Light: Mirrors and Lenses NCERT Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Probe and Ponder (Page 152) |

|
| InText (Page 155 - 165) |

|
| Keep the Curiosity Alive (Page 165 - 169) |

|
| Discover, Design, and Debate (Page 169) |

|
Probe and Ponder (Page 152)
Q1: Can we make mirrors which can give enlarged or diminished images?
Ans: Yes, we can make mirrors that produce enlarged or diminished images. Specifically, concave mirrors can form both enlarged and diminished images depending on the object’s distance from the mirror, while convex mirrors always produce diminished images.
Q2: On side-view mirrors of vehicles, there is a warning that says "Objects in mirror are closer than they appear". Why is this warning written there?
Ans: The warning “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear” is written on the side-view mirrors of vehicles because these mirrors are typically convex. Convex mirrors make objects appear smaller and farther away than they are, which can lead to misjudging distances. The warning is there to alert drivers to this effect and prevent accidents caused by inaccurate distance perception. Side View MirrorQ3: Why is there a curved line on some reading glasses?
Side View MirrorQ3: Why is there a curved line on some reading glasses?
Ans: The curved line on reading glasses is due to the convex shape of the lens. These lenses are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges, causing light rays to converge (bend inward) and improve near vision for individuals with presbyopia. This curvature is essential for correcting the vision by focusing light properly on the retina.
Q4: Share your questions _______________
Ans: Here are some fun questions you might think of from the chapter:
- How does a magnifying glass make things look bigger?
- Why do spoons act like funny mirrors?
- Can lenses in our eyes change shape?
- What happens if you use a concave mirror to focus sunlight?
InText (Page 155 - 165)
Q1: How can we distinguish between concave and convex mirrors? (Page 155)
Ans: To distinguish between concave and convex mirrors, observe how they reflect light and the images they form. Concave mirrors curve inward, causing parallel light rays to converge at a focal point, and can form both real and virtual images. Convex mirrors curve outward, causing parallel light rays to diverge, and always form virtual, diminished images.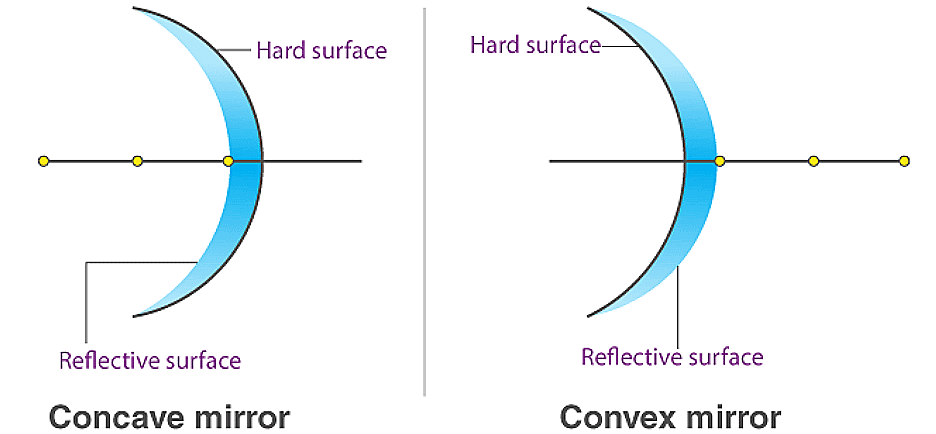
Q2: We have observed images formed by three types of mirrors – plane, concave, and convex. But are there any laws that govern the image formation? (Page 157)
Ans: Yes, some laws govern image formation by mirrors, including plane, concave, and convex mirrors. These laws are based on the laws of reflection, which state that the angle of incidence (the angle at which light hits the mirror) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which light bounces off the mirror). Additionally, the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal (an imaginary line perpendicular to the mirror’s surface at the point of incidence) all lie in the same plane.
Q3: Are the laws of reflection applicable to spherical mirrors also? (Page 160)
Ans: Yes, the laws of reflection apply to spherical mirrors. These laws state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane. These laws hold for all types of reflecting surfaces, including spherical mirrors like concave and convex mirrors.
