Short and Long Answer Questions: Light: Mirrors and Lenses | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1. Why does the warning “Objects in mirror are closer than they appear” appear on vehicle side mirrors?
Ans: Side mirrors in vehicles are usually convex mirrors. They make images smaller than the actual object size, so the objects seem farther away than they really are. The warning is to remind drivers about this illusion for safety.

Q2. How can you tell if a mirror is concave, convex, or plane just by looking at its image?
Ans: A concave mirror shows a large upright image when close and an inverted one when far. A convex mirror always shows a smaller upright image. A plane mirror always shows an upright image of the same size.
Q3. Why are convex mirrors useful at road intersections?
Ans: Convex mirrors give a wider field of view than plane mirrors. At intersections, they help drivers see vehicles coming from different directions, reducing the risk of accidents.
Q4. How are spherical mirrors shaped during manufacturing?
Ans: They start as flat glass pieces that are ground and polished into a curved shape. Then a thin reflective coating, like aluminum, is added to make them work as mirrors.
Q5. What happens if a beam of light strikes a mirror along the normal?
Ans: The light is reflected back along the same path. In this case, both the angle of incidence and reflection are zero.
Q6. How do laws of reflection apply to spherical mirrors?
Ans: The laws work for each ray of light, even if the mirror surface is curved. In concave mirrors, parallel rays converge, while in convex mirrors, parallel rays diverge, but each ray still obeys the reflection rules.
 Laws of Reflection
Laws of Reflection
Q7. Why is it dangerous to look at the Sun through a concave mirror?
Ans: A concave mirror focuses sunlight into a small spot. The intense light and heat can damage the eyes permanently.
Q8. Why does the size of an image change when the object distance changes for a convex lens?
Ans: Changing the object’s distance changes the point where light rays meet after passing through the lens. This changes whether the image is upright or inverted and also its size.
Q9. How can you differentiate a convex lens from a concave lens by just touching it?
Ans: A convex lens feels thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. A concave lens feels thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges.
Q10. Why does a convex lens focus sunlight to a hot point?
Ans: A convex lens converges parallel rays from the Sun to a single spot. This concentrated light produces heat that can burn paper.
Q12. How does the human eye’s lens help us see both near and far objects?
Ans: The eye’s natural convex lens changes shape to adjust focus. It becomes thicker for near objects and thinner for far objects, so we can see both clearly.
Long Answer Questions
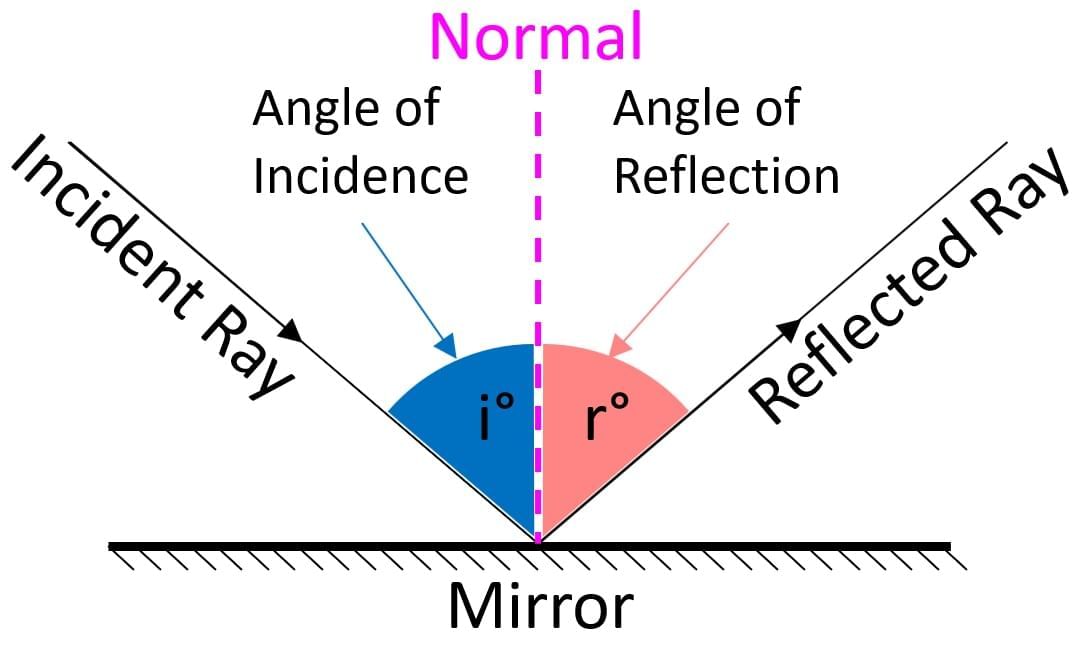
Q. 1. What is reflection of light? State the laws of reflection.Ans. Reflection is a phenomenon in which a beam of light falls on some surface and returns back in different directions. It may be regular or irregular.
Following are the laws of reflection:
(i) When a ray of light falls on a reflecting surface it is reflected back in such a way that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, i.e. ∠i = ∠r.
