Earth, a Unique Life Sustaining Planet NCERT Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Probe and Ponder (Page 210) |

|
| InText (Page 212 - 221) |

|
| Keep the Curiosity Alive (Page 226 - 227) |

|
| Discover, Design, and Debate (Page 227) |

|
Probe and Ponder (Page 210)
Q1: What do you think Earth would look like if there were no life on it at all?
Ans: Earth would look like a barren, rocky planet with vast empty lands, dry oceans, and no green forests or animals. There might be more dust storms, eroded mountains, and a thinner atmosphere without plants to produce oxygen or hold soil in place. It would be silent and lifeless, like Mars or the Moon.
Q2: Life on Earth has survived for billions of years. What allows it to keep going despite major changes and disasters?
Ans: Earth's balance of air, water, sunlight, and soil, plus its position in the habitable zone, helps life adapt. Reproduction passes on traits that help survive changes, like disasters or climate shifts. Ecosystems recover through interactions between living things (like plants regrowing after a fire) and non-living parts (like nutrient recycling in soil).
Q3: Why don't dogs lay eggs? Or hens give birth to live chicks?
Ans: Dogs are mammals, so they give birth to live young because their embryos develop inside the mother, getting nutrition directly. Hens are birds, so they lay eggs where the embryo grows outside with stored food. This is due to how each species evolved—mammals protect babies inside, while birds use eggs for safety in nests.
Q4: If a spaceship carried soil and water to Mars, could plants start growing there?
Ans: Maybe simple plants or microbes could grow if we add the right conditions, like protection from Mars' thin atmosphere, extreme cold, and radiation. But most Earth plants would struggle without enough air pressure, liquid water stability, or Earth's magnetic shield. Experiments show some bacteria survive, but full growth needs more, like a greenhouse dome.
Q5: Share your questions ___________
Ans: Here are some fun questions from the chapter:
- Why is Earth called the Blue Planet?
- How does the ozone layer protect us?
- What would happen if Earth's magnetic field disappeared?
- Could life exist on other planets in the habitable zone?
InText (Page 212 - 221)
Q1: What makes the Earth unique for living beings to grow and survive? (Page 212)
Ans: Earth’s uniqueness for supporting life stems from a rare combination of factors. Its distance from the Sun, about 93 million miles, places it in the habitable zone where temperatures (-88°C to 58°C) allow liquid water, essential for life. The atmosphere, rich in nitrogen and oxygen, supports breathing, regulates climate, and shields against harmful radiation via the ozone layer. A strong magnetic field protects the atmosphere from solar wind erosion. Plate tectonics and volcanic activity recycle nutrients and stabilize the climate, while Earth’s size and gravity retain a breathable atmosphere without crushing organisms. The Moon stabilizes axial tilt, ensuring predictable seasons, and the planet’s chemical composition provides life’s building blocks, carbon, hydrogen, and more. This delicate balance, unlike conditions on Mars or Venus, creates diverse ecosystems where life thrives.
Q2: Is the temperature or distance from the sun the only factor that makes the Earth habitable? (Page 215)
Ans: Earth’s habitability isn’t solely due to its temperature or distance from the Sun, though its position in the habitable zone is crucial for liquid water. Other key factors include a protective atmosphere, a magnetic field shielding against solar wind, active geology like plate tectonics, and a stable rotation and tilt influenced by the Moon. Earth’s size, gravity, and chemical composition also provide the essential elements and conditions for life, creating a delicate balance that makes our planet uniquely suited for diverse ecosystems.
Q3: What would happen if the size of the Earth were too small or too big? (Page 215)
Ans: If Earth were significantly smaller or larger, its habitability would be compromised due to changes in gravity, atmosphere, and geological processes. A smaller Earth, with weaker gravity, would struggle to retain a dense atmosphere, leading to insufficient pressure for liquid water and poor protection from solar radiation, much like Mars. It might also lack the mass to sustain plate tectonics, limiting nutrient cycling and climate regulation. Conversely, a larger Earth with stronger gravity could trap a thick, oppressive atmosphere, like Venus, potentially causing extreme temperatures and pressure that crush life. Increased geological activity might lead to excessive volcanism, disrupting stable climates. Both scenarios would likely prevent the delicate balance of conditions, liquid water, breathable air, and stable ecosystems required for life as we know it.