Q4: What changes can be seen in the objects when viewed through lenses? (Page 163)
Ans: When an object is viewed through a lens, several changes can be observed in its image compared to the object itself. The most common changes include alterations in size, orientation, and whether the image is real or virtual. Specifically, concave lenses typically produce diminished, virtual, and upright (erect) images.
Q5: Do lenses also converge or diverge the light beam? (Page 163)
Ans: Yes, lenses can both converge and diverge light beams. Convex lenses converge (focus) light, while concave lenses diverge (spread out) light.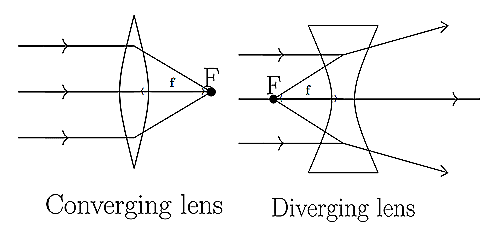
Q6: Since a convex lens converges a light beam, can it also burn a paper? (Page 164)
Ans: Yes. In simple terms, the convex lens acts like a magnifying glass, focusing the sun’s rays and intensifying the heat at a specific spot, which can be enough to ignite a flammable material like paper.
Q7: Where are all the lenses used? (Page 165)
Ans: Lenses are used in a variety of applications, both in everyday life and in scientific instruments. These include eyeglasses, cameras, microscopes, telescopes, and projectors, as well as simple magnifying glasses and spyholes indoors.
Keep the Curiosity Alive (Page 165 - 169)
Q1: A light ray is incident on a mirror and gets reflected by it (Fig. 10.21). The angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the mirror is 40°. What is the angle made by the reflected ray with the mirror?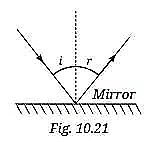
(i) 40°
(ii) 50°
(iii) 45°
(iv) 60°
Ans: (ii) 50°
If the incident ray makes a 40° angle with the normal, then:
Angle of incidence (i) = 40°
According to the law of reflection,
Angle of reflection (r) = Angle of incidence (i) = 40°
Now, Angle between reflected ray and mirror = 90° – angle of reflection
= 90° – 40°
= 50°
Q2: Fig. 10.22 shows three different situations where a light ray falls on a mirror: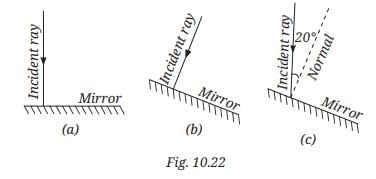 (i) The light ray falls along the normal
(i) The light ray falls along the normal
(ii) The mirror is tilted, but the light ray still falls along the normal to the tilted surface.
(iii) The mirror is tilted, and the light ray falls at an angle of 20° from the normal.
Draw the reflected ray in each case (Use a ruler and protractor for accurate drawing). What is the angle of reflection in each case?
Ans: (i) Light ray falls along the normal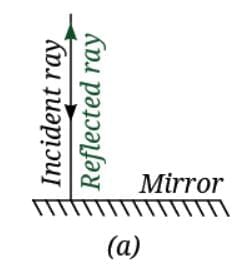
Angle of incidence = 0°
Angle of reflection = 0°
The ray retraces its path. It reflects straight back along the same line.
(ii) The mirror is tilted, but the light ray still falls along the normal to the tilted surface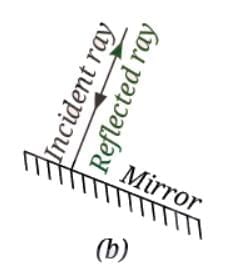
Even though the mirror is tilted, the ray is still perpendicular to the surface.
Angle of incidence = 0°
Angle of reflection = 0°
The ray again retraces its path — the tilt doesn’t affect the reflection if the ray is normal to the surface.
(iii) The mirror is tilted, and the light ray falls at 20° from the normal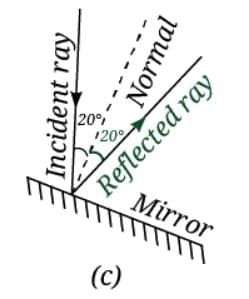
Angle of incidence = 20°
By the law of reflection:
Angle of reflection = 20°
The reflected ray will make a 20° angle with the normal, on the opposite side.
