Worksheet Solutions: Natural Resources and Their Use | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| True or False |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Question Answers |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Resources that we find in nature and are used without much modification are called ___________
(a) Human Resource
(b) Natural Resource
(c) Renewable Resource
(d) Human Made Resource
Ans: (b) Natural Resource
Natural resources are those that we find in nature and can be used without much modification, such as air, water, minerals, and forests.

Q2. How are natural resources primarily categorized?
(a) By color
(b) By use and renewability
(c) By size
(d) By location
Ans: (b) By use and renewability
Natural resources are classified by how they’re used and whether they can be renewed — renewable (like sunlight) or non-renewable (like coal).
Q3. Which of the following is an example of a renewable resource?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Solar energy
(d) Natural gas
Ans: (c) Solar energy
Solar energy is an example of a renewable resource because it is continuously replenished by the sun and will not be depleted with use.
Q4. What factor can change substances into resources?
(a) Air
(b) Time and technology
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Ans: (b) Time and technology
Time and technology are factors that can change substances into resources. Over time, advancements in technology can make previously unusable substances valuable resources.
Q5. What is the main focus of sustainable development?
(a) Exploiting resources for short-term gain
(b) Using resources carelessly
(c) Balancing present needs with future conservation
(d) Wasting resources
Ans: (c) Balancing present needs with future conservation
The main focus of sustainable development is to balance present human needs with the conservation of resources for future generations, ensuring that resources are used responsibly and not depleted.
Q6. Which of the following is a non-renewable resource?
(a) Solar energy
(b) Timber
(c) Coal
(d) Wind
Ans: (c) Coal
Non-renewable resources are those that exist in limited amounts and take millions of years to form, so they cannot be replenished quickly. Coal is a non-renewable resource used for energy, as its formation takes a very long time, and once used, it is gone.
Q7. What is the "natural resource curse"?
(a) When resources are evenly distributed across a region
(b) When resource-rich regions experience slower economic growth
(c) When renewable resources are overexploited
