Very Short Answer Questions: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1. What are microorganisms or microbes?
Ans: The organisms that are not seen with our naked eyes are called microorganisms.
Q2. Give two examples of microorganisms.
Ans: Bacteria and Fungus.
Q3. What are the four major groups of microorganisms?
Ans:
(i) Bacteria
(ii) Fungi
(iii) Protozoa
(iv) Algae
Q4. What are viruses?
Ans: Very tiny microscopic organisms that reproduce only inside the cells of host organisms are called viruses.
Q5. What tool helps us see tiny organisms that are invisible to the naked eye?
Ans: A microscope helps us see tiny organisms that our eyes cannot see directly.
Q6. Why can’t we see most microorganisms without help?
Ans: Most microorganisms are too small to be seen with the unaided eye.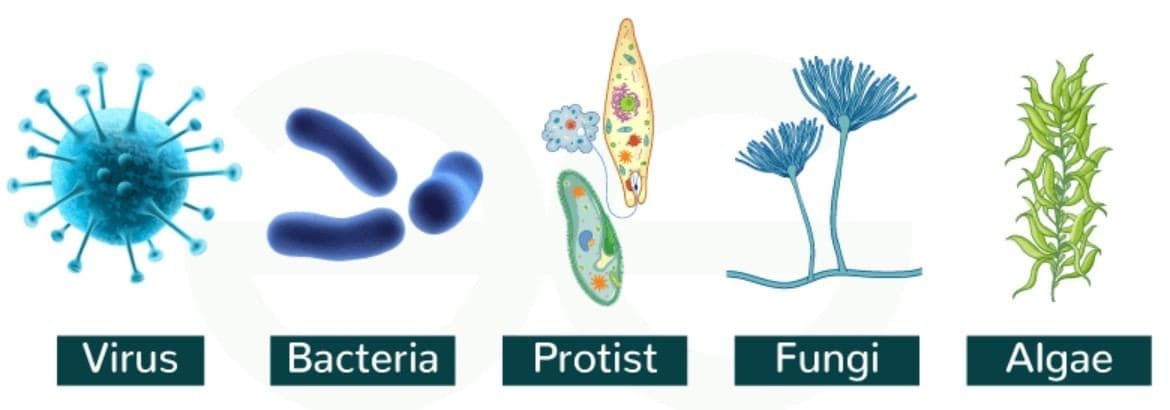 Microorganisms
Microorganisms
Q7. What simple object filled with water can act like a magnifying glass?
Ans: A round-bottom flask filled with water can act like a magnifying glass.
Q8. Who first used the word “cell” in science?
Ans: Robert Hooke first used the word “cell” after observing cork under a microscope.
Q9. Who is called the Father of Microbiology?
Ans: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek is called the Father of Microbiology.
Q10. What is the basic unit of life?
Ans: The cell is the basic unit of life.
Q11. Which part of the cell controls all activities?
Ans: The nucleus controls all cell activities.
Q12. Which cell part is a thin, flexible boundary around the cell?
Ans: The cell membrane is the thin, flexible boundary around the cell.
Q13. Name the jelly-like substance inside the cell where life processes occur.
Ans: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance where life processes occur.
Q14. Name two single-celled microorganisms.
Ans: (i) Bacteria (ii) Some algae.
Q15. Name two multicellular microorganisms.
Ans: (i) Fungi (ii) Algae.
Q16. What are the two types of microorganisms on the basis of their functions?
Ans: (i) Useful microorganisms. (ii) Harmful microorganisms.
Q17. Name the microorganisms which promote the formation of curd.
Ans: Bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd.
Q18. Which extra layer is present in plant cells but not in animal cells?
