Short and Long Answer Questions: How Nature Works in Harmony | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1. What does it mean that nature is interconnected?
Nature is interconnected means plants, animals, humans, water, and air all affect each other through many links. A change in one part can cause changes in many other parts.
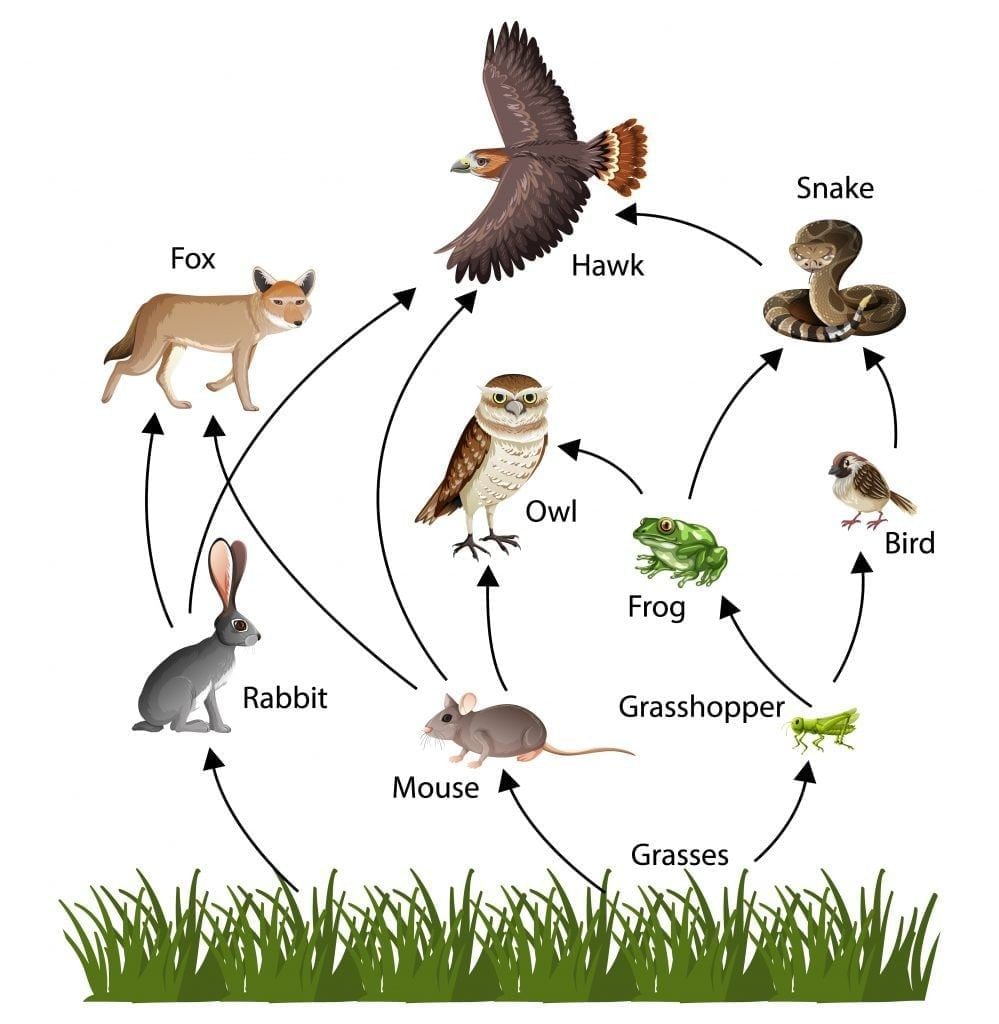 Food Web showing nature is interconnected
Food Web showing nature is interconnected
Q2. How can a small change cause big effects in an ecosystem?
A small change, like less rainfall, can reduce plant growth and then reduce food for animals. This can push animals to move and disturb nearby farms and villages.
Q3. Why do organisms adapt to their habitats?
Organisms adapt so they can survive better in the conditions of their home, like temperature, water, and food. Adaptations help them find shelter, breathe, and get food.
Q4. How do different species share the same habitat without direct conflict?
Species can use resources at different times or in different ways, like one being active at night and another in the day. This reduces competition and helps both survive.
Q5. What is resource competition and why is it important?
Resource competition is when organisms try to use the same limited food, water, space, or light. It helps control population sizes and keeps balance in the ecosystem.
Q6. What is a niche in a community?
A niche is the role an organism plays, including what it eats, where it lives, and when it is active. Clear niches reduce conflict and support harmony.
Q7. How do abiotic factors influence a habitat’s conditions?
Abiotic factors like sunlight, temperature, water, and soil shape how organisms live and grow. They decide which plants and animals can survive in that place.

Q8. How do abiotic components interact with each other?
Sunlight can warm air and water, changing temperature and speeding evaporation. Wind can move air and water, forming waves and spreading moisture.
Q9. Why are food webs more realistic than food chains?
Food webs show that most organisms eat and are eaten by more than one species. This makes the network of feeding relationships more accurate and stable.
Q10. How do migratory birds support ecosystems?
Migratory birds help pollinate flowers and spread seeds between faraway places. They also eat pests, which helps farmers protect crops.