Q3: In Fig. 10.23, the cap of a sketch pen is placed in front of three types of mirrors. Match each image with the correct mirror.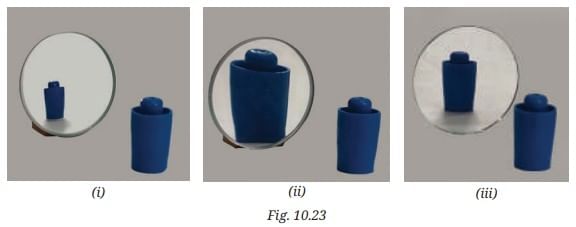
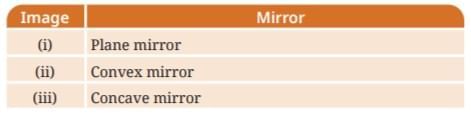
Ans: 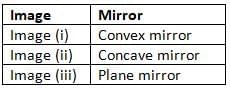
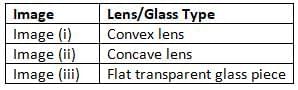
Q4: In Fig. 10.24 the cap of a sketch pen is placed behind a convex lens, a concave lens, and a flat transparent glass piece — all at the same distance. Match each image with the correct type of lens or glass.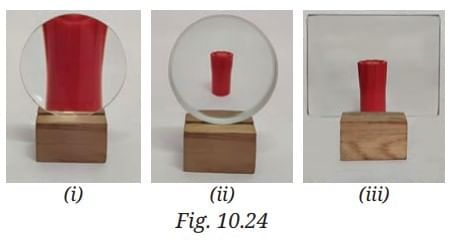
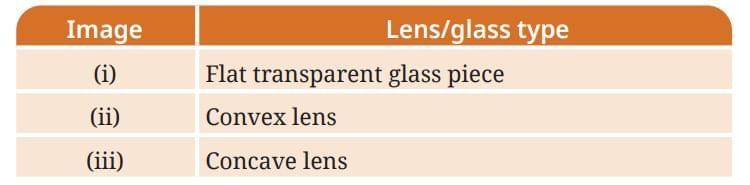
Ans:
Q5: When the light is incident along the normal on the mirror, which of the following statements is true:
(i) Angle of incidence is 90°
(ii) Angle of incidence is 0°
(iii) Angle of reflection is 90°
(iv) No reflection of light takes place in this case
Ans: (ii) Angle of incidence is 0°.
When light hits a surface at a 90° angle (perpendicular), it is considered to be incident normally.
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection: In reflection, the angle of the reflected light is always equal to the angle of the incident light. Since the light is hitting the mirror normally (at a 0° angle), the reflected light will also be at a 0° angle.
Q6: Three mirrors—plane, concave and convex are placed in Fig. 10.25. On the basis of the images of the graph sheet formed in the mirrors, identify the mirrors and write their names above the mirrors.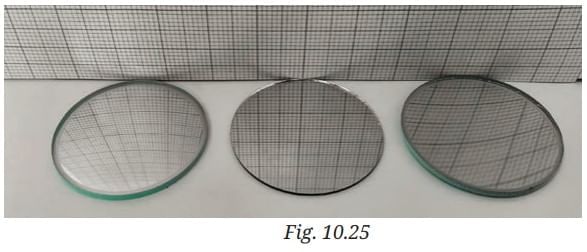 Ans:
Ans: 
Q7: In a museum, a woman walks towards a large convex mirror (Fig. 10.26). She will see that:
(i) her erect image keeps decreasing in size.
(ii) her inverted image keeps decreasing in size.
(iii) her inverted image keeps increasing in size and eventually it becomes erect and magnified.
(iv) her erect image keeps increasing in size.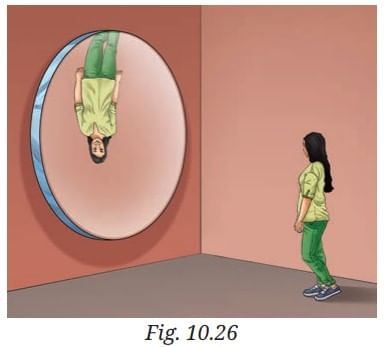
Ans: (i) her erect image keeps decreasing in size.