Q4: Does the magnetic field of the Earth have any role in sustaining life on Earth? (Page 217)
Ans: Yes, the Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in sustaining life. It protects the Earth from harmful solar wind and cosmic radiation by deflecting charged particles from the Sun, which could otherwise strip away the atmosphere and harm living organisms.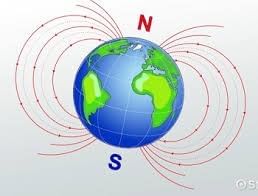
Q5: How is life supported and sustained on Earth? (Page 217)
Ans: Life on Earth is supported and sustained by several factors, including:
- The presence of water is essential for all living organisms.
- The atmosphere, which provides oxygen, carbon dioxide, and protects from harmful radiation.
- The Sun’s energy, which drives photosynthesis and regulates the climate.
- The Earth’s magnetic field shields life from harmful solar radiation.
Q6: How do bamboo and sugarcane grow into new plants? (Page 221)
Ans: Bamboo and sugarcane grow into new plants through vegetative propagation. New plants develop from the stems, roots, or shoots of the parent plant without the need for seeds.
For example, sugarcane grows new shoots from nodes of the stem, and bamboo spreads through underground rhizomes.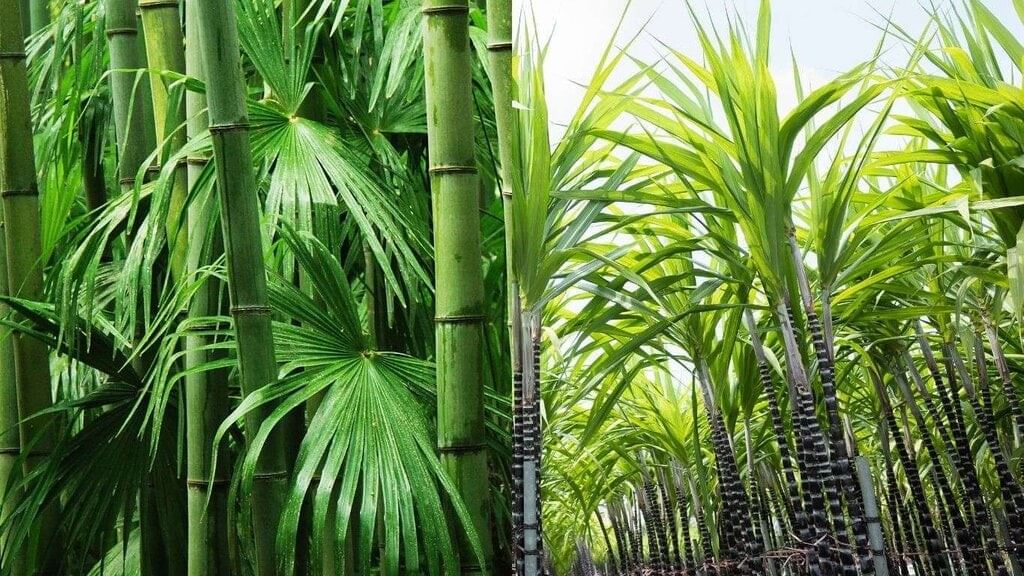 Bamboo and Sugarcane
Bamboo and Sugarcane
Keep the Curiosity Alive (Page 226 - 227)
Q1: What is one major reason Mars cannot currently support life like Earth?
(i) It has too many volcanoes.
(ii) It is too close to the Sun.
(iii) It lacks a thick atmosphere and liquid water.
(iv) Its magnetic field is too strong.
Ans: (iii) It lacks a thick atmosphere and liquid water.
Mars is at the edge of the habitable zone, but its thin atmosphere can't trap heat or hold liquid water, making it too cold and dry for most life.
Q2: Which of these is an example of geodiversity?
(i) Variety of bird chirping in a forest.
(ii) Different landforms like mountains, valleys, and deserts.
(iii) Changing weather during monsoons.
(iv) Number of different types of fish in a pond.
Ans: (ii) Different landforms like mountains, valleys, and deserts.
Geodiversity is the variety of rocks, soils, and landforms that create unique habitats, supporting different plants and animals.
Q3: If the Earth were smaller with the same density, what might happen to its atmosphere?
(i) It would become thicker and hotter.
(ii) It would escape into space due to weaker gravity.
(iii) It would become frozen.
(iv) It would cause stronger winds.
Ans: (ii) It would escape into space due to weaker gravity.
A smaller Earth couldn't hold gases tightly, so the atmosphere would leak away, like on Mercury, leaving no air to breathe or protect life.
Q4: In sexual reproduction, why are offspring different from their parents?