Ans: The cell wall is present in plant cells but not in animal cells.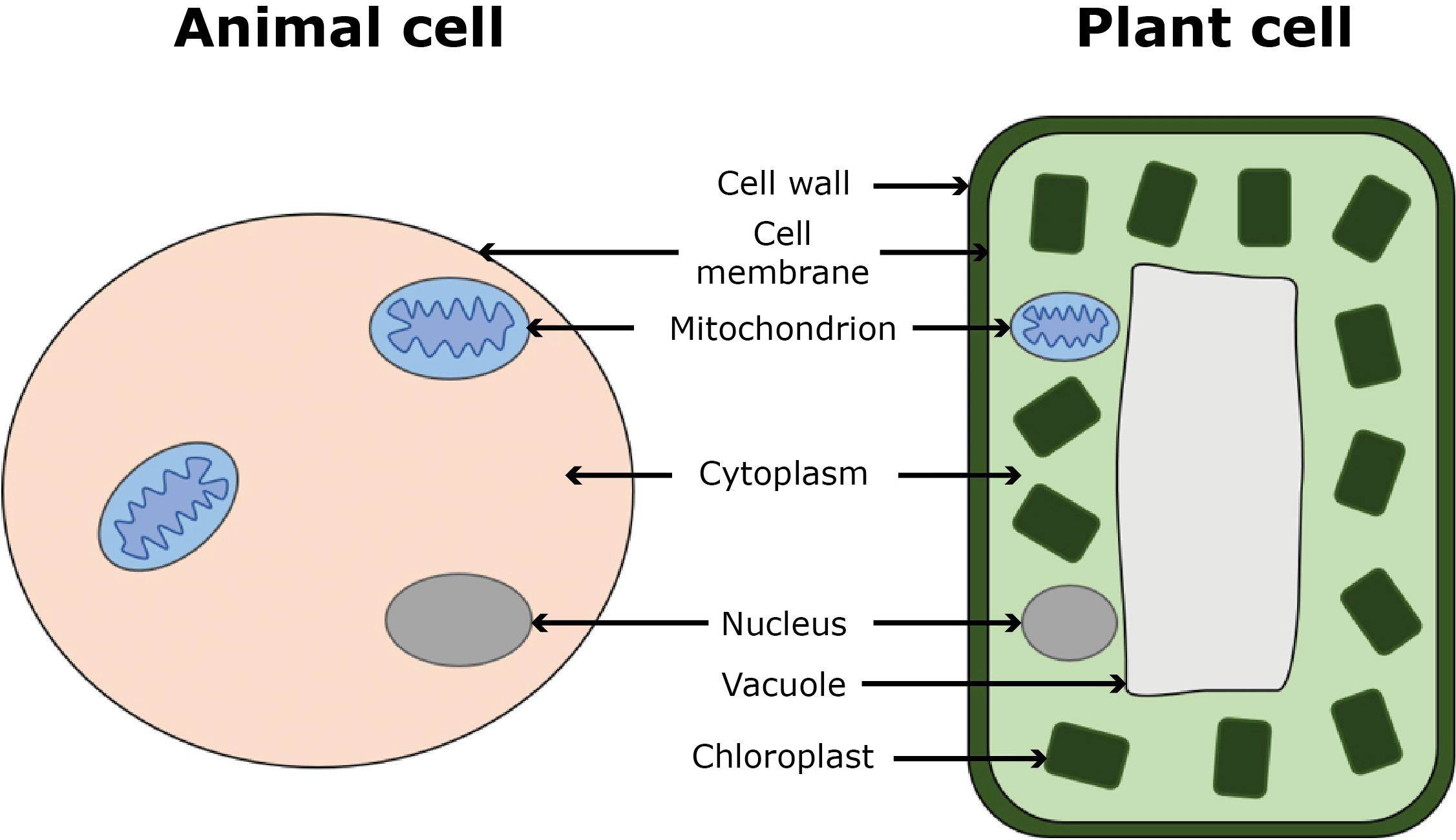
Q19. Which plant cell part contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis?
Ans: Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Q20. Which cell part stores food, water, and waste in plant cells?
Ans: The vacuole stores food, water, and waste in plant cells.
Q21. How do onion peel cells appear under a microscope?
Ans: Onion peel cells look rectangular and are closely packed.