Because a convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image.
Q8: Hold a magnifying glass over text and identify the distance where you can see the text bigger than they are written. Now move it away from the text. What do you notice? Which type of lens is a magnifying glass?
Ans: A magnifying glass uses a convex lens to make text appear larger. When we hold the magnifying glass close to the text and then slowly move it away, the image of the text will first appear larger and sharper, then progressively get larger and more blurred, and finally invert and appear smaller again.
Q9: Match the entries in Column I with those in Column II.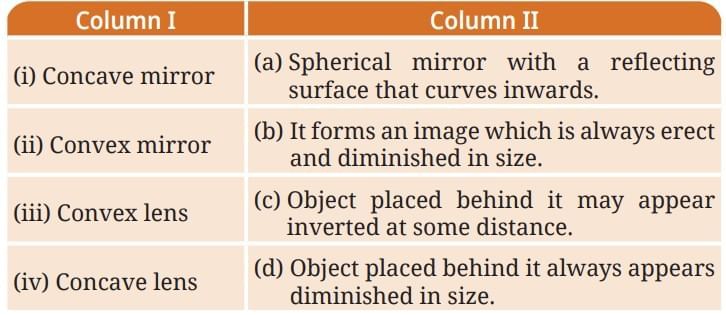
Ans: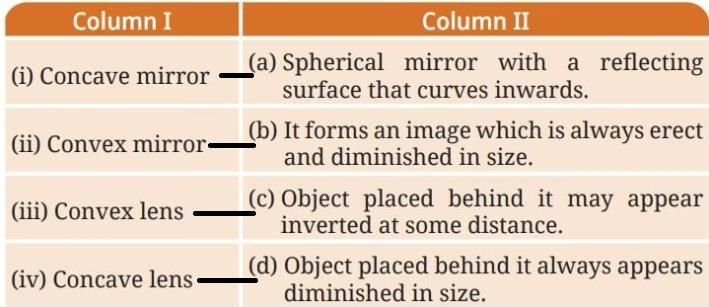
Q10: The following question is based on Assertion/Reason.
Assertion: Convex mirrors are preferred for observing the traffic behind us.
Reason: Convex mirrors provide a significantly larger view area than plane mirrors.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(ii) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(iii) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(iv) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Ans: (i) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Convex mirrors give a wider view, helping see more traffic, even if images are smaller.
Q11: In Fig. 10.27, note that O stands for object, M for mirror, and I for image.
Which of the following statements is true?
(i) Figure (a) indicates a plane mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
(ii) Figure (a) indicates a convex mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
(iii) Figure (a) indicates a concave mirror and Figure (b) indicates a convex mirror.
(iv) Figure (a) indicates a plane mirror and Figure (b) indicates a convex mirror.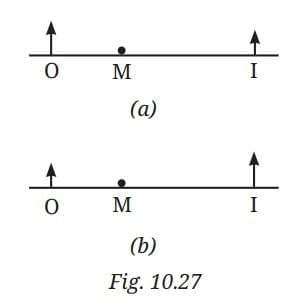
Ans: Figure (a) indicates a convex mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
Concave mirror shows enlarged image; convex shows smaller image.
Q12: Place a pencil behind a transparent glass tumbler (Fig. 10.28a). Now fill the tumbler halfway with water (Fig. 10.28b). How does the pencil appear when viewed through the water? Explain why its shape appears changed.
Ans: When we place a pencil behind a transparent glass tumbler and fill the tumbler halfway with water, the pencil will appear to be bent or broken at the point where it enters the water. The submerged portion of the pencil might also appear slightly thicker or shifted from its actual position. This phenomenon is called refraction of light.
Why it Happens
Change in medium: Light travels at different speeds in different materials (media). Air is an optically rarer medium, meaning light travels faster in it, compared to water, which is an optically denser medium where light travels more slowly.