(i) They grow in different climates.
(ii) They eat different food.
(iii) They acquire new instructions after birth.
(iv) They get mixed instructions (genes) from both parents.
Ans: (iv) They get mixed instructions (genes) from both parents.
Gametes from each parent combine, mixing genetic material, so kids have traits from both but are unique, like varying eye colors in a family.
Q5: You notice tiny green plants growing in cracks on your school wall after the monsoon. Where do you think the seeds came from? What conditions helped these plants grow there?
Ans: The seeds likely came from nearby plants, carried by wind, birds, or insects. For example, a bird eating a fruit may have dropped or excreted the seed into the crack. The monsoon provided water, which is essential for seed germination. The crack in the wall likely trapped some soil or organic matter, offering nutrients. Sunlight and air, available in the outdoor environment, support photosynthesis and respiration. The moist, sheltered crack created a microhabitat suitable for growth.
Q6: A city has recently cut down a large patch of forest to build new roads and buildings. Discuss the possible effects this could have on the local climate and biodiversity? How might this affect water availability or quality in the area?
Ans:
- Effects on Local Climate: Deforestation reduces trees that absorb carbon dioxide, potentially increasing local temperatures due to less shade and a weakened greenhouse gas balance. It may also disrupt rainfall patterns, as trees contribute to water vapour for cloud formation.
- Effects on Biodiversity: Loss of forest habitat threatens plants and animals, reducing biodiversity. For example, animals like deer or predators like tigers may lose food sources or habitats, disrupting ecosystems. Deforestation can reduce water availability by disrupting the water cycle, as trees help retain soil moisture and contribute to rainfall. Soil erosion from cleared land can pollute nearby water bodies with sediment, affecting water quality.
Q7: A friend says, “The Earth has always had climate changes in the past, so today's global warming is nothing new.” How would you respond using what you've learnt in this and other chapters of your science book?
Ans: While Earth has experienced natural climate changes in the past (e.g., ice ages), today’s global warming is different because it is primarily driven by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, which release large amounts of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. These gases intensify the greenhouse effect, causing rapid warming, melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather, unlike slower natural changes. The triple planetary crisis (climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution) shows how human actions are disrupting Earth’s balance, threatening life. Unlike past changes, current warming requires urgent action, like using renewable energy, to protect ecosystems.
Q8: Imagine Earth's magnetic field suddenly disappeared. What kinds of problems could arise for life on Earth? Explain.
Ans: Without Earth’s magnetic field, high-energy particles like cosmic rays and solar wind would directly hit the atmosphere, potentially depleting the ozone layer and allowing harmful UV rays to reach the surface. This could damage living cells, increasing risks like skin cancer in humans and harming plants and animals. The atmosphere might erode over time, reducing oxygen levels and altering the climate, making Earth less habitable. Satellites and communication systems could also be disrupted by unshielded particles, affecting human technology.
Q9: You are tasked with designing a new settlement for humans on Mars. Name three things you would need to recreate from Earth to support human life there. Which of these do you think is the hardest to replicate, and why?
Ans: Three Things Needed:
- Liquid Water: Essential for drinking, growing crops, and supporting life processes.
- Breathable Atmosphere: An oxygen-rich atmosphere for respiration, protected from Mars’ thin, carbon dioxide-heavy atmosphere.
- Temperature Control: A system to maintain Earth-like temperatures, as Mars’ average temperature is around -60°C.
- Hardest to’ Replicate: Creating a breathable atmosphere is likely the hardest. Mars’ atmosphere is 100 times thinner than Earth’s and is mostly carbon dioxide, requiring complex systems to produce and maintain oxygen at the right pressure for humans. Generating enough oxygen for a settlement, shielding it from radiation, and preventing leaks in a harsh environment is technologically challenging compared to providing water (which can be transported or extracted) or temperature control (achievable with insulated habitats).
Q10: In a village, the temperature has been increasing and rainfall has become unpredictable over the past few years. What could be causing this change? Suggest two ways the village could adapt to these new conditions.
Ans: Causes: The changes are likely due to climate change, driven by increased greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels, leading to global warming and altered weather patterns. Deforestation or local land use changes could also reduce moisture and affect rainfall.
Adaptation Strategies:
- Water Conservation: Implement rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation systems to store water during unpredictable rainfall.
- Sustainable Farming: Use drought-resistant crops and sustainable farming practices to cope with higher temperatures and reduced water availability.
