:
- When too much sugar is added, the tea becomes a saturated solution, and excess sugar settles at the bottom as it can no longer dissolve at that temperature.
- To solve this, heat the tea to increase the solubility of sugar, allowing more to dissolve, as solubility generally increases with temperature for solids in liquids.
Q3: Why do sugar and salt dissolve in water but not in oil? Why is water considered a good solvent?
Ans: Sugar and salt dissolve in water because water mixes evenly with many substances and can break them down into smaller particles, forming a uniform solution.
They do not dissolve in oil because oil cannot mix well with them.
Water is considered a good solvent because it can dissolve a large number of substances, so it is often called a universal solvent.
 Mixture of sugar,salt and water
Mixture of sugar,salt and water
Q4: Why are water bottles usually tall and cylindrical in shape instead of spherical?
Ans:
- Water bottles are tall and cylindrical as they are easy to hold, store, and use efficiently.
- They provide better grip, stability, and use less material for the same volume compared to spheres, which would roll and be harder to handle.
Q5: Share your questions
Ans: Based on the chapter, potential questions could include:
- How does temperature affect the solubility of gases differently from solids?
- Why does ice float on water despite being a solid?
- What role does density play in everyday phenomena like hot air balloons?
InText (Pages 135-145)
Q1: We know air is a mixture. Would a mixture of gases also be considered a solution? (Page 135)
Ans: Yes, if it is a uniform mixture.
Q2: What will happen if we keep adding more salt to a given amount of water? (Page 136)
Ans: The salt will dissolve until the solution becomes saturated; extra salt will remain undissolved.
Q3: Do gases also dissolve in water? (Page 139)
Ans: Oxygen dissolves in water only in small amounts.
Q4: Why are measuring cylinders always designed narrow and tall instead of wider and shorter like a beaker? (Page 144)
Ans: Narrow and tall cylinders give a more accurate measurement of volume.
Q5: I wonder how the level of a coloured liquid is measured? (Page 145)
Ans: In the case of coloured liquid, the mark on the measuring cylinder should coincide with the top of the meniscus.
Keep the curiosity alive (Pages 149 - 151)
Q1: State whether the statements given below are True [T] or False [F]. Correct the false statement(s).
(i) Oxygen gas is more soluble in hot water rather than in cold water.
Ans: False
Oxygen is more soluble in cold water.
(ii) A mixture of sand and water is a solution.
Ans: False
A Mixture of sand and water is not a solution. Sand does not dissolve in water but settles down.
(iii) The amount of space occupied by any object is called its mass.
Ans: False
The amount of space occupied by any object is called its volume.
(iv) An unsaturated solution has more solute dissolved than a saturated solution.
Ans: False
A saturated solution has more solute dissolved than an unsaturated solution.
(v) The mixture of different gases in the atmosphere is also a solution.
Ans: True
The mixture of different gases in the atmosphere is a solution, with nitrogen as the solvent.
Q2: Fill in the blanks.
(i) The volume of a solid can be measured by the method of displacement, where the solid is __________ in water and the ____________ in water level is measured.
Ans: (i) The volume of a solid can be measured by the method of displacement, where the solid is placed in water and the rise in water level is measured.
(ii) The maximum amount of _______________ dissolved in _______________ at a particular temperature is called solubility at that temperature.
Ans: The maximum amount of solute dissolved in solvent at a particular temperature is called solubility at that temperature.
(iii) Generally, the density ____________ with increase in temperature.
Ans: Generally, the density decreases with increase in temperature.
(iv) The solution in which glucose has completely dissolved in water, and no more glucose can dissolve at a given temperature, is called a __________ solution of glucose.
Ans: The solution in which glucose has completely dissolved in water, and no more glucose can dissolve at a given temperature, is called a saturated solution of glucose.
Q3: You pour oil into a glass containing some water. The oil floats on top. What does this tell you?
(i) Oil is denser than water
(ii) Water is denser than oil
(iii) Oil and water have the same density
(iv) Oil dissolves in water
Ans: (ii) Water is denser than oil.
Oil floats because its density is lower than water's, causing less dense substances to float on denser ones.
Q4: A stone sculpture weighs 225 g and has a volume of 90 cm³. Calculate its density and predict whether it will float or sink in water.
Ans: Density = Mass / Volume = 225 g / 90 cm³ = 2.5 g/cm³.
Since this is greater than water's density (1 g/cm³), the sculpture will sink in water.
Q5: Which one of the following is the most appropriate statement, and why are the other statements not appropriate?
(i) A saturated solution can still dissolve more solute at a given temperature.
(ii) An unsaturated solution has dissolved the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature.
(iii) No more solute can be dissolved into the saturated solution at that temperature.
(iv) A saturated solution forms only at high temperatures.
Ans: Statement (iii) is most appropriate.
(i) It is not appropriate as a saturated solution cannot dissolve more solute at a given temperature.
(ii) An unsaturated solution can have more solute dissolved at a given temperature.
(iii) Correct.
(iv) A Saturated solution can be formed at all temperatures.
Q6: You have a bottle with a volume of 2 litres. You pour 500 mL of water into it. How much more water can the bottle hold?
Ans: The bottle of 2 litres capacity can hold 1500 mL more of water besides 500 mL.
Q7: An object has a mass of 400 g and a volume of 40 cm³. What is its density?
Ans: Density = Mass / Volume = 400 g / 40 cm³ = 10 g/cm³.
Q8: Analyse Fig. 9.25a and 9.25b. Why does the unpeeled orange float, while the peeled one sinks? Explain.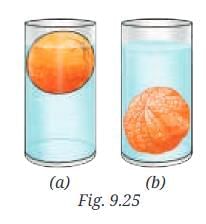 Ans: An unpeeled orange displaces more water, and so it floats. Peeled orange displaces less water than its weight, so it sinks.
