Short and Long Answer Questions: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1. What makes a mixture a solution rather than just a mixture of substances?
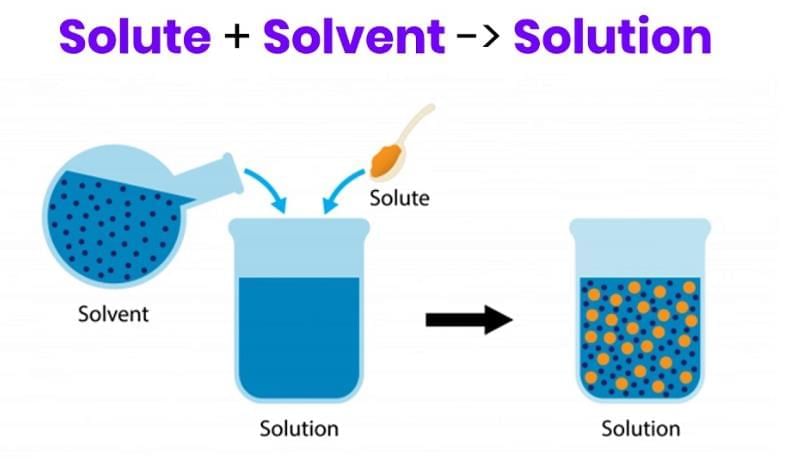
Answer: A solution is a homogeneous mixture where the solute particles are evenly spread in the solvent and cannot be seen or separated easily.
Q2. How do you decide which liquid is the solute and which is the solvent when two liquids mix?
Answer: The component present in the smaller amount is the solute, and the component in the larger amount is the solvent.
Q3. Why does sugar dissolve in water but sand does not form a solution?
Answer: Sugar particles interact with water and disperse evenly to form a clear solution, while sand does not dissolve and settles at the bottom.
Q4. What does it mean when a solution becomes saturated?
Answer: A saturated solution has dissolved the maximum amount of solute at that temperature, so any extra solute remains undissolved.
Q5. How do we compare dilute and concentrated solutions in simple terms?
Answer: A dilute solution has less solute in a given amount of solvent, while a concentrated solution has more solute in the same amount of solvent.
Q6. How can heating turn a saturated solution into an unsaturated one?
Answer: Heating usually increases solubility for many solids, so the solvent can dissolve more solute and the previously saturated solution becomes unsaturated.
Q7. Why is air called a gaseous solution, and which gas acts as the solvent?
Answer: Air is a uniform mixture of gases, and nitrogen acts as the solvent because it is present in the largest amount.
Q8. Why do aquatic animals need cold water more than warm water for breathing?
Answer: Gases like oxygen dissolve better in cold water, so there is more dissolved oxygen available for aquatic life in colder water.
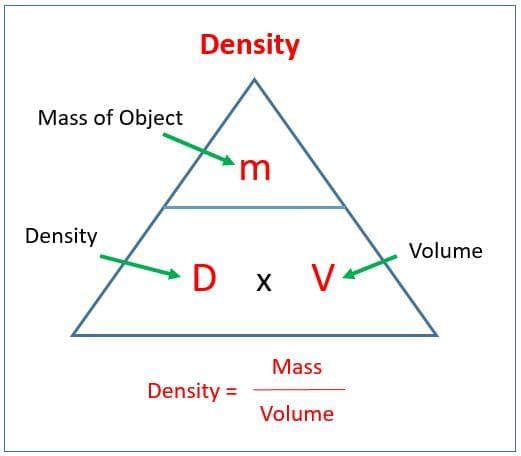
Q9. What is density and how does it help explain floating and sinking?
Answer: Density is mass per unit volume; objects with lower density than the liquid float, while those with higher density sink.
Q10. How can you measure the density of a small stone in the school lab?
Answer: Measure its mass using a balance, find its volume by water displacement in a measuring cylinder, then calculate density using Density = Mass/Volume.
Q11. Why does ice float on water even though both are made of the same substance?
