Very Short Answer Questions- Light: Mirrors and Lenses | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1: What makes things visible?
Ans: Light.
 Light
Light
Q2: Can you see an object in the dark?
Ans: No.
Q3: What is a mirror?
Ans: A smooth and shiny surface is called a mirror.
 MirrorQ4: What kind of image is formed by a plane mirror?
MirrorQ4: What kind of image is formed by a plane mirror?
Ans: Virtual and erect image.
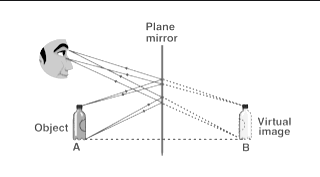 Q5: Where is the image formed by a plane mirror?
Q5: Where is the image formed by a plane mirror?
Ans: Behind the mirror.
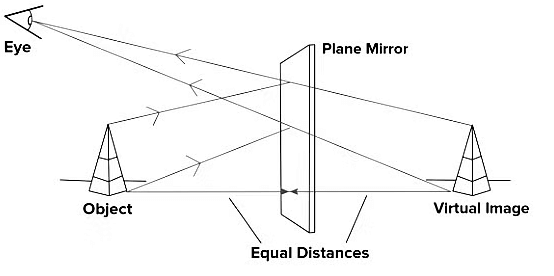
Q6: What is the size of the image formed in a plane mirror?
Ans: Same size of the object.
Q7: The distance between the object and its image formed by a plane mirror appears to be 18 cm. What is the distance between mirror and the object?
Ans: 9 cm
Q8: A ray of light is incident on a mirror at an angle of 40°. What is the angle of reflect?
Ans: 40°
Q9: What do we call the image that cannot be obtained on a screen?
Ans: Virtual
Q10. What type of mirror is the inner side of a spoon?
Ans: The inner side of a spoon is a concave mirror.
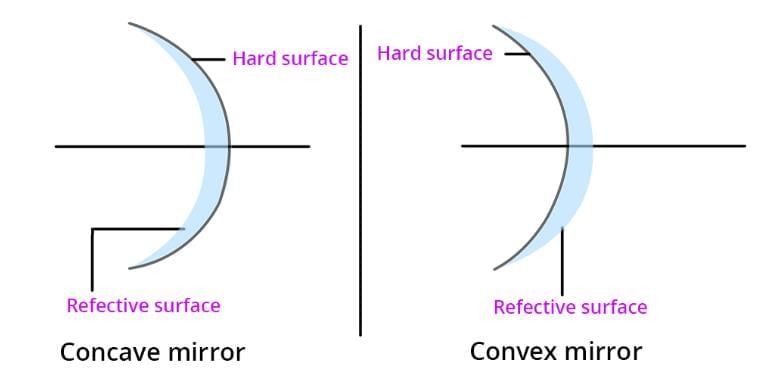
Q11. What type of mirror is the outer side of a spoon?
Ans: The outer side of a spoon is a convex mirror.
Q12. Define a spherical mirror.
Ans: A spherical mirror is a mirror whose reflecting surface is a part of a hollow sphere.
Q13. In a concave mirror, is the center curved inward or outward?
Ans: In a concave mirror, the center is curved inward.
Q14. In which type of mirror is the reflecting surface curved outward?
Ans: In a convex mirror, the reflecting surface is curved outward.
Q15. What is placed on the glass surface to make a mirror reflective?
Ans: A thin reflective coating like aluminum is placed on the glass surface.
Q16. How does a concave mirror form an image when the object is very close?
Ans: A concave mirror forms an erect and enlarged image when the object is very close.
Q17. How does the image in a convex mirror appear at any distance?
Ans: In a convex mirror, the image is always erect and smaller than the object.
Q18. What type of image does a plane mirror always form?
Ans: A plane mirror always forms an erect image of the same size as the object.
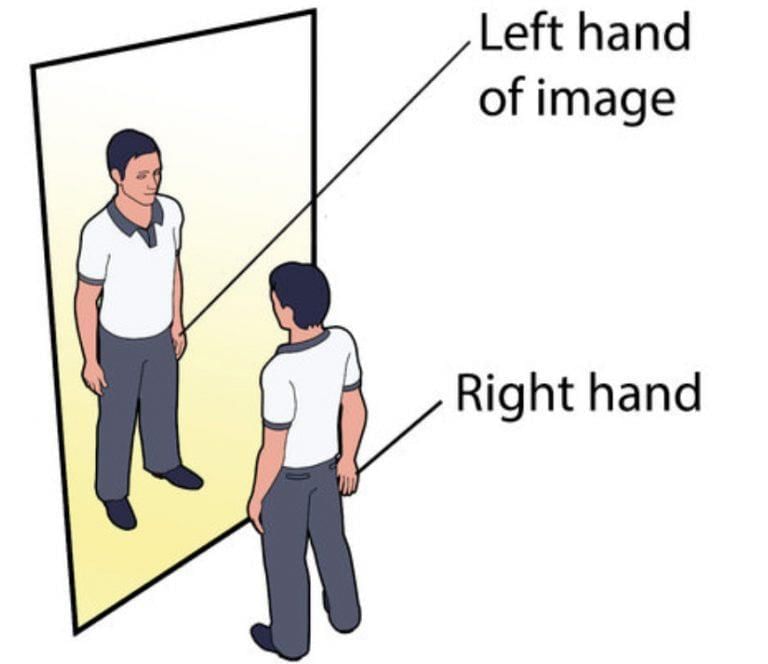
Q19. What is lateral inversion?
Ans: Lateral inversion is the left-right reversal of an image in a mirror.
Q20. Which mirror is used as a reflector in torches and headlights?
Ans: A concave mirror is used as a reflector in torches and headlights.
Q21. Why is a convex mirror used as a vehicle’s side-view mirror?
Ans: A convex mirror gives a wider view and forms smaller, erect images.
Q22. What type of mirror is used in modern telescopes?
Ans: Modern telescopes use a large concave mirror.
Q23. What is the First Law of Reflection?
Ans: The First Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Q24. What is the Second Law of Reflection?
Ans: The Second Law of Reflection states that the incident ray, normal, and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Q25. Name the type of mirror that converges parallel light rays.
Ans: A concave mirror converges parallel light rays.
Q26. Why can a concave mirror burn paper in sunlight?
Ans: A concave mirror focuses sunlight to a small point, increasing heat enough to burn paper.
Q27. What is a lens made of?
Ans: A lens is made of transparent material like glass or plastic.
Q28. Which lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges?
Ans: A convex lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges.
Q29. Which lens is thicker at the edges than in the middle?
Ans: A concave lens is thicker at the edges than in the middle.
Q30. How does a convex lens change an image when the object is very close?
Ans: A convex lens forms an erect and enlarged image when the object is very close.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Very Short Answer Questions- Light: Mirrors and Lenses - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main types of mirrors and how do they differ? |  |
| 2. How do lenses work and what are the different types? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the focal point in mirrors and lenses? |  |
| 4. How do we determine the nature and size of the image formed by mirrors and lenses? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of mirrors and lenses? |  |





