Ans: An unpeeled orange displaces more water, and so it floats. Peeled orange displaces less water than its weight, so it sinks.
Q9: Object A has a mass of 200 g and a volume of 40 cm³. Object B has a mass of 240 g and a volume of 60 cm³. Which object is denser?
Ans: Density of A: 200 g / 40 cm³ = 5 g/cm³.
Density of B: 240 g / 60 cm³ = 4 g/cm³.
Conclusion: Object A is denser, having more density than B.
Q10: Reema has a piece of modeling clay that weighs 120 g. She first moulds it into a compact cube that has a volume of 60 cm³. Later, she flattens it into a thin sheet. Predict what will happen to its density.
Ans: The density of the modeling clay will not change. Density is an intrinsic property of a substance. When Reema flattens the clay, she changes its shape, but she doesn’t change the amount of matter (its mass, 120 g) or the space it takes up (its volume, 60 cm³). Since both the mass and the volume remain the same, its density (120 g / 60 cm³ = 2 g/cm³) also remains exactly the same.
Q11: A block of iron has a mass of 600 g and a density of 7.9 g/cm³. What is its volume?
Ans: We know density = mass / volume
∴ Volume = Mass / Density = 600 g / 7.9 g/cm³ ≈ 75.94 cm³.
Q12: You are provided with an experimental setup as shown in Fig. 9.26a and 9.26b. On keeping the test tube (Fig 9.26b) in a beaker containing hot water (~70 °C), the water level in the glass tube rises. How does it affect the density?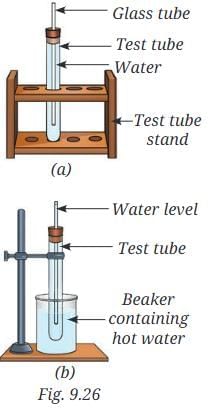 Ans: The density of water in setup (b) will decrease.
Ans: The density of water in setup (b) will decrease.
Discover, design, and debate (Page 151)
Q1: Research project on Dead Sea: Why is there no aquatic life in the Dead Sea? Try to find out if there are any other similar water bodies.
Ans: The Dead Sea is super salty—about 34% salt! That's way too much for most fish, plants, or animals to live there because the salt pulls water out of their bodies, stressing them out. Only tough bacteria can survive. This happens because the water evaporates a lot, leaving salt behind, and there's no river to wash it away. Other places like this are the Great Salt Lake in Utah, USA (too salty for most life), and Lake Assal in Djibouti (one of the saltiest spots on Earth with very few living things).
Q2: Investigate how well common salt dissolves in different solvents, such as water, vinegar, and oil. Compare the solubility of salt in each solvent and record your observations.
Ans: When common salt is added to different solvents, its solubility varies:
- In water: Salt dissolves completely and forms a clear solution. Water is an excellent solvent for salt because it can mix evenly and spread the salt particles throughout.
- In vinegar: Some salt dissolves, but not as much as in water. The solution may appear slightly cloudy because vinegar can only dissolve salt to a limited extent.
- In oil: Salt does not dissolve at all and settles at the bottom. Oil cannot mix with salt, so no solution is formed.
Observation:
Water shows the highest solubility for salt, vinegar shows partial solubility, and oil shows no solubility. This proves that water is the best solvent for common salt among the three.
Q3: Debate in class—Is water truly the most versatile solvent?
Ans: Let's debate!
Yes side: Water is awesome because it's polar, so it can dissolve salts, sugars, gases, and more. It helps in our blood, oceans, and even rain—keeping life going!
No side: Water isn't perfect—it can't dissolve oily stuff like fats or petrol. Other solvents like alcohol (ethanol) can handle both watery and oily things better in some cases, like in medicines or cleaning.
Conclusion: Water is super useful for many things, but it's not the only star—it depends on what you're trying to dissolve.
The document The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions NCERT Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions NCERT Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are solutes, solvents, and solutions? |  |
Ans. Solutes are substances that are dissolved in a solvent to form a solution. The solvent is the substance that dissolves the solute. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of solutes and solvents, where the solute particles are uniformly distributed throughout the solvent.
| 2. How does temperature affect the solubility of a solute? |  |
Ans. Temperature generally affects the solubility of solids and gases in liquids. For most solid solutes, solubility increases with an increase in temperature; this means that more solute can dissolve in the solvent at higher temperatures. Conversely, the solubility of gases typically decreases with an increase in temperature, as warmer temperatures tend to allow gas particles to escape from the liquid.
| 3. What are some common examples of solutions in daily life? |  |
Ans. Common examples of solutions in daily life include saltwater (where salt is the solute and water is the solvent), sugar dissolved in tea or coffee, and vinegar (which is a solution of acetic acid in water). These solutions are important for cooking, cleaning, and various chemical reactions.
| 4. What is the difference between a saturated solution and an unsaturated solution? |  |
Ans. A saturated solution is one in which no more solute can dissolve at a given temperature, meaning it has reached its maximum concentration of solute. An unsaturated solution, on the other hand, is one where more solute can still be dissolved. In other words, an unsaturated solution has not yet reached the limit of solute that can be dissolved in the solvent.
| 5. Why is it important to understand the concept of solutions in science? |  |
Ans. Understanding solutions is crucial in science because many chemical reactions occur in solution. Knowledge of solutes, solvents, and solutions is essential for fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science. It helps in understanding processes like digestion, chemical reactions in laboratories, and the behavior of substances in natural water bodies.
Related Searches