Q22. What shape are cheek cells generally?
Ans: Cheek cells are thin, flat, and irregular in shape.
Q23. Why do different cells have different shapes?
Ans: Different cells have different shapes to perform specific functions.
Q24. Arrange these levels of organization from simplest to most complex: organ, cell, tissue, organism, organ system.
Ans: Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism.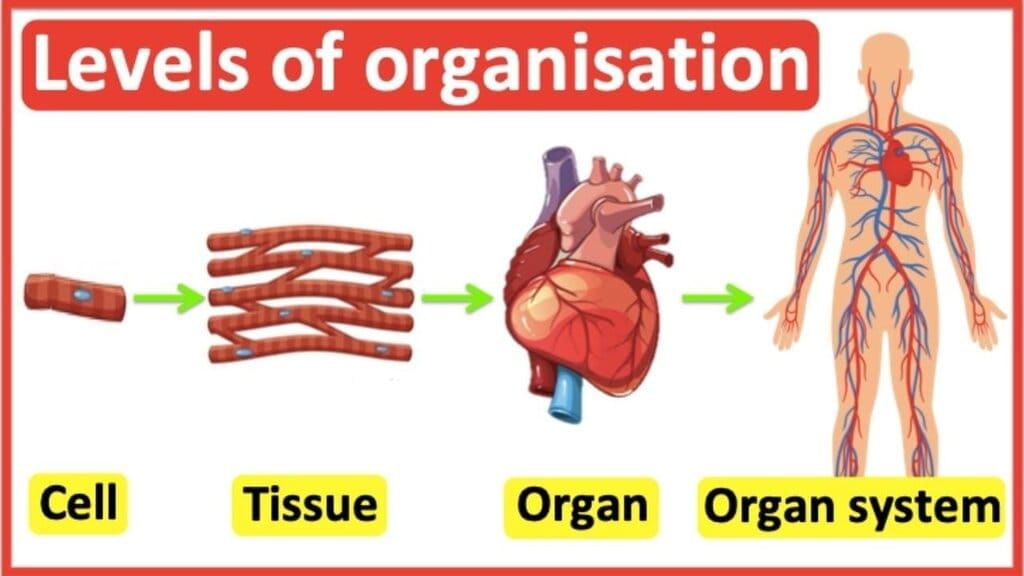
Q25. What do microbes that decompose waste help form in soil?
Ans: They help form dark, nutrient-rich manure called compost.
Q26. Why don’t pickles spoil easily?
Ans: High salt or sugar prevents microbes from growing in pickles.
Q27. What gas is the main component of biogas made by microbes?
Ans: Methane is the main component of biogas.
Q28. Which microbe is used to make dough rise?
Ans: Yeast is used to make dough rise. Rising Dough
Rising Dough
Q29. Which bacteria turn milk into curd?
Ans: Lactobacillus bacteria turn milk into curd.
Q30. Which bacteria living in legume roots fix nitrogen?
Ans: Rhizobium bacteria fix nitrogen in legume roots.
Q31. What are very small, plant-like organisms in water that release much of Earth’s oxygen?
Ans: Microalgae are tiny plant-like organisms that release much oxygen.
Q32. Name a microalga known as a “superfood.”
Ans: Spirulina is a microalga known as a superfood.
Q33. What do you mean by symbiotic relationship?
Ans: The relationship between two organisms in which both organisms benefit is called a symbiotic relationship.
Q34. Name some preservatives.
Ans: Sugar, salt, oils, and vinegar are some common preservatives.
Q35. Where do Rhizobium bacteria commonly live?
Ans: Rhizobium bacteria live in the root nodules of leguminous plants
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Very Short Answer Questions: The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the invisible living world and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How do microorganisms affect human health? |  |
| 3. What techniques are used to study microorganisms? |  |
| 4. What role do microorganisms play in the environment? |  |
| 5. Can microorganisms be beneficial in agriculture? |  |






















