Very Short Ans: Questions: Exploring Forces | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q. 1. How can we change the speed and the direction of a moving body?
Ans. By applying force. Force changes speed or direction.
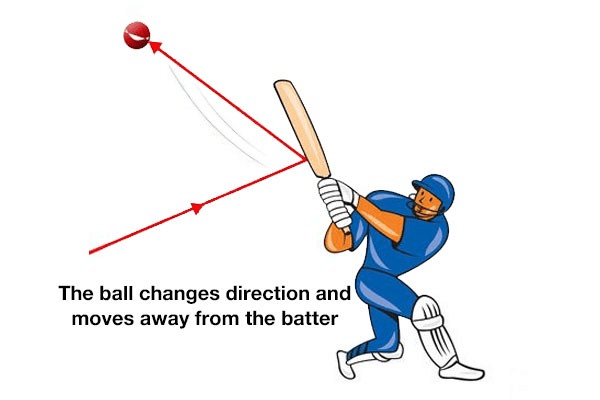 Q. 2. What is force?
Q. 2. What is force?
Ans. A push or pull acting on an object is called force.
Q. 3. What is the requirement for a force to come into play?
Ans. Interaction between two objects is necessary for force.
Q. 4. What is the resultant force when two forces act in same direction?
Ans. Forces applied on an object in the same direction add to one another.
Q. 5. What will be the resultant force when two forces act in opposite directions on an object?
Ans. When two forces act in opposite directions on an object then the net force will be the difference between two forces.
Q. 6. What happens when two teams pull equally hard in a tug of war?
Ans. When two teams pull equally hard then the rope does not move in any direction.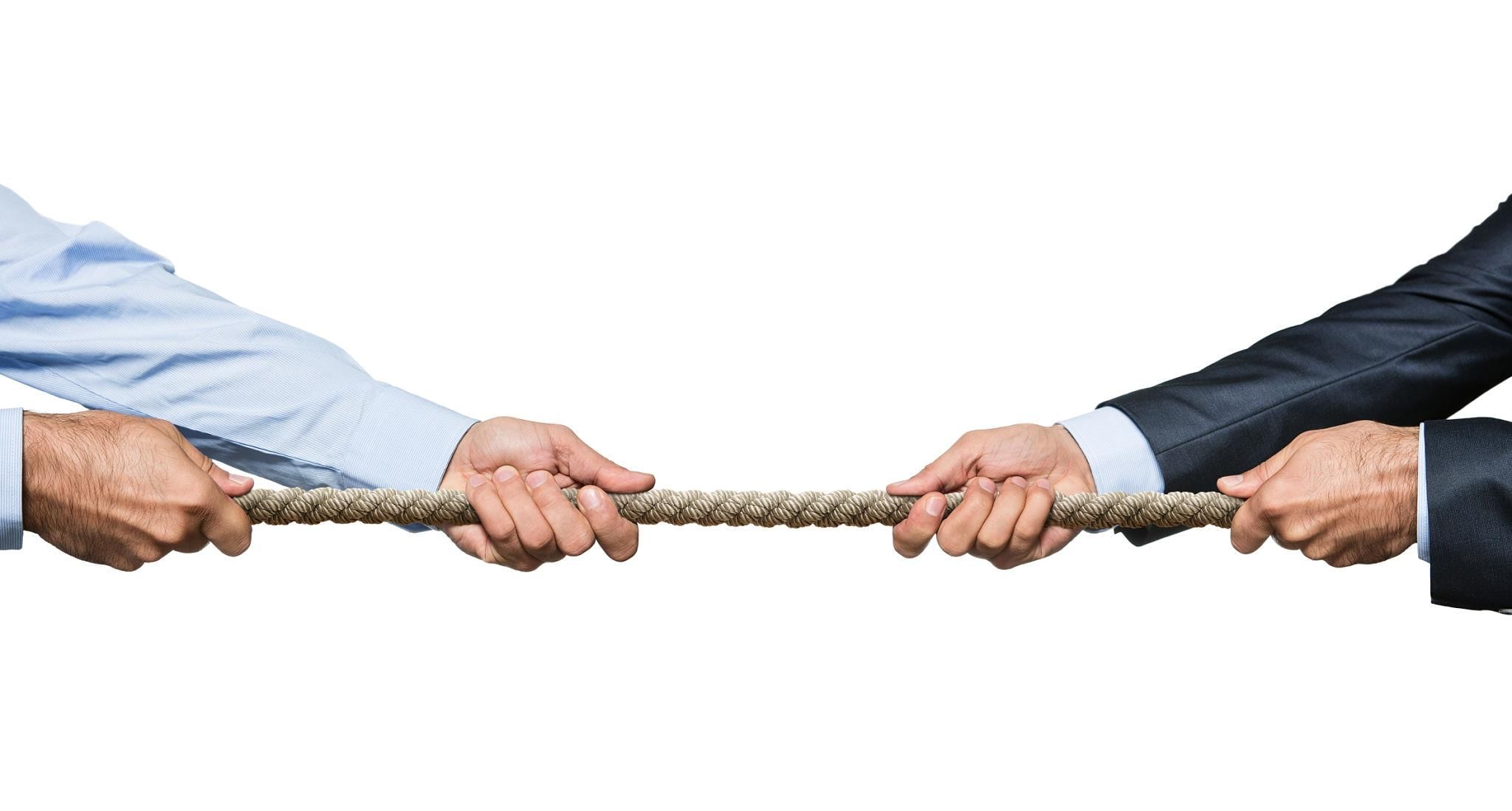