(ii) The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
Q. 2. What are the characteristics of image formed by plane mirror?
Ans. Characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror are:
(i) Plane mirror forms virtual images.
(ii) Plane mirror forms erect images.
(iii) Image is laterally inverted.
(iv) Image formed is of the same size as the object.
(v) The distance of image from the mirror is equal to the distance of object from the mirror.
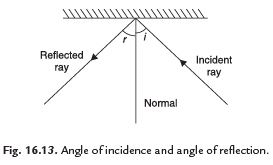
Q. 3. How will you prove that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Ans.
- Draw lines showing the position of the plane mirror, the incident ray and the reflected ray on the paper with the help of your friends. Remove the mirror.
- Draw a line making an angle of 90º to the line representing the mirror at the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror. This line is known as the normal.
- The angle between the normal and incident ray is called the angle of incidence (∠i). The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is known as the angle of reflection (∠r).
- Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. Repeat the activity several times by changing the angle of incidence. You will see that at every time the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- This proves that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Q4. Explain how spherical mirrors are made and how the placement of the reflective coating determines the type of mirror.
Ans:
- Spherical mirrors are made by grinding and polishing a flat piece of glass into a curved shape. A thin reflective coating, such as aluminum, is then applied to make it work as a mirror.
- If the coating is placed on the outer curved surface, the mirror becomes a concave mirror. If the coating is placed on the inner curved surface, it becomes a convex mirror.
- The curvature of the surface changes how light is reflected. This is why the same manufacturing process can produce two different types of mirrors.
Q5. Describe in detail the differences in image formation between plane mirrors and spherical mirrors.
Ans:
- Plane mirrors always form erect images that are the same size as the object, regardless of the object's distance. In contrast, the size and orientation of images in spherical mirrors depend on distance.
- A concave mirror can produce enlarged or diminished images, which may be upright or inverted depending on the object's position. A convex mirror always produces small, upright images.
- Lateral inversion happens in all mirror types. These differences arise because of the way the surfaces reflect light rays.
Q6. How do concave and convex mirrors differently direct parallel rays of light? Explain why.
Ans:
- A concave mirror reflects parallel rays towards a single point called the focus, which means it converges light. A convex mirror reflects parallel rays outwards so that they spread apart, meaning it diverges light.
- This happens because of the way the curved surfaces bend the paths of the light rays. In concave mirrors, the inward curve bends light inward. In convex mirrors, the outward curve bends light away from each other. This property is important in deciding their uses in real life.
Q7. Explain the role of the two laws of reflection when light strikes spherical mirrors.
Ans:
- The first law says that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and this holds true for every ray on the mirror’s surface. The second law says that the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
- These laws apply to all mirrors, whether plane, concave, or convex. In concave mirrors, the curve makes the reflected rays converge. In convex mirrors, the curve makes the rays diverge. Even though their paths differ, each ray still follows the reflection laws exactly.
Q8. How can a concave mirror be used to demonstrate the focusing of sunlight, and why is it potentially dangerous?
Ans:
- To demonstrate, you can use a concave mirror on a sunny day, facing it towards the Sun and holding a piece of paper at different distances from the mirror.
- When the paper is at the focal point, a small bright spot appears. This spot is concentrated sunlight, and after a few seconds, the heat can ignite the paper. It is potentially dangerous because the intense light and heat can also damage skin or eyes if focused on them.
- That’s why such demonstrations must be done with caution. This property is used in solar cookers and concentrators.
Q9. Explain why a water droplet can act as a simple lens, using the experiment described.
Ans:
- A water droplet has a curved surface that makes it behave like a convex lens. When placed on a transparent surface over printed text, it bends the light passing through.
- This bending causes the letters underneath to appear larger than their actual size. The curve of the droplet focuses the light, similar to a magnifying glass.
- This simple experiment shows how lenses work to change the appearance of objects. It’s an easy demonstration of refraction and magnification.
Q10. How does the image formation in a convex lens change as the distance between the object and lens changes?
Ans:
- When the object is close to a convex lens, the image formed is upright and larger than the object. As the object moves further away, the light rays from it meet differently after passing through the lens.
- This results in the image becoming inverted. The size of the image also reduces as the object distance increases. At certain distances, the image size can become smaller than the object.
- This is why convex lenses are used for both magnifying and focusing purposes.
Q11. Compare the effect of a convex lens and a concave lens on parallel beams of light.
Ans:
- A convex lens bends parallel beams inward until they meet at a focal point, making it a converging lens. A concave lens bends parallel beams outward, making them spread apart; this is why it is called a diverging lens.
- In both cases, the bending is due to refraction caused by the lens’ curved surfaces. Convex lenses can focus light to form real images on a screen.
- Concave lenses cannot form real images because they never make the rays meet. These properties decide their use in instruments like cameras, eyeglasses, and telescopes.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Short and Long Answer Questions: Light: Mirrors and Lenses - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the different types of mirrors and how do they work? |  |
| 2. How do lenses differ from mirrors in terms of image formation? |  |
| 3. What is the law of reflection and how is it applied in real life? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of concave and convex mirrors? |  |
| 5. How does the focal length of a lens affect image formation? |  |





















