Worksheet Solutions: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. Which of the following forms a true (clear) solution with water?
a) Sand
b) Sawdust
c) Sugar
d) Chalk powder
Ans: c) Sugar
Sugar dissolves uniformly in water to give a clear, homogeneous solution; sand/sawdust/chalk do not.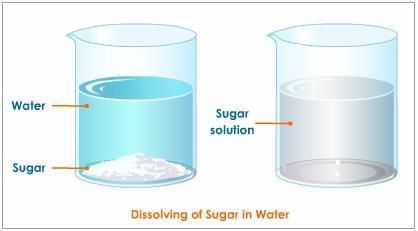
Q2. In a salt-water solution, which is the solvent?
a) Salt
b) Water
c) Both are solvents
d) Neither is solvent
Ans: b) Water
The component present in larger amount and determining the state (liquid) is the solvent.
Q3. Air is a gaseous solution in which the major component (solvent) is:
a) Oxygen
b) Nitrogen
c) Carbon dioxide
d) Argon
Ans: b) Nitrogen
Nitrogen is about 78% of air and acts as the solvent; other gases are solutes.
Q4. As more salt is added to a fixed amount of water, undissolved salt starts settling. The solution has become:
a) Dilute
b) Unsaturated
c) Saturated
d) Concentrated but unsaturated
Ans: c) Saturated
At saturation, no more solute dissolves at that temperature and excess settles.
Q5. Which statement about dilute vs. concentrated is correct?
a) They are absolute, fixed terms
b) They are comparative terms for amount of solute
c) They depend only on solvent type
d) They only apply to gases
Ans: b) They are comparative terms for amount of solute
“Dilute” and “concentrated” compare relative amounts of solute in solutions.
Q6. For most solid solutes in water, increasing temperature generally:
a) Decreases solubility
b) Increases solubility
c) Has no effect
d) Makes solution non-uniform
Ans: a) Decreases solubility
Heating often turns a saturated solution into an unsaturated one so more dissolves.
Q7. The solubility of gases in water generally:
a) Increases with temperature
b) Is highest at boiling point
c) Is unaffected by temperature
d) Decreases with temperature
Ans: d) Decreases with temperature
Cold water holds more dissolved oxygen; warm water holds less.
Q8. If in a syrup (chashni) sugar amount is more than water, the solvent is still:
a) Sugar, because it is more
b) Water, because it is liquid and determines state
c) Both are solvents
d) Neither is solvent
Ans: b) Water, because it is liquid and determines state
Even in large solute amounts, the liquid remains the solvent.
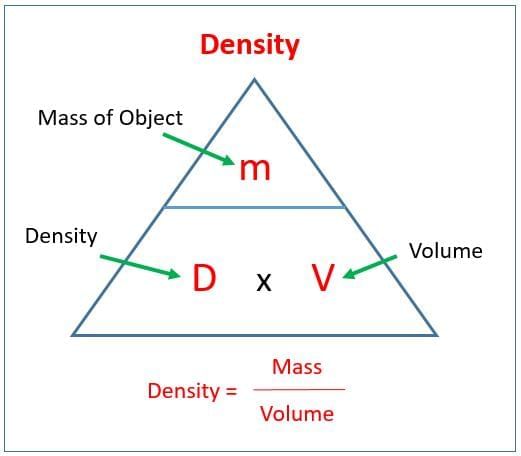
Q9. Density is defined as:
a) Volume per unit mass
b) Mass per unit volume
c) Weight per unit mass
d) Weight per unit volume
Ans: b) Mass per unit volume
Density = Mass / Volume; units include g/cm³ or kg/m³.
Q10. Which statement explains why ice floats on water?
a) Ice has more mass
b) Ice has higher density
c) Ice has lower density than liquid water
d) Ice has no mass
Ans: c) Ice has lower density than liquid water
On freezing, water expands, increasing volume and lowering density.
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. A solution is a __________ mixture in which components are evenly distributed.
Ans: homogeneous
All parts of a true solution have the same composition.
Q2. In a solid–liquid solution, the solid is the __________ and the liquid is the __________.
Ans: solute; solvent
The solute dissolves; the solvent does the dissolving.
Q3. When no more solute can dissolve at a given temperature, the solution is __________.
Ans: saturated
Extra solute remains undissolved at the bottom.
Q4. The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a fixed quantity of solvent at a given temperature is called __________.
Ans: solubility
It indicates dissolving capacity.
Q5. Oxygen dissolves only in __________ quantities in water, yet it is vital for aquatic life.
Ans: small (minute)
Even small dissolved oxygen is essential for fish and plants.
Q6. For gases, solubility generally __________ with increase in temperature.
Ans: decreases
Warm water holds less dissolved gas than cold water.
Q7. Density = __________ / __________.
Ans: Mass / Volume
It is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume.
Q8. The SI unit of density is __________.
Ans: kg/m³
Liquids are often expressed in g/mL or g/cm³ for convenience.
Q9. When temperature increases, volume tends to increase and density tends to __________ (if mass stays same).
Ans: decrease
Density falls because Density = Mass / Volume.