Q. 7. Name the term used to express the strength of a force.
Ans. Magnitude.
Q . 8. When does the net force become zero?
Ans. When two forces acting on an object in opposite directions are equal then the net force becomes zero.
Q . 9. A ball is at rest. Push it gently. Does the ball begin to move?
Ans. Yes, the ball begins to move.
Q . 10. What happens when we push again while the ball is moving?
Ans. When we push a moving ball, then its speed increases.
Q . 11. Place your palm in front of a moving ball. Does your palm apply any force on the ball?
Ans. Yes, our palm applies a force on the ball.
Q . 12. What happens to the speed of the ball when you place your palm in front of the moving ball?
Ans. The speed of the ball is decreased.
Q . 13. What are the two states of motion?
Ans. There are two states of motion: (i) The state of rest (ii) The state of motion.
Q . 14. Does the application of a force would always result in a change in the state of motion of an object?
Ans. No, it does not always change the state of motion of an object.
Q . 15. What is muscular force?
Ans. The force resulting due to the action of muscles is known as muscular force.
Q . 16. Give two examples of muscular force.
Ans. Bending of our body and kicking the ball.
Q . 17. Does the force can change the speed of a moving object?
Ans. Yes.
Q . 18. What effect does a force have on the shape of an object?
Ans. The force may cause a change in shape of the object.
Q . 19. Is muscular force a type of contact force?
Ans. Yes, muscular force is a type of contact force.
Q . 20. What is force of friction?
Ans. The force which acts on all moving objects in opposite directions to the motion of the body is called the force of friction.
Q . 21. What kind of force is friction?
Ans. The force of friction is also a type of contact force.
Q . 22. Why is force of friction called contact force?
Ans. Since the force of friction arises due to contact between the surfaces of a moving body and other surfaces, it is called a contact force.
Q . 23. Give two examples of contact forces.
Ans. (i) Muscular force (ii) Force of friction
Q . 24. What are non-contact forces?
Ans. The forces acting from a distance without making contact are called non-contact forces.
Q . 25. Give an example of a non-contact force.
Ans. Magnetic force.
Q . 26. What is magnetic force?
Ans. The force exerted by a magnet on any magnetic object is called magnetic force.
Q . 27. What are the interaction of poles of two magnets?
Ans (i) Like poles repel each other.
(ii) Unlike poles attract each other.
Q. 28. What do you mean by electrostatic force?
Ans. The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or non-charged body is called electrostatic force.
Q . 29. What kind of force is an electrostatic force?
Ans. It is a non-contact force.
Q . 30. What is gravitational force?
Ans. The force by which earth or any other object attracts objects towards itself is called the gravitational force.
Q . 31. Is the gravity a property of earth only?
Ans. No, gravity is not a property of earth only.
Q. 32. Is the gravitational force a contact or non-contact force?
Ans. The gravitational force is non-contact force.
Q . 33. Name the force due to which every object falls on the earth.
Ans. Due to gravitational force.
Q . 34. What is weight?
Ans: Weight is the force with which Earth pulls an object due to gravity.
Q . 35. Does mass change from place to place?
Ans: Mass does not change from place to place.
Q . 36. Does weight change from place to place?
Ans: Weight can change from place to place if gravity changes.
Q . 37. What instrument measures weight as a force?
Ans: A spring balance measures weight in newtons.
Q . 38. What is upthrust or buoyant force?
Ans: Upthrust is the upward force a liquid exerts on an immersed object.
Q . 39. What does Archimedes’ principle state about floating?
Ans: Archimedes’ principle states that an object experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the displaced liquid.
|
59 videos|235 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Very Short Ans: Questions: Exploring Forces - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the different types of forces in physics? |  |
| 2. How does gravity affect objects on Earth? |  |
| 3. What is the role of friction in motion? |  |
| 4. What is Newton's First Law of Motion? |  |
| 5. How can forces be represented in diagrams? |  |





