(d) When non-renewable resources are used sustainably
Ans: (b) When resource-rich regions experience slower economic growth
The natural resource curse refers to the paradox where countries rich in natural resources often grow more slowly due to poor governance or overreliance on resource income.
Q8. Which of the following is an example of an ecosystem service provided by forests?
(a) Producing cement
(b) Filtering water and preventing soil erosion
(c) Extracting petroleum
(d) Mining coal
Ans: (b) Filtering water and preventing soil erosion
Forests help clean water, prevent soil erosion, and support biodiversity—key ecosystem services that sustain the environment.
Q9. What is a key focus of Vrikshayurveda in promoting sustainable agriculture?
(a) Using chemical fertilizers
(b) Crop rotation and natural pest control
(c) Overexploitation of groundwater
(d) Mining non-renewable resources
Ans: (b) Crop rotation and natural pest control
Vrikshayurveda emphasizes sustainable farming practices like crop rotation and using natural methods to control pests instead of chemicals.
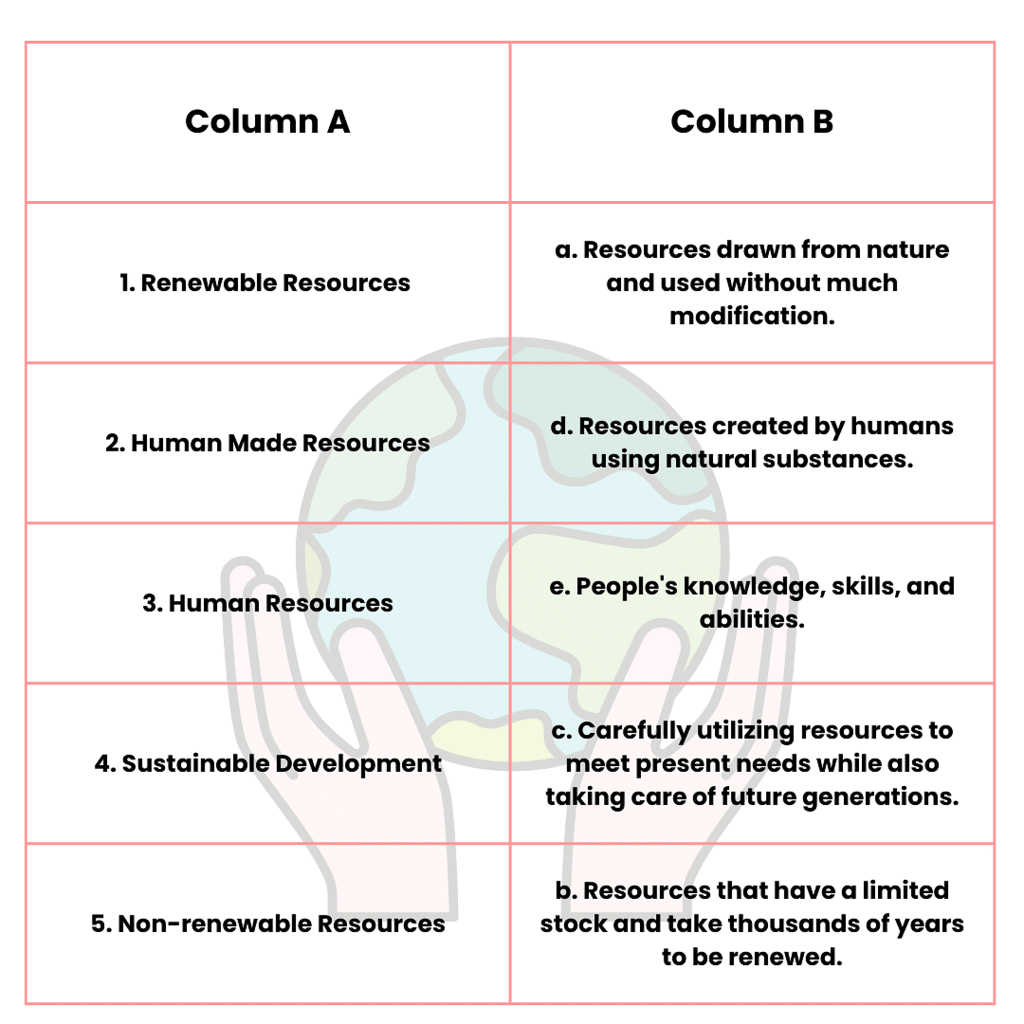
Match the Following
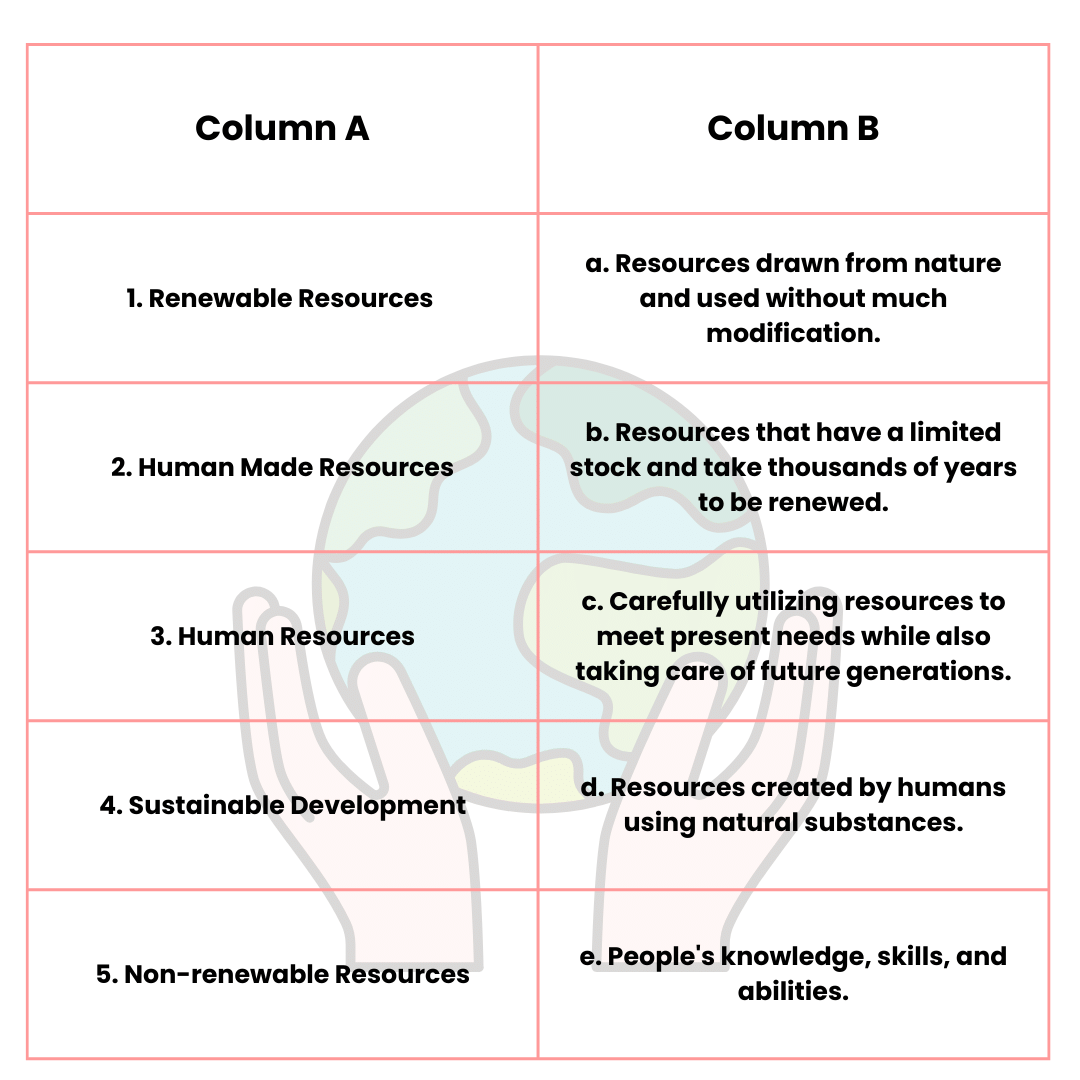
Ans:
True or False
Q1. Natural resources include only those substances that have economic value.
Ans: False
Natural resources include substances found in nature, whether or not they have economic value. For example, air and water are natural resources that are essential for life but may not have direct economic value.
Q2. Renewable resources can never be depleted or exhausted.
Ans: False
While renewable resources can be replenished over time, they can still be depleted or exhausted if used unsustainably. For example, forests can be depleted if trees are cut down faster than they can regrow.
Q3. Overexploitation of renewable resources can disrupt nature’s restoration and regeneration cycles.
Ans: True
Using renewable resources faster than they can naturally replenish can harm ecosystems and reduce their long-term availability.
Q4. Resource conservation involves using resources carelessly without thinking about the future.
Ans: False
Resource conservation involves using resources carefully and responsibly, considering the needs of both the present and future generations. It aims to avoid wasteful consumption and ensure the long-term sustainability of resources.
Q5. Sustainable development aims to balance the use of resources for current needs and conserve them for the future.
Ans: True