Q11. How can human actions disturb ecological balance?
Activities like overfishing, pollution, and cutting forests remove key species and damage habitats. This can cause population explosions or crashes and harm people’s livelihoods.
Q12. What steps can communities take to protect ecosystems?
Communities can reduce pollution, save water, and protect local green areas and wetlands. They can also support protected areas and use resources wisely to keep nature balanced.
Long Answer Questions
Q1. Explain how biotic and abiotic components interact in an ecosystem. Give suitable examples.
Ans:
- Biotic components are the living parts of an ecosystem, while abiotic components are the non-living parts. These two are closely linked and depend on each other for survival.
- For example, plants (biotic) need sunlight, water, and soil (abiotic) to grow. Animals eat plants or other animals for food, but they also depend on water, air, and temperature for survival.
- In a pond, fish (biotic) need oxygen dissolved in water (abiotic) to live. Without these interactions, life processes cannot continue and ecosystems would not be balanced.
Q2. Why is balance in nature important, and what are the effects when it is disturbed?
Ans:
- Balance in nature means that the number of plants, animals, and other organisms remains stable over time. This happens when resources like food, water, and shelter are used sustainably, and no species grows uncontrollably.
- If the balance is disturbed, such as by cutting forests or overfishing, it can start a chain reaction affecting many other species. For instance, removing too many fish can increase insect numbers, reduce pollinators, and lower plant growth.
- Human activities like pollution and habitat destruction often cause such imbalances. Restoring balance takes time and careful conservation efforts.
Q3. Describe the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem.
Ans:
- Producers, such as green plants, make their own food using sunlight through photosynthesis. Consumers depend on others for food—herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat animals, and omnivores eat both.
- Decomposers like fungi and bacteria break down dead plants and animals into simpler substances, returning nutrients to the soil. This cycle ensures that energy and matter are reused in the ecosystem.
- Without producers, there would be no source of energy for other organisms. Without decomposers, waste and dead material would pile up, and nutrients would not return to the soil for plants to use.
Q4. Differentiate between a food chain and a food web with examples.
Ans:
- A food chain is a simple, linear sequence showing "who eats whom" in an ecosystem, such as grass → grasshopper → frog → snake → eagle. Each organism passes energy to the next in the chain. A food web is more complex and shows how different food chains are interconnected.
- For example, grass may be eaten by rabbits or mice, and mice can be eaten by snakes or owls. This network of feeding relationships makes ecosystems more stable because organisms have multiple food sources. If one food source is removed, others can still sustain the population.
Q5. Explain with an example how a small change in an ecosystem can cause a chain reaction.
Ans:
- In nature, every part is connected, so even a small change can affect many others. For example, if pollution kills plants in a pond, the oxygen level decreases.
- This causes fish populations to drop because they need oxygen to survive. With fewer fish, insect numbers may grow rapidly because fish are their predators.
- These insects can damage nearby crops, leading farmers to use more pesticides. Such pesticides harm the environment further, showing how one change spreads through the ecosystem in a series of reactions.
Q6. How do migratory birds contribute to ecosystem balance and why do they migrate?
Ans:
- Migratory birds travel long distances to avoid harsh weather and find food. They play important roles in maintaining ecosystem balance. Many act as pollinators, helping flowers reproduce, and as seed dispersers, spreading plant species over wide areas. They also feed on pests like insects, helping farmers reduce crop damage.
- For example, the Demoiselle Cranes visit Khichan village in Rajasthan every winter, adding beauty and ecological value. By linking distant habitats, migratory birds ensure that ecosystems remain interconnected across regions.
Q7. Discuss the threats faced by the Sundarbans and why its conservation is important.
Ans:
- The Sundarbans is the world's largest mangrove forest and protects coastal areas from floods and storms. It is home to endangered species and supports rich biodiversity. However, it faces threats from deforestation, illegal hunting, overuse of forest resources, and pollution from industries. Cutting mangroves weakens natural flood protection and harms wildlife.
- Since the Sundarbans also absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide, their loss would contribute to climate change. Protecting this ecosystem is important not just for local communities but also for global environmental health.
Q8. What are the harmful effects of unsustainable farming practices and how can they be avoided?
Ans:
- Unsustainable farming practices include overusing chemical fertilizers, monoculture (growing only one crop), and excessive irrigation. These harm the soil by reducing organic matter and killing beneficial microorganisms. Soil erosion increases without humus, and pests may become resistant to pesticides.
- Such practices also disturb natural predators and pollinators, reducing biodiversity. To avoid these problems, farmers can use organic manure, rotate crops, and adopt natural pest control methods. Sustainable farming helps maintain soil fertility and keeps ecosystems healthy for future generations.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short and Long Answer Questions: How Nature Works in Harmony - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key principles of how nature works in harmony? |  |
| 2. How does biodiversity contribute to the harmonious functioning of nature? |  |
| 3. What role do humans play in maintaining or disrupting natural harmony? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of an ecosystem and its importance in the harmony of nature? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of natural processes that demonstrate harmony in nature? |  |
















