Unit Test (Solutions): Our Home: Earth, a Unique Life-Sustaining Planet | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
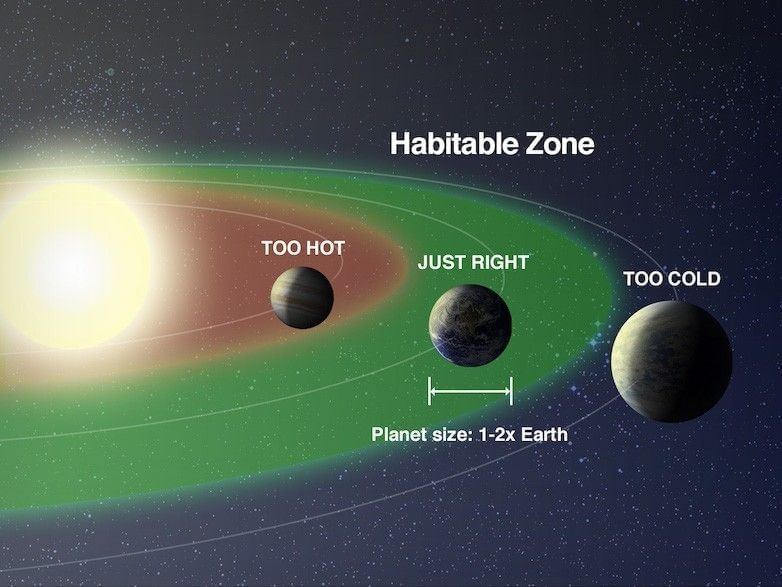
Q1: The Earth can sustain liquid water mainly because (1 Mark)
(i) it is the largest planet
(ii) it is in the star’s habitable zone at the right distance
(iii) it has rings
(iv) it has many moons
Ans: (ii)
Earth lies at a “just right” distance from the Sun (Goldilocks/habitable zone), where temperatures allow water to remain mostly liquid—critical for life to evolve and persist.
Q2: Which factor helps Earth retain its atmosphere? (1 Mark)
(i) Extremely small size
(ii) Appropriate mass and gravity
(iii) Absence of magnetic field
(iv) Being the closest to the Sun
Ans: (ii)
Earth’s size/mass provides sufficient gravity to hold gases; if much smaller, gases would escape; if much larger, gravity could be crushingly high for life forms.
Q3: Venus is hotter than Mercury primarily because (1 Mark)
(i) it is nearer to the Sun
(ii) it rotates faster
(iii) it has a thick CO2 atmosphere causing strong greenhouse effect
(iv) it has more volcanoes
Ans: (iii)
Venus’ dense CO2 atmosphere traps outgoing radiation, producing extreme greenhouse warming—hotter than Mercury despite being farther from the Sun.
Q4: Which of the following is an example of geodiversity? (1 Mark)
(i) Variety of bird songs
(ii) Range of landforms (mountains, valleys, deserts)
(iii) Number of tree species
(iv) Seasonal monsoon winds
Ans: (ii)
Geodiversity concerns the diversity of non-living Earth features—rocks, soils, minerals, and landforms—and the processes shaping them.
Q5: In sexual reproduction, offspring differ from parents because (1 Mark)
(i) only the mother passes instructions
(ii) only the father passes instructions
(iii) both parents pass mixed genetic instructions via gametes
(iv) instructions are acquired after birth
Ans: (iii)
Male and female gametes carry half-sets of genetic instructions; mixing during fertilisation produces unique combinations, so offspring differ from both parents.
Q6: State two ways the Earth’s atmosphere supports life. (2 Marks)
Ans:
(i) Provides oxygen for respiration and CO2 for photosynthesis;
(ii) Greenhouse gases retain sufficient heat to keep temperature suitable; also, ozone layer filters harmful UV radiation.
Q7: Give one difference between greenhouse warming of a planet and a plant greenhouse. (2 Marks)
Ans: Planetary greenhouse: gases (e.g., CO2) absorb outgoing infrared radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere. Plant greenhouse: a physical enclosure (glass/plastic) reduces convective heat loss; warmed air is retained—not the same radiative mechanism.
Q8: Explain briefly how Earth’s magnetic field helps protect life. (2 Marks)
Ans: The geomagnetic field deflects many charged particles from the solar wind and cosmic rays, safeguarding the atmosphere (including ozone) from erosion and limiting radiation that could harm living cells.
Q9: Why is Mars currently less hospitable to life than Earth? Mention any two reasons from planetary conditions. (3 Marks)
Ans:
(i) Very thin atmosphere (~1% of Earth’s), offering little greenhouse warming and poor protection from radiation;
(ii) Limited liquid water at surface under current conditions (cold and low pressure). These factors reduce habitability compared to Earth.