Sustainable development seeks to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves balancing economic, social, and environmental factors to ensure that resources are used efficiently and equitably.
Q6. The uneven distribution of natural resources can lead to conflicts between states or countries.
Ans: True
Uneven resource distribution shapes settlements, trade, and conflicts, citing examples like the Kaveri River water-sharing disputes.
Q7. Traditional practices, such as regulating fishing during spawning seasons, help maintain ecosystem balance.
Ans: True
Traditional practices like regulating fishing to maintain fish populations, which supports ecosystem balance.
Q8. Cement production is one of the least polluting industries.
Ans: False
Cement production is highly polluting, releasing fine dust that harms health and the environment.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1. All ___________ have some utility and value.
Ans: All resources have some utility and value.
Q2. _______ is an example of a resource essential for life.
Ans: Water is an example of a resource essential for life.
Q3. Human beings use ________ and _________ to develop resources.
Ans: Human beings use technology and knowledge to develop resources.
Q4. _________ is an example of a renewable resource that can be depleted if overused.
Ans: Forest is an example of a renewable resource that can be depleted if overused.
Q5. _______or _______ makes an object or substance a resource.
Ans: Utility or value makes an object or substance a resource.
Q6. _____________ is an example of a non-renewable resource used for energy
Ans: Petroleum is an example of a non-renewable resource used for energy
Q7. The _______ River water-sharing dispute among Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Puducherry is an example of tensions caused by uneven resource distribution.
Ans: The Kaveri River water-sharing dispute among Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Puducherry is an example of tensions caused by uneven resource distribution.
Q8. _______ is a traditional Indian science that promotes sustainable agriculture through practices like crop rotation and natural pest control.
Ans: Vrikshayurveda is a traditional Indian science that promotes sustainable agriculture through practices like crop rotation and natural pest control.
Q9. The _______ Solar Park in Rajasthan is an example of India’s efforts to transition to renewable energy sources.
Ans: Bhadla Solar Park as a symbol of India’s renewable energy ambitions.
Very Short Question Answers
Q1. What are non-renewable resources?
Ans: Non-renewable resources are those which have a limited stock.