Answer: When water freezes, its structure expands and its volume increases, making ice less dense than liquid water, so it floats.
Q12. Why do we read the bottom of the meniscus when measuring water in a cylinder?
Answer: Water curves at the surface, so reading the bottom of the meniscus at eye level gives an accurate volume measurement.
Long Answer Questions
Q1. Explain how particles behave at the microscopic level when a solute dissolves in a solvent, and why the mixture looks clear.
Answer:
- When a solute dissolves, its tiny particles spread out evenly between the solvent particles due to mixing and attraction. These particles become so small and uniformly distributed that they cannot be seen even with a hand lens.
- Because light passes through without scattering much, the mixture looks clear. This even spreading is why a true solution is homogeneous. The uniformity remains stable as long as conditions do not change.
Q2. Explain with an example how the same substances can form different types of mixtures depending on proportion, and how to identify them.
Answer:
- Oil and water usually form a non-uniform mixture with separate layers when oil is added in ordinary amounts, so it is not a solution.
- However, a very small amount of acetic acid in water forms vinegar, which is a true solution because it is uniform and clear.
- To identify them, look for clarity, absence of layers, and particles that do not settle on standing. If the mixture is cloudy or separates, it is not a true solution. If it remains clear and uniform, it is a solution.
Q4. Discuss why some saturated solutions crystallize on cooling and what this shows about solubility and temperature.
Answer:
- When a hot saturated solution cools, the solvent’s capacity to keep the solute dissolved decreases. The extra solute that can no longer stay dissolved comes out as crystals, showing that solubility has dropped with lower temperature.
- The size and shape of crystals depend on cooling speed and purity. Slow cooling often forms larger, well-shaped crystals. This behavior demonstrates the relationship between temperature and solubility for many solids.

Q5. Explain how relative density helps predict floating and sinking better than mass alone, using two same-sized objects made of different materials.
Answer:
- Mass alone can be misleading because it does not consider volume, but relative density compares a material’s density to water. If a same-sized wooden block and an iron block are placed in water, the wood floats and iron sinks because wood’s density is less than water’s, while iron’s is greater.
- Relative density less than 1 means it will float in water; greater than 1 means it will sink. Thus, relative density accurately predicts behavior in a liquid.
Q6. Describe a step-by-step method to determine the density of an irregular solid in the lab and explain how to reduce errors.
Answer:
- First, measure the mass of the dry solid using a digital balance and note it. Next, partially fill a measuring cylinder with water and record the initial volume at the bottom of the meniscus.
- Carefully lower the solid tied to a thread into the water and record the new volume; the volume difference gives the solid’s volume. Calculate density using Density = Mass/Volume.
- To reduce errors, remove trapped air bubbles, read at eye level, and use a suitably sized cylinder for better accuracy.
Q7. Explain how temperature changes can create convection in liquids and gases due to density differences, and give one everyday example for each.
Answer:
- Heating a region of a liquid or gas makes particles move apart, increasing volume and lowering density there. The warmer, less dense part rises, while the cooler, denser part sinks, creating a convection current.
- In liquids, heating water from below in a pot sets up rising warm currents and sinking cool currents. In gases, warm air rising from a heater or sun-warmed ground creates upward motion and draws in cooler air, helping circulate room air naturally.
Q8. Discuss how solvents are chosen in traditional and modern extraction of useful plant compounds, and why solvent choice matters.
Answer:
- In both traditional systems and modern chemistry, the solvent is chosen based on its ability to dissolve the desired compounds without damaging them.
- Water, alcohol-water mixtures, oils, or milk may be used to extract different types of molecules depending on their solubility. The right solvent improves yield, purity, and safety of the extract.
- It also affects taste, storage, and how the extract is used as a medicine. Careful selection ensures effective and consistent preparation.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short and Long Answer Questions: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between a solute and a solvent? |  |
| 2. How does temperature affect the solubility of a solute? |  |
| 3. Can you explain what a saturated solution is? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of solutions in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of solutions in scientific research and industry? |  |





