Q10: Distinguish asexual and sexual reproduction with one plant example each and state the outcome for variation. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Asexual (e.g., vegetative propagation in potato eyes/ginger/money plant): one parent produces genetically identical offspring (clones), minimal variation.
- Sexual (flowering plants via pollen–ovule fertilisation and seed formation): two parents contribute; mixed genes increase variation among offspring.
Q11: Describe how water sustains life through the hydrosphere and the water cycle (two points). (3 Marks)
Ans:
(i) As a universal solvent, water carries nutrients in plants (soil to leaves) and supports transport, temperature regulation, and metabolism in animals.
(ii) Evaporation–condensation–precipitation cycles replenish freshwater in rivers, lakes, groundwater, supporting ecosystems, agriculture, and human needs.
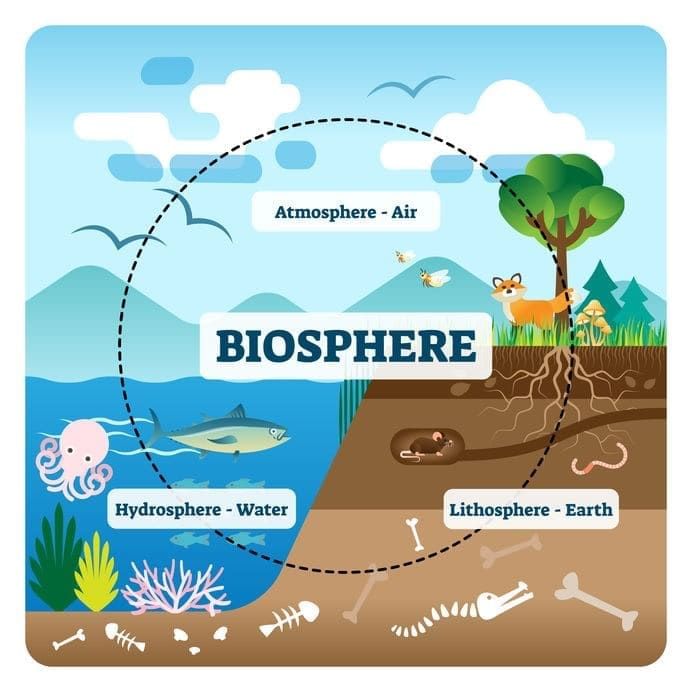
Q12: Earth’s life-support system integrates geosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. (5 Marks)
(a) Explain with one example each how any two spheres support or influence the others.
(b) A city clears a large forest patch for roads. Predict impacts on local climate, biodiversity, and water over time.
Ans:
(a) Geosphere–Biosphere: Soils provide minerals (N, K, P) and substrate for plant roots; roots stabilise soils and prevent erosion. Atmosphere–Biosphere: Photosynthesis uses CO2 to produce O2; respiration uses O2, cycling gases and energy. Hydrosphere–Biosphere: Water bodies host aquatic life; water transports nutrients and supports life processes.
(b) Forest loss reduces evapotranspiration and surface shading, tending to increase local temperatures and alter rainfall patterns; habitat removal lowers biodiversity and ecosystem resilience; with less infiltration and more runoff, streams may flash-flood, groundwater recharge declines, and sediment/pollutant loads increase, degrading water quality.
Q13: Continuity and change in life. (5 Marks)
(a) Why is reproduction essential for life continuity? Contrast development pathways of birds and mammals after fertilisation.
(b) A friend says “Today’s global warming is just like past natural climate changes.” Respond scientifically.
Ans:
(a) Reproduction replaces individuals and transmits genetic instructions. Birds: fertilisation internal; nutrient-rich eggs are laid; embryo develops outside the body until hatching. Mammals: fertilisation internal; embryo develops inside the mother with continuous nutrient/oxygen supply until live birth.
(b) Past climate varied naturally, but current rapid warming correlates strongly with elevated greenhouse gases from human activities (fossil fuel combustion, land-use change). The rate and global pattern of change, alongside measured CO2 rise, sea-level increase, and cryosphere loss, distinguish it from typical natural variability and raise risks to ecosystems and societies.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Our Home: Earth, a Unique Life-Sustaining Planet - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What makes Earth unique among the planets in our solar system? |  |
| 2. How does Earth's atmosphere contribute to sustaining life? |  |
| 3. What role does water play in sustaining life on Earth? |  |
| 4. What are some of the key factors that contribute to Earth’s biodiversity? |  |
| 5. How has human activity impacted Earth’s environment and its ability to sustain life? |  |




