Bending of Light (Refraction): When light rays from the pencil travel from the water (denser medium) into the air (rarer medium) and then into our eyes, their speed changes. This change in speed causes the light rays to bend or deviate from their original path. Specifically, when light goes from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal (an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface at the point where light enters the new medium).
Apparent Position: Because our brains interpret light rays as traveling in straight lines, the bending of light at the water-air interface makes the submerged part of the pencil appear to be at a different location than its actual position, creating the illusion of a bent or broken pencil. The extent of this bending depends on the angle at which we view the pencil and the difference in optical density between the two media (water and air). If we view the pencil straight from above, we won’t observe the bending as the light rays would be traveling perpendicular to the surface, and refraction would be minimal.
Discover, Design, and Debate (Page 169)
Q1: Visit a nearby hospital or the clinic of an ENT specialist, or a dentist, with your teacher or parents. Request the doctor to show you the mirrors used for examining ear, nose, throat, and teeth. Identify the kind of mirror used in these instruments.
Ans: Dentists use concave mirrors to get a bigger, clearer view of your teeth—it makes small areas look enlarged so they can spot problems easily. ENT doctors also use concave mirrors (sometimes on a headband) to focus light and see inside your ear, nose, or throat better. These mirrors curve inwards to magnify things when held close. It's safe and helps doctors do their job without hurting you!
Q2: Harnessing sunlight is key to solving future energy challenges. In devices like solar cookers (Fig. 10.29), mirrors are used to converge sunlight and generate heat. In India, such designs are used in villages, thus saving electricity and reducing fossil fuel use. Think of a design for a solar cooker for your school or home and prepare a detailed proposal for it including the budget required. Ans: Solar cookers are great for using free sunlight to cook food without gas or electricity—perfect for saving energy in villages or at home!
Ans: Solar cookers are great for using free sunlight to cook food without gas or electricity—perfect for saving energy in villages or at home!
Design Idea: Let's make a simple box-type solar cooker. It's like a cardboard box lined with shiny materials to trap heat. Inside, place a big concave mirror at the bottom to focus sunlight onto a black cooking pot (black absorbs heat better). Cover the top with a clear glass lid to let light in but keep heat inside. Add aluminum foil on the inside walls for extra reflection. You can adjust the box to face the sun.
How It Works: The concave mirror curves inwards to converge sunlight, making a hot spot on the pot to cook things like rice or veggies in 1-2 hours on a sunny day.
Materials and Budget (in ₹):
- Cardboard box (big enough for a pot): ₹100
- Aluminum foil (for lining and reflecting): ₹50
- Concave mirror (small one from a science kit): ₹150
- Glass sheet for lid: ₹200
- Black paint for the pot: ₹50
- Glue and tape: ₹50
Total Budget: ₹600. This is affordable and eco-friendly—try building it with friends and test cooking something simple!
Q3: Use online tools or animation to do virtual experiments with spherical mirrors and lenses. Move objects in the simulation and observe how the image changes.
Ans: Activity: Use online tools to play with spherical mirrors and lenses. Move objects and see image changes.
Go to free websites like PhET Interactive Simulations (search "PhET geometric optics" or "mirrors and lenses"). They're like virtual labs!
What I Observed:
- Concave Mirror: Place an object close—it shows a big, upright (erect) image, great for magnifying. Move it farther—the image flips upside down (inverted) and gets smaller.
- Convex Mirror: Always shows a small, upright image that gives a wide view, like in car mirrors—things look tinier but you see more area.
- Convex Lens: Close object = big, upright image (like a magnifying glass). Far object = inverted and smaller.
- Concave Lens: Always small, upright images that spread out light—used in glasses to fix vision.
It's super fun - change distances and see how images flip or resize. This helps understand why dentists use concave mirrors or why cameras have lenses!
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Light: Mirrors and Lenses NCERT Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between concave and convex mirrors? |  |
| 2. How do lenses work in focusing light? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of mirrors and lenses in daily life? |  |
| 4. What are the key properties of light related to mirrors and lenses? |  |
| 5. How do we determine the focal length of a lens or mirror? |  |




