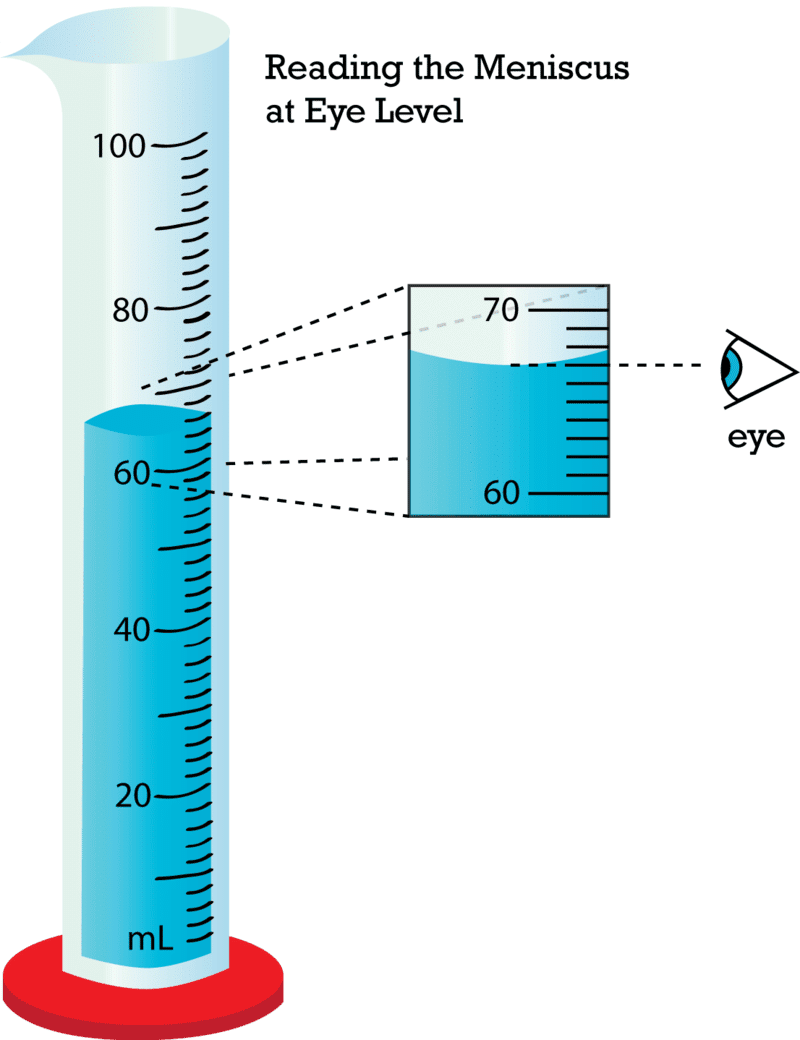
Q10. Reading liquids in a measuring cylinder is done at the bottom of the __________ for water and colorless liquids.
Ans: meniscus
Keep eyes level with the meniscus for accuracy.
Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
Q1. Define solute and solvent with an example.
Ans: In salt water, salt is the solute (dissolves) and water is the solvent (does the dissolving).
Q2. What happens when a saturated salt solution is heated?
Ans: It becomes unsaturated, allowing more salt to dissolve.
Q3. Name the major component of air that acts as the solvent.
Ans: Nitrogen.
Q4. State the formula for density.
Ans: Density = Mass / Volume.
Q5. Which has higher dissolved oxygen: cold water or warm water?
Ans: Cold water.
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
Q1. Why does sugar dissolve in water but sand does not form a solution?
Ans: Sugar breaks into tiny particles that occupy interparticle spaces in water, forming a homogeneous solution. Sand does not dissolve; its particles remain separate and settle, so no true solution forms.
Q2. Explain dilute vs. concentrated solutions with an example.
Ans: These are relative terms. For 100 mL water, 1 spoon of salt makes a dilute solution compared to 3 spoons making a concentrated solution.
Q3. How does temperature affect solubility of solids vs. gases in water?
Ans: Most solids become more soluble on heating, while gases become less soluble as temperature increases.
Q4. How do you measure the volume of an irregular solid using a measuring cylinder?
Ans: Note initial water level, immerse the object, note final level; volume of object = final − initial (in mL = cm³).
Q5. Why does ice float on water and why is this important for aquatic life?
Ans: Ice is less dense than liquid water due to expansion on freezing, so it floats and insulates water below, helping aquatic life survive in cold climates.
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

Ans:
Saturated solution — d) No more solute dissolves; excess settles
At saturation, added solute remains undissolved.Solubility — b) Maximum amount of solute dissolving at a given temperature
Measures dissolving capacity.Nitrogen in air — c) Major component acting as solvent in a gaseous solution
Nitrogen (~78%) is the solvent; others are solutes.Meniscus — e) Curved surface of a liquid used for volume reading
Read bottom of meniscus for water/colorless liquids.Relative density — a) Ratio of density of a substance to density of water (unitless)
It is a pure number with no units.
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What are solutes and solvents, and how do they differ? |  |
| 2. What are some common examples of solutions found in everyday life? |  |
| 3. How do temperature and pressure affect the solubility of substances? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of concentration in solutions? |  |
| 5. Can solutions be separated, and if so, how? |  |