Q11: If there were no atmosphere on the Earth, would it affect life, temperature, and water on the planet? Explain.
Ans: Without an atmosphere:
- Life: Life would struggle to survive, as most organisms require oxygen for respiration. The absence of the ozone layer would allow harmful UV rays to damage cells, affecting plants, animals, and humans.
- Temperature: Earth would lose heat to space without the greenhouse effect, becoming extremely cold, similar to the Moon. Daytime temperatures could soar due to unfiltered sunlight, and nights would be freezing.
- Water: Liquid water would evaporate or freeze due to extreme temperature swings and low pressure, making it unavailable for life processes. The water cycle (rainfall, clouds) would cease without atmospheric water vapour.
Q12: Discuss five examples of vegetative propagation.
Ans: Vegetative propagation is asexual reproduction where plant parts like stems, roots, or leaves grow into new plants.
Five examples:
- Money Plant: A stem cutting with a node grows roots when placed in water or soil, forming a new plant.
- Potato: The “eyes” (buds) on a sprouted potato can be planted to grow a new potato plant.
- Ginger: A piece of ginger rhizome with a bud, when planted in soil, develops into a new plant.
- Sugarcane: Stem cuttings with nodes are planted to produce new sugarcane plants, as sugarcane rarely produces seeds.
- Bamboo: Sections of bamboo stems or rhizomes can be planted to grow new bamboo plants, relying on vegetative propagation.
Discover, Design, and Debate (Page 227)
Q1: Design an ‘Earth Survival Kit’. Imagine you’re building a tiny model of Earth for another planet. What must it have to support life, and why?
Ans: My kit would include:
- Liquid water (essential for cells, plants, and drinking—keeps things hydrated).
- Breathable air with oxygen and carbon dioxide (for respiration and photosynthesis).
- Soil with nutrients (to grow plants and recycle waste).
- Sunlight simulator (for energy and warmth).
- Magnetic shield model (to block harmful rays).
These recreate Earth's balance—water and air sustain life, soil supports growth, sunlight provides energy, and the shield protects. Build a model with jars, plants, and magnets to show it!
Q2: India is planning for a challenging lunar mission, Chandrayaan-4, which will bring back samples of soil from the Moon. If the Moon had water, could plants grow in that soil? Think of some experiment that could help you explore whether plant growth is possible on the Moon.
Ans: Plants might grow if we add water, but Moon soil (regolith) lacks nutrients and has sharp particles that could harm roots. Experiment: Mix Moon-like soil (use fine sand or volcanic ash) with Earth soil in pots. Add water and plant seeds like beans. Compare growth in pure "Moon" soil vs. mixed—track height, leaves, and roots over weeks. If nothing grows in pure regolith, it shows we need to add nutrients or protection for lunar farming!
Q3: Flowers are often brightly coloured and have a pleasant smell. How do you think these features help the plant reproduce?
Ans: Bright colors and sweet smells attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, or birds. They visit for nectar, picking up pollen (male gametes) and carrying it to other flowers for fertilization. This helps plants make seeds without moving—nature's way of mixing genes for stronger offspring!
Q4: Why do animals like fish and frogs lay hundreds or even thousands of eggs at a time, while other animals lay only a few? What might be the advantages and disadvantages of laying so many eggs?
Ans: Fish and frogs lay many eggs because most get eaten by predators or don't survive in water—it's a numbers game to ensure some hatch. Advantages: Increases survival chances without parental care.
Disadvantages: Wastes energy if most fail, and no protection means high loss. Birds lay fewer but care for them, improving each egg's odds!
Q5: Birds like sparrows build nests and care for their eggs and chicks, while reptiles like snakes usually lay their eggs and leave them without protection. How might this difference in parental care affect the chances of survival for the young ones in each case?
Ans: Sparrow chicks have higher survival because parents feed, warm, and protect them from predators—leading to more reaching adulthood. Snake eggs are hidden but face risks like weather or animals eating them, so fewer survive. Bird care boosts success but needs more energy; snake strategy spreads risk but has a higher loss.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Earth, a Unique Life Sustaining Planet NCERT Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the essential components of an 'Earth Survival Kit' for humans? |  |
| 2. How does Chandrayaan-4 aim to contribute to plant growth on the Moon? |  |
| 3. What role do flowers play in the reproduction of plants? |  |
| 4. What are the different methods of egg-laying in animals? |  |
| 5. Why is parental care important in the animal kingdom? |  |