Q2. How are natural resources classified by their use?
Ans: Natural resources are classified by their use into those essential for life (e.g., air, water), for materials (e.g., wood, marble), and for energy (e.g., coal, solar energy).
Q3. Why must renewable resources be used sustainably?
Ans: Renewable resources must be used sustainably to allow nature’s restoration and regeneration cycles to replenish them, preventing depletion.
Q4. How does the uneven distribution of natural resources affect human life?
Ans: Uneven distribution shapes settlements, trade, and conflicts, as people settle near resources for jobs, trade them, or compete for control.
Q5. What is resource conservation?
Ans: Using resources carefully and giving them time to get renewed is called resource conservation.
Q6. Name some natural resources.
Ans: The air we breathe, the water in our rivers and lakes, the soils, minerals are all natural resources.
Q7. What is sustainable development?
Ans: Balancing the need to use resources and also conserve them for the future is called sustainable development.
Q8. What is the natural resource curse?
Ans: The natural resource curse is when regions rich in natural resources experience slower economic growth due to poor management or over-reliance on resources.
Q9. What is an ecosystem service? Give one example.
Ans: An ecosystem service is a benefit humans receive from natural processes. Example: Forests filter water to provide clean drinking water.
Q10. How does overexploitation of groundwater in Punjab affect sustainability?
Ans: Overexploitation of groundwater in Punjab has depleted water tables, making water inaccessible at shallow depths and causing health hazards due to chemical contamination.
Q11. What role does the International Solar Alliance play in promoting renewable energy?
Ans: The International Solar Alliance, launched by India and France, promotes solar energy in sunshine-rich countries by funding projects and sharing technical expertise.
Q12. Why is responsible stewardship of natural resources important?
Ans: Responsible stewardship ensures the restoration and regeneration of renewable resources and the judicious use of non-renewable ones, preventing pollution, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
Q13. Name a traditional practice that helps keep soil healthy.
Ans: Using cow dung as a natural fertilizer helps maintain soil health.
Q14. What makes a substance a resource?
Ans: Utility or usability is what makes an object or substance a resource.
Q15. What are renewable resources?
Ans: Renewable resources are those which get renewed or replenished quickly.
Q16. What is Vrikshayurveda, and how does it promote sustainable resource use?
Ans: Vrikshayurveda is an ancient Indian science of plant care that promotes sustainable agriculture through practices like crop rotation, natural pest control, and soil management.
Q17. What is technology?
Ans: Technology is the application of latest knowledge and skill in doing or making things.
Q18. What are natural resources?
Ans: Resources that are drawn from nature and used without much modification are called natural resources.
Long Answer Questions
Q1. How does the uneven distribution of natural resources affect where people live and the economic activities they pursue? Give an example.Ans: Uneven distribution of natural resources influences human settlements and the types of economic activities in an area. Regions with abundant minerals, water, or fertile soil attract industries, creating jobs and encouraging towns and cities to develop. However, resource-rich areas may also face challenges, such as the displacement of local communities or harm to sacred and environmentally sensitive sites.
Example: Industries near mineral resources provide employment and boost the local economy, but they can also lead to conflicts with nearby communities over land and environmental impacts.
Q2. What are the consequences of overusing renewable resources? Explain with an example from Punjab.
Ans: Overexploiting renewable resources disrupts nature’s restoration and regeneration cycles, leading to shortages and environmental damage. In Punjab, excessive groundwater extraction for high-yielding crops during the Green Revolution depleted water tables, making water inaccessible at depths up to 30 meters. Chemical fertilizers and pesticides have also contaminated groundwater, posing health risks. This shows that unsustainable use can compromise long-term food and water security.
Q3. How does Sikkim’s adoption of organic farming show sustainable use of resources?
Ans: Sikkim’s move to 100% organic farming is an excellent example of sustainable resource use. Farmers replaced chemical fertilizers and pesticides with compost, natural pest repellents, and practiced multi-cropping to maintain soil fertility. This approach restored soil health, increased biodiversity, and improved farmers’ incomes by around 20%. Sikkim’s model demonstrates that using resources responsibly can simultaneously protect the environment and support economic growth.
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Natural Resources and Their Use - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What are natural resources and why are they important for human survival? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of natural resources? |  |
| 3. How do human activities affect natural resources? |  |
| 4. What are some ways to conserve natural resources? |  |
| 5. Why is sustainable development important in relation to natural resources? |  |















